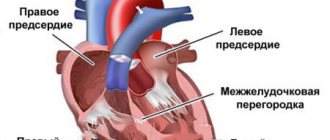
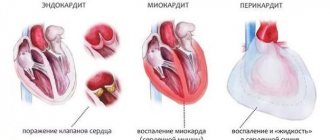
Electrocardiography is one of the most necessary, universal, accessible and in demand diagnostic methods, including in pediatric practice. Every medical worker, especially in emergency situations, needs to be fluent in the ECG analysis method.
Decoding an ECG in children has its own characteristics. But before you start studying them, you need to understand how a cardiograph works and what is the mechanism for the occurrence of parameters recorded on paper?
Interpretation of ECG results in a child: norms of indicators and causes of violations
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a fast and high-quality way to obtain information about the functioning of the heart. Often, such an examination is prescribed to children to identify a particular heart disease. It has some differences from the ECG of an adult. Parents of babies should know what this procedure is, how to properly prepare their child for it, and how the cardiogram results are interpreted.
An ECG of the heart will help identify arrhythmias and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system
What you can find out
A cardiogram can indicate the presence of a heart defect and a number of other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Based on the results of an ECG, the presence of the following health problems can be determined:
- lack of potassium, magnesium, calcium and other electrolytes;
- hypertrophy of the heart and its parts;
- pulmonary embolism;
- myocarditis;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart defect, congenital or acquired;
- metabolic disorders in the heart;
- tachycardia;
- blockade of the heart muscle;
- arrhythmia;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- heart power.
Shows whether the result meets the age norm.
In what cases is an ECG prescribed for a child?
The pediatrician prescribes an ECG for children in certain cases. These include:
- heart murmurs (we recommend reading: how are heart murmurs treated in a 3-year-old child?);
- dizziness;
- headaches and fainting;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in the chest area;
- swelling of the limbs;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- preparation for surgery;
- hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular pathologies;
- high pressure;
- endocrine system disorders;
- slow physical development.
Children are also given an ECG before being discharged from the maternity hospital to exclude heart defects and during a routine medical examination before entering kindergarten or school. A cardiac examination is also indicated before starting sports.
Features of the child’s body that should be taken into account during an ECG
The work of the heart in young children has its own characteristics. Compared to the heartbeat of adults, it is much faster in babies. For clarity, below is a table of normal heart rate indicators depending on a person’s age:
ECG readings in newborns, infants, and adolescents often differ from normal values. When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the deviations acceptable for each age group. Also, during the procedure, some features of the child’s body are taken into account:
- in infants the right ventricle often predominates, which is not a pathology; this discrepancy disappears with age;
- the younger the child, the shorter the cardiogram intervals;
- the size of the atrium in children is larger than in adults;
- the T wave on the graph of electrical signals from the heart muscle has a negative value;
- rhythm sources migrate within the atria;
- alternans of teeth on the ventricular complex;
- the likelihood of incomplete blockade on the right bundle branch;
- respiratory and sinus arrhythmia;
- possible occurrence of a deep Q wave in the 3rd standard lead.
Adviсe
The main thing is that your baby is absolutely calm at the time of the ECG.
There have been cases where indicators were inaccurate due to non-compliance with certain rules. Therefore, you need to know how to behave.
- The child should not be cold. Even a slight tremor can affect the cardiogram readings.
- It is recommended to feed the baby two hours before the procedure.
- It is very important that the child does not worry and is able to breathe smoothly. Anxiety, at a minimum, can affect a rapid pulse, which will allow one to suspect tachycardia without its presence.
- If the baby has severe shortness of breath, then he should not have a cardiogram while lying down. For such a patient, the procedure is performed while sitting.
- An hour before the ECG, be sure to exclude strong emotions and active games.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Folliculometry on which days of the cycle to do it
Remember that an electrocardiogram is an informative diagnostic method and does not cause any harm to the child’s health, and is also painless. Therefore, you should not be afraid, if a specialist directs you to this study, you can safely go there. Even if any abnormalities are detected, it is better to find out about them earlier and begin appropriate treatment in a timely manner.
The procedure for children
Before an ECG, children should not have anxiety or fear of the doctor and the device. It is recommended to bring infants to the procedure after feeding or during sleep. For an older child, parents should explain on the eve of the examination how it is carried out and convince them that the child will not experience any painful sensations. Before conducting an ECG, you should choose clothes for your child that make it easy to undress.
An hour before the procedure, children over 1 year of age must be provided with complete rest. Active games and emotional stress are prohibited; the baby should get a good night's sleep. The last meal should be one and a half hours before the test.
An ECG for a one-year-old baby uses special electrical conductors that are attached to the skin. Small patients can wear a belt with fixed sensors. After the electrodes are attached to the body, the baby’s movements are limited by tight swaddling; parents should convince older children not to talk or move during the procedure.
The doctor will receive reliable information by registering at least 10-15 contractions and relaxations of the heart muscles; in some cases, a larger number may be needed. During and after the procedure, the child feels well, it is completely painless and lasts no more than 15 minutes. When conducting an ECG, it is necessary that one of the parents be next to the small patient.
If the child is over 3 years old, an ECG is performed with stress to obtain more reliable data. First, indicators of the work of the heart muscle are taken from the baby in a calm state, then after active physical activity. Examination of the heart under stress is indicated to identify disturbances in its rhythm and conduction. An ECG with stress has contraindications, so the doctor analyzes data on the diseases of the little patient before prescribing it.
The video above shows how electrocardiography is performed on children. You can watch it with your child so that he can be convinced that the procedure is not at all scary and the doctor will not cause him pain.
Description of the essence of the technique for performing an ECG under stress
ECG with stress is an effective method for diagnosing the resistance of the cardiovascular system to physical stress.
Carrying out an ECG under stress allows you to detect hidden problems that only appear when the whole body is actively working, which includes the cardiovascular system.
In fact, this method is designed to artificially provoke a heart attack in a controlled situation, which makes it possible to see deviations from the norm and record a number of important parameters that will help understand the causes of the pathology.
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Functional tests. Functional tests have several options and represent a simple method for determining the disease under stress. They do not require special equipment except an electrocardiograph and a stopwatch. Most often, the patient is asked to perform 20 squats, run in place, or take several dozen steps on a step platform. Such tests are often used for children during medical examinations, as well as to determine the health group for physical education at school.
- Treadmill. Treadmill is an analogue of bicycle ergometry of American origin. It differs from it by using a treadmill rather than a bicycle ergometer, so it can also be used for children, as it gives more correct results for them than VEM. In addition, for a child the meaning of such a test is much clearer, and execution is easier than on a bicycle ergometer, where it may be difficult for him to reach the pedals and steering wheel. On a treadmill, such difficulties do not arise, and even a very small child can run in place. To conduct the test, data is recorded both while driving along the track and immediately after it. At certain intervals, the angle of inclination of the path is increased, simulating the ascent of a pedestrian uphill, which creates additional stress on the heart and contributes to the emergence of a clear picture of the pathology.
- Holter monitoring. Holter is a special device that records heart rhythms throughout the day. The patient records everything he does during the day in a special diary, and then the ECG data is compared with these records. This allows you to get a complete picture of the state of the cardiovascular system. Holter is often used to obtain data from people with weak hearts before various surgical interventions that are not necessarily related to the activity of the cardiovascular system. Such data helps to correctly select the optimal dose of anesthesia.
- Bicycle ergometry. But the most informative and accessible method for diagnosing heart disease remains bicycle ergometry. It is performed according to certain rules on a special device - a bicycle ergometer. It is an exercise bike connected to a special powerful computer. All data that comes from sensors placed on the patient’s body is transferred to this computer, recorded and recorded by it for further assessment of the data by a specialist. Carrying out bicycle ergometry is not only very informative, but also relatively simple for the patient. In case of poor health, the process can be instantly interrupted, and the patient is provided with prompt medical assistance by medical personnel who are constantly present nearby.
Almost every person has had to undergo a procedure called electrocardiography (ECG) at least once. It is a registration of electrical impulses (currents) during contraction of the heart muscle. A special device, an electrocardiograph, allows you to record data and display it on a graph. The resulting result looks like a complex curved line. The doctor usually deciphers the obtained values.
A fairly simple method for diagnosing heart disease allows you to get accurate results. An electrocardiogram is one of the cheapest and most accessible methods. Another advantage is the absence of violations of the integrity of the skin.
Norms and interpretation of indicators for children of different ages
The diagnosis is made taking into account indicators such as teeth, segments and intervals. Their presence or absence, height, location, duration, sequence and direction are taken into account.
Heart problems are identified by analyzing the following data:
- Sinus rhythm. This is the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle under the influence of the sinus node. This indicator allows you to evaluate the nature of contractions of the ventricles and atria.
- Heart rate.
- Source of excitation. It is determined by examining the P wave.
- Cardiac conduction.
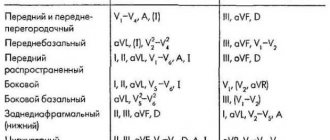
- Electric axis. In leads 1 and 3, the Q, R and S waves are analyzed, which makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of the His bundle.
Only an experienced specialist should interpret the results of the electrocardiogram.
The interpretation of the ECG results is carried out by a competent cardiologist who knows the specifics of the functioning of the heart of each age group. On the cardiogram, the processes occurring in the heart muscle are indicated by capital letters of the Latin alphabet - P, Q, R, S, T. Each designation on the diagram indicates certain processes:
- ventricular relaxation - T;
- contraction and relaxation of the atria - P;
- excitation of the septum between the ventricles - Q, S;
- ventricular excitation - R;
- duration of passage of an electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles - PQ;
- relaxation of the heart muscle in the interval between contractions - TP;
- peak excitation of the ventricle - ST;
- the duration of its contraction is QRST.
The psycho-emotional state of a child can negatively affect the accuracy of ECG readings.
ECG results can be affected by factors such as the time of day, the psycho-emotional state of a small patient, food intake, incorrect application or displacement of electrodes, and interference from operating foreign devices. The following indicators are normal for a child:
- for QRS – 0.06–0.1 s;
- for P - ≤ 0.1 s;
- for PQ – 0.2 s;
- for QT - ≤ 0.4 s.
ECG results often indicate a poor cardiogram with deviations from the norm. In this case, if necessary, the child is prescribed an additional examination, and then the optimal treatment method is selected.
Possible causes of rhythm disturbances and other parameters
Electrocardiography in children often reveals heart rhythm disturbances. The causes of disorders are divided into cardiac and extracardiac. The first type of factors provoking arrhythmia include:
- birth defects;
- autoimmune and other pathologies of the heart;
- heart tumors and injuries;
- severe infectious diseases;
- anomaly of organ development;
- carrying out probing and contrast X-ray examination of blood vessels.
An ECG allows timely detection of heart rhythm disturbances.
Extracardiac causes of arrhythmia are pathologies of the nervous and endocrine systems, blood diseases, and premature birth. Intense exercise also makes the heart rhythm irregular. Along with this, high air temperature, emotional stress and the simultaneous course of heart disease and failure of the neurohumoral regulation of the heart can provoke arrhythmia.
Electrocardiography often records tachycardia (we recommend reading: how does sinus tachycardia manifest itself in children on an ECG?). The cardiac causes of the disease are similar to the factors that provoke the development of arrhythmia. Extracardiac sources of the disease include:
- acidosis;
- low blood sugar levels and disturbances in its electrolyte composition (we recommend reading: what is the normal blood sugar level for a 12-year-old child?);
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- tonsillitis and conditions arising after a sore throat;
- neurotoxicosis;
- intoxication syndrome with elevated temperature;
- side effects of a number of medications.
In accordance with the ECG results, the pediatric cardiologist prescribes the necessary treatment.
An ECG can detect bradycardia. Among the most common causes of the disease are:
- disruption of the nervous and endocrine systems;
- high intracranial pressure;
- diagnosis of hypoxia at birth and a tendency to bradycardia during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases;
- severe hypothermia;
- large dosages of potent medications or their prolonged use;
- rapid growth of internal organs;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland.
Often, a child’s heart rate deviates from the norm after a strong fright, holding his breath for a long time and under the influence of vivid emotions and events experienced during the day. These phenomena are temporary and do not indicate pathology.
Source: vseprorebenka.ru
How to do an ECG with stress: preparation for the study
To get a reliable result, you need to properly prepare for an ECG with stress. Before the test, you should avoid emotional and physical stress and stop drinking alcoholic beverages. For several days, you should avoid taking medications that affect the functioning of the heart muscle. Heavy foods can have a negative impact on the test result.
An ECG test with exercise requires preliminary preparation, during which the patient should refrain from eating and drinking for several hours before the test. However, the use of clean, still water is not prohibited. In addition, medications that can affect the test and its results should also be excluded from the daily diet.
It is also important to consider here that a stress ECG will show incorrect results if the patient is affected by the following factors:
- High ambient temperature, high humidity;
- Stress or nervous tension;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Drinking alcohol, caffeine, and smoking before the procedure.
Medical professionals give recommendations regarding clothing before the procedure. Since stress ECG in Moscow is measured during physical exercise on an exercise bike, clothing should be appropriate: comfortable and not restricting movement.
Before the procedure, men should depilate the areas in which the electrodes will be located. Usually it is enough to shave the chest.
Interpretation of ECG results in a child: norms of indicators and causes of violations
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a fast and high-quality way to obtain information about the functioning of the heart. Often, such an examination is prescribed to children to identify a particular heart disease. It has some differences from the ECG of an adult. Parents of babies should know what this procedure is, how to properly prepare their child for it, and how the cardiogram results are interpreted.
An ECG of the heart will help identify arrhythmias and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system
In what cases is an ECG prescribed for a child?
The pediatrician prescribes an ECG for children in certain cases. These include:
- heart murmurs (we recommend reading: how are heart murmurs treated in a 3-year-old child?);
- dizziness;
- headaches and fainting;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in the chest area;
- swelling of the limbs;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- preparation for surgery;
- hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular pathologies;
- high pressure;
- endocrine system disorders;
- slow physical development.
Children are also given an ECG before being discharged from the maternity hospital to exclude heart defects and during a routine medical examination before entering kindergarten or school. A cardiac examination is also indicated before starting sports.
Features of the child’s body that should be taken into account during an ECG
The work of the heart in young children has its own characteristics. Compared to the heartbeat of adults, it is much faster in babies. For clarity, below is a table of normal heart rate indicators depending on a person’s age:
ECG readings in newborns, infants, and adolescents often differ from normal values. When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the deviations acceptable for each age group. Also, during the procedure, some features of the child’s body are taken into account:
- in infants the right ventricle often predominates, which is not a pathology; this discrepancy disappears with age;
- the younger the child, the shorter the cardiogram intervals;
- the size of the atrium in children is larger than in adults;
- the T wave on the graph of electrical signals from the heart muscle has a negative value;
- rhythm sources migrate within the atria;
- alternans of teeth on the ventricular complex;
- the likelihood of incomplete blockade on the right bundle branch;
- respiratory and sinus arrhythmia;
- possible occurrence of a deep Q wave in the 3rd standard lead.
The procedure for children
Before an ECG, children should not have anxiety or fear of the doctor and the device. It is recommended to bring infants to the procedure after feeding or during sleep. For an older child, parents should explain on the eve of the examination how it is carried out and convince them that the child will not experience any painful sensations. Before conducting an ECG, you should choose clothes for your child that make it easy to undress.
An hour before the procedure, children over 1 year of age must be provided with complete rest. Active games and emotional stress are prohibited; the baby should get a good night's sleep. The last meal should be one and a half hours before the test.
An ECG for a one-year-old baby uses special electrical conductors that are attached to the skin. Small patients can wear a belt with fixed sensors. After the electrodes are attached to the body, the baby’s movements are limited by tight swaddling; parents should convince older children not to talk or move during the procedure.
The doctor will receive reliable information by registering at least 10-15 contractions and relaxations of the heart muscles; in some cases, a larger number may be needed. During and after the procedure, the child feels well, it is completely painless and lasts no more than 15 minutes. When conducting an ECG, it is necessary that one of the parents be next to the small patient.
If the child is over 3 years old, an ECG is performed with stress to obtain more reliable data. First, indicators of the work of the heart muscle are taken from the baby in a calm state, then after active physical activity. Examination of the heart under stress is indicated to identify disturbances in its rhythm and conduction. An ECG with stress has contraindications, so the doctor analyzes data on the diseases of the little patient before prescribing it.
The video above shows how electrocardiography is performed on children. You can watch it with your child so that he can be convinced that the procedure is not at all scary and the doctor will not cause him pain.
Description of the essence of the technique for performing an ECG under stress
There are several ways to perform stress electrocardiography. One of the common methods is functional tests. No special devices are used, other than a stopwatch and a cardiograph. The patient is asked to perform simple exercises. This could be squats or steps on a step platform.
Bicycle ergometry is considered one of the most informative methods for diagnosing the performance of the heart muscle. To carry it out, an exercise bike is used, equipped with special sensors and a powerful computer. When performing an ECG with physical activity, all data will be transferred to a computer for recording and analysis.
The treadmill test has a similar diagnostic technique, only a treadmill is used for physical activity. If the patient begins to feel unwell, the diagnosis will be completed and the necessary medical care will be provided.
Norms and interpretation of indicators for children of different ages
The diagnosis is made taking into account indicators such as teeth, segments and intervals. Their presence or absence, height, location, duration, sequence and direction are taken into account.
Heart problems are identified by analyzing the following data:
- Sinus rhythm. This is the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle under the influence of the sinus node. This indicator allows you to evaluate the nature of contractions of the ventricles and atria.
- Heart rate.
- Source of excitation. It is determined by examining the P wave.
- Cardiac conduction.
- Electric axis. In leads 1 and 3, the Q, R and S waves are analyzed, which makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of the His bundle.
Only an experienced specialist should interpret the results of the electrocardiogram.
The interpretation of the ECG results is carried out by a competent cardiologist who knows the specifics of the functioning of the heart of each age group. On the cardiogram, the processes occurring in the heart muscle are indicated by capital letters of the Latin alphabet - P, Q, R, S, T. Each designation on the diagram indicates certain processes:
- ventricular relaxation - T;
- contraction and relaxation of the atria - P;
- excitation of the septum between the ventricles - Q, S;
- ventricular excitation - R;
- duration of passage of an electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles - PQ;
- relaxation of the heart muscle in the interval between contractions - TP;
- peak excitation of the ventricle - ST;
- the duration of its contraction is QRST.
The psycho-emotional state of a child can negatively affect the accuracy of ECG readings.
ECG results can be affected by factors such as the time of day, the psycho-emotional state of a small patient, food intake, incorrect application or displacement of electrodes, and interference from operating foreign devices. The following indicators are normal for a child:
- for QRS – 0.06–0.1 s;
- for P - ≤ 0.1 s;
- for PQ – 0.2 s;
- for QT - ≤ 0.4 s.
ECG results often indicate a poor cardiogram with deviations from the norm. In this case, if necessary, the child is prescribed an additional examination, and then the optimal treatment method is selected.
We correctly decipher the results
When deciphering the results of a stress ECG, normal indicators include:
- ECG with stress: normal – regular rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle, heart rate in the range of 60-140 beats per minute;
- ECG after exercise: normal - a smooth decrease in the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle and heart rate by 12-15 beats.
An ECG under stress allows you to evaluate more than 10 indicators indicating the presence or absence of problems in the functioning of the heart muscle. The overall result of the study with a comprehensive transcript can be obtained 1-2 days after the procedure. Only an experienced cardiologist can interpret the results.
An ECG with stress allows you to obtain the most reliable information about the condition of the heart muscle and blood vessels. The conclusion contains the following indicators:
- Work performed by the patient (J).
- Threshold power (W).
- Reasons for early termination of the study.
- Conclusion about performance.
- Dynamics of pulse and blood pressure.
- The time it took for heart rate and blood pressure to normalize.
- The value of blood pressure at the peak of physical activity.
- Heart rhythm disturbances (normally there should not be one).
- Coronary disorders (detailed description of the type of disorder, time of its occurrence).
- IHD class depending on the level of physical activity at which the deviations appeared.
Only a specialist is responsible for interpreting the results of a stress ECG. The norm of indicators differs depending on the age and gender of the patient. The slightest deviations from generally accepted norms do not indicate the presence of a pathological condition. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated after some time.
Excessive anxiety, especially in children, can distort ECG results in the first place. In infants this is crying. All this will cause tachycardia, which the doctor will need to differentiate from the pathological condition.
Also, the ECG can be affected by the cold room where the examination is performed.
Tea, coffee, smoking can also give a false picture of electrocardiography.
Before any heart examination, you must tell the doctor what medications you are taking, especially cardiac medications. It is also advisable, if possible, not to take pills at least two hours before the examination.