Scientific editor: Strokina O.A., therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. Practical experience since 2020. December, 2020.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a very common diagnostic method for diseases of the cardiovascular system. The examination allows you to obtain the most accurate data on the condition of tissues, organs and blood vessels, as well as establish a diagnosis, predict the further development of the disease and develop an effective treatment regimen.
MRI of the heart, with a competent and timely approach, can significantly facilitate diagnosis, and therefore increase the patient’s chances for a speedy recovery.
The main and important advantages of this study are:
- non-invasiveness – the ability to obtain accurate data without surgical or other external influences;
- the ability to visualize the heart in various planes using computer processing of the received information;
- simultaneous analysis of moving blood with assessment of speed and other functional features;
- obtaining high contrast and clarity images.
MRI diagnostics is based on the interaction of a magnetic field, high-frequency radio waves and hydrogen atoms in the human body, and the use of modern computer technologies makes it possible to create a 3D model of the heart and determine the exact location of the pathology. A minimal list of contraindications and a short duration of the procedure make MRI the most popular type of examination.
The ability to diagnose heart disease using MRI is impressive.
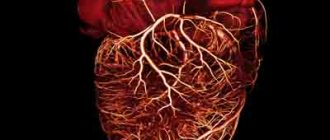
- Using "gradient echo" you can quickly assess the condition of the coronary arteries, valves and ventricles of the heart.
- The spin echo method is indispensable when studying large vessels and cardiac chambers.
- Cine-MR tomography allows you to combine and arrange all phases of the cardiac cycle into a single picture.
- Cardiac MRI with contrast can be used to predict heart attacks and assess post-infarction changes.
- The phase-contrast MRI technique allows you to measure the speed of blood flow.
- Magnetic resonance angiography provides a three-dimensional image of the heart and allows assessment of damage to large vessels.
Indications for cardiac MRI
Only a qualified specialist can tell you whether an MRI is necessary. A cardiologist will insist on this study in the following cases:
- the presence of acquired (after previous diseases - rheumatism, atherosclerosis, endocarditis) or congenital heart defects;
- suspicion of diseases of the coronary vessels and aorta;
- inflammatory heart diseases (pericarditis, myocarditis);
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- diagnosis of tumors and other space-occupying formations in the heart;
- cardiomyopathy;
- pathology of the right ventricle (poorly visualized on ultrasound of the heart);
- storage diseases and other myocardial pathologies (hemochromatosis, amyloidosis,)
- examination of the pulmonary arteries;
- examination after heart surgery.
It is worth noting that MRI is an absolutely safe (in the absence of contraindications) procedure, which makes it stand out among X-ray examinations (computed tomography, coronary angiography) and has no age restrictions. It can also be performed on children from 5 years of age. Moreover, the possibility of MRI diagnostics often depends not on the patient’s age, but on his ability to lie still during the examination.
Indications
MRI of the heart can, of course, be carried out at the patient’s own request, but if there are the following indications, such a diagnosis is simply mandatory:
- The need to assess the condition of the heart (its ventricles and atria), heart valves, blood vessels if any diseases are suspected.
- Suspicions of benign or malignant tumors with different locations.
- Various infections and diseases that may require an MRI.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Assessment of the condition of the pericardium.
- Pathologies of the coronary arteries, a history of impaired blood flow.
- The need for detailed diagnostics when drawing up a treatment plan for diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- The need to monitor the patient’s health in the presence of pathologies or to monitor the condition after illness or surgery.
- Detection of anomalies in the presence of heart defects.
- Risk of cardiomyopathy.
Cardiomyopathy
Contraindications
The examination procedure itself is usually well tolerated by patients and does not cause much discomfort. However, there are a number of contraindications, absolute and relative, that may interfere with its implementation.
The first group of contraindications makes the procedure impossible. These include:
- the presence in the patient’s body of various devices and metal products for medical purposes (pacemakers, intracardiac catheters, insulin pumps, vascular stents, clips, steel endoprostheses, etc.) - the magnetic field can lead to heating of individual elements, causing device failure or displacement, which will cause injury to surrounding tissues;
- increased body weight (over 120 kg) – the patient’s waist is incommensurate with the diameter of the device.
The second group of contraindications makes the procedure possible subject to strict adherence to a number of conditions and recommendations of the attending physician:
- fear of confined spaces;
- pregnancy (first trimester);
- nervous and mental disorders;
- serious condition due to any illness;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation (usually III, IV functional classes);
- the patient's inability to remain completely still;
- the presence of tattoos with metal-containing dyes.
Contraindications to the procedure
Magnetic scanning of the heart and blood vessels has certain contraindications – absolute and relative. Absolute prohibitions include:
- the presence of an electronic system - pacemaker, insulin pump, ferramagnetic implant;
- implants, brackets or clamps made of metal.
Relative contraindications mean that magnetic scanning is not recommended, but may be used in extreme cases. Such contraindications include:
- pregnancy (especially the first trimester);
- claustrophobia;
- obesity (more than 180-200 kg);
- increased muscle activity;
- chronic kidney disease;
- postoperative condition requiring the use of resuscitation equipment.
MRI cannot be performed after cardiac bypass surgery. This ban is valid only for the first month and a half. If stents are installed, magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended for the first six months.
Preparation
No special preparatory procedures are required for cardiac MRI. Only tomography with contrast is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
Before the examination, the patient removes all jewelry, watches and other metal objects that may affect the operation of the device. Also, the doctor conducting the examination must make sure that the patient does not have implants containing steel (prostheses, catheters, etc.).
The subject will be asked to wear a special uniform made of cotton fabric and use earplugs or headphones to protect their hearing from the various noises of the operating device.
Patients suffering from fear of confined spaces or other nervous disorders should take a mild sedative before the procedure, and patients with acute pain should take a painkiller.
Methodology
The person lies on the MRI capsule transport table on his back. Special electrodes are attached to the patient's chest, and if necessary, an intravenous catheter is installed in the ulnar or subclavian vein to administer a contrast agent. The procedure requires complete immobility of the patient, so the patient’s limbs and chest are fixed with special fasteners.
The procedure is completely painless and safe. However, people with very serious diagnoses are usually examined, and excessive anxiety before and during the examination can worsen their condition. In this case, the patient can always report his health to the doctor using the two-way communication system built into the MRI scanner.
The duration of cardiac MRI depends on the complexity of the examination and can range from 10 minutes to 1 hour.
Features of the examination
What a cardiac MRI shows depends on the choice of a specific examination mode. To study cardiovascular activity, the tomograph can operate in five main modes:
- Spin echo. This method detects changes in the condition of the heart sac (pericarditis), heart tissue, the presence of neoplasms, inflammatory processes and cysts. Determines functional failures of the ventricles and atria, an increase in the volume of the heart chambers (dilatation), cardiac hypertrophy syndrome (proliferation of cardiac tissue cells), disturbances in heart rhythm and the lumen of the coronary vessels.
- Kinotomography. The method of parallel magnetic resonance and electrocardiographic examination (ECG) provides the most accurate information about the capabilities of the muscular layer of the heart (myocardium). Allows you to determine the stability of valves and blood vessels in all phases of cardiac activity.
- Magnetic resonance imaging with contrast. Used to study blood conduction through the heart muscle (myocardial perfusion). This mode is effective in assessing the degree of risk of developing ischemic myocardial necrosis (infarction) and the post-infarction condition of the patient.
- Gradient echo. This mode is used for MRI of the heart and coronary vessels. It helps to establish circulatory disorders in the arteries and aorta.
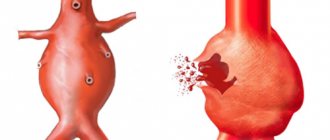
- Angiography. It is an MRI of blood vessels using a contrast agent. The mode determines: the degree of blockage of blood vessels with cholesterol (atherosclerosis), local protrusion of the heart wall (aneurysm), the presence of blood clots inside the vessels (thrombosis), and the stage of hypertension.
Such a diverse approach to cardiac examination ensures prompt diagnosis, which increases the chances of recovery and saves the lives of patients with pathological abnormalities in the cardiovascular system.
Possible complications after MRI
The MRI procedure in most cases does not cause discomfort or side effects, with the exception of:
- slight physical discomfort in a state of immobility during a particularly long examination;
- fear and fear of loneliness in the patient (occurs in 1 out of 20 cases);
- unpleasant sensation from the installation of an intravenous catheter;
- allergic reaction to a contrast agent (occurs extremely rarely, less than 1% of all subjects react);
- an increase in the temperature of the scanned body area (considered normal).
Cardiac MRI results
After the examination is completed, the results are given to the patient, who hands them over to the doctor who ordered the MRI.
The doctor, by analyzing layer-by-layer images of the heart and blood vessels, can assess the state of coronary blood flow, study the functional characteristics of cardiac activity and note changes in the functioning of the heart chambers. In addition, MRI of the heart allows you to identify defects of the interventricular and interatrial septa, various space-occupying formations and congenital malformations, as well as assess the localization and degree of development of atherosclerosis.
What can an MRI scan of the heart show?
MRI of the heart and blood vessels allows you to assess the condition of tissues and blood vessels and identify a lot of pathologies:
- neoplasms of any nature;
- ischemic changes;
- myocardial condition;
- altered anatomy of valves and vessels;
- defects (congenital and acquired);
- diseases of the vascular system;
- diseases of the pericardium and myocardium;
- deviations in the structure of the myocardium.
Magnetic resonance imaging may also be performed on other organs of the chest, including the lungs, diaphragm, esophagus, trachea, and bronchi. Contrast tomography is usually used for myocardial infarction, scar changes after it, and for the assessment and prognosis of cardiomyopathy.
Alternative methods for examining the heart
The MRI technique has much in common with ultrasound (US) and X-ray computed tomography (CT) in terms of the principle of scanning tissues and internal organs, processing and obtaining their images. However, the MRI method has some advantages. This:
- safety of the procedure for all groups of patients, including pregnant women and children;
- increased image contrast, available thanks to the special “sensitivity” of the device;
- the ability to examine even small objects (less than 1 centimeter);
- the ability to study in detail both longitudinal and transverse sections and create a three-dimensional model of organs.
That is why today MRI is the “gold” standard, the most informative and health-safe diagnostic method. However, due to the much higher cost of the examination, MRI is still only the second line in diagnosing the disease after echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
- Bacca M.S. MRI is the “gold standard” in assessing the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. – Remedium Privolzhye, 2020.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology Ed. A.J. Camm, T.F. Lyushera, P.V. Serrius. Translation from English / Ed. E.V. Shlyakhto “GEOTAR-Media” 2011
Magnetic resonance imaging of the heart and blood vessels is a highly informative method that allows identifying pathological changes in the myocardium, coronary arteries, and pericardium. MRI is based on the use of a magnetic field that creates a resonance of hydrogen atoms, which distort the radio frequency signal. Special sensors capture the converted pulses. The program processes images and creates a spatial model. Visual display of the model allows you to study the smallest details, the subtle anatomical elements of the heart valves.
Determining changes in the coronary arteries and aorta requires a procedure with contrast. Intravenous injection of the drug helps monitor the internal and external condition of the vessel. The method reveals obstructions in patency, areas of narrowing, and locations of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots. Magnetic resonance scanning better shows pericarditis, cardiomyopathy, ventricular and atrial septal defects, and other defects. Modern innovative technologies make it possible to visualize small inflammatory foci of the myocardium and impaired microcirculation in the coronary artery.
Is it possible to do MRI of the heart and blood vessels?
During magnetic resonance imaging of the heart and blood vessels, several hundred tomograms are made with a step of several millimeters. It is difficult for a doctor to analyze each image, so a software application processes the images. Innovative devices are equipped with a three-dimensional reconstruction mode.
Thus, MRI of blood vessels and the heart is not only performed, but is also recommended for suspected pathologies of the myocardium, pericardium, and heart valves. The examination allows you to verify the dissection of the arterial wall (aneurysm), thromboembolism of the vessel. After intravenous administration of contrast, it is possible to identify areas of microcirculation disturbance and areas of arterial narrowing.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed if there are contraindications:
- First trimester of pregnancy;
- Artificial metal heart valves;
- Mental disorders;
- State of drug or alcohol intoxication;
- Renal failure (when examined with contrast);
- Fear of enclosed spaces.
High-quality images are obtained only if you remain stationary during scanning. The duration of tomography of the cardiovascular system is 20-30 minutes. During this interval, you must remain motionless. Due to increased excitability, examination in children is difficult. Infants and preschoolers undergo MRI of the chest cavity under anesthesia.
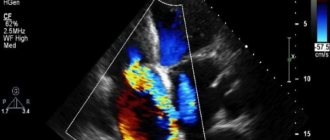
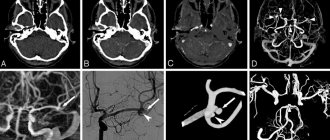
Example of MRI tomograms of the heart and blood vessels
Preparing for an MRI
MRI of the heart and blood vessels does not require special preparatory measures. Women of childbearing age should be sure that they are not pregnant. People suffering from kidney and liver diseases are required to undergo preliminary tests.
Immediately before the MRI scan, you need to get rid of metal objects (jewelry, glasses, watches, etc.).
If a contrast study is planned, the patient should refrain from eating and drinking 6-8 hours before the procedure. In some cases, before the tomography, the specialist prescribes sedatives to the patient.
MRI of the heart - what does it show?
MRI scanning is the most effective method for examining the cardiovascular system. The possibilities of nuclear magnetic resonance of the mediastinum are quite extensive. Only visualization of the lungs is limited due to increased airiness of the alveoli.
What does a cardiac MRI show:
- The condition of the heart cavities, aorta, large vessels is examined by devices with a spin echo;
- Valves, ventricles, coronary artery are devices with a “gradient echo”;
- Analysis of the phases of cardiac activity is carried out with the presence of “cine-MRI”;
- Contrast magnetic resonance imaging is done after heart attacks to assess changes in cardiac blood supply;
- The speed of microcirculation is assessed by phase-contrast tomography;
- Three-dimensional reconstruction matches the existing model of the heart and blood vessels.
The procedure is performed according to indications. The harmlessness of the study allows scanning to be done at the request of the patient. The high cost of tomography limits the widespread use of the method.
What does the study show?
The result of magnetic resonance imaging is presented in the form of a series of images - layer-by-layer “slices” with a step of several millimeters. Thanks to the high resolution of the equipment, the smallest details and anatomical features are visible. A special computer program creates a 3D model. You can visualize the results in video mode to evaluate myocardial contractions.
Thanks to contrast, large coronary arteries and small vessels are clearly visible, entwining the heart muscle in a dense network - areas of decreased or absent blood flow are identified, and the viability of tissues in case of circulatory disorders can be determined. The doctor will evaluate the following parameters:
- anatomical structure of the heart and blood vessels;
- volume of chambers and blood flow in them;
- valve movements;
- the presence of foci of damage, inflammation, scarring or oxygen starvation in the myocardium;
- when performing contrast, damage to the coronary arteries by atherosclerosis.
Main indications for cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
A cardiologist gives a referral for an MRI of the heart. Common indications:
- Diagnosis of inflammatory changes in the myocardium and pericardium;
- Study of the condition of the heart valves after a number of diseases - endocarditis, rheumatism, congenital heart defects;
- Verification of the degree of changes in coronary heart disease;
- Study of the condition of the heart arteries;
- Study of the condition after stenting, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG);
- Determination of the severity of cardiomyopathy.
The safety and harmlessness of nuclear magnetic resonance allows children from the age of five to perform the procedure.
What are the contraindications to MRI of the heart and blood vessels?
Metal objects inside the human body limit the scope of examination. A magnetic field causes objects to heat up or move. Pacemakers and insulin pumps are a limitation to magnetic resonance scanning. In such a situation, a CT scan of the lungs is done with contrast, which also qualitatively shows the pathology of the cardiovascular system.
Classification of contraindications to MRI of the cardiovascular system:
The first category of properties does not allow the patient to scan. Taking medications will not help return your health to a state that allows you to conduct nuclear magnetic resonance.
Absolute contraindications to cardiac MRI:
- Presence of a cardioverter (defibrillator);
- Pacemaker;
- Rhythm imitators;
- In-ear prostheses;
- Ilizarov apparatus.
MRI of heart valves
Heart defects lead to mixing of arterial and venous blood through additional defects of the interventricular or interatrial septum and valve apparatus. The disease leads to a lack of oxygen supply to the internal organs along with blood. To eliminate hypoxia and normalize the blood supply, artificial valves (aortic, mitral) are installed.
Three-dimensional modeling mode (3D reconstruction) helps create a spatial representation of the object with visualization of the cardiac cavities, aorta, coronary and pulmonary arteries. Intravenous administration of a contrast agent improves the visibility of the inner wall of blood vessels.
Valve replacement requires dynamic diagnostics. The position of the products may change, the formation of additional passages will lead to mixing of arterial and venous blood. Computed tomography (CT) with contrast is capable of visualizing the condition of blood vessels, identifying atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, and air emboli. X-ray examinations lead to radiation exposure of tissues, so they cannot be performed several times in a row.
MRI is a safe procedure (in the absence of contraindications). Nuclear magnetic resonance does not cause any harm to health, so the examination is done an unlimited number of times. Innovative tomographs with a power of three Tesla show even the smallest changes in the heart muscle and valves. The examination has a high price. Most types of heart disease can be detected by high-field tomography with a tube power of 1.5-3 Tesla. There is no rationality for using more powerful devices in medicine.
What diseases can be detected by cardiac MRI?
The main diagnostic purpose of performing magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the cardiovascular region is to determine blood supply defects (aortic, mitral valve defects, septal defects).
What diseases can be detected by cardiac MRI:
- Stenosis of the coronary arteries;
- Narrowing of the aorta;
- Aortic, mitral insufficiency;
- Atherosclerosis, vascular thromboembolism;
- Pericarditis, myocarditis;
- Pericardial tamponade.
A number of cardiovascular diseases are accompanied by regurgitation - the backflow of blood. Magnetic resonance imaging is a priority study for identifying the symptom of vortex, verifying valvular dysfunction, and narrowing of the arteries.
After coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), MRI can be used to measure systolic and diastolic blood flow and diagnose antegrade and retrograde volumes.
The procedure also reveals associated complications - aortic and mitral insufficiency, rheumatic changes, atherosclerosis plaques.
What are the advantages of MRI diagnostics of the heart?
MRI is an expensive method that justifies itself due to its level of safety and information content. Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging:
- helps to diagnose the smallest pathological processes at the initial stage of their development;
- eliminates radiation exposure to the patient’s body;
- the contrast component used in MRI rarely causes an allergic reaction (unlike iodine-containing drugs);
- no pain.
MRI of the heart after bypass surgery
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery is performed to restore the state of blood flow through the coronary artery. Artificial creation of shunts helps to eliminate the obstacle to myocardial microcirculation, prevent coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
Dynamic observation after surgery is performed:
- To assess the quality of manipulation;
- Determination of blood movement through the stenting site;
- Identification of complications.
Repeated scanning after a few months allows you to study the thickness of the myocardium, identify areas of hypoxia, and features of the circulation of arterial and venous blood.
MRI after CABG is contraindicated if the patient has a pacemaker or metal valve installed. The first tomography is performed 1.5 months after bypass surgery.
When is a cardiac MRI prescribed?
MRI of the heart and its arteries and veins is prescribed to patients with disturbances in the functioning of the organ to determine the causes or in the presence of diagnoses such as angina pectoris, tachycardia, ventricular hypertrophy, tumors. Also indications for MRI are heart failure and myocarditis. The study is also prescribed if there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors and cysts in the heart and surrounding tissues, with defects, pericarditis.
When prescribing an MRI of the heart, the doctor takes into account what it shows and the blood vessels. Tomography of the large heart (aorta, pulmonary veins) and coronary vessels is necessary in the following cases:
- Diagnosis of arterial atherosclerosis (to check the arteries for the presence of plaques and stenoses).
- Diagnostics of thrombosis (to check vessels for the presence of blood clots).
- Diagnosis of aortic aneurysm (including for the purpose of monitoring treatment results).
- Suspicion of an aortic aneurysm (it will show whether it is there or not).
- Suspicion of aortitis - inflammation of the walls of the aorta.
- Suspicions of thromboembolism and other diseases of the pulmonary artery.
- MRI of the heart vessels is mandatory after cardiac surgery (for example, after coronary artery bypass surgery, in order to monitor the operation of the shunts). The study is also indicated for people with coronary disease, inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis), abnormalities of the valves and aorta.
Where to get a cardiac MRI in Moscow and St. Petersburg
Several dozen medical centers offer magnetic resonance imaging in St. Petersburg and MSK. Private clinics are equipped with more modern tomographs compared to public institutions, but the rationality of examination with innovative installations does not always exist.
We offer you to choose where to have a cardiac MRI in Moscow and St. Petersburg in the “medical centers” sections. An optimized search using dozens of parameters allows you to find the desired medical institution by price, location, and opening hours.
Call us by phone from 7:00 to 00:00 or leave a request on the website at any convenient time
Cardiac MRI has been used in clinical practice since the early 90s of the 20th century. In 2003, P. Mansfield and P. Lauterbur received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the development of this diagnostic method based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance.
Content
Frequently asked questions that arise from patients who are prescribed cardiac MRI: what does this study show, is it possible to get by with more accessible and inexpensive methods of instrumental diagnostics?
After all, for an MRI of the heart and coronary vessels the price reaches tens of thousands of rubles, while an ECG or ultrasound will cost several times less. Cardiac MRI is usually used in the final stages of diagnosis if other methods have not provided accurate, comprehensive information about structural abnormalities and functional deficits. What cardiac pathologies does MRI detect?
Cost of the study
Magnetic resonance imaging is a rather expensive procedure, since the tomograph itself is not cheap. The price of MRI of the heart and coronary vessels depends on the type of equipment, as well as the specialization of the clinic and the qualifications of the specialist. In addition, the use of contrast plays a role: in this case, the procedure becomes more expensive.
An MRI without contrast costs on average 7,000-8,000 rubles. The minimum price is from 3,000. An examination using contrast costs from 12,000 rubles and above. On average, diagnostics will cost 20,000 rubles.
Heart pathologies
MRI of the heart and coronary vessels has a wide range of indications: verification of diagnosis and monitoring of the dynamics of heart defects; preoperative monitoring and analysis of changes after surgery; cardiomyopathy; pathological processes in the pericardium and mediastinum; detection of neoplasms; cardiac ischemia; detection of vascular thrombosis.
MRI of cardiac vessels in most cases allows you to do without direct invasive angiography, which is fraught with complications. However, if “jewelry” cardiac surgery is indicated, it is preferable for the doctor to have the clearest possible picture of the area of the operation: such as that provided by MRI of the heart with contrast.
To do this, the patient is injected with a contrast agent (gadolinium) before the procedure. Cardiac MRI with gadolinium is also prescribed for patients for whom computed tomography (CT), accompanied by radiation exposure, is contraindicated.
Unlike CT, MRI provides a clearer picture of soft tissues, the ability to examine in detail the narrowing of the coronary vessels, and identify the localization of dying areas of the heart muscle suffering from ischemia.
Features of performing cardiac MRI
During this study, a special coil is installed on the patient's chest, and electrodes can also be installed to take an ECG to synchronize the scan with the heartbeat.
During cardiac MRI, the patient will need to hold their breath for certain short periods of time to obtain clear, artifact-free images.
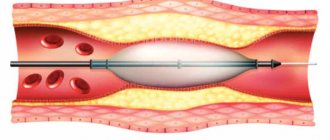
Let us note one more feature of this study: if the patient has artificial valves and stents in the heart, the possibility of tomography is discussed with the attending physician individually. MRI for artificial heart valves can be performed, but these structures can cause image defects, thereby reducing the informativeness of the diagnosis. MRI for stents in the heart is not prescribed immediately after the operation, since the tomograph field can cause displacement of these elements. Typically, diagnosis is carried out 1.5-2 months after the stenting procedure.
Otherwise, the procedure is no different from MR examinations of other tissues - there is no preliminary preparation, and the patient must lie motionless on his back during the entire examination. MRI of the heart and coronary vessels is recommended to be performed on ultra-high-field devices with a field induction of 3.0 Tesla.
The duration of diagnosis ranges from 30-45 minutes, the contrast procedure increases the duration by 15-20 minutes.
Limitations for MRI
The widespread use of MRI is limited by the high cost of the method. To conduct research, expensive equipment, highly qualified medical personnel, and specially equipped premises are required.
Therefore, when asked whether cardiac MRI is performed in regular clinics to which the patient is assigned, the answer will most often be negative. Specialists from large cardiological institutions, such as the Scientific Center for Cardiovascular Surgery named after. them. A.N. Bakuleva.
When examining cardiac MRI in Bakuleva, the price ranges from 2.5 to 35 thousand rubles. A preliminary verifiable diagnosis and the complexity of the analysis determine the cost of cardiac MRI: the price in most clinics starts at 8 thousand rubles; additional costs will be required by contrast when prescribing the most informative version of the study with gadolinium. Prices for a contrast agent range from 5 thousand rubles.
Other limitations include the impossibility of examining patients who have metal implants or artificial heart pacemakers. In these cases, CT must be prescribed instead of MRI.
How to sign up for the study?
When choosing a clinic, patients are faced with a number of questions, which makes the search a difficult task:
- Where can I get the examination, what type of tomograph do I need?
- Consultation with a practitioner is required
- You need to undergo an MRI examination with a magnetic field strength of 3 Tesla. Where can I find such devices?
- Do you need a medical center open 24 hours a day?
- It is recommended to undergo a study with contrast, what are the features, are there any contraindications?
- Where can I get an MRI for my child?
- How is pricing structured? It is necessary to search for the optimal option.
Finding a clinic for your unique case is really difficult. Some patients do not need to undergo research using expensive equipment at all, while others urgently need advice from the best specialists in a particular field.
The MRI and CT Appointment Service can help you choose a clinic. They work with a large number of clinics, and often have exclusive discounts. Thus, making an appointment through them is even cheaper than calling clinics yourself.
Phone numbers of the City Appointment Service for MRI and CT in St. Petersburg in Moscow;
Phone numbers of the City Appointment Service for MRI and CT
Sign up for MRI and CT in St. Petersburg:
- selection of the optimal clinic and registration for examination - registration in all areas of the city - free consultation with a doctor after the examination!
Working days: 08:00—24:00; Weekends: 09:00—21:00
Promotions and discounts
The city registration service records in a large number of clinics, many of which provide significant discounts to certain categories of citizens.
You can also save a lot by booking at night or on weekends.
| MRI at night | Discount up to 25% |
| MRI on a day off | Discount up to 10% |
| For pensioners | Discounts 10% |
| For students | Discounts 10% |
| Schoolchildren | Discounts 5% |
| Veterans of the Great Patriotic War and residents of besieged Leningrad | Discounts up to 30%! |
| Participants in wars and hostilities, liquidators of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant | Discounts up to 10% |
*For questions about undergoing an MRI or CT scan at the specified discounts, please contact the City Registration Service (812) 313-26-79 .