5 December 2020 Admin Home page » Ultrasound of the chest organs Views: 1854
Echocardiography is an important method for studying the heart, which has many branches. One of these is transesophageal echocardiography (also called transesophageal echocardiography), which is performed when classical techniques do not provide more complete information.
The difference from conventional echocardiography is that this method is uncomfortable (the patient has to swallow a sensor with an ultrasound detector), and therefore is performed in a hospital setting. And if it is normal for Echo CG to carry out research even every day and in a simple office with a device, then this method is used exclusively by professional personnel under the strict supervision of a cardiologist. Moreover, general anesthesia or at least local anesthesia is required.
What is transesophageal echocardiography?
If we move away from complex terms, we can say that this procedure is an ultrasound of the heart through the esophagus. During this procedure, a special camera is inserted into the patient's esophagus, which uses ultrasound to create a clear image of the organ.
According to the principle of the technique, it resembles an examination of the stomach using endoscopy.
This approach allows:
- avoid distortion due to other fabrics,
- get a comprehensive picture of the heart condition,
- diagnose complex heart diseases.
TEE provides complete information about the current state of the heart muscle.
Heart ultrasound indications
An ultrasound of the heart is necessary if the following symptoms are present:
- pain in the heart area,
- heart murmurs were detected,
- heart defects,
- high blood pressure,
- cardiopalmus,
- pathological heart sounds,
- fainting,
- dyspnea,
- swelling,
- bluishness of the skin,
- hypertension,
- weakness,
- loss of consciousness,
- increased body temperature without an identified cause,
- high blood pressure,
- bronchial asthma,
- Chronical bronchitis,
- acute pneumonia,
- rheumatism.
Using ECHO-CG, a number of pathological diseases in cardiology are diagnosed:
- heart failure,
- myocardial infarction,
- cardiac ischemia,
- valve pathology,
- endocarditis,
- myocarditis,
- cardiomyopathy,
- heart tumors,
- aneurysm of the heart and aorta.
Recommendations for the use of TEE
There are a number of indications and recommendations on the basis of which such a procedure is prescribed. First of all, it is worth understanding that the patient can refuse it at will. In this case, it is important to be aware of the consequences of such a decision:
- risk of obtaining a less accurate display,
- untimely detection of pathological changes,
- difficult diagnosis.
TEE is necessary if:
- serious heart disease is suspected,
- valve replacement is planned,
- the quality of other studies is unsatisfactory.
Some cardiac dysfunctions can be detected at an early stage only using this method. Thus, transesophageal echocardiography does an excellent job of identifying:
- aortic dissection,
- infective endocarditis,
- problems with the functioning of the prosthetic valve.
Important! Do not refuse to conduct research just because of discomfort! During the procedure, everything necessary is done to alleviate the patient’s condition, and the procedure itself takes no more than 15 minutes.
Refusal of the doctor’s recommendations can lead to untimely detection of cardiac muscle dysfunction.
The study can be carried out non-invasively and through the esophagus.
Non-invasive research
Allows you to identify changes in the heart that are not manifested by any painful sensations and are not detected during an ECG.
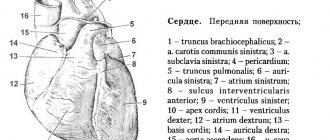
Using echocardiography, it is easy to determine the area of ischemia, myocardial pericarditis, aneurysms, hypertrophy of the heart chambers, damage to blood vessels and the valvular apparatus of the heart, assess the level of pressure in the pulmonary artery, identify intracardiac blood clots and heart tumors.
Ultrasound with assessment of myocardial deformation
Assessment of myocardial deformation using the Speckle-tracking technique is a recently emerged quantitative technique for accurately assessing myocardial function, systolic and diastolic dynamics of the left ventricle, allowing the assessment of global and regional myocardial function regardless of the angle and translational movements of the heart.
Application of the method is limited
with tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, extrasystole, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation.
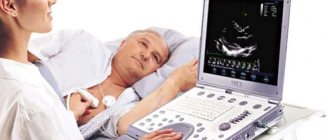
No preparation is required for echocardiography.
Transesophageal ECHO-CG
Transesophageal ECHO-CG
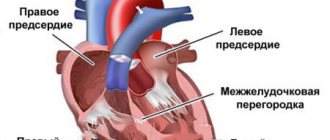
is a method of ultrasound diagnostics of the heart using a special sensor inserted through the esophagus. Allows you to improve the “ultrasound window” and allows for significantly better visualization of small structures of the heart.
TEE is used in cases where the resolution of transthoracic chocardiography does not allow making an accurate diagnosis, studying in detail the anatomy of various intracardiac structures and assessing intracardiac hemodynamics.
Main indications for TEE:
- diagnosis of intracardiac thrombosis (source of embolism);
- infective endocarditis;
- dissection (dissection) of the aorta, aortic aneurysm;
- diagnosis of mitral regurgitation and evaluation of valve prostheses.
Contraindications
Diseases of the esophagus: malignant neoplasms, esophageal diverticulum, fistulas, strictures, esophageal varices, inflammatory diseases of the esophagus, bleeding from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Complications
TEE is recognized as a safe diagnostic method. Serious complications occur in less than 1% of cases. Among the possible complications in the literature, in the form of isolated cases, injuries to the pharynx or trachea, bleeding from the veins of the esophagus, perforation of the esophagus, transient bacteremia, hemodynamic instability, and rhythm disturbances are listed.
How to prepare for TEE
A prerequisite for TEE is a 6-hour fast before the study. Removable dentures (if present) must be removed. You must have the results of an ECG, fibrogastroscopy (no more than one year), and ultrasound of the heart with you.
Transesophageal echocardiography: contraindications
Despite the popularity of this research method, there are a number of contraindications to such a procedure:
- diseases of the esophagus,
- difficult insertion of the endoscope,
- diseases of the pharynx or oral cavity.
Important! If the patient refuses in writing, this procedure cannot be prescribed by the doctor. It is strongly recommended not to reject an offer without reason.
The basis for refusing TEE may be any factor that poses a serious threat to the patient’s health. Despite the miniature size of the equipment, the delicate tissues of the esophagus are still slightly injured. This aspect is extremely undesirable for certain diseases.
With an increased gag reflex or inflammation in the oral cavity, the procedure is also difficult.
What are the benefits of TEE?
This technique has become widespread for a number of reasons, the main one being the high accuracy of displaying the current state of the heart muscle. Conventional cardiac echocardiography, like other research methods, does not always provide the required level of detail. The ultrasonic beam may encounter:
- bones,
- adipose tissue,
- other organs,
- various educations.
All this will lead to cloudiness of the picture and complicate diagnosis. Modern transesophageal echocardiography eliminates such problems, since the point from which the beam emanates is as close as possible to the target.
What is 3D ultrasound?
Thanks to the development of three-dimensional ultrasound, it is possible to obtain images of valves taken from all sides, optimize heart diagnostics, and carry out planimetric measurements. All this is most relevant for cardiac surgeons. The main advantage of such an ultrasound is the ability to obtain images of the valves, the entire perimeter of the fibrous ring, measure the diameters required by the doctor and assess the mobility of the valve.
Thus, transesophageal echocardiography is rightfully considered the most advanced and effective technique that allows a detailed examination of the patient’s condition and the necessary surgical interventions.
Carrying out TEE
Before the procedure, the patient must adhere to certain requirements. They are the same either way:
- do not eat food 8 hours before the appointed time,
- minimize the amount of drinking, do not drink 2 hours before the procedure,
- quit smoking, alcohol,
- stop taking medications not prescribed by your doctor.
Important! If you have diseases of the esophagus or oral cavity, inform your doctor! Otherwise, ultrasound diagnostics can be harmful to health.
Before starting, the doctor informs the patient about the diagnostic plan. Most often, only the throat is treated with an anesthetic - this is enough to reduce discomfort. However, in some cases, general anesthesia is also possible. Indications for placing a patient under this type of anesthesia may vary, but in the vast majority of cases it is the desire to obtain more accurate images.
In the first case, a special preparation in the form of a spray is sprayed onto the walls of the throat, thereby ensuring its insensitivity. In the second case, before administering the drug, the patient is examined for contraindications or allergic reactions.
Regardless of the choice, the patient is placed on his left side and asked to fix a special mouthpiece in his mouth. A special hose is inserted into the throat through it, and then into the esophagus. Due to the structure of the body, it is perpendicular to the heart, so the beam is directed to the sides and not directly. Transesophageal echocardiography itself provides three-dimensional projections of the heart muscle, information about its defects and dysfunction.
The procedure itself does not take much time - on average 15 minutes. During this period, a special beam examines all layers of the organ and gives doctors a comprehensive picture.
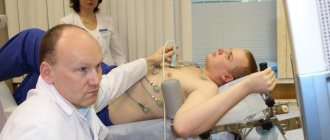
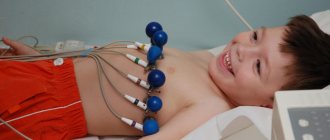
How is echocardiography performed?
Before the procedure, the patient undresses to the waist.
After this, the diagnostician applies a special acoustic gel to the chest area and places the patient on the couch in a reclining position on the left side. Next, the specialist installs the echocardiograph sensors in several positions. This position is most comfortable for the patient. In addition, it is necessary for accurate diagnosis, since the heart, which is located at the anterolateral chest wall, is in this place least covered by lung tissue. When a person lies on his left side, the acoustic window expands, so ultrasonic sensors pick up any vibrations and noise of the organ structures. The echocardiograph does its job within 15 minutes. It processes and synchronizes data received from sensors via an electrocardiographic channel. At this time, the patient can relax, as the procedure is painless and does not cause discomfort.
Recommendations after the procedure
No matter how gentle transesophageal echocardiography is and no matter how precautions it is performed, the walls of the esophagus will still receive some damage. When carried out correctly, they are not serious and do not pose any danger, however, they impose some restrictions on the patient’s behavior after the procedure:
- You can’t eat anything for 2 hours,
- liquid and food should be at room temperature,
- It is recommended to give up tea and coffee.
The duration of this regimen is determined by the doctor, but on average it lasts no longer than 3-4 days until minor damage to the mucous membrane is restored.
Important! You can’t eat immediately after surgery! The effect of the anesthetic may negatively affect swallowing function; normal swallowing reflexes are not immediately restored. All this can lead to the patient choking while eating or triggering a gag reflex.
How to prepare for the procedure
Transesophageal ultrasound of the heart is prescribed after passing mandatory general blood and urine tests, and a biochemical blood test. It is also mandatory to undergo a preliminary ECG and a routine ultrasound of the heart. The last meal should be no later than 6 hours before the procedure, fluid intake should be at least 2 hours. If the patient is taking any medications, there is no need to stop them before the study. If the patient has dentures, they must be removed before the procedure.
If there is a possible need to perform an emergency ECHO CG under general anesthesia, it is imperative to warn the doctor about possible allergic reactions to medications. During the study, it is possible to administer medications that affect concentration. Therefore, it is not recommended for the patient to drive a car for the next 12 hours after the transesophageal echocardiography procedure.
What is required for the procedure?
In addition to the endoscope, from the tip of which an ultrasonic beam emanates, other equipment is used:
- mouthpiece,
- apparatus for pumping saliva,
- resuscitation kit,
- medications (anesthetics).
All this can only be achieved in a treatment room, so conducting the study at home is excluded.
To ensure the safety of the patient, he is required to undergo an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in advance. If such a procedure is not possible, an X-ray with contrast of the esophagus is performed. All this makes it possible to identify problems with the esophagus even before the introduction of an endoscope.