An extrasystole is an extraordinary contraction of the heart, resulting in a certain pause in the rhythm, which people are simply accustomed to calling the heart fading. Such changes in heart rate cause many people to become confused and overcome with fear.
This pathology can appear for a variety of reasons - as a result of diseases of the respiratory tract, heart. In addition, there is a connection between the appearance of arrhythmia and problems in the functioning of the thyroid and pancreas.
This pathology is not always dangerous; it can occur in completely healthy people who have never had heart problems; the cause of its appearance may be VSD.
But if doctors diagnose extrasystole due to osteochondrosis, the situation becomes more complicated, because it is quite difficult to cure this disease. And after recovery, for a long period, a person needs a certain lifestyle and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
What is extrasystole?
Extrasystole is a contraction of the heart muscle with deviations from the norm. At the same time, a person may feel a strong heartbeat or, conversely, his pulse is very difficult to palpate.
Common symptoms of arrhythmia include the following:
- A person complains of a strong heartbeat, it is so strong that sometimes it does not even allow him to fall asleep.
- There is a feeling that the heart has suddenly stopped. In this case, it is almost impossible to feel the pulse. There are long pauses between heartbeats.
- The patient's skin becomes pale.
- Sweating increases.
- There is a feeling of panicky lack of air.
- The corners of the lips turn blue.
Arrhythmia is not always harmless. Sometimes its consequence can be poor blood flow to the brain, which leads to serious problems and diseases.
Only a qualified doctor can find out the cause of extrasystole.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the pathology is characterized by the fact that extrasystoles in osteochondrosis are manifested by a constant feeling of muscle tension and tissue soreness. Such symptoms significantly limit the patient’s motor activity; discomfort interferes with the natural movements of the body, upper and lower extremities.
Since the pain syndrome at the onset of the disease is not pronounced, patients rarely seek qualified medical help, believing that the pain will go away spontaneously. Ignoring symptoms can lead to their intensification, which becomes a frightening factor.
Additional signs of extrasystole in osteochondrosis are the following conditions:
- sudden shocks of the heart, accompanied by periodic freezing for several seconds. After this, the heart muscle begins to contract rapidly;
- discomfort, tension in the subscapular area;
- disorientation in space, accompanied by fainting;
- sudden hot flashes, sweating, chills;
- feeling of lack of air to take a deep breath;
- general weakness, blue lips;
- pale skin;
- irregular pulse, sudden jumps in blood pressure.
The occurrence of such symptoms should alert a person and prompt them to seek the necessary medical help. Otherwise, an increase in discomfort in the spine and other areas of the body can lead to serious psychological problems, which will require consultation with a psychotherapist and the prescription of appropriate treatment.

The occurrence of extrasystole in osteochondrosis
Currently, extrasystole in osteochondrosis is a fairly common occurrence. Pain in the heart area can occur for various reasons. One of them may be problems in the functioning of the muscles or spine.
It is important for every person to understand that any pre-fainting conditions or too frequent cardiac arrests can be the result of some serious illness. Therefore, if such symptoms recur, it is better not to hesitate and immediately consult a doctor. Everything may not be as simple as it seems at first glance. Very often, against the background of extrasystole, atrial fibrillation can occur, which is fraught with cardiac arrest (we wrote more about atrial fibrillation here).
Extrasystole occurs due to pinching of the nerve roots that regulate the functioning of the heart.
Heart rhythm disturbances often occur with hypertension, which can accompany osteochondrosis. An increase in blood pressure increases the load on the heart, which in turn leads to disruptions in its functioning.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of extrasystole in patients suffering from osteochondrosis:
- problems in the nervous system;
- physical, emotional tension, stress;
- lack of sleep and overwork;
- inactivity;
- bad habits;
- love for strong coffee and tea.
Improper functioning of the heart in osteochondrosis can be detected on a cardiogram. But its most accurate indicators are possible with a Holter study.
Heartbeats are divided into three types:
- rare ones, which appear from a couple to several dozen times throughout the day;
- medium, characterized by the appearance of 100 to 200 contractions per day;
- frequent, when the number of heartbeats is equal to 1000 times a day.
Osteochondrosis manifests itself differently in different places. It is almost always accompanied by pain in the heart. They appear and grow in paroxysms, but are most often characterized by their duration and persistent nature.

The pain can be boring, deep or pressing, with a mild severity. In most cases, the heart rate increases significantly. Very often, such patients experience a feeling of warmth in the chest area. It is worth noting that such painful symptoms are not relieved by heart medications.
Cervical region
Cervical osteochondrosis and extrasystole are two concepts that often accompany each other. Problems with the spine in the neck area often lead to painful symptoms in the heart area. In addition, there is pain in the neck area, the place where the spinous processes of the lower vertebrae are located.
This symptomatology may be accompanied by a weakening of strength in the muscles of the left hand, especially its little finger. The pain becomes even more noticeable with the slightest movement in the patient’s cervical spine and arms.
Thoracic region
Extrasystole with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region may manifest itself weakly for some time. Pathology can progress only after serious heavy physical exertion, due to insufficient oxygen for the myocardium. In such cases, the person experiences palpitations, complains of lack of air, faintness, increased sweating, pain under the shoulder blade and rapid pulse.
Arrhythmia is often accompanied by increased blood pressure. Moreover, medications for high blood pressure and arrhythmia do not help, and their use leads to addiction, which in the future can lead to the fact that they become ineffective.
Lumbar
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine leads to the release of large amounts of catecholamines from the adrenal cortex, which are chemicals that provoke vasospasm. This process may be accompanied by pressure surges. With each release of these substances, there is a high probability of pressure increasing to maximum levels.
Symptoms
If the appearance of extrasystoles is associated with a disease of the spine, then when different parts of the ridge are affected, the symptoms are somewhat different. Heart rhythm disturbances occur already in the later stages of the disease, when structural changes in the vertebrae are noted. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the patient has:
- tachycardia;
- periodic “fading” of the heart;
- lack of air;
- increased sweating;
- dizziness;
- faintness;
- increase in blood pressure limits.
Extrasystoles together with arterial hypertension indicate the presence of osteochondrosis of the neck. With osteochondrosis in the thoracic region, the above-described symptoms are accompanied by:
- pain in the heart area;
- muscle tension in the shoulder blade area;
- strong heartbeats felt in the chest.
Osteochondrosis in this case acts as a provoking or aggravating factor for hypertension.
Symptoms of extrasystoles
The reasons for its occurrence
Normally, an impulse giving a signal to contract the myocardium is formed in the sinus node. When conduction is disrupted, they appear at any point in the heart muscle, causing it to contract. Chaotic supply of impulses disrupts the coordinated functioning of the heart and disrupts the functioning of the entire mechanism. Interruptions in the heart can manifest themselves as rare extraordinary contractions, causing unpleasant discomfort. This is a normal reaction of the body during physical activity. But if tremors outside the rhythm occur hundreds of times more than normal during the day, then they speak of developing extrasystole. It can be called:
- stress;
- overwork;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- abuse of coffee and strong drinks;
- smoking;
- poisoning with harmful substances;
- diseases of the cardiac system;
- osteochondrosis;
- hormonal imbalance.
With reduced liver or kidney function, as well as endocrine diseases, decay products, that is, toxins, accumulate in the human body. This is one of the reasons for the appearance of extrasystoles. A common cause of rhythm disturbances in women is hormonal imbalance that occurs during menopause.
The reasons that cause extrasystoles are different, but they are all associated with disruption of the autonomic system. Therefore, the main cause of the disease is dysfunction of the nervous system and brain.

Causes beyond rhythmic contractions
Types of extrasystole in osteochondrosis
Extrasystole has varieties, depending on certain factors. By type of education there are:
- ventricular;
- supraventricular;
- later ventricular - an additional impulse is observed before the normal contraction;
- ventricular wound - the next contraction of the heart occurs immediately after a normal contraction;
- ventricular paired - two contractions at once, one of which occurs in the ventricle;
- single;
- multiple;
- group extrasystoles (volley) - more than five beats per second simultaneously from different foci.
According to the number of contractions per day, extrasystoles are classified as;
- rare - less than 30 pieces;
- medium - more than a hundred;
- frequent - more than two hundred.
Depending on the etiology, extrasystoles are:
- functional – not a consequence of pathologies of the cardiac system;
- organic – caused by heart disease, structural damage to the myocardium;
- toxic - is a consequence of poisoning of the body.
In order to prescribe treatment to a patient, you need to know the cause of the disease. Therefore, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive diagnosis, including laboratory and instrumental studies.
Treatment
Therapy for extrasystoles has two directions:
- eliminating the causes that provoke extraordinary contractions (in this case, treat osteochondrosis);
- restore normal heart rhythm with medications.
The classic treatment process includes:
- correction of the way of work and rest;
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- rejection of bad habits;
- taking medications that normalize heart rate;
- sedatives;
- a course of manual therapy;
- physiotherapy sessions.
In addition, patients are advised to perform special physical exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back and neck. A set of exercises is selected by the instructor individually for each patient, depending on the characteristics of the pathological process.

Treatment of extrasystoles
Ventricular extrasystole and osteochondrosis
Ventricular extrasystole is one of the most common cardiac dysfunctions. People suffering from such arrhythmia must undergo special treatment and be constantly under medical supervision.
The symptoms of this pathology are not much different from the symptoms of arrhythmia that occurs for other reasons. Patients are concerned about:
- problems in the functioning of the heart, it seems to turn over in the chest;
- weakness;
- constant feeling of discomfort;
- sweating;
- lack of air;
- constant irritability;
- obsessive fear and anxiety;
- dizziness.
Untreated ventricular extrasystole can lead to serious complications:
- blood clots may form, their separation can lead to serious complications;
- due to poor blood circulation in the brain, there is a risk of stroke;
- the heart may stop and clinical death may occur.
When the first signs of arrhythmia appear, it is better to immediately seek medical help and first of all do an ECG. Only after the examination, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
How is extrasystole diagnosed in osteochondrosis?
Extrasystole can occur in a mild form. In this case, there is no need for treatment. But it’s better to undergo a medical examination and rule out serious pathological processes.
To determine the degree of arrhythmia, the patient is referred to a cardiologist, who takes the following methods:
- determines the type of arrhythmia;
- studies the characteristics of the patient’s body;
- records the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle;
- prescribes laboratory and instrumental studies;
- prescribes Holter monitoring;
- if necessary, refers for MRI and ultrasound of the heart.
Methods of drug and drug therapy
Altered ventricular rhythm and disruptions in heart rate require mandatory medical intervention in the process of heart function. Thanks to modern and most accurate diagnostic methods, combined with obtaining complete information about the patient’s health status, it is possible to obtain data on the basis of which a treatment regimen is drawn up.
With ventricular contraction and a general disruption of the rhythm of the heart muscle, a benign course of the disease can be observed, which is characterized by a high degree of probability of self-relief of the pathological process. In this case, there is no need to take special measures or take medications to stabilize the patient’s condition. To more quickly improve his well-being, the cardiologist can make adjustments to the patient’s lifestyle, indicating recommendations for improving it and preventing possible complications after the current process.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of extrasystoles in osteochondrosis must be started if more than 200 extrasystoles are observed per day and the diagnosis has been confirmed by doctors. Different methods are used for this, each of them is effective in its own way.
Medicines
For severe pain, painkillers are used. If the heart muscle contracts abnormally due to fear or anxiety, doctors recommend resorting to sedatives.
Sometimes arrhythmia can be a consequence of taking medications. It is important to find out which of them the patient reacts to and try to choose a different treatment regimen.
In addition to these measures, the doctor may prescribe medications that help restore metabolism and lower blood pressure.
Manual therapy
This method of treating arrhythmia is considered quite effective. With its help, muscle spasms are relieved, the metabolic process in the body and blood flow are improved. It is only important to approach this issue seriously and entrust yourself exclusively to a qualified specialist, because unprofessional actions can aggravate the situation and cause serious harm to the patient.
Physiotherapy
Among the physiotherapeutic methods for treating extrasystole, therapeutic exercises and massage have proven themselves well. It is only important not to use them during an exacerbation. Individual physiotherapy is selected for each patient.
Traditional therapy
Traditional methods of treating arrhythmia cannot be treated as the main ones. They are more suited to a supporting role.
Recipe No. 1
To prepare this folk remedy you will need 4 tsp. valerian root and 1 tbsp. water. This mixture is simmered in a water bath for half an hour, filtered and taken three times a day, 1 tbsp. l. after eating.

Recipe No. 2
Using lemon and garlic gives positive results. To prepare this folk recipe, you need to take 6 cloves of garlic and 2 lemons, pass it all through a meat grinder, put it in a three-liter jar and fill it with water. Take half a glass of the tincture once a day. This is an excellent cleanser for blood vessels, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart.
Recipe No. 3
Motherwort decoction has excellent sedative properties. To prepare it you need 1 tbsp. l. steam motherwort in 1 tbsp. water. This remedy is taken for 14 days three times, 1 tbsp. l. before eating.
Treatment with folk remedies

To reduce extrasystole, patients are advised to follow a daily routine, eat right and get regular and moderate physical activity.
In addition, several folk recipes for combating extrasystoles can be noted. They, of course, are not the main therapy, but can be used as additional and auxiliary methods of eliminating the problem.
Recipe 1
This remedy uses valerian root (4 teaspoons). It is diluted with cold water (200 ml) and boiled for 25-30 minutes. After this, it is filtered through a double layer of gauze. It is recommended to drink the resulting decoction 3 times a day before meals, 1 tablespoon.
Recipe 2
Lemon and garlic will help actively fight this disease. To do this, take 6 cloves of garlic and 2 lemons. They must be crushed and mixed together. The resulting mixture is placed in a jar (3 liters) and filled with water to the edges of the jar.
You need to consume 100 ml of the product per day. It will cleanse the blood vessels and have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart as a whole.
Recipe 3
Motherwort is considered a famous sedative. For a glass of water you need about 1 tablespoon of motherwort. The resulting solution is steamed and filtered. The course of therapy with a decoction of motherwort lasts 2 weeks, during which you need to drink 1 tablespoon of the product 3 times every day.
Recipe 4
Hawthorn and rosehip are rich in vitamin C, and they have an excellent effect on heart function. The fruits are used very simply: they are brewed like regular tea.
To learn how to properly get rid of osteochondrosis using therapeutic exercises, watch the video:
Disease prevention and nutrition
In order to prevent extrasystole, doctors recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- avoid stressful situations,
- take vitamins and microelements,
- follow a diet
- treat concomitant diseases,
- control potassium levels in the blood.
To ensure that the body does not experience a lack of potassium, it is important to take medications containing it. In addition, it is worth paying attention to products containing this microelement. There is a lot of potassium in dried apricots, apples, bananas, zucchini, and pumpkin.
Products that include magnesium - nuts, beans - are also considered useful for arrhythmia.
To improve your overall well-being, you should give up hot, spicy foods, strong coffee, tea, alcohol and smoking.

Getting rid of extrasystole is possible. The main thing is to approach pathology with all seriousness. It is very important to find the true reason and you should not try to do it yourself. Only the help of qualified doctors can contribute to correct diagnosis and effective treatment. Compliance with all doctor’s orders and a correct daily routine will help with this.
Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky (SSMU, media)
Level of education - Specialist
1990 – Ryazan Medical Institute named after Academician I.P. Pavlova
Extrasystole can occur with any cardiac pathology. But almost half of such arrhythmias are caused by psycho-emotional overload, vegetative-vascular disorders, reflex effects from internal organs, taking certain medications, electrolyte imbalance, and drinking tonic drinks. It is to this half that the causes of resting extrasystole usually refer.
Types of extrasystole
Extrasystole is a change in heart rhythm caused by extraordinary electrical impulses. They form in an additional focus of increased activity during diastole and affect the functional homogeneity of the myocardium. In the absence of cardiac pathologies, the appearance of extraordinary electrical signals (extrasystoles) can provoke increased tone of the vagus or sympathetic nerve.
In this regard, sympathetic and vagal (bradycardic) extrasystoles are distinguished. Vagal symptoms appear at rest, often after meals and against the background of bradycardia, and disappear after exercise. Sympathetic extraordinary impulses, on the contrary, are formed during sports and other physical activities and disappear at rest.
How to get rid of extrasystole and remove its manifestations
Extrasystole does not occur on its own. It is a manifestation of pathological processes occurring in the myocardium or other organs.
To get rid of arrhythmia you need to:
- Find a specialist to assess the risk and draw up a treatment program.
- Make lifestyle adjustments
- quitting smoking, alcohol, coffee and strong tea;
- healthy food;
- adequate physical activity;
- minimizing stress factors.
Make sure that therapy is necessary. Eliminate the cause (surgery may be required). Select a drug treatment regimen.
Clinical symptoms and treatment of extrasystole are directly related: the more serious the changes in the patient’s condition, the more radical therapy he will need.
Reasons for the development of extrasystole at rest
Experts note the influence of increased vagus nerve tone on the development of supraventricular extrasystoles. Vagal influences (reflexes) affecting the functionality of the heart usually arise when:
- axial hernia of the esophagogastric opening in the diaphragm;
- deformations of the walls of the esophagus;
- reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus;
- gastric pneumatosis;
- bloating;
- obesity;
- constipation;
- difficulties in moving food through the gastrointestinal tract;
- gallstones;
- prostate adenoma;
- fibroids of the uterus.
In patients with an unknown etiology of extrasystole, it is necessary to examine the organs located in the abdominal cavity. In addition, reflex extrasystole (extraordinary impulses caused by reflexes) can be provoked by pathological processes in the mediastinum and lungs, and cervical spondyloarthrosis. Sometimes pathological reflexes cause pockets of infection.
Extraordinary impulses that are formed when exposed to small dilated areas of the internal carotid arteries, during prolonged coughing, during the process of swallowing, when lying down and with certain pathologies of the brain, are also considered reflex.

Extrasystole at rest

With organic extrasystole, the heart rhythm is restored after the person takes a horizontal position, but the functional pathology in the supine position is more pronounced.
Doctors note a connection between increased tone of the vagus nerve and the development of extrasystole. Extrasystole at rest can occur for the following reasons:
- dysfunction of the kidneys or pancreas;
- obesity;
- hypertension;
- heart failure;
- various heart pathologies.
Symptoms of vagal extrasystole
The manifestations of vagal extrasystole are influenced by many circumstances, in particular: individual irritability, contractile function of the heart, normal rhythm frequency and the level of prematureness of extraordinary impulses.
The main sign of the occurrence of extraordinary electrical signals against the background of bradycardic heart rhythm disturbances is a decrease in the heart rate. It is often combined with pressure surges. During physical activity, the symptoms of extrasystole almost do not appear, they are noticeable only at rest - the more clearly, the less often the heartbeat. The patient feels as if something like a bag of air is interfering with the normal functioning of the heart, especially when lying on the left side. Observed:
- interruptions in heart rhythm;
- fatigue;
- dizziness;
- a feeling of tightness or retrosternal raw pain;
- decreased muscle tone;
- panic attacks;
- lack of air.

Increased tone of the vagus nerve is expressed by:
- low heart rate (40-60 per minute);
- increased heart rate when inhaling;
- predisposition to hypotension;
- disruptions in the functioning of the vegetative-vascular system (“marbling” and cyanosis of the extremities, cold sweat in the area of the feet and palms, spontaneous urticaria).
The presence of vagal extrasystole is indicated by:
- an increase in the number of extraordinary impulses when reflexes act on the vagus nerve;
- a decrease in the number of extrasystoles or their disappearance when changing body position or after performing several physical exercises;
- reducing the number of extraordinary impulses or eliminating them after the administration of atropine.
Diagnosis and therapy of resting extrasystole
Diagnosis of reflex extrasystole often causes difficulties. An unambiguous diagnosis is made if extraordinary impulses disappear after the elimination of negative stimulation. Complicating the situation is the fact that the manifestations of the reflex form of extrasystole are influenced by the unstable functioning of the autonomic nervous system. In addition, reflexes are sometimes involved in the formation or acceleration of extraordinary electrical signals in organic cardiac lesions. Such circumstances make differentiated diagnosis of organic and reflex extrasystole practically impossible. An accurate diagnosis is made retrospectively.
Treatment of vagal extrasystole
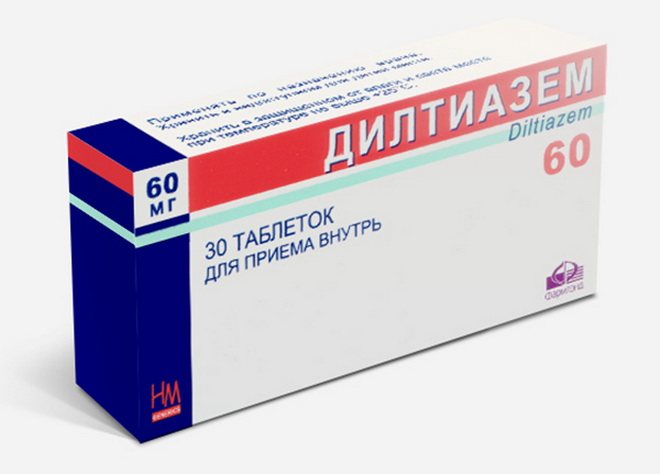
If there are cardiac pathologies, the patient is prescribed appropriate medications. Antiarrhythmic drugs have very serious side effects, so they can only be used as prescribed by a specialist and in recommended dosages. For bradycardia, Diltiazem, Panangin, Carbamazepine are indicated, for surges in blood pressure - Bisoprolol, Atenolol, Metoprolol, for more severe pathology - Amiodarone, Propafenone.
If the symptoms of extrasystole cause physical suffering to the patient in the absence of cardiovascular pathologies, before prescribing medications, he is usually recommended to reconsider his lifestyle while taking mild sedatives. Often the cause of extrasystoles lies in the body’s reflex response to functional failures, so the patient needs to:
- normalize nutrition (constipation, flatulence cause an increase in the level of the diaphragm);
- control body weight (squeezing the diaphragm causes corresponding reflexes);
- cleanse the gallbladder and liver (a bladder overfilled with bile provokes reflex activity of the vagus nerve).
Extrasystoles subject to therapy
Sometimes, even in the absence of heart disease, extraordinary electrical impulses can significantly affect the performance of the body. Frequent contractions of the heart, reducing blood output per unit time, can cause loss of consciousness with the subsequent development of angina. Atrial extrasystoles provoke atrial fibrillation. Frequent multifocal volley ventricular impulses can bring the greatest trouble - they can portend the development of ventricular fibrillation.
Signs of dangerous heart pathologies are often those that appear in a lying position:
- allorhythmia (an extraordinary impulse occurs regularly after several normal heart contractions);
- polytopic extrasystoles (extraordinary impulses are formed in different foci);
- volley impulses (over five per minute);
- extraordinary impulses that occur after atrial fibrillation (with any irritation, the flickering may return).
These conditions require mandatory preventive therapy.
Treatment
Treatment for extrasystole in osteochondrosis should be developed by a specialist based on the data that he was able to obtain during the diagnostic process. In most cases, the therapy process involves the use of a number of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as the elimination of osteochondrosis itself.
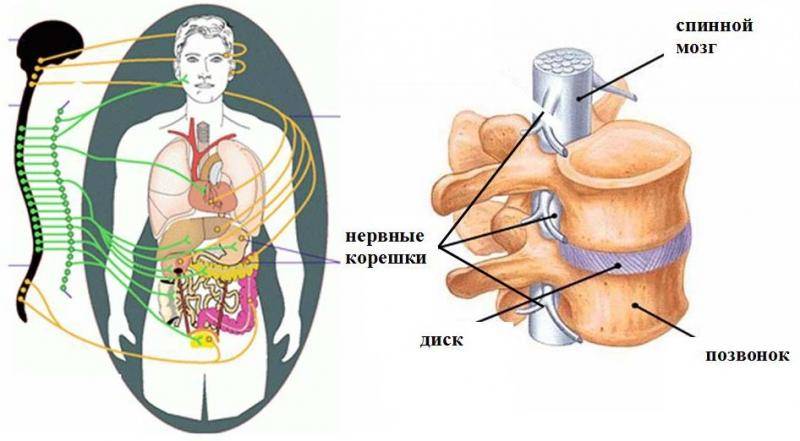
Pinching of nerve roots and blood vessels in the spine can lead to diseases of other internal organs
The most common method of therapy is the use of potassium salts. As a rule, the substance is supplied to the body orally or intravenously if the patient has problems with the gastrointestinal tract. However, such treatment is effective only in the case of weak extrasystole.
The drug Panangin is often prescribed, which is taken in the form of tablets three times a day, 2 tablets per dose, or by intravenous drip along with glucose solution or saline.
The dose of the drug can be reduced if there are visible improvements, so it is important to regularly monitor your heart rhythm using an electrocardiogram
Another remedy that is used in the treatment of this disease is the drug Novocainamide. It is introduced into the body intravenously or intramuscularly. The medicine has side effects and contraindications. So, with a strong decrease in blood pressure, Mezaton can be prescribed, but in the presence of sclerosis of the heart vessels and heart failure, Novocainamide is not prescribed at all.
If the disease has not affected the ventricles, beta-blockers are often used, as well as drugs such as Ephedrine, Alupent, Isuprel and other drugs against the development of possible bradycardia. Lidocaine, in turn, is used as an anesthetic that reduces excessive atrial activity and atrioverticular conduction of the nervous system.
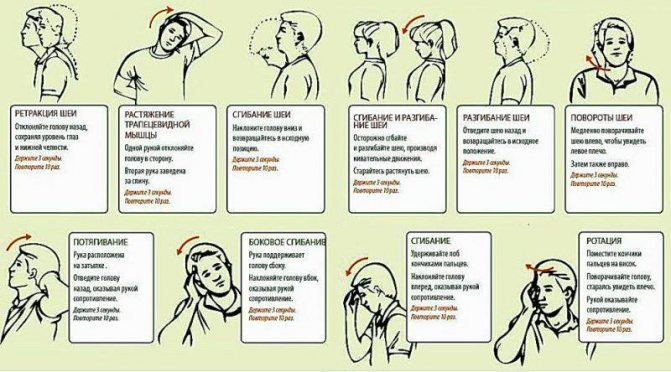
In order to prevent osteochondrosis, it is recommended to resort to special gymnastics for the spine
To eliminate inflammatory processes in the myocardium, medications such as Delagil, Plaquenil and other anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. The disadvantage of these drugs is that they tend to accumulate in the body, especially in the eye area, so it is recommended to be periodically examined by an ophthalmologist.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures and a special course of therapeutic exercises, which normalizes breathing, heartbeat, and strengthens the muscles of the back and chest. Traditional medicine methods are not recommended for use in this case.
Folk recipes
The list of folk remedies for the treatment of vagal extrasystole is quite large. But they are applicable only as auxiliary methods as part of complex treatment. After consulting with a specialist, you can use “grandmother’s” recipes:
- Hawthorn – use dried flowers as tea leaves (a tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water). Drink three glasses every day. You can prepare a tincture: per tablespoon of flowers - 200 ml of vodka. After leaving for 10 days in a dark place, drink a teaspoon three times a day;
- Calendula - pour a teaspoon of flowers into a glass of boiling water, let it brew, strain. Drink 100 ml four times a day;
- Horsetail - pour a tablespoon of horsetail into 600 ml of boiling water, leave for three hours. Strain, drink a tablespoon six times a day;
- Cornflower - add a teaspoon of dried flowers to 200 ml of boiling water and leave. Strain, drink on an empty stomach three times a day;
- Lumbago – add two teaspoons of dried flowers to 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew. Drink a third of a glass three times a day;
- Honey and chopped radish - mix in equal proportions, drink a tablespoon three times a day.
Causes
In approximately a third of cases, SVES is not accompanied by organic changes in the heart and is functional. They can also occur in healthy people. In this case, SVES is caused by autonomic disorders, often accompanied by a rare heartbeat, arterial hypotension, increased tone of the vagus nerve, in particular, sweating of the extremities.
SVES often appears with excessive consumption of tea, coffee, alcoholic beverages, and also with smoking. They can be triggered by emotional or physical stress, or changes in body position. With functional extrasystole during the daytime, patients often do not notice the arrhythmia. Extrasystoles begin to bother them in the evening, in a lying position, before bedtime.
SVES accompanies many heart diseases. Most often they are recorded in chronic ischemic heart disease (angina pectoris, post-infarction cardiosclerosis), as well as against the background of an active rheumatic process. The appearance of this arrhythmia is facilitated by enlargement of the atria and stretching of their walls, for example, with mitral stenosis. In this case, supraventricular extrasystole is subsequently replaced by atrial fibrillation.
SVES can occur during acute myocardial infarction and accompany the course of myocarditis, hypertension, and congenital heart defects. They occur in chronic cor pulmonale, pheochromocytoma (hormone-producing tumor of the adrenal gland), thyrotoxicosis, and menopausal myocardial dystrophy. In addition, SVES can be caused by hypokalemia, that is, a lack of potassium in the blood. In rare cases, they appear with an overdose of cardiac glycosides (digitalis intoxication).
SVES occur in acute and chronic infections, tonsillitis, as well as in chronic cholecystitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs.
Types and classification
Extrasystole can be detected by analyzing round-the-clock ECG monitoring.
Classification of extrasystoles by place of origin:
Myocarditis, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, chronic pulmonary heart disease
More often they are functional in nature, due to stress, drinking alcohol, coffee and strong tea, smoking
Ischemic disease (acute - myocardial infarction, chronic - angina), acquired valvular heart disease, hypertension, non-coronary myocardial damage
For diseases of the biliary tract, diaphragmatic hernia
Monomorphic extrasystoles appear on the ECG in the form of identical single extraordinary complexes. Their shape depends on the location. The frequency of occurrence of rare ones is up to 29 per hour, frequent ones – from 30 times and above.
Attacks of allorhythmia are characterized by a correct change between normal heart rhythm and extrasystolic episodes:
Two extrasystoles in a row are called paired. Early ones are those that occur before the full cycle of cardiac activity, recorded electrographically, ends.
Polymorphic extrasystoles
An ECG is a recording of electrical potentials that arise during the work of cardiomyocytes. Their sum appears in the form of a curve obtained by electrocardiography. The line has a standard outline provided that an impulse originates in the sinus node. If the generation of potential begins in a different place, a complex of teeth and segments of a completely different nature is displayed. As a result, the right ventricular extrasystole differs from the left ventricular one.
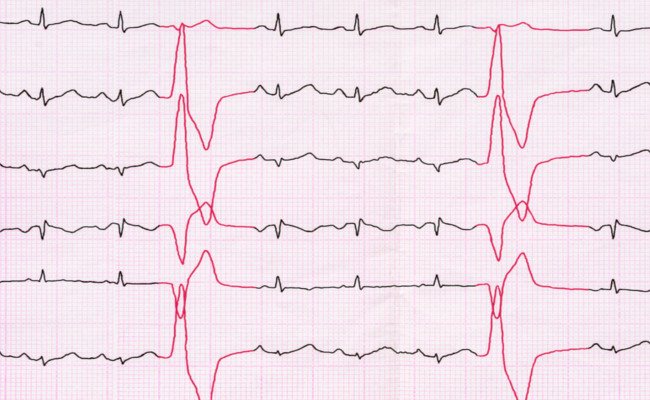
Polymorphic (different in shape) extrasystoles are visible on the ECG, provided that each extraordinary contraction was started in a different part of the myocardium than before. This means that the cause of arrhythmia is not local dysfunction, but damage to a large area of the heart muscle.
Group extrasystoles
They appear in quantities of 3-5 pieces one after another. The impulse circulates through the myocardium, which has lost the ability to become refractory (immune to depolarization).
If only extrasystoles are recorded on the ECG for half a minute, they are called “unsustained tachycardia.”
Clinical signs
Complaints of patients with supraventricular extrasystole depend on many factors. It is believed that young people with functional extrasystole tolerate SVES worse. They may complain of various sensations in the chest and neck, reminiscent of turning over, “fish fluttering,” or freezing. In some cases, extrasystole is accompanied by dizziness and weakness.
If extrasystole occurs against the background of an organic heart disease, it is often not felt, patients get used to it and do not pay attention to it. Complaints are mainly due to the underlying disease.
Diagnostics
SVES is diagnosed using resting electrocardiography (ECG) and 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring.
Atrial extrasystole is characterized by the premature appearance of an altered P wave, reflecting excitation of the atria from an ectopic focus. It is most often followed by a normal or slightly deformed ventricular complex. Sometimes ventricular contraction does not occur, in which case they speak of blocked SVES. After an atrial extrasystole, an incomplete compensatory pause is usually recorded. This means that the distance between two adjacent beats is less than twice the distance between two normal sinus beats. If the ectopic focus is located in the atrioventricular junction, a premature, unchanged ventricular complex is recorded on the ECG. The P wave is not detected. In other cases, excitation is carried out retrogradely to the atria, so a negative P wave appears after the extrasystolic ventricular complex.
When analyzing 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring, the functional diagnostics physician determines the total number of SVES, clarifies their topic (source), and identifies paired and group SVES. This study provides information about the distribution of extrasystoles over time, their relationship with heart rate, sleep period, physical activity and medication use. Therefore, daily ECG monitoring is an important part of the patient’s examination.
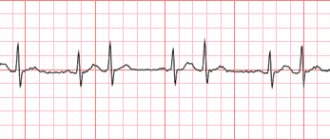
Extrasystole on ECG
Signs of extrasystole on an ECG depend on its type. Ventricular extrasystole, the diagnosis of which is extremely important, is defined as follows.
Read also: Extrasystoles tortured
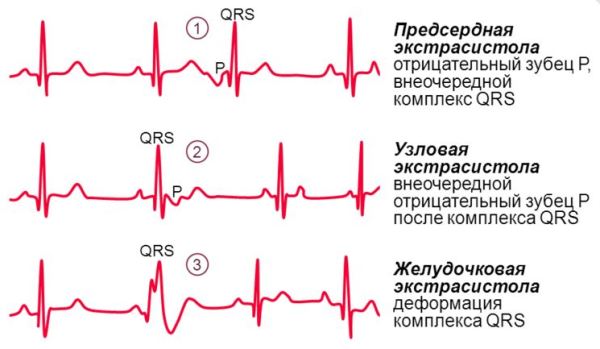
ECG signs of ventricular extrasystole:
- increased duration and deformation of the QRS complex;
- formation of an asymmetric T wave and displacement of the ST segment below or above the isoline;
- complete compensatory pause (may be absent if ventricular extrasystole develops against the background of atrial fibrillation).
ECG signs of atrial extrasystole:
- extraordinary appearance of the P wave, followed by a normal QRS complex;
- the ventricular complex does not change;
- the compensatory pause is incomplete.
In addition to the standard ECG, Holter monitoring can be used to diagnose extrasystole, when the patient carries a portable ECG device with him for a day.