Causes of extrasystole during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the cause of extrasystole may be the following:
- endocrine system disorders, hormonal imbalance (the level of production of T4 and TSH hormones is disrupted);
- the influence of certain groups of drugs;
- stressful situations;
- smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages;
- sedentary lifestyle, refusal of physical activity;
- high blood pressure that appears over a long period of time;
- heart surgery;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system - cardiomyopathy, valve disease, etc.
Description of the disease
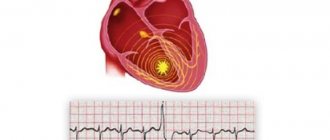
Extrasystoles are called extraordinary contractions of the myocardium that disrupt its normal beating rhythm. It is considered normal for a healthy person if up to 200 extrasystoles occur in the heart per day. During pregnancy, doctors say that a similar picture is observed in almost every case. This problem is typical for 50% of women, but it does not negatively affect the bearing of a child. However, if the threshold of 200 extraordinary contractions is exceeded or in the presence of heart pathology, the disease can be dangerous.
Complications
During pregnancy, frequent extrasystole threatens to progress to more serious types of arrhythmia; in the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, atrial fibrillation and heart failure can quickly develop. In severe cases, a woman experiences atrial flutter, and in this case immediate hospitalization is required.
If medical assistance is not provided on time, this can lead to death, since the pathological condition will provoke atrial fibrillation. Prolonged extrasystole can result in hypoxia, which negatively affects the fetus. In advanced situations, it even leads to the death of the child in the womb.
Extrasystole during pregnancy occurs in half of women, so you should not be afraid of such a diagnosis. Most often, the cause is hormonal imbalance, which is typical for the body of a pregnant woman. However, therapeutic measures must also be taken, since there are a number of unpleasant consequences and complications.
But if the reason lies in the presence of diseases, then measures must be taken urgently. What consequences and complications may arise in the absence of adequate treatment:
- the disease develops into ventricular tachycardia;
- further develops atrial fibrillation and flutter;
- circulatory disorders;
- lack of blood supply;
- hypoxia of heart tissue;
- hypoxia of the fetus and placenta.
In the absence of complications, labor is carried out naturally.
If there are consequences such as hypoxia, the doctor may prescribe an emergency delivery (before the scheduled time). There are no contraindications to carrying a pregnancy during extrasystole, unless it is a severe form against the background of defects and other pathologies of the heart. About 50% of pregnant women have rare extrasystoles without any manifestations. Childbirth is carried out naturally under the control of blood pressure and heart rate.
The danger of extrasystole is that it can develop into ventricular tachycardia and its complications in the form of atrial fibrillation and flutter. These are life-threatening conditions with circulatory disorders, dangerous for the mother and fetus. With frequent attacks of extrasystole, chronic circulatory failure can form, which will lead to tissue hypoxia, especially the tissues of the placenta and fetus. In such cases, the question of emergency delivery arises.
Forecast
Extrasystole during pregnancy is dangerous because it can develop into more complex forms of rhythm disturbance. The main danger is ventricular tachycardia or atrial fibrillation. Due to frequent irregular heartbeats, a pregnant woman may develop chronic circulatory failure, which causes oxygen starvation.
Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor in time to determine whether medication treatment is necessary. Do not forget about preventive measures and lifestyle changes during pregnancy.
It is worth noting that the prognosis is generally favorable, but only the attending physician can confirm this.
lechiserdce.ru
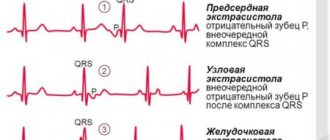
Classification of extrasystoles
In fact, extrasystoles during pregnancy are a fairly common phenomenon. According to statistics, almost half of women carrying a child are faced with one form or another of this disease. Therefore, today many expectant mothers are interested in questions about why this disorder appears and how dangerous it is.
Extrasystole is a disorder that is associated with the occurrence of an extraordinary electrical impulse. Moreover, it can appear in almost any part of the conduction system of the heart. Accordingly, such a violation leads to premature contractions of the heart muscle.
It is worth noting that extrasystoles during pregnancy can have different origins. For example, impulses may appear in the ventricular conduction system, in the atrioventricular node, or in the atria.
- Chlamydia in the blood during pregnancy
- Rapid heartbeat during pregnancy
- Ureaplasma urealiticum during pregnancy - how to treat?
- Causes of protein in urine
- Redness of the cervix
- Extrasystole with osteochondrosis
- Signs and causes of menstruation during pregnancy
The reasons for the development of extrasystole may be different. But quite often, such a disorder during pregnancy is the result of dramatic changes in a woman’s body, in particular hormonal changes and additional stress on the cardiovascular system.
On the other hand, extrasystole often manifests itself against the background of various diseases of the heart, vascular and endocrine systems (for example, patients with thyroid pathologies often suffer from extrasystole). Lung diseases may also be the cause.
As for the attacks themselves, they can be triggered by physical activity, nervous strain, stress, consumption of products containing caffeine, etc.
What do the symptoms of extrasystole look like? Most women note periodic interruptions in the functioning of the myocardium - they may feel sudden strong beats or, conversely, a sinking heart. Shortness of breath, chest pressure or pain in the heart area are much less common. Signs may also include weakness and dizziness.
Extrasystole is diagnosed quite easily. In most cases, such irregularities in heart rhythm do not pose a threat to the health of the woman or child. Most often, the presence of extrasystoles is not an obstacle to natural childbirth.
Treatment, of course, must be individualized, since the choice of therapy depends on many factors. Fortunately, most often women who develop this disease during pregnancy just need to create a calm and stress-free environment and adjust their diet. If extrasystoles are a consequence of heart disease, then the patient should remain under the supervision of a cardiologist throughout pregnancy.
- polytopic, that is, when there are several foci sending impulses;
- monotopic - one focus.
By localization they distinguish:
- Ventricular
- Atrial.
Also, extrasystoles can appear singly or follow each other several times.
Symptoms
Ventricular extrasystole usually, as it develops, begins to show signs noticeable to the woman, but most cases of the disease occur without clear expression. This is why pregnant women are diagnosed with pathology by chance during routine examinations. Signs of the disease are the following symptoms:
- feeling of fear or sudden anxiety;
- weakness;
- pain syndrome;
- dyspnea;
- feeling of heat during an attack, sweating;
- a feeling of interruptions in the rhythm of the heartbeat.
Diagnostics
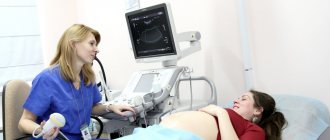
The main way to diagnose extrasystole during pregnancy is ECG monitoring. In other words – Holter monitoring. The examination can be carried out both in a public clinic and in any private one. The main thing is to have a referral from the treating specialist. The purpose of the research method is to obtain data on changes in the electrocardiogram of a pregnant woman throughout the day.
During diagnostic procedures, a special recording device, which is small in size (slightly larger than a mobile phone), is hung around the woman’s neck. This device is equipped with thin wires that are attached to the body in the chest area using stickers. The fixation points of the wires are determined by the doctor - they cannot be swapped.
A woman should walk with such a device for 24 hours. But the maximum monitoring period is three days. It is undesirable to take certain groups of medications and lead an overly active lifestyle during the examination. A pregnant woman should live at a normal daily rhythm. This is the only way to achieve the most accurate results.
Treatment
What can you do
The basis of treatment is a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits. You also need to give up stress and control emotions, spend a long time in the fresh air, and protect yourself from physical activity. It is important to eat properly so that your diet contains a lot of potassium - dried apricots, bananas, cereals, citrus fruits, persimmons. The use of sedative herbal mixtures with valerian, motherwort, lemon balm decoction, tea with honey is recommended.
What does a doctor do
Treatment of extrasystole in pregnant women is complex, the range of drugs to eliminate it is very limited. In rare cases, drugs against arrhythmia that have minimal effect on the fetus will be used under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital. Potassium supplements and beta blockers can also be used in minimally effective dosages only under the supervision of a doctor and blood pressure and pulse. Treatment is carried out only for severe arrhythmias of ventricular origin when ventricular complications develop.
In case of cardiac arrhythmia, the woman is referred to a cardiologist.
To date, there are no medications for the treatment of extrasystole that are safe for the body of a pregnant woman. That is why traditional therapy is used only in advanced forms of pathology. That is, in cases where the number of extrasystoles exceeds the norm excessively.
Medicines are also used in severe cases of the disease and the presence of serious complications. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor with constant diagnostic measures. As soon as improvements are noted, therapy is stopped. This will minimize the risk of complications from drugs for the fetus.
Drug therapy involves the use of the following drugs:
- Blocker drugs: Digoxin, Novocainamide, Verapamin.
- Beta blocker group: Metoprolol.
- Products based on potassium and vitamins.
- Diuretics.
When choosing a medication, the doctor takes into account all the risks for the fetus and the life of the mother, the characteristics of the course of the disease and the individual parameters of the body.
Extrasystole associated with physiological factors or overexertion is not considered dangerous, but in the future it can have a negative impact on the fetus. The main difficulty is that most drugs cannot be used during pregnancy.
Antiarrhythmic medications are selected only for those women whose risk of ventricular arrhythmia is significantly increased. Its severe forms even threaten the life of the patient. Drug treatment is prescribed only in this case. Ultrasound data helps identify the threat. If cardiac output drops to 40%, beta blockers will be prescribed.
Folk remedies
If the ventricle is rarely excited by an impulse, only as a result of stress or experiences, then it can be treated using traditional medicine.
- Mix honey and black radish juice in equal portions. Drink a spoonful daily before meals.
- Grind the valerian roots and boil them in 0.5 cups of water for about 15 minutes. After filtering, the dosage regimen is as follows: 1 tbsp. l. before a full meal.
- Brew a spoonful of lemon balm in a glass of water. It is better to replace your usual tea with such a drink, and you should drink it no more than 3 times a day.
Adviсe
What can a woman who suffers from extrasystole during pregnancy do?
- The first and most important thing is a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol, cigarettes, strong coffee - all this is an unnecessary burden, both on the hearts and on the entire body as a whole, so they must be excluded.
- Nerves. The expectant mother needs to learn to control herself and her emotions in order not to expose herself to unnecessary stress and not worry about trifles.
- Doctors also advise spending more time outdoors, so walking will not hurt pregnant women.
- Proper nutrition. It is recommended to eat foods that contain large amounts of potassium, namely persimmons, cereals, citrus fruits, dried apricots.
Extrasystole can be avoided during pregnancy. To do this, you need to follow simple rules that will help a woman feel much better.
To prevent heart rhythm disturbances and return your health to normal, doctors recommend following simple recommendations throughout pregnancy:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. For 9 months it is necessary to completely eliminate the consumption of alcohol, tobacco and coffee. All this puts a lot of stress on the heart, which can cause serious problems.
- Try to reduce stressful situations. Strong excitement disrupts the full functioning of the autonomic system, which stimulates the development of extrasystole. A woman needs to be less nervous and not get irritated over trifles.
- Spend a lot of time outdoors. This rule will help increase the overall tone of the body and make it more resistant to external irritants.
- Provide a varied and healthy diet. The diet should be rich in vitamins, potassium, calcium and other beneficial substances. It is important to completely avoid fast food.
- Do light exercise. Pregnant women should do exercises that were developed by specialists specifically for pregnant women. In case of heart rhythm disturbances, breathing exercises are useful.
These simple recommendations will help not only avoid the development of extrasystole, but also overcome the disease at the initial stage of development.
Folk remedies
During pregnancy, the best way to treat extrasystole is traditional medicine. This is due to the fact that many medications are simply contraindicated, while medicinal herbs and other components of natural origin do not cause harm, but have a comprehensive effect on the body.
The best traditional medicine recipes:
- Make a decoction from the root part of valerian. It can be bought at a pharmacy. Take 2 tbsp. l. product, pour a glass of boiling water and simmer over low heat for 15-20 minutes. To prevent the liquid from evaporating, use a lid. After the broth has cooled, strain it and drink 1 tbsp before each meal. l.
- Melissa or mint tea. For 0.5 liters of water you will need one and a half tablespoons of herbs. Pour boiling water over it and let it brew. Drink 100 ml before meals 3 times a day. Duration is 50-60 days.
- Buy black radish, peel it and rinse it. Pass through a meat grinder and squeeze out the juice. Combine it in equal proportions with natural honey and take a spoonful three times a day, always before meals.
- You can buy blue cornflower leaves at the pharmacy. Separate 1 teaspoon of herb and add a glass of boiling water. Let it sit until it cools completely. Take a tablespoon 20-30 minutes before meals.
- Take 3 lemons, wash and grind through a meat grinder along with the zest (remove the seeds). Add 10 cloves of peeled garlic, stir. Place the resulting mass in a 3-liter glass jar and fill with boiled warm water. Leave for 2-3 days. The daily norm is 100 ml. You can divide it into several steps.
- You can prepare a motherwort decoction in a water bath. For 200 ml of water you will need only 2 teaspoons of herb. This dosage is calculated per day. You need to drink in several doses before meals. The recommended course duration is 21 days.
- Use hawthorn and rose hips - prepare decoctions according to the standard recipe. You can drink an unlimited amount. The same healing tea can be prepared from thyme.
- Calendula is used as a tincture. To do this, brew the herb according to the recipe indicated on the package and take half a glass 3-4 times a day.
- Horsetail has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart. It is this medicinal plant that strengthens the heart muscles, the weakening of which leads to extrasystole. For 500 ml of boiling water you need to take a full tablespoon of herb. It is advisable to use a thermos for infusion. Leave for 3-4 hours, then strain. Drink a tablespoon 5-6 times a day.
- You can make a healing tincture from hawthorn. Take 10-15 grams of the fruits of the plant, pour 100 ml of high-quality vodka. Leave for 10-12 days in a dark place. Next, strain and take orally. Please note that the tincture is alcoholic, so the maximum dosage should be no more than 10 drops at a time. Take three times a day before meals.
Arrhythmias in pregnant women
It's no secret that the load on the heart increases during pregnancy. As a result, a restructuring occurs in a woman’s body, including changes in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, blood circulation and metabolism.
All of these processes can provoke the development of heart rhythm disturbances in the expectant mother, even in the absence of organic heart pathology.
How does the heart work?
The heart is the main organ of the cardiovascular system, performing the function of a pump and ensuring blood circulation. Thanks to the work of the heart, oxygen and nutrients are delivered to organs and tissues and released from metabolic products and carbon dioxide. The heart consists of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
Blood circulation occurs due to alternating contractions (systole) and relaxations (diastole) of the heart. During contraction, the heart pushes blood out of the left ventricle and moves it to the organs through the vessels, and from the right - into the pulmonary artery, where the blood is enriched with oxygen. When you relax, the “pump” is filled with a new portion of blood.
The heart works autonomously. It is capable of independently generating electrical impulses. The function of automaticity is possessed by the cells of the sinus node (SU), located in the wall of the right atrium, and the fibers of the conduction system of the heart.
Sinus impulses, spreading throughout the heart, ensure its rhythmic and coordinated contraction. If the sinus node ceases to produce the required number of impulses, it is replaced by the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is located on the border of the atria and ventricles.
You can feel your heart rate, or heartbeat, by placing your hand on your heart or taking your pulse.
Extrasystole
Extrasystole is the most common type of arrhythmia, which is based on premature contraction of the heart muscle (extrasystole), resulting from excitation of the myocardium.
Rare single extrasystoles can occur; in any healthy person, the heart can produce about 200 extraordinary contractions. A deviation from the norm is the presence of more than 200 extrasystoles per day.
This type of arrhythmias can be functional in nature, occurring against the background of complete health during stress, severe physical activity, smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea or coffee. Also, extrasystole can be a consequence of the following pathology:
— heart diseases (myocarditis, coronary heart disease, valve defects, cardiomyopathies, etc.);
- severe allergic reactions;
- poisoning;
- chronic renal failure.
Extrasystoles do not always cause any complaints. Most people do not feel discomfort and are unaware of this arrhythmia until it is accidentally detected on an ECG.
However, many patients tolerate extrasystole very difficult. They feel it in the form of a freezing or short-term cardiac arrest followed by a strong push to the chest.
Extrasystoles can be accompanied by both pain in the heart and various vegetative and neurological symptoms: pallor of the skin, anxiety, the appearance of fear, a feeling of lack of air, increased sweating.
In pregnant women, extrasystole is observed quite often. When it is detected, it is necessary to exclude the above pathology, which provokes extraordinary contractions of the heart. You should also limit the impact of those factors that lead to arrhythmia: drinking coffee, smoking, stress, etc.
Treatment of extrasystole in pregnant women is carried out only if there is a threat to her life. This can occur if an arrhythmia causes problems in the heart, and it stops pumping enough blood.
The presence of a threat to life is determined by the doctor based on ultrasound data, assessing the ejection fraction (EF), which reflects the state of the pumping function of the heart. EF is the proportion of blood pumped into the aorta of the total volume of blood in the left ventricle.
The critical value of this indicator is less than 40% (normally 60%). In this case, the patient is prescribed cardioselective β-blockers (bisoprolol). This therapy significantly reduces the occurrence of cardiovascular complications, primarily myocardial infarction, during potentially dangerous estrasystoles in expectant mothers.
Atrial fibrillation
The group of atrial fibrillation (AF) includes:
- atrial flutter - a significant increase in their contractions up to 200-350 per minute while maintaining the correct regular atrial rhythm;
— atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by frequent (from 350 to 700 beats per minute) chaotic excitation and contraction of groups of atrial muscle fibers throughout the entire cardiac cycle. This creates a “shimmering” effect in the heart tissue.
The main signs of MA are: interruptions in the functioning of the heart, a feeling of “bubbling” in the chest, shortness of breath, sweating, weakness, trembling, fear, darkening of the eyes, pre-syncope, fainting. Sometimes atrial fibrillation can be asymptomatic.
Depending on the nature and duration of attacks, MA is divided into:
- paroxysmal, in which attacks last from several seconds to several weeks;
- constant.
To identify atrial fibrillation and select therapy, a comprehensive examination is necessary, including daily ECG monitoring and ultrasound of the heart. It is also advisable to exclude diseases that lead to the occurrence of this type of arrhythmias: heart diseases (myocarditis, coronary heart disease, valve defects, cardiomyopathies, etc.); viral infections; thyrotoxicosis; poisoning, etc.
The presence of atrial fibrillation can lead to the formation of blood clots in the heart, which often cause strokes, pulmonary embolism (PE) and other life-threatening diseases. In this regard, restoration of sinus rhythm is an important task.
For this purpose, for atrial fibrillation in pregnant women, the following are used:
— electropulse therapy (EPT),
- novocainamide (administration rate no more than 30-50 mg per minute),
— radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with maximum protection of the fetus from radiation.
The choice of treatment method for arrhythmia depends on the form of the disease and the specific clinical situation.
Ventricular tachycardia
Persistent ventricular tachycardia (VT) is understood as an acceleration of the rhythm of ventricular contractions up to 150-200 per minute, persisting for more than 30 seconds.
Ventricular tachycardia usually occurs with certain heart diseases: myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathies, metabolic disorders, drug intoxication. Pregnancy can provoke VT in patients with a completely healthy heart. But, fortunately, this happens quite rarely.
VT begins and ends suddenly. In some patients, ventricular tachycardia is asymptomatic, while in others it causes fainting. Ventricular arrhythmias are the leading cause of sudden death. Therefore they deserve special attention. Diagnosis of this type of arrhythmia is based on characteristic ECG data.
To stop an attack, EIT, novocainamide and lidocaine are used. To prevent a recurrent attack in expectant mothers, the following are used: sotalol, amiodarone (for health reasons), a combination of amiodarone with β-blockers.
Among ventricular tachycardias, the so-called polymorphic ones are distinguished. They are the most difficult and always threaten the patient’s life. Such VT often manifests itself as a fainting state, which can be fatal. The diagnosis is established by ECG data during paroxysm.
To stop an attack of polymorphic VT in pregnant women, magnesia and lidocaine are used intravenously.
To prevent attacks of polymorphic VT, β-blockers are prescribed, and at any stage of pregnancy, a cardioverter-defibrillator is installed, which guarantees the restoration of normal heart rhythm within seconds after the onset of a life-threatening arrhythmia. It is fully automatic and is implanted under the skin.
Blockades of the conduction system of the heart
Blockades can occur at various levels of the cardiac conduction system. The so-called “upper” blockades that occur inside the atrium (sinoatrial and intraatrial) do not lead to hemodynamic disturbances and, therefore, do not cause any complaints. Therefore, “upper” conduction disorders in pregnant women do not need to be treated.
“Lower” blockades are formed at the level of the atrioventricular node and are divided into 3 degrees of severity. The most common cause of their occurrence is organic damage to the myocardium - a scar after a heart attack.
They can also be congenital and not manifest themselves in any way for the time being. The benefit of the “lower” blockade can occur during pregnancy, causing loss of consciousness in the expectant mother.
Treatment of lower blocks is carried out in the presence of fainting and pauses in heart rate lasting more than 3 seconds (2nd-3rd degree AV block). For the purpose of therapy, electric pacemakers are used, which are implanted under the skin and maintain the correct rhythm in the expectant mother. Installation is possible at any stage of pregnancy.
In other cases (1st degree AV block) in the absence of hemodynamic disturbances, treatment is not carried out.
General principles of treatment of arrhythmias in pregnant women
If any arrhythmia is detected in a pregnant woman, a comprehensive examination is necessary in order to diagnose diseases leading to the occurrence of such disorders: pathologies of the lungs, heart, thyroid gland, viral infections, etc.
You should also exclude the influence of those factors that can trigger the occurrence of arrhythmia: drinking coffee, smoking, stress, etc.
Antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed only if there are hemodynamic disturbances and a threat to the woman’s life:
— EF less than 40% according to cardiac ultrasound,
— polymorphic VT according to ECG results,
since there are no absolutely harmless and safe antiarrhythmics for pregnant women.
The safest groups of drugs used for arrhythmias in pregnant women include:
- antiarrhythmic drugs (sotalol, propafenone, quinidine, amiodarone);
- cardiac glycosides (digoxin);
- β-blockers (atenolol);
- anticonvulsants (diphenine).
The following antiarrhythmic drugs are not recommended during pregnancy:
Prevention measures
- Regular visits for routine inspections and strict implementation of all recommendations.
- Proper nutrition and maintaining optimal weight, without exceeding BMI.
- Taking vitamins, especially potassium and magnesium.
- Good sleep, rest, lack of stress.
- Daily walks.
During pregnancy, it is important to monitor your own condition, visit a doctor and take the necessary tests on time. It must be remembered that the life and health of the child depend entirely on the expectant mother.
To prevent extrasystole, you need to carefully monitor your condition, especially those prone to cardiac pathologies. It is also important to conduct a routine examination by a therapist with listening to the heart and a routine ECG. If there is a pre-existing arrhythmia, it is necessary to manage the pregnancy together with a cardiologist and take medications for prevention.
In order to prevent the development of extrasystole during pregnancy, adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, even in small doses. This not only harms the condition of the fetus, but also negatively affects the functionality of the heart muscles.
- Avoid stressful situations, learn to react to them more restrained and calm. If you cannot cope with this problem on your own, contact a psychologist.
- Spend more time outdoors by walking.
- Eat in accordance with the norms of proper and healthy nutrition.
- All citrus fruits, persimmons and dried apricots are very beneficial for the heart.
- Arterial hypertension in pregnant women
How to prevent the disease?
Despite the fact that many pregnant women do not notice the presence of extrasystole, there are patients who have a hard time tolerating this disease. They, unlike the first ones, may experience a feeling of “fading” of the heart, which cannot but frighten. Accordingly, fear and panic are mixed into this feeling, so it is advisable to prevent the occurrence of the disease by all means. To do this, you need to visit your doctor in a timely manner, follow all his recommendations and take prescribed medications strictly as prescribed.
In expectant mothers, extrasystole is observed quite often
Some women do not feel any signs of extrasystole throughout their entire pregnancy, but others have a hard time with this disease. They are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms for 9 months, which have a detrimental effect on the unborn child.
Important! In 95% of cases, no special measures are taken during childbirth. The whole process takes place naturally. Surgical delivery is recommended only if many dangerous extrasystoles appear.
Avoiding the pathological process and protecting the fetus from possible problems is the responsibility of every pregnant woman. To do this, you need to regularly visit the doctor, follow all his recommendations and take prescribed medications. This is the only way to achieve good results and give birth to a healthy child.