- What kind of drug?
- Indications for use
- What is the composition?
- Action
- Instructions for use
- Can it be taken during pregnancy and lactation?
- Adverse reactions
- Overdose
- Interaction with other drugs
- Contraindications and restrictions
- Analogues of the drug
- Difference from Enap-N
- Are pills addictive?
- Reviews
For arterial hypertension, combination medications are often prescribed, and one of these is Enap-NL. This is an ACE inhibitor, which has a hypotensive effect, that is, it helps lower blood pressure. The tablets must be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
What kind of drug?
Enap-NL is a domestically produced drug, which is produced by KRKA-RUS LLC. It is taken to lower blood pressure, hence it can be called a high blood pressure medicine. It is important to note that the drug has only a therapeutic effect, and does not cure the disease itself, therefore it is prescribed in combination with other drugs.
It is important to note that taking pills for hypertension helps not only stabilize blood pressure, but also prevent negative consequences associated with the impact on many internal organs:
- eyes (prevents retinal detachment, hemorrhage, loss of vision);
- heart (prevents myocardial infarction);
- kidneys (prevents kidney failure);
- brain (prevents circulatory disorders, stroke).
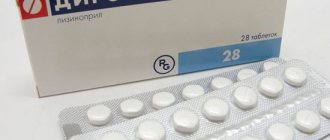
Enap-NL is produced in the form of flat round white tablets, on one side of which there is a dividing strip and a chamfer. One blister contains 10 tablets, and one package can contain 2, 3, 6 or 9 blisters. The price for these tablets varies from 246 rubles (20 tablets) to 472 rubles (60 tablets).
Indications for use
Indications for therapy with the described drug are arterial hypertension and combined treatment against the background of this diagnosis. As a rule, Enap-NL is taken when blood pressure rises from 140/90 mm Hg. Art.
In rare cases, a doctor may prescribe medication for chronic heart failure and to prevent coronary artery disease caused by dysfunction of the left ventricle. In other cases, its use is not only inappropriate, but also dangerous.
Enap-NL is available in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
At what pressure is it used?
Enap NL is an antihypertensive drug, the main indication for which is arterial hypertension. The official instructions for use of Enap NL do not indicate at what pressure the medicine should be taken. But this is logically clear: the patient must have hypertension, which has clear pressure readings for diagnosis. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe medication if blood pressure rises from 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and higher. The drug is also prescribed:
- for chronic heart failure;
- for the prevention of coronary ischemia in case of left ventricular dysfunction.
It is important to note that arterial hypertension should not be ignored and must be treated (most often lifelong). Lack of treatment leads to worsening hypertension, deterioration of the cardiovascular system and exacerbation of various cardiac diseases.
Atherosclerosis, the process of formation of cholesterol plaques that cause narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, is one of the main causes of hypertension. At the same time, constant high blood pressure accelerates the process of sclerotization: blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels leads to the appearance of microscopic cracks in them, which is why the vascular walls are even more “sealed” with cholesterol (as well as other substances present in the blood).
Over time, atherosclerotic plaques lead to a significant narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which further aggravates hypertension. Atherosclerosis leads to coronary heart disease, causes blockage of blood vessels, promotes aneurysmal changes in the vascular wall, and increases the risk of thrombosis, which results, among other things, in myocardial infarction. Therefore, treating arterial hypertension is vital. The drug Enap NL and its forms show high effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy.
What is the composition?
The drug consists of two main active ingredients and other auxiliary elements.
Enalapril maleate
Its content in one tablet is 10 mg. This is an ACE inhibitor that has the following characteristics:
- promotes the conversion of angiotensin of the first type into the second;
- reduces the concentration of aldosterone in the blood serum;
- suppresses the sympathetic nervous system.
These actions in combination help eliminate vascular spasm and expand their lumen, due to which the pressure decreases.
The maximum effect of the substance appears after 6-8 hours and lasts up to 24 hours. Absorption is 60% and does not depend on food intake. It breaks down in the liver and forms an active metabolite - enalaprilat. This is an ACE inhibitor, which is more effective than enalapril. Its connection with blood plasma proteins is 50-60%.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Its concentration in 1 tablet is 12.50 mg. This is a thiazide diuretic that slows down the absorption of sodium salts in the kidneys and accelerates their excretion in the urine, thereby reducing the amount of fluid in the tissues and unloading the blood vessels and heart.
It takes 1-2 hours for the diuretic effect to develop. It turns out maximum after 4 hours, and lasts about 10-12 hours. Helps reduce pressure by reducing the volume of circulating blood and changing the reactivity of vessel walls.
The diuretic is absorbed mainly in the duodenum and the proximal part of the small cat. Its absorption is 70%, but can increase to 80% when taken simultaneously with food. The connection with blood plasma proteins is about 40%, and its maximum concentration in the serum is observed after 1.5-5 hours.
Additional components
In addition to the two main substances, the drug also contains the following elements:
- lactose monohydrate – 130.08 mg;
- corn starch – 32.1 mg;
- pregelatinized starch – 6 mg;
- talc – 6 mg;
- sodium bicarbonate – 5.1 mg;
- Magnesium stearate – 2 mg.
Enap-NL (Enap-HL)
Name:
Enap-NL (Enap-HL)
Release form, composition and pack
The tablets are white, round, flat, with a beveled edge and a notch on one side. 1 tab. enalapril maleate 10 mg hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg. Excipients: sodium bicarbonate, lactose monohydrate, calcium hydrogen phosphate (anhydrous), corn starch, talc, magnesium stearate.
Clinical and pharmacological group: Antihypertensive product.
pharmachologic effect
A combined product, the effect of which is determined by the properties of the components included in its composition. Enalapril, an ACE inhibitor, is a prodrug: as a result of its hydrolysis, enalaprilat is formed, which inhibits ACE. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. Acts at the level of the distal renal tubules, increasing the excretion of sodium and chlorine ions.
At the beginning of treatment with hydrochlorothiazide, the volume of fluid in the vessels decreases as a result of increased excretion of sodium and fluid, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure and a decrease in cardiac output. Due to hyponatremia and decreased fluid in the body, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is activated. A reactive increase in angiotensin II concentration partially limits the decrease in blood pressure. With continued therapy, the hypotensive effect of hydrochlorothiazide is based on a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system results in metabolic effects on blood electrolyte balance, uric acid, glucose and lipids, which partially counteract the effectiveness of antihypertensive treatment.
Despite their effective reduction in blood pressure, thiazide diuretics do not reduce structural changes in the heart and blood vessels. Enalapril enhances the antihypertensive effect: it inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, i.e. angiotensin II production and its effects. Additionally, it reduces the production of aldosterone and enhances the effect of bradykinin and the release of prostaglandins.
Because it often has its own diuretic effect, which may enhance the effect of hydrochlorothiazide. Enalapril reduces pre- and afterload, which unloads the left ventricle, reduces regression of hypertrophy and collagen proliferation, and prevents damage to myocardial cells.
As a result, the heart rhythm slows down and the load on the heart decreases (in case of chronic heart failure), coronary blood flow improves and oxygen consumption by cardiomyocytes decreases. Thus, the susceptibility of the heart to ischemia is reduced, and the number of dangerous ventricular arrhythmias is also reduced. It has a beneficial effect on cerebral blood flow in patients with arterial hypertension and chronic cardiovascular diseases.
Prevents the development of glomerulosclerosis, maintains and improves kidney function and slows the progression of chronic kidney disease even in those patients who have not yet developed arterial hypertension.
It is known that the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors is greater in patients with hyponatremia, hypovolemia and elevated serum renin levels, while the effect of hydrochlorothiazide does not depend on the serum renin level. Therefore, the simultaneous administration of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide has an additional antihypertensive effect.
In addition, enalapril prevents or reduces the metabolic effects of diuretic therapy and has a beneficial effect on structural changes in the heart and blood vessels. The simultaneous administration of an ACE inhibitor and hydrochlorothiazide is used when each product individually is not sufficiently effective or monotherapy is carried out using maximum doses of the product, which increases the incidence of undesirable effects. This combination allows you to obtain a better therapeutic effect with lower doses of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide and reduce the development of undesirable effects. The antihypertensive effect of the combination usually persists for 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Enalapril
Suction
Enalapril is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The suction volume is 60%. Food does not affect the absorption of enalapril. Tmax is 1 hour. Tmax of enalaprilat in blood serum is 3-6 hours.
Distribution
Enalaprilat penetrates most tissues of the body, mainly the lungs, kidneys and blood vessels. Binding to blood plasma proteins is 50-60%. Enalapril and enalaprilat cross the placental barrier and are excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism
In the liver, enalapril is hydrolyzed to the active metabolite, enalaprilat, which is the carrier of the pharmacological effect and is not subject to further metabolism.
Removal
Excretion is a combination of glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. The renal clearance of enalapril and enalaprilat is 0.005 ml/s (18 l/h) and 0.00225-0.00264 ml/s (8.1-9.5 l/h), respectively. It is produced in several stages. When multiple doses of enalapril are prescribed, T1/2 of enalaprilat from blood serum is approximately 11 hours. Enalapril is excreted in the urine - 60% and in feces - 33%, mainly in the form of enalaprilat. Enalaprilat is 100% excreted in the urine. Enalaprilat is removed from the bloodstream by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis clearance of enalaprilat is 0.63 - 1.03 ml/s (38-62 ml/min). The serum concentration of enalaprilat after 4-hour hemodialysis is reduced by 45-57%.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In patients with reduced renal function, excretion slows down, which requires dosage adjustments in accordance with renal function, especially in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
In patients with hepatic impairment, the metabolism of enalapril may be slowed without affecting its pharmacodynamic effect.
In patients with heart failure, the absorption and metabolism of enalaprilat slows down, and Vd also decreases. Since these patients may have renal failure, their elimination of enalapril may be slower. In elderly patients, the pharmacokinetics of enalapril may change to a greater extent due to concomitant diseases than older age.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Suction
Hydrochlorothiazide is absorbed mainly in the duodenum and proximal small intestine. Absorption is 70% and increases by 10% when taken with food. Tmax is 1.5-5 hours.
Distribution
Vd within 3 l/kg. Binding to blood plasma proteins is 40%. The drug accumulates in red blood cells, the mechanism of accumulation is unknown. Penetrates the placental barrier and accumulates in the amniotic fluid. The serum concentration of hydrochlorothiazide in the umbilical vein blood is almost the same as in maternal blood. The concentration in amniotic fluid exceeds that in blood serum from the umbilical vein by 19 times. The level of hydrochlorothiazide in breast milk is very low. Hydrochlorothiazide was not detected in the serum of infants whose mothers took hydrochlorothiazide during breastfeeding.
Metabolism
Hydrochlorothiazide is not metabolized in the liver.
Removal
Hydrochlorothiazide is excreted primarily in the urine - 95% unchanged and within 4% in the form of 2-amino-4-chloro-m-benzenedisulfonamide hydrolyzate. The renal clearance of hydrochlorothiazide in healthy volunteers and patients with arterial hypertension is approximately 5.58 ml/s (335 ml/min). Hydrochlorothiazide has a biphasic elimination profile. T1/2 in the initial phase is 2 hours, in the final phase (10-12 hours after administration) - within 10 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In elderly patients, hydrochlorothiazide does not have a negative effect on the pharmacokinetics of enalapril, but the serum concentration of enalaprilat is higher.
In patients with heart failure, when using hydrochlorothiazide, it has been found that its absorption is reduced in proportion to the degree of the disease by 20-70%. T1/2 of hydrochlorothiazide increases to 28.9 hours. Renal clearance is 0.17-3.12 ml/s (10-187 ml/min), average values 1.28 ml/s (77 ml/min).
In patients undergoing intestinal bypass surgery for obesity, the absorption of hydrochlorothiazide may be reduced by 30% and serum concentration by 50% than in healthy volunteers. The simultaneous use of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide does not affect the pharmacokinetics of either of them.
Indications
- arterial hypertension (patients for whom combination therapy is indicated).
Dosage regimen
Treatment of arterial hypertension should not begin with a combination of drugs. Initially, adequate doses of the individual components must be determined. The dose must always be selected individually for each patient. The product should be taken regularly at the same time (preferably in the morning). The tablets are swallowed whole during or after meals with a small amount of liquid. The usual dose is 1 tablet/day.
If you miss taking the next dose of the product, it should be taken as soon as possible if there is a sufficiently large amount of time left before taking the next dose. If there are several hours left before the next dose, you should wait and take only that one. Do not double the dose. If a satisfactory therapeutic effect is not achieved, it is recommended to add another drug or change therapy.
In patients on diuretic therapy, it is recommended to discontinue treatment or reduce the dose of diuretics at least 3 days before starting treatment with Enap-NL to prevent the development of symptomatic hypotension. Before starting treatment, kidney function must be examined. The duration of treatment is not limited. Patients with creatinine clearance >30 ml/min or serum creatinine <265 µmol/l (3 mg/dl) can be prescribed the usual dose of Enapa-NL.
Side effect
- From the cardiovascular system: palpitations, various cardiac arrhythmias, marked decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular stroke, angina pectoris, Raynaud's syndrome, necrotizing angiitis.
- From the digestive system: dry mouth, glossitis, stomatitis, inflammation of the salivary glands, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, epigastric pain, intestinal colic, ileus, pancreatitis, liver failure, hepatitis, jaundice, melena.
- From the respiratory system: rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, hoarseness, bronchospasm, asthma, pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates, eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, respiratory distress (including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema).
Attention! Before using the drug "Enap-NL (Enap-HL)" you should consult your doctor. The instructions are provided solely for familiarization with “ Enap-NL (Enap-HL) ”.
Action
It is due to the composition of the drug, so it is worth highlighting the key properties of two active components:
- enalapril promotes the release of venous relaxing factor, reduces aldosterone levels in the blood, inhibits the sympathetic nervous system and releases renin;
- hydrochlorothiazide acts as a medium-acting diuretic, promoting the removal of water, chlorine and sodium, due to which its concentration in the walls of the vessel decreases, it is possible to reduce the pressure and bring it back to normal.
If enalapril inhibits the movement of potassium in the blood, then hydrochlorothiazide reduces its level. Thanks to this complex effect, it is possible to normalize the concentration of potassium in the bloodstream, which is extremely important for hypertension.
The combined use of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide promotes a more pronounced reduction in blood pressure than with monotherapy with each drug separately. In addition, the combination of these components, in addition to reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure, allows you to achieve the following effect:
- reduce total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR);
- eliminate spasms of blood vessels;
- dilate arteries;
- reduce pre- and afterload on the myocardium;
- improve blood supply to ischemic myocardium;
- increase renal blood flow, maintaining the glomerular filtration rate at the same level.
The achieved hypotensive effect lasts for 24 hours.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Enap H/Enap HL/Enap 20HL
Pharmacodynamics. Enap N, Enap NL, Enap 20NL - a combination of enalapril maleate and hydrochlorothiazide. Enalapril has an antihypertensive effect - it reduces the concentration of angiotensin II and aldosterone in the blood circulation, suppresses the pressor (sympathoadrenal) and stimulates the vasodepressor (kallikrein-kinin and prostaglandin) systems of the body. Enalapril reduces afterload, which facilitates the functioning of the left ventricle, reduces its hypertrophy, dilatation and prevents damage to myocardial cells. Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic. Thiazide diuretics inhibit the reabsorption of Na+ and Cl– in the distal tubules, increasing the excretion of sodium, potassium, chlorine and water. The hypotensive effects of each of the components of the drug complement each other, and their effect lasts up to 24 hours. Enalapril prevents or reduces the metabolic effect of diuretics and has a beneficial effect on structural changes in the cardiovascular system. Pharmacokinetics. Enalapril is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, 60% of enalapril is absorbed. In the liver, enalapril is converted into the active substance - enalaprilat. Enalapril is excreted in urine (60%) and feces (33%), mostly in the form of enalaprilat. Enalaprilat is distributed into most tissues of the body, mainly in the lungs, kidneys and blood vessels. 50–60% of enalaprilat is bound to plasma proteins. Enalaprilat is excreted in the urine. Excretion is a combination of glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. The maximum effect after oral administration of enalapril appears after 6–8 hours. After oral administration, 70% of hydrochlorothiazide is absorbed in the duodenum and upper colon. It is approximately 40% bound to plasma proteins. 95% of hydrochlorothiazide is excreted by the kidneys. Elimination is the result of tubular excretion. The half-life is from 5.6 to 14.8 hours. Typically, the therapeutic effect of hydrochlorothiazide appears 2 hours after administration, and the maximum after 3-4 hours. The effect of this combination usually lasts up to 24 hours. An optimal decrease in blood pressure is observed after 3-4 weeks treatment.
Instructions for use
The described medication is taken orally. The recommended daily dose is 1 tablet per day. It can be increased to 2 tablets, but only on the recommendation of a doctor. Regardless of the dosage, the schedule for taking the tablets does not change - they need to be taken only once a day. The course of treatment is drawn up by the doctor individually based on the patient’s condition.
You need to take Enap-NL according to a clear schedule at the same time, with a small amount of water. There is no need to chew or crush the tablets.
It is important to ensure regular use, otherwise the effectiveness of the medicine will decrease sharply. In addition, attention should be paid to the following nuances:
- if you have previously taken other diuretics, 3 days before the start of treatment you need to either reduce the dose of diuretics or completely stop taking them to prevent the development of symptomatic arterial hypotension;
- if studies of renal function have revealed abnormalities, for example, renal failure with a creatinine clearance of 30-80 ml/min, Enap-NL can be taken only if the enalapril content is adequate when titrating its dose.
The high effectiveness of the drug is observed already during the first 8 weeks of treatment - a person manages to bring his blood pressure back to normal, as well as avoid the occurrence of adverse negative reactions from some body systems.
Can it be taken during pregnancy and lactation?
In the first trimester of pregnancy, you should not take the described drug, since research data indicate a possible teratogenic effect on the fetus, that is, taking Enap-NL can cause developmental defects and congenital deformities in the child.
The drug should not be used in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, since studies of the drug have confirmed a negative effect on the newborn. Infants may experience the following pathologies:
- renal failure;
- arterial hypertension;
- hypoplasia of the skull.
If a pregnant woman needs therapy, she needs to take care in advance to select other drugs that will not harm the fetus and are allowed during pregnancy.
Since the active ingredients of Enap-NL pass into breast milk, it cannot be taken during lactation. However, if a woman stops breastfeeding, she can begin therapy with this drug.
Adverse reactions
The use of Enap-NL can cause a number of adverse reactions from many body systems.
From the reproductive system:
- decreased libido;
- lack of erection;
- gynecomastia.
From the cardiovascular system:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- myocardial infarction;
- angina pectoris;
- heart failure;
- Raynaud's syndrome.
From the respiratory system:
- sinusitis;
- asthma;
- hoarseness;
- pulmonary embolism;
- pulmonary edema;
- rhinitis;
- pneumonia;
- pulmonary infarction.
From the digestive system:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- gas formation;
- intestinal colic;
- jaundice;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- anorexia;
- stomatitis;
- vomit;
- constipation;
- hepatitis;
- pancreatitis.
From the nervous systems (peripheral and central):
- insomnia;
- depression;
- drowsiness;
- anxiety;
- anxiety.
From the circulatory system:
- anemia;
- leukocytosis;
- leukopenia;
- pancytopenia.
From the urinary system:
- renal failure;
- nephritis;
- oliguria;
- impaired kidney function.
From the senses:
- loss of taste;
- noise in ears;
- dry eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- lacrimation.
Dermatological adverse reactions:
- rash;
- itching;
- shingles.
Other adverse reactions:
- allergy;
- hives;
- anaphylactic shock;
- fever;
- weakness;
- Steven-Johnson syndrome.
To avoid adverse reactions, you should undergo a full diagnostic examination before starting to take the drug described. A blood test will help identify individual intolerance to the drug.
Overdose
It poses a threat to human health, so in no case should you increase the dose prescribed by your doctor. An overdose of drugs is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- convulsions;
- severe decrease in pressure;
- bradycardia;
- renal failure;
- paresis;
- disturbances of consciousness (maybe coma).
In case of an overdose of the drug, it is necessary to call an ambulance, and before its arrival, lay the patient horizontally so that the surface has a low headboard. In case of mild overdose, gastric lavage can be done, but in more severe cases, a number of other procedures are required that can only be performed in a hospital.
Interaction with other drugs
The use of Enap-NL with such drugs as:
- antidepressants;
- Ethanol;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- narcotic drugs.
Taking them together can cause not only an exacerbation of adverse reactions, but also reduce the antihypertensive effect of Enap-NL.
Caution should be taken when taking the drug with:
- analgesics;
- Cholestyramine;
- Colestipol;
- products containing lithium.
Special instructions for the use of Enap H/Enap HL/Enap 20HL
Avoid prescribing the drug to patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery of a solitary kidney. Patients with moderately severe renal impairment should take the drug under medical supervision. In patients with severe heart failure, hyponatremia, hypovolemia associated with treatment with diuretics, adherence to a salt-free diet, diarrhea, vomiting, hemodialysis, as well as in elderly patients, severe arterial hypotension may be observed several hours after taking the first dose, which is usually manifested by nausea, tachycardia, dizziness and general weakness. Transient arterial hypotension is not a contraindication for further use of the drug. The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with severe forms of coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular diseases, severe stenosis of the aortic mouth or idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, generalized atherosclerosis in elderly patients, in whom an excessive decrease in blood pressure can cause hypoperfusion and ischemia. The hypotensive effect of the drug may increase after certain surgical interventions on the nervous system (sympathectomy). Due to the increased risk of anaphylactic reactions, the drug should not be prescribed to patients undergoing hemodialysis using polyacrylonitrile membranes or apheresis using dextran sulfate, as well as to patients undergoing desensitization to wasp or bee venom. The effectiveness and safety of the drug in children have not been established. Before a functional study of the parathyroid glands, the drug should be discontinued. In some patients, taking the drug may reduce the ability to drive vehicles or operate potentially dangerous machinery, especially at the beginning of treatment. Cross-allergy to thiazides, sulfonamides and sulfonylurea derivatives may occur.
Contraindications and restrictions
The drug should not be taken if there are contraindications such as:
- hypersensitivity to active ingredients;
- anuria;
- serious impairment of kidney function;
- severe liver dysfunction;
- taking Aliskiren against the background of diabetes mellitus or impaired renal function;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- lactose intolerance;
- age under 18 years;
- lactase deficiency;
- glucose-galactose malabsorption.
The drug should be taken with extreme caution for the following indications:
- aortic stenosis;
- diabetes;
- gout;
- elderly age;
- stenosis of the arteries of a single kidney;
- rehabilitation period after kidney transplantation;
- severe autoimmune diseases.
Contraindications
The main contraindications to taking the medicine are:
- individual hypersensitivity to ACE inhibitors;
- tendency to angioedema;
- severe renal failure;
- diabetes;
- lactose intolerance.
Important! Any ACE inhibitors, including enalapril, are prohibited for use during pregnancy, breastfeeding and children under 18 years of age. Enalapril maleate is able to penetrate the placental barrier and enter breast milk. The active substance can have an extremely negative effect on the process of formation and development of the fetus and complications during pregnancy, including termination. The ban on use in childhood is due to insufficient knowledge of the effect of the substance on the child’s body.
Difference from Enap-N
Enap-N tablets are also used to lower blood pressure and contain the same main active ingredients. The difference between Enap-NL and Enap-N lies only in the dosage of one of the active substances, namely hydrochlorothiazide. So, its content per 1 tablet of Enap-NL is 12.5 mg, and for Enap-N - 25 mg. The dose of enalapril is the same – 10 mg.
Only the attending physician can select and prescribe a more suitable drug, based on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. For example, patients over 65 years of age are predominantly prescribed a higher dosage of the drug.
What are Enap HL tablets for?
Enap HL is a combination antihypertensive drug used as the main therapeutic agent for lowering blood pressure (BP).
Therefore, the answer to the question of what Enap NL tablets are for is obvious - high blood pressure. The drug is based on the following substances:
- enalapril (enalapril maleate) - angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor - total weight 10 mg in one tablet (therefore the drug is sometimes called Enap NL 10);
- hydrochlorothiazide - 12.5 mg.
The action of the drug is to block the process of converting the hormone angiotensin I into angiotensin II. This biological process occurs under the influence of a special enzyme - ACE, as a result of which the concentration of angiotensin II, which has a vasoconstrictor effect, increases in the blood.
Vasoconstriction (the scientific name for the process of narrowing the lumen of blood vessels) is the main cause of increased blood pressure. ACE reduces the concentration of the hypertensive hormone angiotensin II, helping to lower blood pressure. At the same time, ACE slows down the breakdown of bradykinin, which has the opposite effect of angiotensin II. Bradykidin causes vasodilation (expansion of the lumen of blood vessels, which in turn causes a decrease in blood pressure). Thus, Enap NL has a good stabilizing effect on blood pressure, allowing it to be kept within normal limits.
Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide drug with a moderate diuretic effect. It slows down the reabsorption (reabsorption) of water and sodium salts in the kidney tubules and promotes their accelerated excretion in the urine. Due to this action, the fluid content in the tissues is reduced. This effect reduces the load on blood vessels and the heart, having a beneficial effect on the condition of the cardiovascular system.
WHO blood pressure classification
Are pills addictive?
The instructions for the drug indicate that the tablets can be addictive if taken for a long time, but hypertension is a disease that requires long-term treatment, so it will not be possible to achieve any positive changes in health with short-term therapy. And the drug itself will not have the desired effect if taken irregularly.
To maintain normal blood pressure, patients are forced to take the described drug for years, since hypertension returns after stopping its use. One of the positive aspects is the absence of a withdrawal effect. This means that even if the body gets used to the drug, stopping it will not affect its overall health.
No sharp surges in blood pressure were recorded after stopping taking the pills, and therefore even long-term use of Enap-NL does not affect the metabolism, which is usually characteristic of addictive drugs.
Reviews about the drug
The medicine has found popularity among doctors involved in the treatment of arterial hypertension. Most of the reviews about Enap HL are positive, which explains the high demand for the medicine among patients.
People suffering from chronic hypertension often take medication for a long time without noticing significant side effects. Negative effects from the respiratory system that accompany taking pills (dry cough) are observed quite rarely.
Among the positive reviews about taking Enap NL, the following most often appear:
- rapid normalization of blood pressure;
- long-lasting effect throughout the day after morning use (no need to take a second tablet);
- absence of side effects (the total number of negative side effects was clinically confirmed in only 6.9% of cases in the patients studied);
- general availability (available in every pharmacy);
- prevention of angina attacks.
There are significantly fewer negative reviews about the medicine, but they still exist:
- the appearance of a dry cough with prolonged use;
- pronounced diuretic effect;
- inability to take during pregnancy and lactation;
- addiction.
The last side effect, as mentioned above, is not mentioned in the official instructions and description of the drug. Most likely, there is a subjective assessment and incorrect interpretation by patients of the principle of action of Enap NL. The drug is not addictive, by which many people understand dependence (for example, as with psychotropic substances). But when you stop taking the medicine, its effect quickly stops, although without withdrawal symptoms.
Many patients expect the drug to have a lifelong hypotensive effect and permanently cure hypertension. However, this is impossible, since the causes of hypertension in most cases cannot be eliminated with treatment. Therefore, it is impossible to say about the addictive effect of the drug based only on reviews.
Regarding the cost of the medicine, patient reviews are divided: for some the drug is affordable, others find it quite expensive. But this is a subjective assessment, depending on the level of people’s well-being.