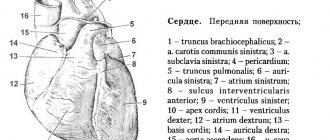
Role of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate is a macroergic (capable of storing and transmitting energy) compound that is formed in the human body as a result of various oxidative reactions and during the breakdown of carbohydrates. It is found in almost all tissues and organs, but most of all in skeletal muscles.
The role of ATP is to improve metabolism and energy supply to tissues. By breaking down into inorganic phosphate and ADP, adenosine triphosphate releases energy, which is used for muscle contraction, as well as for the synthesis of protein, urea and metabolic intermediates.
Under the influence of this substance, smooth muscles relax, blood pressure decreases, the conduction of nerve impulses improves, and myocardial contractility increases.
Considering the above, a lack of ATP causes a number of diseases, such as dystrophy, cerebral circulatory disorders, coronary heart disease, etc.
Instructions for the use of ATP injections
Diseases of the heart and peripheral vessels, as well as pathologies of the retina, can be successfully treated with ATP (adenosine triphosphate) drugs. Most often, for the treatment of the heart, it is practiced to prescribe courses of ATP intramuscularly in combination with vitamins for the most stable and long-lasting effect of treatment.
Composition and pharmacological action
The described drug is produced in the consistency of a solution for parenteral administration. It is a transparent, colorless liquid with an acceptable light yellow tint. The composition is contained in 1 ml ampoules, which are packaged in cardboard boxes of 10 pieces.
The injection drug contains an active compound - sodium adenosine triphosphate (triphosadadenine) in a volume of 10 mg.
Auxiliary component: water for injection.
The active substance is a high-energy compound, which during the reaction is capable of accumulating and transferring energy. ATP synthesis occurs during the oxidation of glucose. In the body, the generated energy is used to ensure synthetic cellular processes, stimulate muscle contractions, and transmit nerve impulses at a number of synapses.
The drug optimizes metabolic processes, eliminates arrhythmia of atrial and ventricular origin (through inhibition of the automatism of the sinus node), expands the vascular walls of the heart and brain tissue, and has a mild hypotensive effect.
After entering the body, the active substance immediately begins to take part in metabolic processes, so information on the elimination of drug residues and its metabolites is limited.
Indications and contraindications for use
The prerogative when prescribing ATP is pathologies of the cardiovascular system, including acute conditions, as well as diseases in which there is an imbalance of energy metabolism at the cellular level. For the use of ATP, indications are determined only by physicians.
In therapeutic practice, the drug is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- dystrophic changes in skeletal muscles;
- atonic phenomena in smooth muscle tissue;
- degenerative pathologies of the retina;
- attacks of arrhythmia and tachycardia;
- diseases of peripheral arteries and veins, including endarteritis, Raynaud's disease;
- inactive progress of labor.
There are such pathophysiological conditions when the use of the drug is strictly contraindicated, namely:
- acute allergic reactions to the components of the drug in an individual or family history;
- period of acute myocardial infarction;
- severe hypotension, up to complete collapse;
- slowing heart rate;
- pronounced manifestations of atrioventricular blockade of degrees II-III;
- failure of the heart in the presence of edema and ascites;
- obstructive pulmonary diseases - asthma, recurrent bronchitis, bronchiectasis;
- high levels of free potassium and magnesium in the blood;
- recovery after a cerebral stroke with hemorrhage into the tissues or ventricles;
- conditions requiring emergency care, especially the stage of cardiogenic shock;
- therapy with shock dosages of cardiac glycosides.
Classically prescribed by injection. Is it possible to administer it intramuscularly to treat the heart and other pathologies, or is it better to stick only to intravenous jet/drip administration by healthcare workers? It depends on the indications - there are no restrictions in this regard in the manufacturer's instructions.
Method of administration
The ATP solution in ampoules is administered parenterally: mainly by intramuscular injection, in case of severe condition of the patient - intravenously and exclusively by medical staff.
Dosage regimen and overdose
The attending physician, taking into account the main diagnosis, concomitant diseases and the fact of taking other drugs, selects an individual dose, duration of prescribed treatment and methods of monitoring the patient’s condition.
According to clinical protocols, it is recommended to use standard dosages in the treatment of a number of diseases in adult patients:
- diseases of arteries, veins and capillaries in the periphery, muscular dystrophy - the drug ATP is injected intramuscularly with 1 ml of solution once for 2 days, and then the dose is increased to 1 ml in the morning and evening. The course lasts 30-40 days. It is recommended to repeat therapy quarterly;
- genetically determined retinal pigmentary degeneration is treated with intramuscular injection of 5 ml of the drug in the morning and evening for 2 weeks. The recommended frequency of courses is at least 2 times a year;
- relieving an attack of supraventricular tachycardia requires the introduction of ATP under ECG control quickly intravenously to 2 ml of solution over 5-10 seconds, and a repeat is possible after 2-3 minutes.
An overdose of the drug can manifest itself with symptoms such as confusion and fainting, symptoms of severe hypotension, and arrhythmic heartbeat.
Providing assistance in case of overdose occurs as follows:
- if the substance was injected in a stream, then its administration is stopped without delay, and the short half-life will lead to a rapid improvement in the condition;
- symptoms can be relieved with antagonists as prescribed by a doctor.
Interaction
The combination of ATP and high doses of cardiac glycosides leads to sudden manifestations of atrial or ventricular arrhythmia.
Particular attention is required in the treatment of patients during the recovery period after myocardial infarction and with manifestations of severe cardiac decompensation.
Concurrent use with magnesium compounds causes an unwanted excess of magnesium ions in the blood.
The use of potassium medications and some diuretics together with ATP injections significantly increases the level of potassium in the blood.
Consumption of caffeine and medications or foods containing it will reduce the effect of ATP therapy.
The course of treatment may provoke seizures in patients prone to seizures.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
During a course of drug administration, attentiveness and concentration while driving various types of transport or technologically complex devices have not been studied, but the performance of these actions during drug therapy should be correlated with the general condition of the patient.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the drug can be prescribed only for health reasons.
Use in childhood
In pediatrics, the medicine has restrictions and can only be prescribed to children under 18 years of age by specialists.
Terms of sale and storage
The medication is sold exclusively in pharmacy chains upon presentation of a prescription form certified by the attending physician.
Stored in the refrigerator while maintaining the temperature from +2 to +7 oC.
The storage place intended for the drug should be inaccessible to children.
Pharmacological properties of ATP
Thanks to its original structure, the adenosine triphosphate molecule has a pharmacological effect characteristic only of it, not inherent in any other chemical component. ATP normalizes the concentration of magnesium and potassium ions, while reducing the concentration of uric acid. By stimulating energy metabolism, it improves:
- Activity of ion transport systems of cell membranes;
- Membrane lipid composition indicators;
- Antioxidant protective system of the myocardium;
- Activity of membrane-dependent enzymes.
Due to the normalization of metabolic processes in the myocardium caused by hypoxia and ischemia, ATP has an antiarrhythmic, membrane-stabilizing and anti-ischemic effect.
This drug also improves:
- Myocardial contractility;
- Functional state of the left ventricle;
- Indicators of peripheral and central hemodynamics;
- Coronary circulation;
- Cardiac output (due to which physical performance increases).
Under conditions of ischemia, the role of ATP is to reduce myocardial oxygen consumption and activate the functional state of the heart, resulting in decreased shortness of breath during physical activity and a reduction in the frequency of angina attacks.
In patients with supraventricular and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, in patients with atrial fibrillation and flutter, this drug restores sinus rhythm and reduces the activity of ectopic foci.
Is it possible to inject ATP for hypertension?
Adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP molecule in biology) is a substance produced by the body. It is the source of energy for every cell in the body. If ATP is not produced enough, then disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular and other systems and organs occur. In this case, doctors prescribe a drug containing adenosine triphosphoric acid, which is available in tablets and ampoules.
Adenosine triphosphate, Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate that is a universal source of energy for all living cells. The molecule provides communication between tissues, organs and systems of the body. As a carrier of high-energy bonds, Adenosine Triphosphate carries out the synthesis of complex substances: transfer of molecules through biological membranes, muscle contraction, and others. The structure of ATP is ribose (a five-carbon sugar), adenine (a nitrogenous base) and three phosphoric acid residues.
In addition to the energy function of ATP, the molecule is needed in the body for:
- relaxation and contraction of the heart muscle;
- normal functioning of intercellular channels (synapses);
- excitation of receptors for normal conduction of impulses along nerve fibers;
- transmission of excitation from the vagus nerve;
- good blood supply to the brain and heart;
- increasing the body's endurance during active muscle activity.
It is clear how ATP stands for, but what happens in the body when its concentration decreases is not clear to everyone. Biochemical changes are realized in cells through adenosine triphosphoric acid molecules under the influence of negative factors. For this reason, people with ATP deficiency suffer from cardiovascular diseases and develop muscle tissue dystrophy. To provide the body with the necessary supply of adenosine triphosphate, medications containing it are prescribed.
The medicine ATP is a drug that is prescribed for better nutrition of tissue cells and blood supply to organs. Thanks to it, the patient’s body restores the functioning of the heart muscle, reducing the risk of developing ischemia and arrhythmia. Taking ATP improves blood circulation processes and reduces the risk of myocardial infarction. Thanks to the improvement of these indicators, general physical health is brought back to normal, and a person’s performance increases.
The pharmacological properties of the ATP drug are similar to the pharmacodynamics of the molecule itself. The drug stimulates energy metabolism, normalizes the level of saturation with potassium and magnesium ions, reduces the content of uric acid, activates ion transport systems of cells, and develops the antioxidant function of the myocardium. For patients with tachycardia and atrial fibrillation, the use of the drug helps restore natural sinus rhythm and reduce the intensity of ectopic foci.
During ischemia and hypoxia, the drug creates membrane-stabilizing and antiarrhythmic activity, due to its ability to improve metabolism in the myocardium. The drug ATP has a beneficial effect on central and peripheral hemodynamics, coronary circulation, increases the contractility of the heart muscle, improves the functionality of the left ventricle and cardiac output. This entire range of actions leads to a decrease in the number of attacks of angina pectoris and shortness of breath.
The active ingredient of the drug is the sodium salt of adenosine triphosphoric acid. The ATP medicine in ampoules contains 20 mg of the active ingredient in 1 ml, and in tablets - 10 or 20 g per piece. The excipients in the injection solution are citric acid and water. The tablets additionally contain:
- anhydrous colloidal silica;
- sodium benzoate (E211);
- corn starch;
- calcium stearate;
- lactose monohydrate;
- sucrose.
As already mentioned, the medication is available in tablets and ampoules. The first ones are packaged in blister packs of 10 pieces, sold in 10 or 20 mg doses. Each box contains 40 tablets (4 blister packs). Each 1 ml ampoule contains 1% solution for injection. The cardboard box contains 10 pieces and instructions for use. Adenosine triphosphoric acid in tablet form comes in two types:
- ATP-Long is a drug with a longer action, which is available in white tablets of 20 and 40 mg with a notch for division on one side and a chamfer on the other;
- Forte is an ATP medicine for the heart in lozenges of 15 and 30 mg, which shows a more pronounced effect on the heart muscle.
ATP tablets or injections are often prescribed for various diseases of the cardiovascular system. Since the spectrum of action of the drug is wide, the drug is indicated for the following conditions:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- angina pectoris at rest and exertion;
- unstable angina;
- supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia;
- supraventricular tachycardia;
- cardiac ischemia;
- post-infarction and myocardial cardiosclerosis;
- heart failure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- allergic or infectious myocarditis;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- coronary syndrome;
- hyperuricemia of various origins.

ATF-Long is recommended to be placed under the tongue (sublingually) until completely absorbed. Treatment is carried out regardless of food 3-4 times a day at a dosage of 10-40 mg. The therapeutic course is prescribed by the doctor individually. The average duration of treatment is 20-30 days. The doctor prescribes a longer appointment at his own discretion. It is allowed to repeat the course after 2 weeks. It is not recommended to exceed the daily dose above 160 mg of the drug.
ATP injections are administered intramuscularly 1-2 times/day, 1-2 ml at a rate of 0.2-0.5 mg/kg of patient weight. Intravenous administration of the drug is carried out slowly (in the form of infusions). The dosage is 1-5 ml at the rate of 0.05-0.1 mg/kg/min. Infusions are carried out exclusively in a hospital setting under careful monitoring of blood pressure. The duration of injection therapy is about 10-14 days.
The drug ATP is prescribed with caution in combination therapy with other drugs that contain magnesium and potassium, as well as with drugs intended to stimulate cardiac activity. Absolute contraindications for use:
- breastfeeding (lactation);
- pregnancy;
- hyperkalemia;
- hypermagnesemia;
- cardiogenic or other types of shock;
- acute period of myocardial infarction;
- obstructive pathologies of the lungs and bronchi;
- sinoatrial block and 2-3 degree AV block;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- severe form of bronchial asthma;
- childhood;
- hypersensitivity to the components included in the drug.
If the drug is used incorrectly, an overdose may occur, in which the following are observed: arterial hypotension, bradycardia, AV block, loss of consciousness. If such signs occur, you should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor who will prescribe symptomatic treatment. Adverse reactions also occur with long-term use of the medication. Among them:
- nausea;
- skin itching;
- discomfort in the epigastric region and chest;
- skin rashes;
- facial hyperemia;
- bronchospasm;
- tachycardia;
- increased diuresis;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- feeling of heat;
- increased motility of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hyperkalemia;
- hypermagnesemia;
- Quincke's edema.

You can buy ATP medicine in tablets or ampoules at a pharmacy chain after presenting a prescription from a doctor. The shelf life of the tablet preparation is 24 months, the solution for injection is 12 months. Prices for medications vary depending on the form of release, the number of tablets/ampoules in the package, and the marketing policy of the outlet. Average cost of the drug in the Moscow region:
The agent “ATP” is adenosine triphosphoric acid – triphosphoric ester. It contains three phosphoric acid residues, and also includes a monosaccharide of the pentose group, ribose with adenine (adenosine).
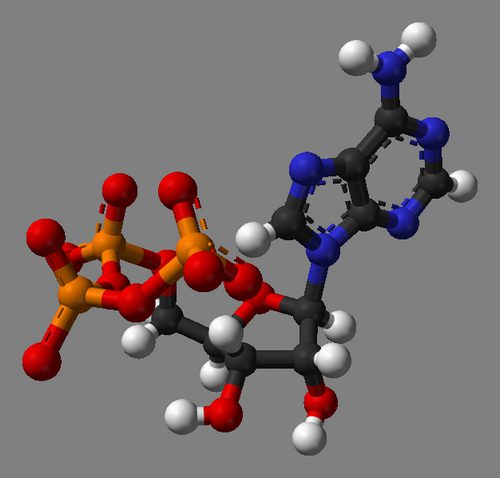
Adenosine triphosphoric acid is one of the most important elements in the metabolism of cardiac and skeletal muscles. The compound is found in animal tissues. Adenosine triphosphoric acid is a direct source of energy for muscle contractions. The compound is also an energy accumulator for organisms. Adenosine triphosphoric acid normalizes metabolism in various degenerative processes. The substance affects the trophism of muscle tissue. Adenosine triphosphoric acid is a substrate for the process of nucleic acid biosynthesis. The compound also helps to dilate coronary and peripheral vessels, while improving nutrition of the heart muscles. In this article we will take a closer look at the instructions for using the drug “ATP”. For what pathologies is it prescribed? What is the dosage regimen? More on this later.
The product is available in tablet form. The main components included in its composition: tripotassium octahydrate with NaCl 10 mg, magnesium triphosphate-histidinato (II), adenosine-5. The drug also contains the following components: corn starch, tabletose-80, sucrose, calcium stearate, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, sodium benzoate. The drug "ATF-Long" is also produced. Instructions for use characterize the drug as an original medicine, which includes a new class of substances of coordination multi-ligand compounds. They, in turn, consist of high-energy phosphates with a molecule of adenosine-5-triphosphate, magnesium salt, potassium salt, and histidine amino acid.
The product “ATP” (the instructions for use indicate this) helps directly stimulate energy metabolism, normalize the concentration of magnesium and potassium ions in tissues. The medication increases myocardial contractility. The drug reduces the concentration of uric acid in the body and participates in increasing the activity of ion transport structures in cell membranes. The drug has anti-ischemic, membrane-stabilizing, antiarrhythmic effects. The drug improves the quality of coronary circulation. During ischemia, this medication can reduce oxygen consumption by the myocardium, can improve coronary circulation, and activate the overall functional state of the heart. This, in turn, reduces the number of angina attacks, as well as shortness of breath due to physical activity. The drug "ATP" is capable of restoring the correct sinus rhythm in people with paroxysmal supraventricular supraventricular tachycardia, with flutter, atrial fibrillation, and has the ability to reduce the activity of ectopic foci (atrial and ventricular extrasystoles).
The instructions for use of the drug "ATP" are recommended for patients with muscle dystrophy, endarteritis and intermittent claudication. A remedy is prescribed for hypertension, angina pectoris, and to relieve spasms of the coronary vessels. The drug is used in gynecology to enhance the contractile activity of the uterus during childbirth. The drug "ATF-Long" is prescribed in the complex treatment of unstable angina, ischemic heart disease, diffuse, focal cardiosclerosis (myocardial cardiosclerosis). Indications also include myocarditis, increased fatigue, and chronic fatigue.
The instructions for use of the drug "ATP" do not allow it to be prescribed to patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction (acute) and who have hypersensitivity to the medication. Contraindications also include hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia, stroke (hemorrhagic), bronchial asthma (especially in severe cases). Due to the lack of safety data, the drug is not used in pediatrics.
The instructions for use recommend dissolving ATP tablets in the mouth until they are completely dissolved. The drug is recommended at 10-40 mg 2-4 times a day. The treatment course is determined individually for each patient by the doctor. On average, the duration of therapy is about three to four weeks. If necessary, the doctor may recommend continuing the course after 14-21 days.
The medicine (the instructions contain such information) can cause allergies, various rashes, and redness of certain areas on the skin. Undesirable consequences include vomiting and nausea. Some patients may develop hypermagnesemia or hyperkalemia.
With prolonged use of the drug, control over normal levels of magnesium and potassium in the blood is necessary. When prescribing to patients with arterial hypertension, special care should be taken. If there is a tendency to bronchospasm, dosage adjustment will likely be required. Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. It is also recommended to limit or completely eliminate the consumption of black and green tea, coffee and any other drinks that contain caffeine. Using the drug during pregnancy is strictly prohibited. Lactation should be suspended during therapy. The effect on reaction speed when driving a vehicle has not been established (data not available). In case of an overdose of the drug, there is a high possibility of arterial hypotension, as well as atrioventricular block, and the development of bragycardia. If you take an increased dose, you should immediately consult a doctor. In cases of overdose, symptomatic therapy is recommended.
Use together with cardiac glycosides is prohibited, as there is a risk of the occurrence and development of atrioventricular block and other diseases. Use together with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and potassium-sparing diuretics is prohibited, as there is a risk of the occurrence and development of hyperkalemia. Use together with the drug Magnerot is not allowed. This is because there is a risk of hypermagnesemia.
The drug should be stored in a dark place, protected from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep away from children. The storage temperature of the drug is 2-5˚C. The shelf life of the medicine "ATF" is 12 months from the date of release. You should not take the medicine after the period indicated on the package.
Prices in online pharmacies:
ATP (sodium adenosine triphosphate) is a drug that improves energy supply and tissue metabolism.
ATP is available in the form of a solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration in 1 ml ampoules. One cardboard box contains 10 ampoules of the drug.
The active ingredient in the product is sodium adenosine triphosphate (triphosadenine). One ampoule of solution contains 10 mg of the active component, which enhances coronary and cerebral circulation and is involved in many metabolic processes.
According to the instructions, ATP is used for the following conditions:
- Peripheral vascular diseases (Raynaud's disease, intermittent claudication, thromboangiitis obliterans);
- Weakness of labor;
- Muscular dystrophy and atony;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Polio;
- Retinal pigmentary degeneration;
- IBS.
According to the instructions, ATP is also widely used to relieve paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia.
The use of ATP is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the active substance of the drug - sodium adenosine triphosphate, and inflammatory lung diseases.
The drug is also not prescribed for acute myocardial infarction and arterial hypertension.
ATP is intended for parenteral use. In most cases, the drug solution is administered intramuscularly. Intravenous administration of the drug is used for particularly severe conditions (including when stopping supraventricular tachycardia).
The duration of the course of therapy and the dosage of the drug are determined by the doctor individually, depending on the form of the disease and the clinical picture.
At the same time, there are standard dosages for the treatment of specific diseases:
- For peripheral circulatory disorders and muscular dystrophy, adult patients are prescribed 1 ml of ATP per day intramuscularly for 2 days, then 1 ml of the drug is administered twice a day. It is possible to use a dosage of 2 ml 1 time per day from the very beginning of treatment without subsequent dose adjustment. The duration of the course of therapy is usually 30-40 days. After completing the course, if necessary, you can repeat it after 1-2 months;
- For hereditary retinal pigmentary degeneration, adult patients are prescribed 5 ml of ATP twice a day intramuscularly. The interval between drug administration procedures should be 6-8 hours. The duration of the course of therapy is 15 days. The course can be repeated every 8 months to a year;
- When stopping supraventricular tachycardia, ATP is used intravenously for 5-10 seconds. The drug can be re-administered after 2-3 minutes.
According to the instructions, ATP when administered intramuscularly can cause tachycardia, headaches and increased diuresis.
Intravenous administration of the drug in some cases causes nausea, general weakness of the body, headaches and flushing of the facial skin. Rarely, when using the product, allergic reactions occur in the form of itching and redness of the skin.
The simultaneous use of ATP with cardiac glycosides in high dosages is not recommended, since their interaction increases the risk of developing various side effects, including arrhythmogenic effects.
Analogs of the drug ATP are solutions of Phosphobion, Sodium Adenosine Triphosphate-Vial and Sodium Adenosine Triphosphate-Darnitsa.
According to the instructions, ATP should be stored in a dark place, out of reach of children, at a temperature of 3-7 °C.
The shelf life is 1 year.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Indications for use of ATP
As indicated in the instructions for ATP, the drug in tablets is prescribed for:
- Coronary heart disease;
- Post-infarction and myocardial cardiosclerosis;
- Unstable angina;
- Supraventricular and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia;
- Rhythm disturbances of various origins (as part of complex treatment);
- Autonomic disorders;
- Hyperuricemia of various origins;
- Microcardiodystrophies;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
The use of ATP intramuscularly is advisable for poliomyelitis, muscular dystrophy and atony, retinal pigmentary degeneration, multiple sclerosis, weakness of labor, peripheral vascular diseases (thromboangiitis obliterans, Raynaud's disease, intermittent claudication.
The drug is administered intravenously to relieve paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia.
ATP injection drug: indications, contraindications and application features
The coordinated functioning of all body systems is possible with proper energy metabolism, which occurs at the cellular level. The drug ATP is capable of providing all cells with an auxiliary source of nutrition. Its active component not only leads to better metabolism in tissues, but also improves their energy supply.
Indications for use
Injections of the drug ATP are advisable to use in the following cases:
- The patient complains of decreased physical activity, as well as rapid fatigue;
- In the case of an athlete preparing for competitions;
- To restore heart function;
- With reduced blood circulation in the vessels of the brain;
- At risk of heart attack and arrhythmia;
- In order to eliminate the syndrome of “chronic fatigue”.
Injection of the drug is usually prescribed for:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Tachycardia;
- Myocarditis;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Angina pectoris and other diseases leading to heart rhythm disturbances.
Contraindications to the use of ATP
The instructions for ATP indicate that the medication should not be used in patients with hypersensitivity to any of its components, children, pregnant and lactating women, simultaneously with large doses of cardiac glycosides.
It is also not prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with:
- Hypermagnesemia;
- Hyperkalemia;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Severe form of bronchial asthma and other inflammatory lung diseases;
- AV blockade of the second and third degree;
- Hemorrhagic stroke;
- Arterial hypotension;
- Severe form of bradyarrhythmia;
- Decompensated heart failure;
- QT prolongation syndrome.
Contraindications
According to the instructions, ATP-long should be used carefully in parallel with other medications containing potassium and magnesium, as well as those intended to stimulate cardiac function. Absolute contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- pregnancy;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- childhood;
- hypermagnesemia;
- sinoatrial block;
- lactation period;
- hyperkalemia;
- exacerbation of myocardial infarction;
- hypersensitivity to the ingredients contained in the medication;
- obstructive diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
- final stages of bronchial asthma.
Method of application of ATP and dosage regimen
ATP in tablet form is taken 3-4 times a day sublingually, regardless of meals. A single dosage can vary from 10 to 40 mg. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician, but usually it is 20-30 days. If necessary, after a 10-15 day break the course is repeated.
In acute cardiac conditions, a single dose is taken every 5-10 minutes until the symptoms disappear, after which they switch to the standard dose. The maximum daily dosage in this case is 400-600 mg.
ATP is administered intramuscularly at 10 mg of a 1% solution once a day in the first days of treatment, then at the same dose twice a day or 20 mg once. The course of therapy usually lasts from 30 to 40 days. If necessary, after a 1-2 month break, treatment is repeated.
10-20 mg of the drug is administered intravenously over 5 seconds. If necessary, repeat the infusion after 2-3 minutes.
Side effects of ATP
- slight headache;
- hyperuricemia;
- nausea or vomiting (occurs with a significant overdose of the drug);
- increased weakness;
- allergic manifestations (urticaria, increased skin itching);
- increased diuresis;
- discomfort in the stomach.
If any of the above side effects occur, it is recommended to consult your doctor!
In this article, we will look at what ATP helps with, as well as how to drink it correctly.
Effects of ATP
There is a significant difference between trying to “inject” or “eat” additional ATP (which is impossible) and increasing the body’s ability to synthesize ATP (this is how modern ATP-targeting dietary supplements work). The second method is an effective way to increase ATP, endurance and oxygen capacity of the blood, but it does not involve the direct intake of “ATP”, but works through the use of vitamins/adaptogens and dietary supplements. Documented and in Olympic practice, the positive effect of the Cordypsus mushroom on the endurance of athletes has been noted.
Supplemental ATP intake does not lead to an increase in energy or a significant increase in endogenous ATP levels and does not increase muscle mass. Injections, oral or sublingual use - all these ways lead to the inevitable destruction of ATP, long before it enters the muscles, so there is no point in performing painful injections.
After ATP enters the body (the route of administration does not matter), it does not enter the cells, since it has a negative charge. Inside the cell, the environment is also negatively charged, so ATP is simply repelled from the cell membranes. Even in the intestines or in the muscle, ATP begins to be destroyed by the enzyme EctoATP diphosphorylase to AMP, this takes no more than 2-3 seconds. After another 3 seconds, AMP is destroyed (hydrolyzed by the enzyme 5-nucleotidase and adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase) to adenosine. Almost all adenosine is captured by red blood cells, where it is quickly converted to inosine (riboxin) by the enzyme adenosine deaminase.
Thus, ATP cannot be delivered to the muscles, regardless of dose and route of administration. Recently, the indications for the use of ATP drugs have been completely revised; now they are used only to relieve cardiac arrhythmias and, in rare cases, to relax vascular smooth muscles. The effect on other organs is impossible, because ATP is destroyed to inosine long before it enters the organs; it is inosine that causes all the effects of ATP consumption. Therefore, it is wiser to take supplements with inosine, from which ATP is synthesized in the body.
What is ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate that is a universal source of energy for all living cells. The molecule provides communication between tissues, organs and systems of the body. As a carrier of high-energy bonds, Adenosine Triphosphate carries out the synthesis of complex substances: transfer of molecules through biological membranes, muscle contraction, and others. The structure of ATP is ribose (a five-carbon sugar), adenine (a nitrogenous base) and three phosphoric acid residues.
Articles on the topic Cocarboxylase side effects Catabolic effect Contraindications of ACE inhibitors
In addition to the energy function of ATP, the molecule is needed in the body for:
- relaxation and contraction of the heart muscle;
- normal functioning of intercellular channels (synapses);
- excitation of receptors for normal conduction of impulses along nerve fibers;
- transmission of excitation from the vagus nerve;
- good blood supply to the brain and heart;
- increasing the body's endurance during active muscle activity.
ATP drug
It is clear how ATP stands for, but what happens in the body when its concentration decreases is not clear to everyone. Biochemical changes are realized in cells through adenosine triphosphoric acid molecules under the influence of negative factors. For this reason, people with ATP deficiency suffer from cardiovascular diseases and develop muscle tissue dystrophy. To provide the body with the necessary supply of adenosine triphosphate, medications containing it are prescribed.
The medicine ATP is a drug that is prescribed for better nutrition of tissue cells and blood supply to organs. Thanks to it, the patient’s body restores the functioning of the heart muscle, reducing the risk of developing ischemia and arrhythmia. Taking ATP improves blood circulation processes and reduces the risk of myocardial infarction. Thanks to the improvement of these indicators, general physical health is brought back to normal, and a person’s performance increases.
Reviews
Oleg, 42 years old
The cardiac drug ATP is very effective and time-tested. I took it on the recommendation of a doctor, because after taking Torginal drops for a long time, which I prescribed to myself, I started having problems with blood pressure and tachycardia. I took the pills for 30 days, after which all the side effects went away.
Angelica, 37 years old
As part of the complex treatment of ischemia, my grandmother was prescribed intramuscular injections of ATP (I don’t know the meaning). I did them for more than 2 weeks, but there was no improvement. I can conclude that for serious heart pathologies the drug is completely useless. Perhaps it should be perceived as a metabolic medicine from traditional medicine or vitamins.
Valeria, 23 years old
I bought ATF Long in a dosage of 10 mg for a child. Although according to the instructions this drug is not intended for children, our pediatrician has already prescribed it to us several times. The medicine is excellent for treating inflammation of the heart muscle (in complex therapy). The tablets are small and pleasant to the taste, so the baby swallows them with pleasure.
Alena, 30 years old
ATP tablets were prescribed to me by a cardiologist for heart failure. In general, the drug is recommended for vegetative-vascular dystonia and chronic fatigue syndrome, which I also have in stock. I felt a positive result after just a few days of taking it: my heart rhythm was restored and I began to feel more alert in the morning.