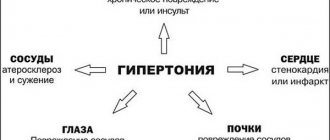
Release forms and composition of the drug
The medicine can be found on pharmacy shelves in the form of tablets for oral use. They are white or almost white in color, small in size and cylindrical in shape. The tablets are packaged in blisters of 10 pieces, which are placed in individual cardboard boxes. Each box contains detailed instructions, as well as 1 or 3 tablet strips.
Perindopril
In the pharmacy you can also find plastic bottles with tablets containing 10 or 30 pieces. They are placed in cardboard packaging, along with instructions for use. The tablets contain the active substance erbumine perindopril in an amount of 4 mg. There are tablets containing 8 mg of the active ingredient.
The product contains auxiliary ingredients:
- Magnesium stearate.
- Microcrystalline cellulose.
- Lactose.
- Croscarmellose.
Additional substances do not have therapeutic properties.
Synonyms of Perindopril
Synonyms for the pharmaceutical drug: Perinpress, Pfizer, Perindopril erbumine, Perindopril tert-butylamine, Perinidid.
In some cases, when purchasing the original medicine is impossible for a number of reasons, patients are interested in what can replace Perindopril.
The search for an absolute analog (that is, a drug with an identical composition) for the treatment of hypertension is not always justified, because drugs with other active ingredients of similar pharmacological action are usually no less effective. The main thing is to select an analogue together with your doctor.
Experts know exactly (from practice) which is better - Perindopril or Ramipril, Perindopril or Lisinopril, and so on.
The antihypertensive drug from the French manufacturer Servier Laboratories Prestarium is a one-component analogue of Perindopril. The excipients contain lactose monohydrate; the medicine is available in the form of tablets for oral administration and for resorption under the tongue.
The question of which is better, Perindopril or Prestarium, can only be answered after the practical use of these medications. One thing is certain - a medicine from a French manufacturer will be several times more expensive than, say, the Russian drug Perindopril SZ.
The active ingredient lisinopril in the drug of the same name, produced by a large number of European, Russian and Indian companies, is an ACE inhibitor. That is, the pharmacological effect of the drug is similar to Perindopril and its analogues and can be used in the treatment of hypertension instead of these drugs.
The auxiliary components do not contain lactose, and the drug itself is excreted unchanged from the body through the kidneys. There are no conditions for which Perindopril tablets would be powerless, but Lisinopril would cope with incredible efficiency. Therefore, discussions about the advantages of a particular remedy should be based on an individual approach to each case.
You should not try to find out which is better - Perindopril or Enalapril - at the pharmacy. Of course, the pharmacy worker will describe the benefits of the medicine that is available at the pharmacy outlet. If you have to choose between these two drugs, it is better to consult a doctor.
Let's compare another pair of drugs - Monopril and Perindopril. It is still difficult to answer which drug is better. The active ingredient of Monopril is fosinopril, an ACE blocker; The composition contains lactose in anhydrous form. The list of side effects presented in the instructions for use is similar to the list under consideration for Perindopril. Most likely, it will be possible to talk about preference only after careful selection of doses and practical use of the medicine.
The antihypertensive drug Perineva, produced by the Russian branch of the KRKA company, can confidently be called synonymous with the drug in question.
According to the instructions for use, the composition of the drug, with the exception of minor differences in excipients, is the same, and accordingly, the pharmacological properties and effectiveness are the same. Which is better - Perindopril or Perineva, as in most cases, should be shown by practical experience in the use of these drugs.
The active ingredient of Ramipril tablets and their direct analogues is ramipril, a precursor to the active metabolite of ramiprilat, an angiotensin-converting enzyme blocker. According to the instructions for use, the composition of the excipients of Ramipril does not differ significantly from the composition of Perindopril, but the list of indications for use is much more extensive, in particular, due to its use in nephropathy (diabetic and non-diabetic), severe proteinuria, especially accompanied by hypertension.
The question of replacing Perindopril with Ramipril should be considered after carefully studying the instructions for use of both medications and comparing them with the characteristics of the course of hypertension in the patient.
Pharmacological properties
Perindopril (reviews from patients who have taken the drug usually talk about the peculiarities of using the tablets) belongs to the group of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, that is, they have pronounced antihypertensive properties.
The drug helps suppress the process of converting angiotensin type 1 into a substance type 2, which significantly improves the condition of patients and prevents the development of complications.
Medicine:
- helps control blood pressure;
- improves heart function;
- helps stop the progression of chronic pathologies.
The substance in the product suppresses the activity of the adrenal glands, which reduces the production of important hormones that provoke an increase in blood pressure. With the use of the drug, there is a significant improvement in the condition and increase in the performance of patients.
pharmachologic effect
Perindopril is an ACE inhibitor. Pharmacological action - hypotensive, vasodilating, cardioprotective, natriuretic. In the body it turns into an active metabolite - perindoprilat (contains a carboxyalkyl group), which interacts with the zinc atom in the ACE molecule. Inactivates ACE in plasma, endothelium of the vascular wall, possibly in the cells of the renal glomeruli and tubules, lung tissue, heart, adrenal glands and brain. Reduces the level of angiotensin II in the blood and tissues, reduces the production and release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands, suppresses the liberation of norepinephrine from the endings of sympathetic nerve fibers and the formation of endothelin in the vascular wall. Reduces peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure (without developing tachycardia), left ventricular filling pressure (improves its diastolic relaxation). Arterial and venous vasodilation is accompanied by a weakening of post- and preload on the myocardium, a decrease in end-diastolic pressure in the ventricles of the heart, a moderate decrease in heart rate, and an increase in cardiac output. Improves regional (coronary, cerebral, renal, muscular) blood circulation, reduces myocardial oxygen demand in coronary artery disease. By inhibiting tissue renin-angiotensin systems, it is cardioprotective (prevents or promotes regression by 19% of hypertrophy and dilatation of the left ventricle) and angioprotective (prevents hyperplasia and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, induces the reverse development of hypertrophy of the vascular wall, restores the elasticity of large vessels and endothelial function, including including the ability to release nitric oxide, endothelial relaxing factor). Reduces excess collagen deposition in the subendocardial layers of the myocardium, normalizes the myosin isoenzyme profile, and reduces the incidence of ventricular and reperfusion arrhythmias. Increases the activity of the kallikrein-kinin system, stabilizes the level of bradykinin, vasodilator PGI2 and PGE2, atrial natriuretic peptide, endothelin-dependent relaxing factor. Minimizes pressor pressure, incl. adrenergic, effects on blood vessels, prevents sodium retention in the body, increases natriuresis and diuresis. Against the background of daily intake, acetylsalicylic acid has an effect on hemostasis (increased levels of fibrinogen and the activity of factors VII and X are compensated by increased fibrinolysis against the background of increased consumption of AT III). Sensitizes peripheral tissues to the action of insulin and improves glucose metabolism. Shows antioxidant properties. Inhibits the development of tolerance to nitrates and enhances their vasodilating effect. After a single dose of 4–8 mg, blood pressure decreases after 4–6 hours. It has a prolonged hypotensive effect that continues with repeated daily doses for 24 hours. The antihypertensive effect depends on the dose (in the range of 2–8 mg). At a dose of 2 mg, it inhibits ACE by 80% at the peak of action and by 60% after 24 hours; when the dose is increased to 8 mg, its inhibitory activity increases to 95% and 75%, respectively. In patients with a positive response to treatment, blood pressure normalizes within 1 month and remains within normal limits during treatment. Discontinuation of therapy is not accompanied by the development of withdrawal syndrome. In patients with chronic heart failure, it statistically significantly reduces the severity of clinical symptoms and increases exercise tolerance. Does not cause fluctuations in blood pressure after the first dose and during long-term therapy. When taken for six months in patients with chronic heart failure, it improves the patency of large, medium and small bronchi (the increase in patency in the small bronchi is more pronounced in smoking patients). Against the background of portal gastropathy, it reduces the vulnerability and bleeding of the gastric mucosa with the disappearance of erosions and ulcers. Long-term therapy is not accompanied by changes in renal function. Increases HDL levels and decreases uric acid levels (in patients with hyperuricemia). In vitro and in vivo studies revealed no signs of mutagenicity; with long-term use in mice and rats, no carcinogenic properties, as well as signs of embryotoxicity and teratogenicity in rats, mice, rabbits and monkeys. In high doses, it has a toxic effect on the maternal and fetal organisms in rodents and rabbits, and penetrates into the breast milk of rats.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The drug has a pronounced effect almost immediately after ingestion and dissolution of the film shell of the tablet. The active substance suppresses the process of angiotensin conversion, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure and helps keep the levels constant.
The medication affects the release of norepinephrine, reduces its amount in the blood, which helps prevent an increase in numbers. The ingredient in the medicine helps increase the production of substances that have a positive effect on the vascular walls. This makes them more elastic and stronger, which significantly reduces the risk of complications.
The drug also eliminates headaches and dizziness, and increases the performance of patients.
Tablets also have other effects on the body:
- Reduces aldosterone production.
- It improves the condition of not only large vessels, but also capillaries, which has a positive effect on microcirculation.
- Suppresses the production of excess collagen.
- Reduces the load on the myocardium, which has a beneficial effect on its condition and reduces the risk of the formation of ischemic foci.
- Increases minute volume of circulating blood without a concomitant increase in heart rate.
- Improves peripheral blood circulation and tissue nutrition, which reduces the risk of developing trophic changes.
- Facilitates the condition of patients with chronic heart failure.
- Increases the patient's tolerance to physical activity.
Thanks to the complex effects of the drug, there is a significant improvement in the condition of patients with acute and chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system. At the same time, the effectiveness of therapy is noted, even in the presence of concomitant abnormalities.
After taking the drug orally, the tablet dissolves and the main substance is absorbed into the blood. Approximately 25% of its total amount enters the systemic circulation 20-30 minutes after administration. The active substance is able to bind to plasma proteins, but its bioavailability does not exceed 70%.
The substance is processed in the liver. The maximum concentration of the main ingredient in the blood is achieved 3-4 hours after consuming the tablet and persists throughout the day. The elimination period after processing takes up to 3 days, which depends on the dose taken and duration of use.
The main amount of ingredients is excreted after processing through the kidneys. Experts note a slower excretion in patients suffering from pathologies of the urinary system. A small amount of substances is evacuated with feces. A slowdown in absorption and metabolism is observed in the presence of chronic pathologies of the digestive tract with impaired intestinal function.
In patients with severe forms of the disease, there is a significant decrease in the effectiveness of therapy, so tablets are prescribed quite rarely.
PERINDOPRIL-SZ
– perindopril erbumine (perindopril)
Release form, composition and packaging
Pills
white or almost white, round, flat-cylindrical in shape with a chamfer.
| 1 tab. | |
| perindopril erbumine | 2 mg |
Excipients: lactose monohydrate (lactopres) (milk sugar) – 72.25 mg, calcium stearate – 0.75 mg.
10 pieces. – contour cell packaging (3) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cell packaging (5) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (1) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (2) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – polymer jars (1) – cardboard packs.
30 pcs. – polymer bottles (1) – cardboard packs.
Pills
white or almost white, round, flat-cylindrical in shape with a chamfer.
| 1 tab. | |
| perindopril erbumine | 4 mg |
Excipients: lactose monohydrate (lactopres) (milk sugar) – 144.5 mg, calcium stearate – 1.5 mg.
10 pieces. – contour cell packaging (3) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cell packaging (5) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (1) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (2) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – polymer jars (1) – cardboard packs.
30 pcs. – polymer bottles (1) – cardboard packs.
Pills
white or almost white, round, flat-cylindrical in shape with a chamfer and a notch.
| 1 tab. | |
| perindopril erbumine | 8 mg |
Excipients: lactose monohydrate (lactopres) (milk sugar) – 289 mg, calcium stearate – 3 mg.
10 pieces. – contour cell packaging (3) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cell packaging (6) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cell packaging (9) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs.
– contour cell packaging (1) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (2) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – contour cell packaging (3) – cardboard packs. 30 pcs. – polymer jars (1) – cardboard packs.
30 pcs.
– polymer bottles (1) – cardboard packs.
pharmachologic effect
Perindopril is an ACE inhibitor. Angiotensin-converting enzyme is an exopeptidase that converts angiotensin I into the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II, as well as the destruction of bradykinin, which has a vasodilator effect, into an inactive heptapeptide.
Suppression of ACE leads to a decrease in the content of angiotensin II in the blood plasma, as a result of which the activity of renin in the blood plasma increases and the secretion of aldosterone decreases.
Since ACE inactivates bradykinin, suppression of ACE is accompanied by an increase in the activity of both the circulating and tissue kallikrein-kinin system, while the prostaglandin system is also activated. It is possible that this effect is part of the mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors, as well as the mechanism of development of some side effects of these drugs (for example, cough).
Perindopril has a therapeutic effect due to its active metabolite, perindoprilat. Other metabolites do not have an ACE inhibitory effect in vitro.
Arterial hypertension
Perindopril is effective for the treatment of arterial hypertension (AH) of any severity. With its use, there is a decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the supine and standing positions.
Perindopril reduces peripheral vascular resistance, which leads to a decrease in high blood pressure and improvement of peripheral blood flow without changing heart rate.
As a rule, the use of perindopril leads to increased renal blood flow, but the glomerular filtration rate does not change.
The antihypertensive effect of the drug reaches its maximum 4-6 hours after a single oral dose and lasts 24 hours. The antihypertensive effect by the end of the day after a single dose of the drug is about 87-100% of the maximum antihypertensive effect.
A decrease in blood pressure is achieved quite quickly. In patients with a positive response to treatment, normalization of blood pressure occurs within a month, and no addictive effect is observed.
Discontinuation of treatment is not accompanied by the development of withdrawal syndrome.
Perindopril has a vasodilating effect, helps restore the elasticity of large arteries and the structure of the vascular wall of small arteries, and also reduces left ventricular hypertrophy.
The concomitant use of thiazide diuretics enhances the severity of the antihypertensive effect. Combining an ACE inhibitor and a thiazide diuretic also reduces the risk of hypokalemia while taking diuretics.
Heart failure
Perindopril normalizes heart function by reducing preload and afterload.
In patients with chronic heart failure taking perindopril, the following was found:
- decreased filling pressure in the left and right ventricles of the heart;
- decrease in OPSS;
- increased cardiac output and increased cardiac index.
It was shown that the decrease in blood pressure after the first dose of Perindopril-SZ in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) functional class I-II according to the NYHA classification was not statistically significantly different from the change in blood pressure in the placebo group.
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
When taking perindopril at a dose of 8 mg/day, there is a significant reduction in the absolute risk of complications provided for by the main criterion of effectiveness (mortality from cardiovascular diseases, the incidence of non-fatal myocardial infarction and/or cardiac arrest with subsequent successful resuscitation), and a decrease in the absolute risk is also observed in patients who have previously suffered a myocardial infarction or coronary revascularization.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, perindopril is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved after 1 hour. Bioavailability is 65-70%.
Cmax of perindoprilate (active metabolite) in blood plasma is achieved 3-4 hours after oral administration. Concomitant food intake slows down the conversion of perindopril to perindoprilat, thereby affecting bioavailability.
Therefore, the drug should be taken orally 1 time/day, in the morning, before meals.
Distribution
The Vd of free perindoprilate is approximately 0.2 l/kg. The binding of perindoprilate to plasma proteins is insignificant and dose-dependent. The equilibrium state is achieved within 4 days. With long-term use, perindopril does not accumulate.
Metabolism
Approximately 20% of the total amount of absorbed perindopril is converted to perindoprilat, the active metabolite. In addition to perindoprilate, 5 more metabolites are formed that do not exhibit pharmacological activity.
Removal
T1/2 of perindopril from blood plasma is 1 hour. Perindoprilat is excreted by the kidneys, T1/2 of the free fraction is 3-5 hours. Effective T1/2 is 25 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
The elimination of perindoprilate is slowed in old age, as well as in patients with heart and renal failure.
In case of renal failure, it is advisable to adjust the dose of the drug taking into account the degree of renal dysfunction and CC. The dialysis clearance of perindoprilate is 70 ml/min.
In patients with liver cirrhosis, the hepatic clearance of perindopril is reduced by 2 times. However, the amount of perindoprilate formed does not decrease, and no dose adjustment is required.
Indications
- arterial hypertension (as monotherapy and as part of combination therapy);
- chronic heart failure;
- stable coronary artery disease: reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications in patients who have previously had myocardial infarction and/or coronary revascularization;
- prevention of recurrent stroke (in combination with indapamide) in patients who have had a stroke or transient ischemic cerebrovascular accident.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to perindopril or excipients included in the drug, as well as to other ACE inhibitors;
- history of angioedema (Quincke's edema) associated with taking ACE inhibitors;
- hereditary/idiopathic angioedema;
- simultaneous use with aliskiren and aliskiren-containing drugs in patients with diabetes mellitus or impaired renal function (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) 1/100, 1/1000, 1/10,000,
Source: https://health.mail.ru/drug/perindoprilsz/
Indications for use
Perindopril is prescribed to patients with various pathologies of blood vessels and heart. Reviews from the majority of patients who have taken the effective drug for a long period confirm its effectiveness when used for the following disorders:
- Arterial hypertension of various forms and degrees of neglect.
- Acute heart failure, transition of pathology to a chronic form.
- The form of coronary heart disease is stable. If the course of the pathology is unstable, there may be no therapeutic effect, so tablets are not used in this case.
- Recovery period after ischemic stroke. The drug is used to prevent the re-development of this condition, as well as to improve the patient’s condition.
- Threat of transient ischemic attack. The condition is a mild form of stroke, and in patients with hypertension the risk of developing it is significantly increased if the indicators are difficult to control.
- Hypertensive disease of renovascular origin.
The drug can be used over a long period or in short courses to prevent complications and correct the condition.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, perindopril is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax is reached after 1 hour. Bioavailability is 65-70%. During metabolism, perindopril is biotransformed to form an active metabolite - perindoprilate (about 20%) and 5 inactive compounds. Cmax of perindoprilat in plasma is achieved between 3 and 5 hours after administration. The binding of perindoprilate to plasma proteins is insignificant (less than 30%) and depends on the concentration of the active substance. Vd of free perindoprilate is close to 0.2 l/kg. Does not accumulate. Repeated administration does not lead to accumulation and T1/2 corresponds to the period of its activity. When taken with food, the metabolism of perindopril slows down. T1/2 of perindopril is 1 hour. Perindoprilat is excreted from the body by the kidneys; T1/2 of its free fraction is 3-5 hours. In elderly patients, as well as with renal and heart failure, the excretion of perindoprilate slows down.
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated if there is an intolerance to its components or a tendency to such manifestations in the patient's history.
Other barriers to therapy include:
- Lactation and pregnancy period. The drug can cause complications in mother and child.
- Hereditary neurological and mental disorders at different stages of development. In mild cases, the drug can be used, but only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Persistent hypotension, accompanied by concomitant abnormalities in the form of weakness, fatigue and decreased performance.
- Stenosis of the aortic and mitral valve of the heart, causing disruption of its functioning.
- Diagnosis of severe pericarditis with a risk of complications.
- Severe autoimmune pathologies accompanied by damage to connective tissue.
- Decreased sodium levels in the blood.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Acute brain pathologies.
- A decrease in platelet levels in the blood, increasing the risk of bleeding. In this condition, the drug is used quite rarely and in short courses.
- Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, accompanied by pronounced narrowing of the lumen and impaired peripheral circulation.
- Detection of excessive potassium in the blood.
- Severe liver failure, viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis.
- Chronic severe renal failure. The condition impairs the removal of ingredients from the body, which increases the risk of overdose.
- Dehydration of the body due to various conditions.
For patients with severe forms of angina, the drug is prescribed with caution and in short courses. If complications occur, treatment is immediately canceled.
Instructions for use, dosage
The tablets are taken only orally in the dosage prescribed by a specialist. The regimen and dose may vary depending on the specific disease.
| Organs and systems | Application regimen and dosage |
| Arterial hypertension | The daily dosage for such patients is 4 mg. It is taken in the morning; the course of therapy can last several weeks or even months, depending on its effectiveness. If there is no result from use, the daily dose is increased to 8 mg. The dosage is increased gradually over 2-4 weeks, since a sharp increase can lead to complications. |
| Stable form of coronary heart disease | For 2 weeks, patients with this disease take 4 mg of the drug per day. The dose is gradually increased to 8 mg per day, and treatment can last several months. Cancellation is also carried out gradually. |
| Heart failure | If a chronic form of the pathology is detected, the medicine is taken 2 mg per day. Gradually increase the dose to 4 mg. Treatment for such disorders is long-term and is often combined with the use of other medications. |
| Preventive therapy for recurrent stroke | For prophylactic purposes, the product is used for 4 weeks. For the first 14 days, the patient takes 2 mg, after which he takes 4 mg per day. Repeated courses are carried out after 3 months, often the intervals between courses increase to 6 months. |
| Hypertension of renovascular origin | For this form of the disease, the daily dosage of the drug is 2 mg. Treatment is continued for several weeks, and the drug is often taken on an ongoing basis if the condition is difficult to correct with medications. |
For any disease, the regimen for using the drug can be changed depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Prenessa® (4 mg)
Prenessa®
Compound
One tablet contains
active substance – perindopril erbumine 2 mg, 4 mg or 8 mg,
excipients: calcium chloride hexahydrate, lactose monohydrate, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate
Description
Tablets are round, white or almost white, slightly biconvex, with a bevel (for a dosage of 2 mg).
The oval-shaped tablets are white or almost white, slightly biconvex, with a score on one side and a bevel (for a dosage of 4 mg).
The tablets are round, white or almost white, slightly biconvex, with a score on one side and a bevel (for a dosage of 8 mg).
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Perindopril
ATX code C09AA04
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, perindopril is rapidly absorbed, and maximum plasma concentrations are achieved within 1 hour. Bioavailability ranges from 65 to 70%.
About 20% of perindopril taken is converted into the active metabolite perindoprilat. In addition to the active metabolite, 5 more inactive metabolites of the drug have been identified. The half-life (T1/2) of perindopril is 1 hour. The maximum concentration (Cmax) of perindoprilate in the blood plasma is achieved within 3 to 4 hours.
Concomitant food intake slows down the conversion of perindopril to perindoprilat, and therefore bioavailability decreases, so perindopril should be taken orally, once a day, before breakfast.
The volume of distribution is approximately 0.2 L/kg for unbound perindoprilate. Protein binding is negligible (perindoprilate binding to angiotensin converting enzymes is less than 30%), but this is concentration dependent.
Perindoprilat is excreted in the urine and T1/2 of the unbound fraction is approximately 3 to 5 hours. The breakdown of perindoprilate associated with ACE leads to an increase in effective T1/2 to 25 hours. With repeated administration of the drug, stabilization of pharmacokinetic parameters is achieved over 4 days. After multiple doses, there was no accumulation of perindopril.
In elderly patients and in patients with cardiac or renal failure, the excretion of perindoprilate is reduced. In case of impaired renal function, it is recommended to change the dose depending on the severity
disorders (creatinine clearance level).
Perindoprilat is eliminated from the circulation by dialysis, its clearance is 70 ml/min.
With liver cirrhosis, the kinetics of perindopril changes, while the hepatic clearance of the initial molecule decreases by 2 times, however, the amount of perindoprilate formed does not change, and therefore, in this disease, the dose of the drug does not need to be changed.
Pharmacodynamics
Prenessa® is an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. The converting enzyme kinase is an oxopeptidase that promotes the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II and destroys the vasodilator bradykinin to an inactive hectapeptide.
ACE inhibition leads to a decrease in the formation of angiotensin II in plasma, which is accompanied by an increase in plasma renin activity (due to inhibition of negative feedback) and a decrease in aldosterone secretion.
Since ACE inactivates bradykinin, suppression of ACE is accompanied by an increase in the activity of both the circulating and tissue kallikrein-kinin system (the prostaglandin system is activated). Perhaps this one
the mechanism contributes to the action of the ACE inhibitor, which lowers blood pressure and partially contributes to the appearance of some side effects (for example, cough).
Perindopril acts through its active metabolite perindoprilate.
Arterial hypertension
Prenessa® is effective at any stage of arterial hypertension: mild, moderate, severe; with a decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (in the “lying” and “standing” positions).
Prenessa® reduces total peripheral vascular resistance, which leads to a systemic decrease in blood pressure.
In this case, peripheral blood flow accelerates, but the heart rate (HR) does not increase.
Renal blood flow increases, but the glomerular filtration rate does not change.
After taking a single dose, the maximum antihypertensive effect is achieved after 4–6 hours and lasts for at least 24 hours; the residual effect is 87-100% of the maximum effect. The decrease in blood pressure occurs quickly.
In patients with a good response to treatment, normalization is achieved within a month and is maintained without the occurrence of tachyphylaxis. Interruption of treatment is not accompanied by withdrawal syndrome.
Perindopril reduces left ventricular hypertrophy.
Perindopril has a vasodilating effect, improves the elasticity of large arteries and reduces the medium/lumen ratio of small arteries. Additional therapy with thiazide diuretics enhances the effect. Combining an ACE inhibitor and thiazide diuretics also reduces the risk of hypokalemia while taking diuretics.
Heart failure
Prenessa® reduces heart work by reducing pre- and afterload.
In patients with heart failure, Prenessa® reduces filling pressure in the right and left ventricles, reduces total peripheral vascular resistance, increases cardiac index and cardiac output.
Patients with a history of cerebrovascular disease
In patients with a history of cerebrovascular diseases (stroke or transient ischemic episodes in the last 5 years), Prenessa® helps reduce the risk of recurrent stroke (both ischemic and hemorrhagic in nature) by 28%.
It was also found that perindopril, in general, reduces the risk of developing: fatal or disabling strokes (by 33%), cardiovascular complications such as death, non-fatal myocardial infarction and non-fatal stroke (by 26%), dementia, associated with stroke (by 34%), severe cognitive decline (by 45%), and major coronary events, including nonfatal myocardial infarction and mortality from coronary heart disease (by 26%).
These therapeutic benefits were observed in both hypertensive and normotensive patients, regardless of age, gender, diabetes, and stroke type. It was found that active therapy for 5 years avoids the development of one stroke per 23 patients and one significant cardiovascular complication per 18 patients.
Patients with stable coronary artery disease:
In patients with signs of coronary artery disease without clinical signs of heart failure who received perindopril at a dose of 8 mg once daily, in addition to conventional therapy (including platelet inhibitors, lipid-lowering drugs and beta-blockers), there was a significant absolute reduction of the primary endpoint by 1 .9% (relative risk reduction by 20%, 95% CI [9.4; 28.6] – p
Source: https://drugs.medelement.com/drug/%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B0-4-% D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BA%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F/101179681477650947?instruction_lang=RU
Side effects
Perindopril (reviews from patients who took the drug help evaluate the effectiveness of therapy before starting to use the tablets) often leads to the development of complications if the instructions are not followed. Following rules is not considered a way to prevent negative reactions.
The most common violations:
- On the part of the central nervous system, seizures and sleep disturbances are noted. The patient may be awake at night and feel drowsy during the day. His condition is aggravated by increased irritability, headache and dizziness, and ringing in the ears. Disturbances may persist for a long period or disappear after discontinuation of therapy.
- Complications from the blood vessels and heart occur most often. They are accompanied by the development of angina and arrhythmia, tachycardia, and a critical decrease in blood pressure is observed. Disorders can lead to myocardial infarction or ischemic stroke, which threatens the patient’s life.
- From the respiratory system, complications manifest themselves in the form of respiratory failure, shortness of breath, and dry cough. Some patients report signs of allergic rhinitis.
- The digestive tract suffers quite often during therapy. Patients note the appearance of pain in the stomach, stool disorders, and loss of appetite. Nausea and indigestion are considered common negative reactions. Some patients with chronic pancreatitis note an exacerbation of the condition, even if all nutritional rules are followed.
- Laboratory tests and urine indicate the appearance of traces of protein, which is considered a dangerous symptom and can provoke concomitant abnormalities in the kidneys.
- Often complications affect the reproductive system, accompanied by sexual dysfunction and menstrual cycle disorders.
Side effects are almost always accompanied by allergic reactions from the skin. Patients report the appearance of a rash and itching of the skin, swelling of the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose. The condition is aggravated by general symptoms such as weakness, fatigue and psycho-emotional disorders.
If negative reactions occur, you should stop using the medication and seek medical help.
Perindopril: a cure for hypertension in old age
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
The drug Perindopril is a reliable treatment for hypertension and cardiac dysfunction caused by various reasons, including kidney diseases. It is used for cardiac ischemia and is prescribed for elderly hypertensive patients and those suffering from type II diabetes mellitus.
Perindopril reduces the risk of another heart attack and is the only drug proven to be effective in preventing stroke recurrence. It gives people in advanced years the opportunity to preserve their memory and good mental concentration, and prevents the development of senile dementia.
Perindopril lowers blood pressure, remains effective throughout the day and is easily tolerated. For those suffering from excess weight and diabetes, it has a beneficial effect on metabolism. The drug is not suitable if you need to quickly reduce blood pressure and stop a hypertensive crisis.
Perindopril: instructions
According to the classification, the medicine belongs to ACE inhibitors. The work of these substances is to reduce the load on the myocardium, which improves the activity of the muscular organ, increasing its intensity.
The use of perindopril causes the formation of the active metabolite perindoprilat. The substance slows down the conversion of angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II, which is a strong vasoconstrictor.
Blood pressure decreases 60 minutes after using the drug, the maximum effect is achieved after 5-7 hours and lasts a day. The medicine is excreted by the kidneys.
Perindopril: indications for use
Perindopril is used for stable coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension and chronic heart failure. The medicine is indicated to reduce the likelihood of another stroke.
Most doctors prescribe it in tandem with the diuretic Indapamide. The drug is also prescribed to diabetics of types I and II for high blood pressure.
Perindopril: doses
Perindopril is prescribed half or a whole tablet per day. The concentration of the drug in the tablet varies, and the doctor must choose the right one. It is important that the doctor is aware of the patient’s diagnosis, measures blood pressure and knows how well the kidneys are functioning. Determining the dosage on your own is strictly not recommended!
Perindopril is usually taken in the first half of the day, but at the beginning of treatment it is allowed to take it before bed, because the first three days the drug can cause drowsiness and increased fatigue. Later the patient gets used to it.
Side effects
Perindopril is tolerated without undesirable consequences, but during the period of use it is necessary to constantly monitor kidney function by doing blood and urine tests.
Severe symptoms are rare. Negative reactions were detected in less than 10% of cases. Side effects of Perindopril manifest themselves in the form of malfunctions of the body systems:
- Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, severe fatigue, worsening mood, ringing in the ears, muscle cramps;
- Increased sweating, impaired sexual function;
- Gastrointestinal tract: indigestion, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth, decreased appetite, inflammation of the pancreas;
- Allergic manifestations: rashes, skin itching, angioedema;
- Cardiovascular system: arrhythmia, angina pectoris;
- Respiratory organs: constant “dry” cough;
- Urinary system: acute renal failure.
Contraindications and precautions
Like all medications, perindopril has contraindications:
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
- Age up to 18 years (Perindopril is not used in pediatrics);
- Pregnancy and lactation: ACE inhibitors are prohibited when carrying a child and breastfeeding; even when planning a pregnancy, the drug must be excluded, since it can harm the health of the unborn child;
- Sensitivity to the components of the drug.
Diabetes mellitus, kidney disease and old age are not considered contraindications. For patients with these characteristics, perindopril is prescribed under close and regular laboratory monitoring.
But there is a list of ailments for which taking perindopril is not absolutely safe and requires continuous medical monitoring. The list of pathologies is quite long, but the most common conditions are:
- Moderate or severe renal failure;
- Transplanted donor kidney;
- Severe autoimmune nosological units of connective tissue;
- Hyperkalemia;
- Dehydration and exicosis;
- Obliterating atherosclerosis.
Drug interactions
It is necessary to combine all kinds of medications with perindopril in consultation with the doctor, since uncontrolled use will provoke an increase in the level of potassium in the blood, which poses a serious threat to health. When prescribing perindopril, the doctor should be aware of the herbal tinctures and decoctions or nutritional supplements consumed by the patient.
Often, for patients, one medication for hypertension is not enough to bring the pressure within an acceptable range. When readings are 160 per 100 mm Hg, a combination of two medicinal substances is usually prescribed for joint use. In difficult cases, a combination of 3-4 drugs is possible.
Perindopril is often paired with indapamide. The effectiveness of this combination has been repeatedly confirmed by the results of scientific research. The combination of perindopril and indapamide significantly reduces blood pressure, reduces the likelihood of death from most diseases, the risk of heart attack and stroke.
A significant plus is that the drugs are easily tolerated. The combination of perindopril and indapamide is most popular in the treatment of elderly patients and large patients suffering from hypertension, metabolic syndrome or type II diabetes.
Patients with severe hypertension and high cardiovascular risk are prescribed simultaneous treatment with perindopril, indapamide and amlodipine.
The satisfactory tolerability of this combination has also been proven by studies conducted in the Russian Federation. The study was carried out over 3 months. Tablets containing perindopril and indapamide - noliprel - were supplemented with amlodipine in severe cases.
If amlodipine provokes swelling of the legs, it is replaced with lercanidipine. The combination of three drugs for hypertension made it possible to maintain blood pressure below 140 over 90 in almost 75% of patients. In those suffering from type II diabetes, 62% of the studied patients achieved blood pressure levels below 135/85.
If there is no effect from taking three medications, the method of sympathetic denervation of the renal arteries is used.
The popular drug Prestance is a mix of perindopril + amlodipine. It is actively used to treat hypertension and reduce the risk of complications in the cardiovascular system. There is an analogue of Dalnev, more affordable in cost.
80% of patients achieved the desired blood pressure level without any side complications. Prestance comes in 4 variations with different dosages of medicinal substances, which allows the doctor to vary when selecting the optimal dose for the patient. If necessary, the patient is transferred to more powerful tablets.
Overdose
The use of perindopril in a dosage exceeding the prescribed one provokes a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Typical signs of overdose are shock, palpitations, anxiety, coughing and dizziness.
Activated carbon tablets and gastric lavage will relieve symptoms. To activate blood flow to the brain and heart, a person needs to be laid on his back and his legs raised. A subsequent call for emergency medical assistance is mandatory!
Terms and conditions of storage
There are no special storage rules. Traditionally - in a place inaccessible to children, protected from sunlight. Temperature limits: no more than 25°C. Shelf life: 3 years (perindopril arginine), 2 years (perindopril erbumine).
Release form
Perindopril is sold in polypropylene bottles with initial opening control of 30 or 90 tablets.
Perindopril and analogues: price
The cost of Perindopril in Russian regions starts from 141 rubles. On average its price:
- Perindopril arginine 10 mg 30 tab. – from 600 rubles,
- Perindopril arginine 5 mg 30 tab. – from 430 rubles,
- Perindopril erbumine 8 mg 30 tab. – from 390 rub.
- Perindopril erbumine 4 mg 30 tab. – from 260 rub.
Perindopril plus indapamide tablets are sold at prices:
- 2.5 mg+8 mg 30 pcs. – from 490 rub.,
- 1.25 mg+4 mg 30 pcs. – from 370 rub.,
- 0.625 mg+2 mg 30 pcs. – from 240 rub.
Perindopril Richter is a combination of perindopril erbumine and indapamide. The effect of the drug lasts a day, a stable therapeutic result is achieved 30 days after the first dose, and completion of treatment is not complicated by withdrawal syndrome. Cost – from 258 rub. for 30 tab. 4 mg each.
You can also read the instructions for use of the drug Kudesan.
The most common substitutes for Perindopril with recommendations for use:
- Captopril (you can lament about the drug in this article). 20 tablets of 25 mg - price from 65 rubles. A popular analogue of perindopril. The range of applications ranges from arterial hypertension and heart failure to diabetic nephropathy.
- Lisinopril. 30 tablets of 5 mg – from 73 rub. Cheap option, same recommendations. A significant advantage is that it can be prescribed to patients with extra pounds.
- Diroton. 14 tablets of 10 mg – from 133 rubles. An available ACE inhibitor with lower bioavailability compared to perindopril. The effect takes longer.
- Parnavel. 30 tablets of 4 mg – from 275 rub. Recommendations for prescribing indicate arterial hypertension and heart failure.
- Perineva. 30 tablets of 4 mg – from 234 rubles. Accelerates blood flow, but does not increase the number of heart contractions. The indications are identical to the previous options.
- Prestarium A. 30 tablets of 5 mg – from 404 rub. An expensive analogue that dilates blood vessels and normalizes the functioning of the heart. Effective in reducing the likelihood of stroke.
Patient reviews
Perindopril is not a powerful medicine for blood pressure, as noted by those suffering from hypertension in numerous reviews. At the same time, its effect is gentle and almost does not provoke side effects.
Tamara Vasilyeva, 40 years old: I have been taking perindopril for 4 months. 3 weeks after the start of the course, the pressure stabilized and remained all day and night at 130 to 80. Before treatment, it jumped every day in the evening.
Andrey Ivanovich, 54 years old: Perindopril was prescribed to me by a cardiologist. I've been taking it for four months now. My average blood pressure is 130 over 80, but when the weather changes, it rises sharply and the pills no longer help. Sometimes it reaches 170 to 110, and the headache grows. I'll ask the doctor to prescribe a stronger medicine.
Vera Stepanovna, 62 years old: I took perindopril for blood pressure for six months. The tablets maintained the desired level perfectly, the pressure never jumped. But the constant coughing tired me. The doctor recommended Losartan plus a diuretic as a replacement. I switched to a new drug, but I don’t know yet whether it’s right for me.
Manufacturers praise the advantages of perindopril in comparison with other ACE inhibitors. But in ordinary medical practice its special advantages are not highlighted. When an inexpensive analogue is required, perindopril is changed to other ACE inhibitors, taken once every 24 hours.
The most popular are enalapril, lisinopril or ramipril. A Belarusian version of Perindopril-Mik is also produced, a feature of which is the use of tert-butylamine salt, which activates metabolic processes. But the doctor must select the medicine.
And no blood pressure medications can replace a healthy lifestyle - a well-planned diet, physical activity, and reduction of anxiety and worry.
Overdose
Doctors draw patients' attention to the possibility of developing an overdose with prolonged use in high doses without a doctor's prescription. The condition is accompanied by a significant deterioration in well-being and a critical decrease in blood pressure.
Sometimes patients develop a state of shock, in which they lose consciousness, bradycardia and a decrease in body temperature are observed. Against the background of such disorders, cardiac arrest is possible, so the condition requires immediate medical attention in a hospital setting.
The condition can provoke other complications:
- Nausea and repeated vomiting.
- Abnormal stool.
- Severe headaches.
- Drowsiness and difficulty concentrating.
An overdose may be accompanied by deterioration of kidney function. When providing care in a hospital, Atropine is used, which fights bradycardia. Patients have their stomach washed, enterosorbents and other medications are prescribed depending on the severity of certain symptoms.
If the body is dehydrated, intravenous infusions of saline and other solutions are prescribed to normalize the electrolyte balance and prevent related disorders.
Side effects
Like all medications, when taking this therapeutic agent there may also be side effects that are not typical for every patient undergoing treatment with this drug. Therefore, it is important to familiarize yourself not only with the indications for the use of Perindopril, but also with the negative effects. If you notice any of the following symptoms, stop taking the medicine and tell your doctor:
- sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty breathing;
- swelling of the face;
- swelling of the tongue and throat, creating difficulty breathing;
- serious skin reactions;
- dizziness, fainting;
- heart problems, fast or abnormal heartbeat;
- pancreatitis.
Negative consequences are divided depending on the frequency of manifestation in patients.
Very common (> 1 in 10):
- edema (retention of water in the body).
Frequent (up to 1 in 10):
- cephalgia;
- drowsiness;
- vertigo;
- tingling in the limbs, numbness;
- visual disturbances (including double vision);
- tinnitus;
- tachycardia;
- redness;
- hypotension;
- cough;
- dyspnea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- abdominal pain;
- disorders of taste perception;
- digestive problems;
- bowel disorders;
- dyspepsia;
- allergic manifestations;
- muscle cramps;
- weakness;
- swelling of the ankles.
Less common (up to 1 in 100):
- mood disorders, mental state;
- sleep disorders;
- tremor;
- pain perception disorder;
- irregular heartbeats;
- runny nose (stuffy or watery discharge);
- hair loss;
- change in skin color;
- backache;
- arthralgia;
- myalgia;
- urination disorders (increased frequency of visiting the toilet, especially at night);
- nausea;
- bronchospasm;
- dry mouth;
- angioedema;
- the appearance of blisters on the skin;
- kidney disorders;
- impotence;
- increased sweating;
- a large number of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell);
- breast enlargement in men;
- increase or decrease in body weight;
- tachycardia;
- vasculitis;
- photosensitivity;
- fever;
- changes in laboratory values: increased potassium levels in the blood (return to normal after stopping treatment), low sodium levels, hypoglycemia, high creatinine and urea levels.
Rare (up to 1 in 1000):
- confusion;
- worsening of psoriasis;
- changes in laboratory parameters: elevated liver enzymes, increased serum bilirubin.
Very rare (up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
- diseases of blood vessels, heart;
- eosinophilic pneumonia;
- erythema multiforme;
- photosensitivity;
- changes in the composition of the blood - a decrease in the number of white and red blood cells, a decrease in hemoglobin, a decrease in platelets;
- acute renal failure;
- abnormal liver function;
- hepatitis;
- increased liver enzymes;
- gastritis;
- nerve damage that can cause limb weakness, tingling, numbness;
- muscle tension;
- swelling of the gums;
- hyperglycemia.
Important! If the above symptoms appear, you should look for analogues and replacements for Perindopril.
special instructions
Perindopril (reviews from patients who took the drug are based on experience of use, which makes them informative) is prescribed only when strict indications appear. Self-administration can cause severe complications, including death.
When using the drug, it is important to constantly monitor your blood pressure and visit a specialist who will adjust the dose depending on these numbers. During therapy, patients should refrain from driving vehicles and performing manipulations that require increased concentration.
If the treatment does not bring the expected result, the specialist prescribes another medication to the patients. It is strictly contraindicated to replace the drug on your own.
Drug interactions
The product should not be used simultaneously with drugs that have a similar effect. This can lead to the development of hypotension. The medicine is not prescribed in combination with muscle relaxants, anesthetics, or tricyclic antidepressants.
Negative reactions may occur when used simultaneously with loop and thiazide diuretics, antipsychotic drugs, and monoamine reuptake inhibitors.
In each case, before using any remedy, you should first consult with a specialist who will determine the advisability of combining a particular medication.
Interactions with drugs
The combination of Perindopril with other drugs should be carried out according to the preliminary assessment of the attending physician. This is necessary to prevent incompatibility and take into account the relationship of the active components for further calculation of the daily dose. Anesthesia drugs, muscle relaxants, and blood pressure lowering agents have a sharp hypertensive effect. A similar reaction is “Perindopril” to diuretics of the thiazide class and organic nitrates.
When taken simultaneously with antidiabetic agents, the risk of hypoglycemia increases. With potassium, lithium and sodium medications, there is a delay and a further increase in the amount of microelements in the body. "Nimodipine" leads to disturbances in heart rhythm. Loop-type diuretics provoke disruptions in the functioning of the kidneys. Combining Perindopril and alcohol is prohibited. This can lead to health problems and cause adverse reactions. Thus, before starting therapy using Perindopril, it is better to carefully study the composition of other medications taken.
Analogs
In the absence of an original medicine, it is allowed to use its analogues with similar medicinal properties.
The most popular substitutes:
- Lisinopril - tablets for oral administration, which belong to the same group as Perindopril. They have a pronounced hypotensive effect, but contain lisinopril as the main active component. The tablets are taken in courses or on an ongoing basis, the dosage ranges from 5-10 mg per day.
Lisinopril
- Dilaprel - tablets based on ramipril, which have pronounced antihypertensive properties, belong to the same pharmaceutical group as Perindopril. The drug is prescribed for hypertension and various forms and degrees of neglect; it is taken in courses or on an ongoing basis.
- Diroton is a drug based on lisinopril, which is available in tablet form, helps improve the condition of hypertension, heart failure, and coronary heart disease. The dosage for patients is selected individually depending on the severity of the condition.
Drug analogues should be used only for their intended purpose. Independent use may cause complications.
Drug analogues
According to reviews, Perindopril can be replaced with analogues of the drug. Both doctors and patients talk about this. Reviews from experts indicate that replacement is advisable in case of a negative reaction to the drug.
If you compare analogues, you should know that they all belong to the same therapeutic group:
- Perineva is a similar active ingredient (in Latin: Perindoprilum);
- Lisinopril;
- Prestarium;
- Ramipril;
- Enalapril;
- Captopril.
Comparison of drugs
All ACE inhibitors have similar effectiveness in treating high blood pressure when the correct dosages are used for the individual medications. One exception is the first Captopril, which has a shorter duration of effectiveness and more side effects. Captopril is the only drug in this group that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, therefore, into the brain. However, this property does not provide any clinical effect.
One large clinical trial found that Ramipril demonstrated the ability to reduce mortality in patients after a heart attack. In addition, these patients had a delayed onset of congestive heart failure, which often occurs due to abnormal heart rhythms. Some experts believe that a similar effect should occur with other ACE inhibitors, including Perindopril.
One meta-analysis, including 158,998 people, 91% of whom had hypertension, examined the effects of perindopril and other ACE inhibitors. Based on comparisons of results from individual studies, the authors of the meta-analysis found that the drugs reduced the risk of mortality in the patients studied by 10%. Perindopril (13%) was most successful in reducing mortality. The authors conclude that ACE inhibitors and Perindopril are rightfully the first choice drugs in the treatment of hypertension.