Occlusion is a broad concept that characterizes the obstruction of the patency of certain vessels, which is caused by persistent blockage of their lumen in any area. Various types of obstruction are classified, which can be combined into one name - arterial occlusion. It is no secret that these vessels are found throughout the human body. Therefore, when establishing a diagnosis, the site of closure of the lumen is constantly clarified - the superficial femoral, carotid or other artery, on the right or left side.
Occlusion and stenosis are diseases that go hand in hand. It cannot be said that occlusion can be a method of surgical intervention; this is reflected in the names of certain operations. As an example, endovascular type of occlusion, X-ray endovascular occlusion of atrial septal deformation (ASD) and other types. All this needs careful consideration, starting with the causes and types of vascular obstruction.
Causes of occlusion
There are certain reasons why occlusion and stenosis of vessels appear on the right and left sides. The main reason is embolism. This is a blockage by a dense formation of the lumen, which is located in the bloodstream. Embolism also appears for various reasons; as a rule, they are infectious in nature. There are such types of embolism , due to which occlusion of the aorta or other vessels may occur:
- Fat. The main reason is a metabolic disorder, or in rare cases, injury. The point is that small fatty particles are concentrated in the blood, which, sticking together, develop into a large fatty clot.
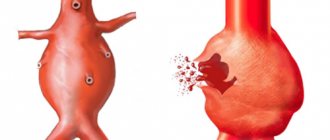
- Arterial, if an artery, vein or vessel is blocked by mobile blood clots that form due to disorders of the valvular heart apparatus.
- Air, if an air bubble gets into the vessels, this can happen if the injection is incorrect, resulting in lung damage.
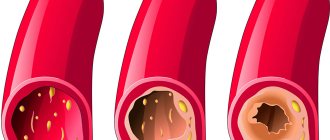
Thrombosis is also a cause of obstruction in the arteries. This is the name for a regular decrease in arterial lumen due to a constant increase in the size and number of blood clots on the internal walls. Thrombosis creates favorable conditions for the development of embolism, therefore the likelihood of occlusion increases.
It is impossible not to mention such a reason for occlusion of varying degrees as vascular atherosclerosis , which also leads to a decrease in the lumen of arteries and veins. Atherosclerosis can develop, that is, transform from one degree to another.
Arterial occlusion can occur due to injury if bone or muscle tissue is damaged. This leads to compression of large blood vessels, causing complications in blood circulation. In the place where the artery is compressed, thrombotic processes can develop.
Diagnostics
Most often, occlusion of the iliac or femoral artery occurs in the legs. A vascular surgeon will tell you what it is and what first aid is for the body.
Advanced occlusion of the vessels of the lower extremities has serious consequences for the body, including amputation of the legs, so any suspicion of the disease requires a thorough examination in a hospital:
- The surgeon visually assesses the site of the suspected blockage, noting the presence of swelling, dryness and other skin lesions.
- Vascular scanning helps to identify injured segments.
- If the picture is unclear, an x-ray or angiography is ordered, in which contrast dye is injected into the artery.
- The ankle-brachial index helps assess the condition of the circulatory system.
Types of occlusions
Next, we will briefly consider several types of occlusions:
- Obstruction of peripheral arteries is the blocking of blood flow by blood clots in these arteries. Typically, this condition appears in the veins of the legs. It is noted that only one third of people with this pathology are subject to diagnosis and treatment. This is explained by the fact that for many it goes away without obvious signs. There may even be no symptoms at all.
- There is also post-thrombotic and thrombotic occlusion. The first is closely related to postthrombotic pathology, its pathogenesis is quite complex. The reasons that determine the process of thrombus recanalization have not yet been studied.
- Vascular occlusion such as nonconduction of the subclavian artery may also develop. This means that one of the most important vessels is affected. A decrease in the size of the subclavian artery can lead to ischemia of the upper extremities and cerebral vascular insufficiency. Non-conduction of the first fragment of the subclavian artery, according to various doctors, is detected in approximately 5-15% of cases. Moreover, quite often concomitant pathologies of the second fragment of the subclavian artery or vertebral artery are diagnosed. When problems with the subclavian artery are identified, immediate treatment is necessary.
- Occlusion of the femoropopliteal segment (FPS). Oxygenated blood does not flow to the lower leg. This condition is accompanied by certain symptoms. The causes of this obstruction, as a rule, are obliterating atherosclerosis.
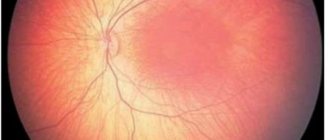
- Retinal vein occlusion is a violation of blood circulation in the main retinal vein or its branches. This most often happens between the ages of 45-60 years.
- Acute occlusion is an acute disturbance of blood circulation. Since blood flow is disrupted in the area of the nonconductivity of the vessel, additional blood clots develop. This condition is severe, but it is reversible when help is provided within 4 hours of onset. After this time, deep ischemia can lead to necrotic irreversible complications.
There are other types of artery occlusion, taking into account their location. Each of these types is dangerous to the body and can lead to irreversible processes . There are different degrees of damage. One way or another, vascular obstruction manifests itself somehow. The diagnosis is quite simple. This can be done both by the main symptoms of arterial obstruction and by special studies.
Early stages of subclavian artery obstruction can be treated conservatively. However, more severe degrees of the disease are often treated with surgery. It must be taken into account that disorders of the subclavian artery can be treated only after the cause of the disease is identified. Removing symptoms is not enough.
Naturally, it is necessary to remember that occlusion is sometimes caused on purpose if it is part of a surgical operation . This includes partial occlusion when the lower part of the glass of the dominant eye is turned off, and endovascular occlusion, and occlusion of the ASD.
Diagnosis and treatment
If signs of illness appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor. At the first examination, the patient is examined, the nature of the clinical picture is clarified, and an anamnesis is collected. Diagnostic procedures that confirm pathology:
After a comprehensive diagnosis, adequate therapy is prescribed. If the pathology occurs at the initial stage, conservative treatment is carried out, the cause of its occurrence is eliminated. The drug therapy regimen includes the following drugs: antispasmodics, thrombolytics, anti-inflammatory drugs. If an occluded heart vessel is identified, it is recommended to take medications that improve the functioning of the main organ. Physiotherapy is carried out in parallel:
- magnetotherapy (use of a magnetic field);
- barotherapy (high or low pressure affects the body);
- plasmapheresis (collection, purification and return of blood to the channel).
In severe cases, surgery, embolectomy, or bypass surgery are prescribed. The decision to perform surgical intervention is based on the severity of ischemia, the location of the thrombus and the general condition of the patient. The acute process is treated with thrombolytic agents. They are inserted using a catheter. The course of treatment lasts up to 14 days.
If indicated, a special protein is introduced. The catheter is inserted into the problematic vessel, and the medicine is supplied at a rate corresponding to the patient’s body weight and the stage of thrombosis. Therapy continues for 24 hours, taking into account the form of ischemia, the state of blood flow is monitored by ultrasound. About 20−30% of patients require amputation of the affected limb within the first month.
If the heart is damaged, it is recommended to relieve spasm and relieve pain. Then the operation is performed using the following methods:
- X-ray endovascularization. Manipulation is carried out through the skin using special surgical instruments.
- Thrombembolectomy. During the operation, the blood clot is removed.
- Endarterectomy. The manipulation is aimed at restoring normal blood flow through the vessels.
- Prosthetics. It is performed in places where a blood vessel is removed.
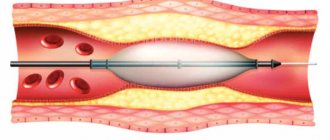
- Stenting. During the operation, a special frame is installed.
In case of tissue necrosis, limb amputation is indicated. After the operation, the patient needs long-term rehabilitation, which includes conservative measures and psychological training. If the limb has healed, a prosthesis is installed.
Symptoms of the disease
Occlusion of the femoral artery is characterized by the following symptoms:
- intermittent claudication – pain and numbness of the muscles in the calves;
- pallor of the skin of the legs;
- cold lower extremities.
During thrombotic occlusion, clinical symptoms are based on the identification of the following signs:
- pain;
- paralysis;
- loss of pulse;
- paleness.
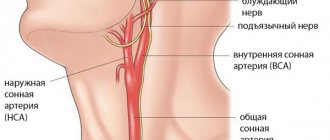
Occlusion of the vertebral artery manifests itself with similar symptoms. Medicine describes several main symptoms present during blockage of any vessel. When obstruction appears in the head or neck area , the signs appear quite quickly:
- Loss of pulse. It must be checked in special areas, that is, in places where the vein is blocked. Such a symptom is usually indefinable, since it is difficult to determine in which vein the blood circulation is impaired.
- The pain that is present in the affected area increases over time. When the blood clot moves on its own, the pain may disappear even when the condition is not treated. Pain is the main symptom of a disease such as occlusion.
- Paresthesia. This is if a person notices such signs - goosebumps, numbness, tingling. Then tactile sensitivity is connected to them. With this long-term condition, paralysis may occur.
- Pallor of the skin and further cyanosis. The patient's face may turn pale. If the skin does not receive the required nutrition for a long time, then symptoms such as wrinkles, peeling, and dryness appear.
Damage to the internal carotid artery (ICA) on the left side usually manifests as a transient ischemic attack. Usually the symptoms are the following: weakening of sensitivity on the opposite side, hemo- or monoparesis. Monocular visual impairment is noted on the affected part.
Classification
During occlusion, 4 degrees can be distinguished. At first, the disease does not have any specific manifestations, but upon examination, the first signs of the disease are detected.
The second degree is an incoming ischemic attack, which occurs against the background of incomplete blockage of the vessel. Moreover, all signs of a transient attack completely disappear within 24 hours.
The third degree is the daily presence of neurological symptoms. The patient constantly complains of headache, high blood pressure and some other signs of the disease.
And finally, the fourth degree is the development of a stroke due to complete blockage of the vertebral artery.
Diagnosis of the disease
Each form of occlusion, be it complete, post-thrombotic or other obstruction of arteries, veins, requires careful diagnosis, which involves examining the symptoms of the disease, as well as prescribing certain tests.
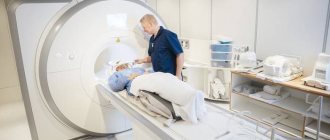
All diagnostic activities are carried out only in stationary conditions . Postthrombotic vein obstruction, occlusion of the subclavian artery, ICA and any other similar pathology are determined using various research methods - cholesterol analysis, general blood test, ECG, coagulogram, REG of neck and head vessels, EEG, Dopplerography of the neck, CT, MRI.
Possible complications
The most severe consequences are caused by occlusion of blood vessels in the brain and lower extremities, as it leads to dementia and heart failure.
Pathology can also cause:
- inflammatory processes;
- cerebral stroke;
- heart attack;
- tissue necrosis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- paralysis;
- amputation.
Occlusion of mesenteric vessels leads to abdominal sepsis and purulent peritonitis.
If timely and qualified assistance is not provided, a person may remain disabled or die.