© Author: Ilya Vitalievich Soldatenkov, general practitioner, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Leukoencephalopathy is a chronic progressive pathology caused by the destruction of the white matter of the brain and leading to senile dementia or dementia. The disease has several equivalent names: Binswanger encephalopathy or Binswanger disease. The author first described the pathology in 1894 and gave it his name. Along with vascular leukoencephalopathy, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), a disease of viral etiology, has become widespread in recent years.
The death of nerve cells caused by impaired blood supply and hypoxia of the brain leads to the development of microangiopathy. Leukoaraiosis and lacunar infarctions change the density of white matter and indicate problems with blood circulation in the body.
The clinical picture of leukoencephalopathy depends on the severity and is manifested by various symptoms. Typically, signs of subcortical and frontal dysfunction are combined with seizures. The course of the pathology is chronic, characterized by frequent alternations between periods of stabilization and exacerbation. Leukoencephalopathy occurs mainly in older people. The prognosis of the disease is unfavorable: severe disability quickly develops.
What is cerebral leukoencephalopathy
The general term refers to a disease that causes damage to the white matter of the brain. The lesions grow due to disruption of blood circulation through the vessels and infection of the patient with a virus. According to WHO, we can conclude that a hereditary factor is involved in the progress of leukoencephalopathy, that is, a modified gene is present.
The disease provokes the development of severe consequences: dementia progresses, visual acuity decreases or complete loss of vision is observed, and convulsive seizures are possible. The main danger is that leukoencephalopathy cannot be treated with medication or surgery. Therapy is palliative in nature, aimed at supporting the patient’s well-being and prolonging the quality of life.
Drug therapy for leukoencephalopathy
Leukoencephalopathy is a pathology that is incurable. The goal of drug treatment is to stop the progression of the disease and extend the patient several years of life.
This pathology must be treated comprehensively with the use of medications, as well as:
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Manual therapy;
- Treatment with phytomedicines;
- Acupuncture.
Drug therapy is selected according to an individual scheme by the treating doctor:
General measures are:
- Healthy lifestyle;
- Timely treatment of all pathologies of the vascular system;
- Culture of nutrition and cessation of bad habits;
- Adequate stress on the body;
- Engage in the prevention and treatment of pathologies that have become provocateurs of leukoencephalopathy.
This pathology is incurable and the prognosis for life depends on timely diagnosis and progression of the disease.
With minimal or incorrect treatment, the disease progresses faster - the prognosis is unfavorable, no more than 6 calendar months.
When carrying out drug therapy for viruses, life expectancy increases by 12 - 18 calendar months.
Leukoencephalopathy of the brain is a pathology in which there is damage to the white matter, causing dementia. There are several nosological forms caused by various reasons. What they have in common is the presence of leukoencephalopathy.
The disease can be provoked by:
- viruses;
- vascular pathologies;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
Other names for the disease: encephalopathy, Binswanger disease. The pathology was first described at the end of the 19th century by the German psychiatrist Otto Binswanger, who named it after himself. From this article you will find out what it is, what are the causes of the disease, how it manifests itself, is diagnosed and treated.
Causes of leukoencephalopathy
The cause of the development of the disease may be acquired or congenital immunodeficiency or damage to the body by polyomaviruses.
The list of factors that provoke the appearance of the disease can be presented as follows:
- AIDS virus;
- AIDS;
- malignant oncological processes of the blood;
- arterial hypertension;
- long-term use of immunosuppressants;
- previous organ transplants;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- tuberculosis;
- lung lesions;
- oncological processes of malignant genesis in the body.
Attention! Leukoencephalopathy of the brain is an incurable process, regardless of the form of the disease or the reasons for its development.
Types of leukoencephalopathy
Medicine distinguishes the following types of disease:
- Finely focal. The condition is considered as a chronic process in which the systematic destruction of all brain cells occurs. Patients over 60 years of age are at risk. The main reason is hereditary predisposition. Often detected in individuals with chronic arterial hypertension. At an early stage, symptoms of senile dementia can be traced, which then lead to the death of the patient.
- Progressive multifocal form. Leukoencephalopathy of this type is of viral origin, characterized by an acute onset and rapid progress. Against the background of a decrease in immune parameters, a liquefaction of the white matter is observed, and irreversible processes are launched. The death of the patient is inevitable.
- Periventricular nonspecific. Brain damage occurs against the background of ischemia. Most often, the process covers the pillar. The cause of development is prolonged hypoxia of cells and blood vessels of the brain. The first sign of the disease is movement disorders. In children, leukoencephalopathy of this type causes cerebral palsy, often the disease progresses as a result of a birth injury.
Classification
There are several types of leukoencephalopathy.
Finely focal
This is leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin, which is a chronic pathology that develops against the background of high blood pressure. Other names: progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy, subcortical atherosclerotic encephalopathy.
Discirculatory encephalopathy—slowly progressive diffuse damage to cerebral vessels—has the same clinical manifestations as small-focal leukoencephalopathy. Previously, this disease was included in ICD-10, but now it is not there.
Most often, small focal leukoencephalopathy is diagnosed in men over 55 years of age who have a genetic predisposition to the development of this disease.
The risk group includes patients suffering from pathologies such as:
- atherosclerosis (cholesterol plaques clog the lumen of blood vessels, resulting in impaired blood supply to the brain);
- diabetes mellitus (with this pathology the blood thickens and its flow slows down);
- congenital and acquired pathologies of the spine, in which there is a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain;
- obesity;
- alcoholism;
- nicotine addiction.
Errors in diet and a sedentary lifestyle also lead to the development of pathology.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
This is the most dangerous form of the disease, which often causes death. The pathology is viral in nature.
Its causative agent is human polyomavirus 2. This virus is observed in 80% of the human population, but the disease develops in patients with primary and secondary immunodeficiency. When viruses enter their body, they further weaken the immune system.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is diagnosed in 5% of HIV-positive patients and in half of AIDS patients. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy used to be even more common, but thanks to HAART, the prevalence of this form has decreased. The clinical picture of the pathology is polymorphic
.
The disease is manifested by symptoms such as:
- peripheral paresis and paralysis;
- unilateral hemianopsia;
- stunned consciousness syndrome;
- personality defect;
- lesion of the cranial nerve;
- extrapyramidal syndromes.
CNS disorders can vary widely from mild dysfunction to severe dementia. Speech disturbances and complete loss of vision may occur. Often, patients develop severe disorders of the musculoskeletal system, which cause loss of performance and disability.
The risk group includes the following categories of citizens:
- patients with HIV and AIDS;
- receiving treatment with monoclonal antibodies (they are prescribed for autoimmune diseases, cancer);
- those who have undergone internal organ transplantation and are taking immunosuppressants to prevent organ rejection;
- suffering from malignant granuloma.
Periventricular (focal) form
Develops as a result of chronic oxygen starvation and impaired blood supply to the brain. Ischemic areas are located not only in the white matter, but also in the gray matter.
Typically, pathological foci are localized in the cerebellum, brain stem and frontal cortex of the cerebral hemispheres. All these brain structures are responsible for movement, therefore, with the development of this form of pathology, movement disorders are observed.
This form of leukoencephalopathy develops in children who have pathologies accompanied by hypoxia during delivery and within a few days after birth. This pathology is also called “periventricular leukomalacia”; as a rule, it provokes cerebral palsy.
Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter
It is diagnosed in children. The first symptoms of the pathology are observed in patients aged 2 to 6 years. It appears due to a gene mutation.
Patients note:
- impaired coordination of movement associated with damage to the cerebellum;
- paresis of arms and legs;
- memory impairment, decreased mental performance and other cognitive impairments;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- epileptic seizures.
Children under one year old have problems with feeding, vomiting, high fever, mental retardation, excessive excitability, increased muscle tone in the arms and legs, convulsions, sleep apnea, coma.
How long do people live with leukoencephalopathy - prognosis
It is currently impossible to recover from leukoncephalopathy of vascular origin. The goal of drug treatment is to maintain the patient’s quality of life and prolong it. The prognosis is not favorable; only 40% of patients diagnosed will survive more than 6 months from the time of diagnosis.
Results can be achieved by resorting to antiretoviral therapy when lesions of the brain structure are first detected. In this case, the life expectancy of the victim will increase to 1-2 years. It is not possible to avoid the symptoms of dementia.
Attention ! In the acute course of the disease against the background of the progressive development of a retrovirus, the patient’s life expectancy is no more than 1 month.
Death is inevitable; it is the result of leukoencephalopathy of any type.
Leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin, periventricular and small focal
Modern medicine allows us to accurately diagnose most existing pathological processes.
A disease such as leukoencephalopathy was previously diagnosed mainly in people with the immunodeficiency virus (HIV infection), but now it is found much more often.
Due to this, patients who do not know about their illness can prolong their lives. Otherwise, it will gradually progress, depriving a person of the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle.
Leukoencephalopathy manifests itself in the form of damage to the white brain matter and affects mainly older people. The origin of the disease is quite confusing, but recent studies have shown that it occurs due to the activation of a polyomavirus.
Causes of development and forms of the disease
Scientists have been able to prove that leukoencephalopathy occurs in people with polyomavirus. However, this is not very good news, since 80% of the world's population is infected with it.
The virus manifests itself, despite the depressing statistics, extremely rarely. For its activation to occur, a combination of a number of factors is necessary, the main one of which is weakened immunity.
Therefore, previously the problem concerned mainly people with HIV infection.
Among other reasons that can influence the development of leukoenphealopathy, the main ones can be identified:
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- AIDS and HIV infection;
- Blood diseases such as leukemia;
- Oncological pathologies;
- Hypertension (high blood pressure);
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Application of monochannel antibodies;
- Sarcoidosis;
- The use of medications with immunosuppressive effects, which are prescribed after tissue or organ transplantation;
- Systemic lupus.
To date, the following forms of leukoencephalopathy have been classified:
- Finely focal. It is characterized by chronic pathologies of cerebral (brain vessels). They have a progressive course, so over time the white matter is damaged. A small focal type of leukoencephalopathy, probably of vascular origin, mainly manifests itself in men over 60 years of age who suffer from hypertension. In addition to them, the risk group includes people with a hereditary predisposition. In most cases, focal pathology of vascular origin leaves certain consequences, for example, dementia;
- Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy of the multifocal (multifocal) type. It is usually the result of a viral infection affecting the nervous system. Due to this phenomenon, the white brain matter is damaged. This process occurs mainly against the background of the development of HIV infection. Among the consequences of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy are rapid death;
- Periventricular leukoencephalopathy. It occurs due to a constant lack of nutrients due to cerebral ischemia. This form of pathology affects the cerebellum, brain stem and subdivisions that are responsible for human movements. It manifests itself mainly in newborns due to hypoxia that occurs during intrauterine development. The most dangerous complications include cerebral palsy.
Signs
Manifestations of the pathological process directly depend on the location of the lesion and its type. Initially, the symptoms are not particularly pronounced. Patients feel general weakness and deterioration of mental abilities against the background of rapid fatigue, but often attribute the symptoms to fatigue.
Psychoneurological manifestations arise differently for everyone. In some cases the process takes 2-3 days, and in others 2-3 weeks. You can independently identify the presence of leukoencephalopathy, focusing on its most basic signs:
- The occurrence of epileptic seizures;
- Increased frequency of headache attacks;
- Failures in coordination of movements;
- Development of speech defects;
- Decreased motor abilities;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Decreased sensitivity;
- Depression of consciousness;
- Frequent outbursts of emotions;
- Decreased mental activity;
- Problems with swallowing due to disruptions in the swallowing reflex.
There have been situations when specialists diagnosed lesions only in the spinal cord. In this case, the patients showed exclusively spinal signs associated with a disorder of the musculoskeletal system. Cognitive impairment was mostly absent.
Course of therapy
Despite the development of modern medicine, scientists have not been able to find an effective cure for leukoencephalopathy. Any of its forms will gradually progress and it will not be possible to completely stop the disease.
The course of treatment drawn up by a neurologist is aimed at maintaining the patient’s condition. Its goal is to slow down the development of pathology, relieve symptoms and restore the level of mental abilities. Corticosteroids are used to prevent inflammation.
If you have an immunodeficiency virus, your doctor will prescribe antiretroviral medications.
It is prohibited to take medications against leukoencephalopathy on your own, since doses are selected individually.
Gradually, some drugs may be completely discontinued or replaced with other drugs with altered dosages.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for leukoencephalopathy is extremely disappointing. In most cases, the patient's life span ranges from 1 month to 2 years. To prevent the development of a pathological process, it is recommended to follow the following rules of prevention:
- Before sexual intercourse, you must ensure that you have a contraceptive;
- You should choose only regular sexual partners, and not change them every month;
- Bad habits, such as smoking cigarettes and using drugs and alcohol, should be abandoned;
- The diet should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits and it is advisable to additionally consume vitamin complexes;
- It is advisable to avoid stressful situations, as well as physical and mental overload.
There is no cure or reliable means of prevention for leukoencephalopathy, but by following certain rules you can reduce the chances of its occurrence to a minimum. If the disease does occur, it is necessary to immediately undergo diagnosis and begin a course of maintenance therapy to prolong life.
Symptoms and signs
Lecoencephalopathy at an early stage of development has a blurred clinical picture, characteristic symptoms appear as the disease progresses.
The first signs of the disease are:
- decreased performance;
- sleep disturbance;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- increased irritability;
- apathy;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- depressed mood;
- absent-mindedness.
At an early stage of progress, the patient loses interest in life, refuses to do homework, and faces difficulties in pronouncing complex words.
The typical clinical picture is as follows:
- weakness in the limbs;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- change in gait;
- paralysis of the upper and lower extremities (bilateral or unilateral);
- speech disorder;
- loss of vision;
- loss of intelligence;
- lack of control over urination;
- dysphagia.
Relatives of patients face particular difficulties as dementia progresses. The victim does not realize that he needs help and care, becomes aggressive, and sometimes socially dangerous.
Types of pathology
The disease is usually divided into 3 types. It is important to determine which of them the disease belongs to as quickly as possible. Not only the main manifestations, but also the treatment method depend on this. These types include:
Finely focal. This disease is chronic and most often occurs against the background of hypertension. However, it often does not develop too rapidly, thereby ensuring a longer life for the patient. Almost always, this form of the disease occurs at a late age and provokes senile dementia. The problem is that such pathology usually does not manifest itself very clearly at an early stage, thereby making diagnosis difficult. Due to the fact that the disease cannot be detected in a timely manner, treatment begins too late. Progressive. This form of pathology has the most unfavorable prognosis. While other forms may affect older people more often, this form is recorded in people of all ages. This form most quickly leads to death due to the fact that the disease develops very rapidly. The direct cause of the disease is damage to the nervous system by viral infections, which entails a negative effect on the body. Viruses destroy the white matter of the brain. This form occurs against the background of general suppression of the immune system. To prevent the development of this form of the disease, simply pay attention to your health and prevent a decrease in immunity. Although, simply under general suppression of the immune system, such a pathology rarely occurs. More often the disease is accompanied by AIDS or other serious damage to the immune system. Periventricular. Against the background of pathologies of the cardiac system, the oxygen supply to the subcortical substance of the brain is disrupted. Because of this, there is a disruption in the overall functioning of the brain. The first symptom in the development of this form of the disease is problems with a person’s motor system, since those brain centers that are responsible for the patient’s motor activity are primarily affected. Other symptomatic manifestations (visual impairment, hearing impairment) occur only depending on which part of the brain is affected. Sometimes this form of the disease can be a consequence of a heart attack or stroke. It does not develop too rapidly, but gradually all the senses and external perception of the surrounding world are affected. Massage for blood circulation
Regardless of what type was diagnosed in the patient, vascular pathologies require prompt treatment. The faster this is done, the greater the likelihood of at least partially returning the person to normal life for a while.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, a brain examination is performed using special equipment:
- dopplerophraphy;
- encephalography;
- CT;
- MRI.
In cases where the above methods are not enough to determine the diagnosis and accurately establish the nature of the disease, invasive methods are used. A biopsy and lumbar puncture may be performed.
Attention! The use of the listed diagnostic tools is possible only with the consent of the patient’s relatives. It should be taken into account that taking a biopsy requires intervention in the tissue of the brain and spinal cord, and therefore can lead to irreversible consequences.
If a suspicion of virus infection is detected, qPCR diagnostics are used.
Treatment
Treatment of leukoencephalopathy of the brain involves the use of the combined effects of medications, physiotherapy and other auxiliary techniques. The disease is classified as incurable, therefore the main goal of the doctor is to improve the patient’s life and improve its quality.
With leukemia cephalopathy, damage to the blood vessels of the brain occurs, therefore the effect of medications is concentrated on restoring their function. It is important to normalize blood flow and increase the permeability of vascular walls. Blood thinners may be used as needed.
Palliative care also includes the use of non-drug methods:
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- reflexology;
- acupuncture;
- massage.
In some cases, the help of a psychologist, speech therapist and psychiatrist is required.
What pills to take
Drug treatment is aimed at providing the following conditions:
- stopping the development of the disease;
- restoration of brain functions;
- elimination of the clinical picture;
- impact on the causes of the disease.
For leukoencephalopathy, patients are recommended to take the following medications:
- Drugs that improve brain metabolism - Cavinton.
- Nootropic drugs – Phenotropil, Piracetam.
- Angioprotectors – Plavix, Curantil.
- Vitamin complexes and adaptogens.
- Anticoagulants – Heparin and its derivatives.
Antiretroviral drugs can be used according to indications.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods are auxiliary means of treatment and can only be used after consultation with a doctor.
The main recipes are presented as follows:
- Liquid honey is mixed in a 2:1 ratio with onion juice. The composition is mixed and left in the refrigerator for 2 days. Take 2 tbsp. l 2 times a day. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
- Mix liquid honey, onion juice and beet juice in equal parts. The mass should have a viscous consistency. Take 1 tbsp. spoon per day. Duration of use – 1 month.
- To prepare a vessel cleaning product, mix the juice of 5 heads of garlic with a squeeze of 3 ripe lemons. The mixture is infused for 2 days and filtered, adding 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey. The composition is taken in 4 tbsp. spoons per day.
- The crushed fruits of fresh, ripened rose hips are poured with boiling water and left to cool. The water is drained and the steamed fruits are mixed with natural honey. The mixture is consumed in 2 tbsp. l per day.
- Hawthorn fruits are poured with boiling water and the contents are infused for 10 hours. Add honey to the chilled drink and drink it in the morning.
Attention! You can start using traditional medicine methods after conducting a sensitivity test to the active substances. Plant components can provoke an acute allergic reaction in the consumer.
Despite their simplicity, the recipes listed above are effective and safe. The ingredients that make up the medicinal mixtures contain vitamins, therefore they allow you to restore the immune parameters of the human body.
Focal encephalopathy of vascular origin what is it |
The brain serves us faithfully throughout our lives. But there are many different diseases that disrupt its functioning and reduce a person’s quality of life.
One of these very insidious and complex diseases is vascular encephalopathy. It can occur against the background of previous infections, as well as due to tumors and various injuries.
The cause of this disease may be pathology of the blood vessels of the brain or a number of other diseases and disorders.
What does the term “vascular encephalopathy” mean? This is an organic lesion that occurs in the brain tissue of a non-inflammatory nature. It occurs due to insufficiency of cerebral circulation. Depending on the causes of occurrence, this disease is divided into atherosclerotic or hypertensive form.
Here you can add mixed and venous forms. But it is not always possible to determine exactly what the nature of the lesion is. Brain vessels can be damaged due to rheumatism against the background of systemic connective tissue diseases. Vascular encephalopathy can be caused by blood diseases or hypodynamic disorders.
In this case, damage can occur in the arteries or veins of the brain, as well as its membranes.
Depending on the stage of this disease, the main symptoms are completely different.
Thus, the signs of encephalopathy at the compensated stage are as follows: the patient’s memory is impaired, he perceives new information poorly, attacks of headaches, dizziness and heaviness in the head appear.
A person becomes anxious, sleeps poorly, has emotional breakdowns, and his mood constantly changes. Most often, patients try to hide such symptoms from others.
If vascular encephalopathy is in a subcompensated stage, then the patient may lose balance, it is difficult for him to move around the city independently, the person constantly forgets everything, and physical activity decreases.
If we talk about the mental status, then speech impairment manifests itself, the patient experiences tearfulness and depressed mood, attention is impaired, and it becomes difficult to swallow.
There is also a decompensated stage, when disturbances occur not only in the neurological and psychological status, but also signs of focal disorders appear. These could be seizures or even epileptic attacks.
To identify at what stage and in what form the disease is, a tomogram of the brain is done, as well as other studies of its blood vessels. To exclude toxic and metabolic encephalopathy, clinical and biochemical blood tests are taken, and the hormonal profile is also examined.
The effectiveness of treatment for this disease depends on how correctly and accurately the nature and extent of vascular damage was identified. For treatment, drugs that affect the blood lipid profile are used.
It is very important to normalize blood pressure and venous outflow. To improve microcirculation processes, various angioprotectors and antiplatelet agents, as well as antispasmodics, are used.
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment; it is simply impossible to cope with such a disease on your own.
There is also a very dangerous condition - acute hepatic encephalopathy or Reye's syndrome. This disease occurs in children aged four to twelve years. The causes may be viral diseases that were treated with acetylsalicylic acid. In this case, cerebral edema develops very quickly and the liver is affected.
Reye's syndrome manifests itself already on the fifth or sixth day of the viral disease. Symptoms include vomiting and disturbances of consciousness. If you do not call a doctor in time, a coma may occur and the child may die.
To prevent this serious disease, you should stop using acetylsalicylic acid drugs in the treatment of viral diseases in children under the age of fifteen.
The main symptom of acute hepatic encephalopathy in adults is a disorder of consciousness. The patient begins to get confused in words and thoughts, and increased or depressed psychomotor activity appears.
After this, drowsiness increases, stupor and coma sets in. Very often this syndrome ends fatally. During treatment, protein intake is limited and mechanical bowel cleansing is performed.
Features of vascular leukoencephalopathy: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin (vascular leukoencephalopathy) is a rare disease that destroys the white matter of the human brain in the subcortical structures.
The disease often occurs in old people and is characterized as vascular dementia (dementia in old age). Occurs against the background of arterial hypertension.
This disease is also called Binswanger's disease or subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy.
Types of leukoencephalopathy
Among leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin, the following types are distinguished:
Small focal leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin is a pathology of the functioning of the vascular system of the cerebral hemispheres. The disease is chronic. The disease gradually affects the white matter of the human brain.
The cause of the disease is a systematic increase in blood pressure. The likelihood of incidence occurs in people over 55 years of age, mainly males. People with a hereditary predisposition also suffer. Vascular dementia (dementia) gradually develops.
Progressive multifocal encephalopathy is a rapidly developing destruction of the central nervous system caused by a viral infection. The white matter of the human brain is asymmetrically destroyed.
The cause of the disease is immunodeficiency of the body. This is one of the most progressive types of the disease, leading to the worst consequences (death).
Periventricular leukoencephalopathy is a disease that affects the subcortical structures of the human brain. Develops due to oxygen deficiency and decreased blood circulation in the brain tissue.
The pathology is localized in the brain stem, in the parts of the brain that are responsible for human motor function, the cerebellum.
Symptoms and causes
Symptoms of leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin develop over several years. Patients themselves often refuse the reality of the appearance of symptoms, so their relatives turn to a medical institution. The disease can be recognized by the signs given in the table:
The first sign of the development of the disease is characterized by weakness in one limb or all at once.
In many cases, there is decreased vision and a constantly tormenting headache, which gets worse when sneezing or coughing. Many patients complain of nausea and dizziness. The severe course of the disease is expressed by psychopathic disorders (increased fatigue, irritability, apathy, phobias, depression syndrome, an inexplicable state of fear).
The degree of manifestation and change in symptoms depends on the body’s immunodeficiency. In patients with stronger immunity, symptoms are less pronounced than in patients with weak immunity.
Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy develops due to damage by the JC virus due to acute immunodeficiency of the body or due to infection with polyomavirus. The main risk factors for the disease are:
- HIV infection, AIDS; leukemia (malignant blood disease); Arterial hypertension; immunodeficiency developed due to treatment with immunosuppressants; lymphatic neoplasms of a malignant nature (lymphogranulomatosis); any malignant neoplasms; damage to lung function (tuberculosis, pleurisy, pneumonia); Sarcaidosis.
Diagnosis and treatment
To correctly diagnose the disease and determine the localization of lesions, the following measures must be taken:
Many of our readers actively use the well-known method based on Amaranth seeds and juice, discovered by Elena Malysheva, to reduce the level of CHOLESTEROL in the body. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with this technique.
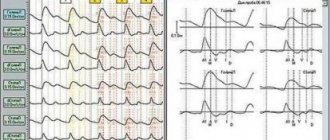
- consultation with a neurologist and infectious disease specialist; At the next stage, electroencephalography is performed; computed tomography (CT); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); diagnostic biopsy, which is performed to identify a viral lesion; laboratory research.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect all focal destruction of the white matter of the human brain. Computed tomography (CT) is weak in terms of informativeness of the definition; with its help, only the striking foci of previous infarctions are displayed.
Laboratory tests are carried out using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method. It allows you to determine the presence of viral DNA in brain tissue.
The information content of this method is 95%. Thanks to this method, it is possible to avoid a biopsy.
A biopsy is necessary when it is necessary to accurately determine the presence of irreversible processes and the degree of their development. Laboratory tests include lumbar puncture.
This method is rarely used, since it is characterized by low information content and shows a low level of protein increase in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment tactics
Therapeutic measures are carried out only with the aim of containing the development of the pathology, since it is simply impossible to recover from it. As described above, the cause of the disease is the JC virus, which destroys the human brain structure, so the primary goal of treatment is only to suppress the JC virus.
The difficulty of the event lies in overcoming the blood-brain barrier, which impedes the movement of medicinal components.
To overcome the path to the very source, the drug must be lipophilic (fat-soluble) in structure. However, most antiviral drugs are water-soluble, and this is where the complexity of drug therapy lies. To date, no effective drugs have been developed that can combat the JC virus.
For many years, doctors have tested medications with different effects and effectiveness, these are:
I recently read an article that talks about natural syrup “Choledol” for lowering cholesterol and normalizing the cardiovascular system. Using this syrup, you can QUICKLY reduce CHOLESTEROL, restore blood vessels, eliminate atherosclerosis, improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, cleanse the blood and lymph at home.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered one package. I noticed changes within a week: my heart stopped bothering me, I started to feel better, I had strength and energy. Tests showed a decrease in CHOLESTEROL to NORMAL. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
- Acyclovir. Dexamethasone. Interferon. Peptide-T. Topotecan. Cidofovir. Cytarabine.
Cidofovir improves brain activity and is administered intravenously. The drug Cytarabine can stabilize the patient’s well-being. If the cause of the disease is HIV infection, then treatment with antiretroviral drugs (Mirtazipime, Ziprasidone) is carried out.
The prognosis for this disease is disappointing: in the absence of treatment, patients with this diagnosis live no more than six months after the first symptoms appear. Treatment with antiretroviral drugs increases the patient's lifespan to one and a half years. If leukoencephalopathy has a sharply progressive form, the patient’s death occurs a month after the onset of the disease.
Source: https://imedic.club/ochagovaya-encefalopatiya-sosudistogo-geneza-chto-eto-takoe/
Consequences
Regardless of the form and intensity of the process, leukoencephalopathy of the brain is fatal. The life expectancy of the victim is within the following limits:
- 1-2 months – with a viral infection with a characteristic acute onset and progressive development;
- up to six months - possible with timely detection of the first symptoms of the disease and correct determination of palliative therapy methods;
- 1-2 years – provided that specific antiviral drugs are taken immediately after the first symptoms of the disease are detected.
Prevention
The disease does not have a developed treatment or prevention regimen. As measures to ensure that the risk of injury is reduced to a minimum, doctors advise using simple recommendations, namely:
- cessation of alcohol consumption and nicotine addiction;
- compliance with the rules of good nutrition;
- elimination of excess body weight;
- adequate treatment of hypertension in elderly patients;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- increased brain and physical activity;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
Attention! A complete set of preventive recommendations has not been developed.