Among endocrine diseases, autoimmune pathology of the thyroid gland, which is associated with the aggression of one’s own immune cells against healthy tissues of the organ, is becoming increasingly widespread. This anomaly can be diagnosed using laboratory tests, in particular determining the level of antibodies.
What patients need to know who have elevated antibodies to TPO - antibodies to thyroid peroxidase: in our review and video in this article we will look at the main causes, symptoms and methods of treating autoimmune diseases.
What is thyroid peroxidase and what happens if antibodies are produced to it
Thyroid peroxidase (microsomal thyroid peroxidase) is an enzyme contained in the cells of the thyroid gland and is responsible for the creation of active forms of iodine, which will subsequently attach to the amino acid residue of tyrosine and turn into molecules (the main thyroid hormone). Thus, thyroid peroxidase is one of the links in a complex biochemical chain, as a result of which thyroid cells synthesize and release thyroid hormones into the blood.
What does elevated antibodies to microsomal thyroid peroxidase mean? If for some reason (they will be discussed below) the immune system begins to attack and destroy TPO molecules, the formation of thyroid hormones is sharply reduced.
This leads to hormonal imbalance and pronounced clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism. Therefore, an increase in antibodies to thyroid peroxidase is an alarming sign that should not go unnoticed by a specialist.
Important! Normal anti-TPO values range from 0-34 IU/ml. For a more reliable result, the instructions require taking the test in the morning on an empty stomach, and also avoiding stress and exhausting physical activity on the eve of the test.
Reasons for the increase in anti-TPO antibody titer
There are several diseases in which the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase may be elevated:
- (HAIT);
- (DTZ);
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- postpartum thyroiditis;
- endocrine pathology in newborns (may be accompanied by both hyper- and hypothyroidism).
Note! If antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are highly elevated, it is more likely that the patient has developed an autoimmune thyroid disease.
When is a test for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase prescribed?
Indications for determining AT to TPO are:
- symptoms of functional disorders of the thyroid gland;
- changes in laboratory tests for thyroid hormones;
- dynamic observation of patients with diagnosed autoimmune pathology;
- examination of women with pregnancy pathologies (recurrent miscarriage, preeclampsia, IVF failure, etc.);
- autoimmune pathology not related to the thyroid gland (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, SLE, etc.);
- examination of patients before prescribing Cordarone (Amiodarone), interferon drugs, lithium;
- examination of patients at high risk of developing autoimmune thyroiditis.
Note! A slight increase in anti-TPO levels is observed in many systemic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Anti-TPO and Hashimoto's disease
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a common autoimmune pathology of the thyroid gland, which is accompanied by irreversible cell destruction and slow inhibition of the functional activity of the organ - chronic hypothyroidism. Elevated antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are detected in CAIT in 90-95% of cases, and the degree of their increase is prognostically significant for determining the prognosis of the disease.
Note! A high level of anti-TPO is not always evidence of Hashimoto’s disease, just as CAIT is not always accompanied by an increase in thyroid peroxidase titer. Diagnosis of thyroid diseases should be comprehensive, based on laboratory tests, ultrasound and additional diagnostic methods.
Anti-TPO testing during pregnancy
So, for example, if while pregnant a woman was diagnosed with an increased level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, the risk of developing an autoimmune process in her thyroid gland increases by 2.5-3 times.
Interpretation of a blood test for antibodies
In diagnostic terms, only three types of immunoglobulins are significant: IgM, IgG, IgA. By their deviation from the norm, one can judge the presence or absence of infection. A negative test result is not a 100% indicator that there is no infectious process. This is due to the fact that after infection, the formation of a chain reaction of immunity takes some time - from 2-3 days to 2-3 weeks. To confirm a negative result, the ELISA test must be repeated after some time.
The presence of antibodies often indicates that allergens, viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms are present in the blood. Moreover, even a positive result is not always considered a pathology. For example, by producing additional immunoglobulins, the body can respond to incorrectly selected treatment, conception, or organ transplantation. Overall, the results of the study help answer the following questions:
- How fully does the immune system respond to the infection, is it necessary to take additional treatment measures;
- at what stage of progression the disease is;
- whether the person has cancer;
- How does the implant healing process proceed?
- what substance caused the allergy;
- whether the infection occurred with viruses, parasites, bacteria and how long ago;
- whether the chronic disease has worsened.
IgA
Immunoglobulin class A is one of the important for differential diagnosis. It is constantly present in the body and makes up approximately 10-25% of all immunoglobulin fractions. IgA reference values may vary depending on age and gender:
| Age | Floor | Minimum value, g/l | Maximum value, g/l |
| up to 3 months | boy/girl | 0,01 | 0,34 |
| 3 months – year | boy/girl | 0,08 | 0,91 |
| 1 year – 12 years | boys | 0,21 | 2,82 |
| girls | 0,21 | 2,91 | |
| 12-60 years | women | 0,65 | 4,21 |
| men | 0,63 | 4,84 | |
| after 60 years | women | 0,69 | 5,17 |
| man | 1,01 | 6,45 |
Deviation of IgA from the norm indicates the presence of pathological processes. Elevated values may indicate the following conditions or diseases:
- myeloma, lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease - malignant diseases of tissue or bone marrow;
- liver diseases – cirrhosis, toxic cell damage due to alcoholism;
- nephropathy – bilateral kidney damage, renal failure;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina, digestive tract, eyes, nose;
- autoimmune diseases – diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, lupus erythematosus, vasculitis;
- chronic or acute infectious diseases of the lungs, skin, liver, lymph nodes - tuberculosis, mononucleosis, actinomycosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic connective tissue disease.
A decrease in protein synthesis can occur when taking certain medications, as well as as a result of the following diseases:
- chronic diseases of the respiratory or olfactory organs - bronchial asthma, respiratory allergies, sinusitis, sinusitis, pneumonia;
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia – blood cancer in remission;
- malabsorption - a disorder of digestion, absorption and breakdown of nutrients;
- congenital dilatation of small blood vessels - telangiectasia;
- atopic dermatitis.
IgM
The concentration of immunoglobulin type M rapidly increases in the initial stages of infection; after the incubation or acute period, its level gradually decreases. IgM are indispensable participants in the process of formation of primary immunity. Protein norms for people of different ages:
| Age | Floor | Minimum indicators, g/l | Maximum values, g/l |
| up to three months | boys/girls | 0,06 | 0,21 |
| children under one year old | boys | 0,17 | 1,43 |
| girls Cost of safasbuvir for treatment genotype 1 price | 0,17 | 1,50 | |
| 1 year – 12 years | boys | 0,41 | 1,83 |
| girls | 0,47 | 2,40 | |
| over 12 years old | women | 0,33 | 2,93 |
| men | 0,22 | 2,40 |
Increased levels of type M antibodies can be caused by massive body burns, injuries, taking hormonal medications, viral, parasitic or bacterial infections, and some autoimmune pathologies (arthritis, diabetes) . IgM protein deficiency can occur due to:
- Bruton's disease (immunodeficiency, develops due to gene mutation);
- treatment with cytostatics (drugs that suppress the growth of malignant cells);
- carrying out radiotherapy;
- exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases characterized by massive loss of proteins;
- lymphoma (tumor, cancer of the lymphatic system);
- taking medications with gold or polysaccharides.
IgG
The main function of class G is to provide a secondary immune response of the body to the infectious agent. The half-life of this group of immunoglobulins is 23-25 days, during which the body actively fights the disease, after which it requires additional drug support. The norm of antibodies in the blood for people of different genders and age groups:
| Age | Floor | Minimum values, g/l | Maximum values, g/l |
| newborns | boys | 3,97 | 17,65 |
| girls | 3,91 | 17,37 | |
| 1 month – year | boys | 2,05 | 9,48 |
| girls | 2,03 | 9,34 | |
| 1-2 years | boys | 4,75 | 12,1 |
| girls | 4,83 | 12,26 | |
| over two years old | boys | 5,4 | 18,22 |
| girls | 5,52 | 16,31 |
High concentrations of IgG are observed in acute or recurrent chronic diseases. The following types of pathologies can also contribute to an increase in antibody levels:
- liver diseases - autoimmune or viral hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- autoimmune diseases - lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, sclerosis;
- sarcoidosis (formation of granulomas in soft tissues);
- oncology;
- cystic fibrosis (damage to organs responsible for the formation of mucus);
- mononucleosis;
- neurosyphilis (damage to the nervous system due to penetration of the syphilis pathogen into the blood);
- AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
A lack of IgG may indicate the presence of viral diseases that have become chronic. The following pathologies can lead to a lack of this protein:
- atopic dermatitis;
- vitamin B12 deficiency;
- leukemia (blood cancer);
- HIV infection;
- nephrotic syndrome (damage to renal corpuscles (glomeruli));
- Bruton's disease;
- hypogammaglobulinemia (deficiency of plasma cells - B-lymphocytes);
- Louis-Bar syndrome (lack of immune T cells);
- genetic muscular dystrophy.
Autoantibodies
Antinuclear proteins are a group of autoantibodies that are produced by the body to fight its own cells: phospholipids, DNA fragments, receptors, hormones . Analysis for such immunoglobulins is considered the most sensitive way to diagnose autoimmune disorders, most of which are characterized by damage to connective or cartilage tissue. Specific antibodies are detected in the presence of the following pathologies:
- systemic lupus erythematosus is a disease of connective tissue and skin;
- periarthritis nodosa – inflammation of the vascular walls of the arteries;
- dermatomyositis - damage to skeletal tissue, skin and muscles;
- rheumatoid arthritis – joint disease;
- scleroderma is a condition in which the connective tissue thickens or hardens;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- autoimmune hepatitis - liver disease;
- Sjögren's disease - decreased production of the sebaceous, lacrimal and salivary glands.
Simultaneously with the determination of autoantibodies, a study is carried out for the presence of class fractions A, M, G. The detection of these components can with a high probability indicate the onset of the development of autoimmune diseases. When performing a quantitative test, a titer of less than 1:160 is considered normal for autoantibodies. Qualitative analysis can have several interpretation options:
- indicator less than 0.9 – negative;
- 0.9-1.1 – a questionable result, it is necessary to repeat the test after 7-10 days;
- more than 1.1 – positive.
Clinical manifestations of autoimmune diseases
An increase in anti-TPO can be accompanied by both hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. Let's look at the main signs of these syndromes in the table below.
Table: Hypo- and hyperthyroidism in diseases accompanied by elevated levels of anti-TPO:
| Characteristic diseases | Typical symptoms | Laboratory picture | |
| Hypothyroidism syndrome |
|
|
|
| Hyperthyroidism syndrome | Diffuse toxic goiter |
|
|
How to return the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase to normal
After further examination of the patient and determining the type of hormonal disorders, the endocrinologist draws up an individual treatment plan, including:
- impact on the cause of the disease (if possible);
- correction of endocrine status;
- symptomatic therapy.
If a person has elevated hormone antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and has clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism, he is usually prescribed long-term replacement therapy with synthetic analogues of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism in DTG is corrected by taking thyreostatic drugs.
Note! There is currently no effective method of therapy that would interfere with the body’s defense system and suppress pathological autoimmune processes. In fact, all treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis is based on taking synthetic hormones, when the body's own thyroid gland is slowly but irreversibly destroyed. Today, large-scale clinical development of a drug is underway that could suppress the process of autoaggression of the body to the cells of the endocrine organ.
Thus, if antibodies to microsomal thyroid peroxidase are elevated, it is important to consult a doctor as early as possible. Do-it-yourself folk remedies will not help cope with the problem and will only aggravate existing hormonal disorders.
A diagnostic plan drawn up by a specialist will make it possible to find out the cause of the autoimmune process in the thyroid gland, and competent treatment will eliminate endocrine disruption.
It's no secret that our immune system allows us to cope with viruses and microbes. Special proteins - antibodies - help her with this. They identify a foreign object, determine its weak points and neutralize it. However, it happens that antibodies begin to fight healthy tissues of their own body.
The key organ of the endocrine system, the thyroid gland, may be targeted. The enzyme that suffers the most is thyroid peroxidase, the purpose of which is to help the gland in the synthesis of hormones such as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. To identify such a failure, a test for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) is prescribed.
Why is it faster, more convenient and more profitable to take tests at Lab4U?
You don't have to wait long at the reception
All order placement and payment takes place online in 2 minutes.
The journey to the medical center will not take more than 20 minutes
Our network is the second largest in Moscow, and we are also present in 23 cities of Russia.
The check amount won't shock you
A permanent 50% discount applies to most of our tests.
You don't have to arrive on time or wait in line
The analysis takes place by appointment at a convenient time, for example from 19 to 20.
You don't have to wait long for results or go to the laboratory to get them.
We will send them by email. mail when ready.
The human immune system is a complex system. Antibodies are its important link. They recognize viruses, bacteria and other foreign agents. It is antibodies that send a signal to immune cells: “Attack the intruder!” An antibody test allows you to determine the general level of immunity, diagnose infections, and identify disorders in the functioning of the immune system.
Indications for anti-TPO
Testing for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase is prescribed in the following cases:
- the presence of symptoms of disruption of the normal functioning of the thyroid gland (drowsiness, irritability, mood swings, fatigue);
- if you have a history of another autoimmune disease (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, Libman-Sachs disease (lupus), pernicious anemia, systemic angiitis (vasculitis) of autoimmune origin);
- before prescribing drug therapy with a negative effect on the functions of the thyroid gland (psychotropic drugs based on lithium, antiarrhythmic drugs (cordarone, amiocardin, etc.), antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs (interferon alpha, interleukin);
- when studying the pathogenesis of female infertility, spontaneous abortion and miscarriage;
- if you suspect thyroid dysfunction (hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism);
- if an ultrasound detects any abnormalities in the thyroid gland (reduction or increase in size, change in structure);
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach (nicotine should also be excluded). A month before the test, stop taking any hormonal medications (there are exceptions, instructions should be given by the treating endocrinologist), and a few days - stop taking any iodine-containing medications. It is advisable to limit physical activity and avoid stressful situations if possible. If you have recently suffered a serious illness (flu, pneumonia, tonsillitis) or undergone surgery, the indicators may be incorrectly assessed. In this case, we advise you to postpone the TPO analysis.
Decoding the results. Reasons for deviation from the norm
Normally, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase for a healthy person under 50 years of age should be 0-35 IU/ml, older - 0-100 IU/ml. If any deviations from the norm are recorded, an autoimmune process in relation to the thyroid gland is evident. Classifying the degree of deviation from the norm, we can distinguish a slight increase in the level, moderate and significant.
Direct or indirect reasons for a slight or moderate increase in anti-TPO may be:
- external factors (radiation, poor environment, toxins);
- physical damage to the thyroid gland;
- hereditary predisposition;
- treatment with high doses of iodine;
- past diseases (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- the presence of foci of chronic infection (adenoiditis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis);
- taking hormonal drugs for a long time and without proper control;
- psychotraumatic factors leading to stressful conditions (change of place of work or residence, death of a loved one, divorce, etc.).
- pregnancy;
The reason for a significant deviation of the results from the norm is most often a disease of the thyroid gland of an autoimmune nature (lymphocytic thyroiditis (Hashimoto's), Graves' disease). An increase in the level of antibodies to TPO during pregnancy indicates a high likelihood that the child will develop a disease such as hyperthyroidism in utero or after birth.
It is important to emphasize that antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are not the primary cause of autoimmune thyroid diseases. More like a consequence. Therefore, attempts to reduce antibody levels are unfounded (even if they deviate significantly from the norm). Likewise, assessing anti-TPO levels over time is meaningless.
Repeated tests
Monitoring of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase may be justified only after surgical treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. In some cases, the level of anti-TPO can be elevated in practically healthy people, mainly women, and the likelihood of this pathology occurring is directly proportional to age.
The sensitivity and informativeness of tests for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are increasing as medical technologies improve and research methods change. Partly because of this, the name of this analysis and the criteria for normality change periodically. Therefore, to achieve comparability of the results obtained, it is recommended to do several tests in different laboratories.
If antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are significantly elevated, additional tests are prescribed to exclude thyroid pathology (levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, triiodothyronine, thyroxine, free thyroid hormones). To make a correct diagnosis and a competent approach to treatment, a thorough assessment of the listed indicators is required. Therefore, do not self-medicate, consult a specialist. Be healthy!
Diseases of the endocrine system (in particular, autoimmune thyroiditis) are diagnosed today with the same frequency as vegetative-vascular dystonia, but almost each of them needs in-depth testing. It would be most correct to get tested for antibodies to TPO and TG.
Antibodies as an indicator of the state of the immune system
Antibodies (or immunoglobulins) are special protein molecules. They are produced by B lymphocytes (plasma cells). Immunoglobulins can either be free in the blood or attached to the surface of “defective” cells.
Having recognized a foreign substance - an antigen, the antibody attaches to it using the so-called protein tail. The latter serves as a kind of signal flag for specialized immune cells that neutralize the “intruders.”
There are five classes of immunoglobulins in the human body: IgA, IgD, IgG, IgE, IgM. They differ in mass, composition, and, most importantly, properties.
IgE and IgD are contained in blood serum in small quantities and have no diagnostic value. The most significant for analyzing the state of the immune system and making a diagnosis are IgM, IgA and IgG.
IgM is the first immunoglobulin that the body begins to produce in response to infection. It is highly active and stimulates various parts of the immune system. Makes up 10% of all immunoglobulin fractions.
About five days after the antigen enters the body, IgG begins to be produced (70–75% of all immunoglobulins). It provides the main immune response. More than half of all immunoglobulins released during illness belong to this class.
IgA is mainly localized in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, stomach, intestines and genitourinary system. That is, where pathogens most often enter our body. This class of immunoglobulins binds foreign substances and prevents them from attaching to the surface of the mucous membranes. The share of IgA is 15–20% of the total number of immunoglobulins present in the body.
When can a blood test for antibodies be prescribed?
The concentration of antibodies to a specific infection helps make a diagnosis, determine the level of immunity after vaccination, and identify hidden diseases. Most often, antibody tests are prescribed for suspected diseases (or to monitor their treatment) such as:
- measles;
- hepatitis;
- chickenpox (chickenpox);
- rubella;
- helminthiasis;
- Helicobacter pylori;
- giardiasis;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- polio;
- herpes.
An analysis for immunoglobulins of a certain class may also be prescribed for:
- sepsis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- oncology;
- chronic purulent otitis, meningitis, pneumonia, sinusitis;
- disruption of the immune system;
- multiple myeloma;
- HIV infections.
The study is also relevant for identifying autoimmune diseases. Such immunoglobulins attach to the cells of the skin, kidneys, liver, and blood vessels and mark them as “dangerous” for their own immune system.
When identifying the causes of infertility, a test for antibodies to hCG or antisperm antibodies may be prescribed. During pregnancy, a test is performed for antibodies to the Rh factor.
Preparation for the study and blood donation procedure
Tests for antibodies to viruses and other infectious agents are carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Blood is given for antibody tests on an empty stomach. The biomaterial is collected from a vein. Before the study, it is advisable for the patient to avoid emotional overload, not engage in heavy physical work, not go to the gym and not drink alcohol.
The essence of the study
Determination of the level of immunoglobulins is carried out using immunofluorescence analysis, or ELISA. A small amount of blood serum and purified antigen is placed on the surface of a special tablet. An antigen and an antibody of the same type fit together “like a key to a lock” and form a special immune complex. After this, a substance is added that stains the immune complex. The intensity of the color determines the concentration of immunoglobulins in the blood serum.
The ELISA method is sensitive even to small amounts of immunoglobulins and has high specificity. This means that the research results will be reliable and accurate.
The study usually takes 1-2 business days. Some laboratories are ready to provide an urgent result in 2-3 hours, but the cost will be approximately twice as high.
Interpretation of antibody test results
Only a doctor can correctly interpret the results of an immunoglobulin test. It takes into account not only the indicators in the study form, but also the patient’s condition, symptoms of the disease or their absence, and data from other studies.
Each laboratory uses its own test systems, therefore the results of tests carried out in different diagnostic centers may differ. The boundaries indicated in the article are approximate.
Total IgA standards for children:
- up to 3 months - from 0.01 to 0.34 g/l;
- from 3 months to 1 year – from 0.08 to 0.91 g/l;
- from 1 year to 12 years:
- girls: from 0.21 to 2.82 g/l;
- boys: from 0.21 to 2.91 g/l;
- 12–60 years – from 0.65 to 4.21 g/l;
- After 60 years - from 0.69 to 5.17 g/l.
- 12–60 years old - from 0.63 to 4.84 g/l;
- after 60 years - from 1.01 to 6.45 g/l.
Immunoglobulin class A increases with chronic infections, cystic fibrosis, and liver damage. Also, antibodies of this type can be actively produced in autoimmune diseases. A decrease in antibody titer occurs with atopic dermatitis, some diseases of the blood and lymphatic system. And also in case of disruption of the synthesis of protein molecules and taking certain medications.
The IgM content in the blood serum of newborns should be in the range of 0.06-0.21 g/l.
- over 3 months and up to 1 year:
- girls: from 0.17 to 1.50 g/l;
- boys: from 0.17 to 1.43 g/l;
Even more interesting:
Echinococcal liver cyst surgery
Apple cider vinegar for dandruff reviews
Antibodies to TPO: what are they?
The abbreviation TPO stands for thyroid peroxidase, and, along with thyroglobulin (TG), is the most frequently tested in women in case of endocrinological problems. Each of them is an enzyme necessary for the body, however, if the thyroid gland malfunctions, the immune system begins to actively produce antibodies - proteins designed to destroy the resulting negative cells. For this reason, in some cases, monitoring of AT TPO is necessary, carried out by taking a blood test and its further interpretation.
TPO acts as a catalyst for the production of the hormones T3 and T4, whose production decreases as the amount of antibodies to TPO increases. Also, this enzyme is important for the natural formation of iodine in the body, so the increase in antibodies to TPO must be blocked in the early stages.
An analysis for antibodies to TPO is carried out both when a specific diagnosis is made, before starting targeted treatment, and when primary symptoms change in their level:
- enlargement of the thyroid gland (appearance of goiter in women);
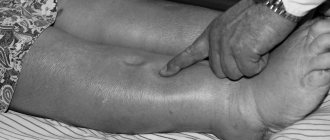
- swelling of the lower leg;
- ophthalmopathy;
- hyperthyroidism in newborns.
Also, experts insist not only on routine tests, but also on mandatory testing of antibodies during pregnancy, since this can not only have an undesirable negative effect on the fetus, but also develop thyroiditis in the young mother.
Antibodies in the blood: what are they?
Its composition depends on all the diseases suffered by a person throughout his life. In addition, antibodies make it possible to identify the cause of various types of pathologies.
.
Antibodies themselves are special protein formations - immunoglobulins
. They can combine infection antigens. Antibodies appear with the participation of lymphocytes.
There are several classes of antibodies:
IgA allows for the creation of mucosal protection
body. These immunoglobulins are awakened when infections occur that affect the skin or during the development of acute respiratory infections. And also the concentration of antibodies of this type increases during intoxication of the body, liver pathologies or alcohol abuse.
IgE refers to immunoglobulins that are activated when a person is exposed to bacteria, fungi, viruses
. These antibodies are capable of eliminating toxic secretions of infectious agents. It is IgE that is responsible for the formation of immunity of the child in the womb and the creation of long-term immunity, which, when a person is infected, prevents infection again.
Antibodies of the IgM type are special immunoglobulins. Their volume in the blood increases sharply during infection and in the initial stages of the disease.
. It is these antibodies that are the first to react to the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood and are the first front of defense.
The study of antibodies allows us to get an idea of the presence of pathogens in the blood. In some cases, antibodies may be present in the blood continuously, even after recovery.
sick.
For this reason, a blood test provides information about some of the diseases a person has had in the past.
Antigen testing is most often prescribed to detect certain diseases:
- hepatitis;
- herpes;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- leptospirosis;
- cytomegalovirus;
- tetanus;
- diphtheria;
- syphilis and others.
You can donate blood to test the concentration of antibodies in the blood in special laboratories. Some tests require a referral specifying the type of test, but independent laboratories provide tests for antibodies to some viruses and infections anonymously.
Increase and decrease in antibodies to TPO in women
In order to correctly decipher the test results yourself, you need to know not only the values of a simple blood test, but also the level of antibodies to TPO in women:
- For people under 50 years of age (before menopause), a value from 0.0 to 35.0 units/l is considered normal.
- After the onset of menopause, the upper limit may increase to 100.0 units/l.
- A number of clinics that take tests can set values in units/ml, then the reference value will be less than 5.6 units/ml, the limit is set from 3.0 units/ml to 1000.0 units/ml.
An increase in antibodies to TPO in women by 18-20 units/ml usually does not require treatment, but requires further monitoring of the patient.
Experts note that a reduced value can be recorded in people without any disorders of the endocrine system and the thyroid gland in particular, and sometimes this is attributed to an error in the testing method. With the increase in antibodies to TPO, everything is not so smooth.
- The main reason for the increase is Hashimoto's thyroiditis (90% of cases), the visual manifestation is a change in the thyroid gland towards enlargement.
- A less common option is Graves' disease or Graves' disease, which manifests itself through an enlarged goiter; Additionally, hyperthyroidism may be diagnosed.
- The “mildest” cause is postpartum thyroid dysfunction, with symptoms similar to general body disorders: fatigue, decreased performance, brittle hair and nails, dry skin.
- Hypothyroidism is rarely diagnosed, but it also occurs. In children it becomes a harbinger of cretinism. Accompanied by rapid fatigue, decreased activity, swelling of the face, and slower metabolic processes.
What treatment should I choose if antibodies to TPO are elevated?
A doctor should prescribe treatment for a serious increase in antibodies to TPO. As for the general recommendations and rules that will be implemented here, in 90% of cases therapy is based on hormonal drugs, so unwanted side effects are quite likely.
In addition to hormones, iodine preparations can be prescribed, whose deficiency with an increase in antibodies to TPO is especially clearly visible, but these alone will not be enough. Therefore, any deviation from the norm in terms of indicators should be referred to a doctor.
It is known that in the human body, the immune system is responsible for the fight against various microbes and viruses - special proteins (antibodies) recognize foreign objects and destroy them. But sometimes it happens that antibodies attack unaffected healthy tissues and cells of the human body.
Thus, antibodies can mistake the useful enzyme thyroid peroxidase
and try to destroy him.
Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme produced by the thyroid gland, thanks to which iron synthesizes hormones such as triiodothyronine and thyroxine. To identify such a disorder, it is necessary to take a test for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase ( anti-TPO
). It is worth saying that most often women suffer from such violations.
When is a thyroid peroxidase antibody test prescribed?
An anti-TPO test is prescribed in the following cases
:
- when you experience irritability, drowsiness, fatigue, mood swings, which may be symptoms caused by a disruption in the natural functioning of the thyroid gland; - before prescribing medications that can negatively affect the activity of the thyroid gland (immunomodulatory, antiviral drugs, such as interleukin, interferon alpha, antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as psychotropic drugs based on lithium); - if thyroid dysfunction is suspected - hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism; - when other autoimmune diseases are detected, such as rheumatoid arthritis, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, vasculitis (systemic angiitis) of autoimmune origin, pernicious anemia, lupus (Libman-Sachs disease); — in the study of female infertility of a pathogenic nature, in case of pregnancy disorders; - if there are changes in the structure or size of the thyroid gland identified during ultrasound.
Anti TPO. Normal for women
For a healthy woman under 50 years of age, antibodies to TPO are within the normal range of 0–35 IU/ml
, for older people –
0–100 IU/ml
. Any deviations from the above norms may indicate autoimmune processes in relation to the thyroid gland. Depending on the level of deviation, there are: significant, moderate and insignificant increase in the degree of antibodies to thyroid proxidase.
Causes of significant increases in anti-TPO are usually autoimmune disorders
thyroid gland: Basedow's disease, Hashimoto's disease (lymphocytic thyroid). During pregnancy, an increased level of antibodies to TPO indicates a high likelihood of hyperthyroidism in the child, both before and after birth.
indirect factors can also serve as reasons for a moderate or insignificant deviation from the norm.
:
- damage to the thyroid gland of a physical nature; — environmental factors (toxins, poor ecology, radiation); - Use of an increased dose of iodine during treatment; - situations that traumatize the psyche and lead to stress (death or serious illness of a loved one, change of place of residence or work, divorce, etc.); — sufficiently long-term use of hormonal drugs without appropriate control; — presence of sources of chronic infections (pharyngitis, adenoiditis, sinusitis, tonsillitis); - pregnancy; - transmission of diseases such as influenza, ARVI, etc.; - hereditary predisposition to the disease.
It should be noted that deviation from the norm of antibodies to TPO is a consequence
autoimmune thyroid disease, not its cause. Therefore, it makes no sense to evaluate the degree of anti-TPO in development, or to try to simply reduce their level, even if the deviations from the norm are significant.
Submission of analysis
It is necessary to stop taking hormonal medications a month before the test, unless otherwise instructed by the treating endocrinologist. Taking iodine-containing medications should be stopped several days before the test. You should also avoid physical activity and try to avoid stressful situations. If, shortly before the analysis, you underwent surgery or a serious illness (sore throat, pneumonia, flu), then you should delay the anti-TPO analysis, since it is possible that the results may be inaccurate. You should go for the test early in the morning on an empty stomach (also exclude nicotine).
In recent years, doctors have often diagnosed disorders of the endocrine system in women and men. For example, a disease such as autoimmune thyroiditis is supposedly found in every 5th person who comes to the clinic.
External symptoms should always be carefully checked. The best option would be to get tested for AT to TPO. To understand the result, you should know what the norm should be for a healthy person. When tested, already every 10th woman and every 20th man are found to have antibodies to TPO, but only when their level is elevated does the situation become dangerous.
TPO or thyroid peroxidase/thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme produced by the thyroid gland that plays a role in the biosynthesis of hormones. These are complex protein compounds formed in the body, which it, along with the immune system, considers something foreign.
Currently, a considerable number of antibodies found in the human body have been identified and studied, each of which has its own function. Mostly such disorders occur in the body of women. Age-related changes are also fertile ground for this - the older the lady, the higher the risk.
Antibodies to TORCH infections
The TORCH complex includes several infections: toxoplasma, herpes, rubella, cytomegalovirus. These infections are extremely dangerous for pregnant women, especially if infection occurs in the first trimester, they can cause spontaneous abortion, developmental abnormalities, stillbirth, and sepsis.
Blood test for antibodies. It is recommended to determine the antibody titer before conception, but if this has not been done, the doctor will prescribe a test during pregnancy.
Antibodies to rubella, toxoplasmosis, herpes and cytomegalovirus during pregnancy can be normal and during illness. IgM and IgG are significant for diagnosis. These immunoglobulins correspond to different phases of the immune response; their presence and titer can indicate the presence and duration of infection.
During pregnancy, the result of a blood test for antibodies can be of four types:
- IgG and IgM are negative (not detected). This result suggests that the expectant mother’s body has not encountered the infection, which means that primary infection may occur during pregnancy. The study must be repeated monthly.
- IgG and IgM are positive. The infection occurred recently, during or before pregnancy. This can be dangerous, so additional research is required (quantitative determination of titer, etc.).
- IgG is positive, but IgM is not detected. This is the most favorable result. He talks about a long-standing infection, which, in most cases, will not be dangerous for the child. If the blood was tested late in pregnancy, this may indicate infection early in pregnancy.
- No IgG was detected, but IgM was positive. Indicates the presence of a recent infection, already during pregnancy. Sometimes it can mean reactivation of the infection, which is not dangerous for the child. Additional examination is definitely required.
Thus, if IgM antibodies are detected during pregnancy, the consequences can be dangerous for the child, but only IgG means that there is no need to be afraid of infection.
In any case, each result is individual and must be assessed by a doctor. Depending on the result, treatment or a repeat antibody titer test may be prescribed.
When is TPO examined?
TPO is most often tested by doctors for thyroid problems. This is a necessary enzyme in the life of the female body, for which the immune system is responsible. But in the event of a malfunction, it is the one that is susceptible to the production of antibodies - proteins that should eliminate the resulting negative type cells. Monitoring of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase in women and men is carried out through blood tests and proper decoding according to the norm. TPO serves as an accelerator for the performance of hormones such as T4 and T3.
In cases where the level of antibodies to TPO is increased, the production of hormones is greatly reduced. This enzyme also plays an important role in the production of iodine in the body in a natural way. To block the growth of antibodies at an early stage, you need to be observed by an endocrinologist as often as possible, especially for women.
Consequences of increasing AT to TPO
As a result, there may be damage to the cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system. The functioning of the nervous and reproductive systems is disrupted.
Pregnant women should pay special attention to themselves, because any violation can affect the child. The most common syndrome at birth is hyperthyroidism in infants. After birth, doctors have only 14 days to identify pathology, so children also need to take tests. Any omissions from the norm can lead not only to disruption of the endocrine system, but also to dementia.
Causes
The reasons for the increase in antibodies in women have not yet been fully identified, but doctors suggest that they are as follows:
- thyroid diseases;
- bad heredity;
- poisoning by toxins;
- some chronic diseases;
- viral infections;
Also, the reason that the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase is increased is carrying a child. The above is due to the fact that during pregnancy, women begin to experience hormonal changes.
Immunoglobulins to thyroid peroxidase are autoantibodies. Their active combination occurs in the body of women during autoimmune processes (i.e., under the influence of the personal immune system) in the thyroid gland and leads to the development of diseases such as:
- chronic or subacute thyroidins;
- organ enlargement (diffuse or nodular);
- hypothyroidism (the process of reducing the basic function of the thyroid gland);
Why get tested for antibodies?
Blood test for antibodies. The results may indicate the course of various diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases. For example, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, syphilis, etc.
It is also recommended in cases of suspected helminthic infestation, thyroid disease, tetanus, immunodeficiency virus, and also as a prevention of Rh conflict in pregnant women.
It is also useful in that it is able to diagnose a decrease in immunity in time, and therefore prevent complications.
All antibodies are usually classified into five types: IgA, IgE, IgM, IgG, IgD. Each of them resists its own group of antigens.
IgM immunoglobulins usually appear at the very beginning of infection. They are designed to provide primary protection against the disease. Indicates early signs of bacterial and parasitic infection. In many cases, IgM levels decrease as class A (IgA) and class G (IgG) increase.
IgA immunoglobulins control the immunity of the mucous membranes. Its main function is to neutralize the virus. They are activated during viral, chronic infections of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract, chronic liver diseases, skin and rheumatological diseases and others.
One of the most important, immunoglobulin G (IgG), is predominant in the blood serum and is especially important for long-term protection of the body. Deficiency or absence of IgG is accompanied by relapses of the disease. The doctor prescribes an IgG test to understand the stage of the disease and whether there is “protection”. If these antibodies are produced in insufficient quantities, it means that the body’s resistance is extremely low.
IgG is the only one that can pass through the placenta, providing intrauterine protection to the child. After birth, the action of maternal immunoglobulins continues during the first three months of life, during this period the child begins to synthesize his own.
Antibodies of the IgE group are produced in places where the body encounters various allergens from the external environment - in the skin, respiratory tract, tonsils, and gastrointestinal tract. The resulting “IgE + antigen” complex leads to the development of a local allergic reaction, which manifests itself in various variations: from rhinitis and rash to anaphylactic shock. Antibodies to IgE are detected in the blood for 2-3 days, in the skin – up to 14 days. An increase in the level of total IgE is associated with an immediate allergic reaction. In people with allergies, IgE antibodies are elevated during and between attacks.
The function of immunoglobulin D (IgD) antibodies is poorly understood. It is located together with M on the surface of the B lymphocyte, controlling its activation or suppression. Found in the tissue of the tonsils and adenoids, which suggests its role in local immunity. It has been found to have antiviral activity.
Prevention
- get rid of bad habits, or better not acquire them at all;
- Healthy food;
- choose the most environmentally friendly area to live;
- follow the daily routine. This is especially important for women, sleep disturbance leads to problems with the thyroid gland;
- maintain psychological health, try to always be balanced and calm;
- monitor the health of the internal genital organs.
To control the level of production of antibodies to TPO, you should not only lead a healthy lifestyle, but also be constantly monitored in medical institutions. Systematic research at least once a year will help you find out about any deviations and relieve you of unnecessary stress.