Surgery on the carotid artery (CA) is mainly indicated for patients suffering from narrowing of the vessel and is intended to ensure adequate blood supply to the brain. The carotid arteries are the largest and most important vessels that supply blood to the brain, which is very sensitive to lack of oxygen. Even a seemingly slight narrowing of these arteries can cause symptoms of damage to nervous tissue, fraught with the danger of stroke and even death of the patient.
The places of close attention of vascular surgeons are the bifurcation zone of the common carotid and the internal carotid artery (ICA) - these are the areas that most often undergo structural changes, and therefore they become the target for surgical treatment.
diagram of the structure of the carotid artery
Stroke (cerebral infarction) is one of the most dangerous diseases of the vascular system and brain, the prevalence of which has become alarming in recent decades. The main cause of cerebral infarction is atherosclerosis, which causes a critical narrowing of the lumen of the artery. Of course, therapeutic approaches have been developed in the treatment of pathology, but, as the results of large studies show, not a single conservative method can give the same result as surgery.
Disturbances in blood flow in the brain do not go away without leaving a trace; serious consequences often remain, making the patient disabled, and it is not always possible to restore lost brain functions, even with surgery. In connection with this circumstance, surgical treatment becomes of great importance in order to prevent vascular catastrophes of the brain, that is, even before the nervous system is damaged.
Prompt prevention of carotid artery stenosis significantly reduces the likelihood of acute circulatory disorders, normalizes blood delivery to the brain, improves the well-being of patients, and after a stroke makes it possible for more successful rehabilitation.
Indications and contraindications for surgical treatment of carotid artery pathology
Surgery on the carotid arteries is most often performed for stenosis - narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. The reason for this narrowing may be atherosclerosis, kinking of the vessel, or the formation of a blood clot. A less common reason for surgery is a carotid aneurysm.
Indications for surgery for carotid artery stenosis are:
- Narrowing of more than 70% even in the absence of symptoms of pathology.
- Narrowing of more than 50% in the presence of symptoms of cerebral ischemia, previous ischemic attacks or stroke.
- Stenosis less than 50% in cases of stroke or transient ischemic attack.
- Sudden disruption of brain activity or progression of chronic ischemia.
- Bilateral damage to the carotid arteries.
- Combined stenosis of the vertebral, subclavian and carotid arteries.
Open interventions on the arterial trunks carry a certain risk. In addition, it is worth considering that the majority of patients are elderly people suffering from a variety of concomitant pathologies, so it is important to highlight not only the indications, but also to determine the degree of risk and contraindications to surgical treatment. Conditions such as:
- Severe diseases of the heart, lungs, kidneys in the stage of decompensation, which make any operation impossible;
- Severe disturbance of consciousness, coma;
- Acute period of stroke;
- Intracerebral hemorrhage due to ischemic necrosis;
- Irreversible brain damage due to complete occlusion of the carotid arteries.
Today, surgeons give preference to minimally invasive procedures, so the number of contraindications is gradually decreasing, and treatment is becoming safer.
Before the operation, the patient is asked to undergo a standard list of examinations - blood and urine tests, electrocardiography, fluorography, blood clotting tests, tests for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis. To clarify the characteristics of the pathology, ultrasound duplex scanning of the arteries, angiography, and possibly MRI, multislice CT are performed.
Indications for surgery
We are talking about surgery if there is a blockage of a segment of a vessel, as well as a narrowing of large blood vessels. But to prescribe surgical intervention, the presence of one or a number of aggravating factors is necessary.
These factors or absolute indications for carotid artery surgery are:
- There is a negative dynamics in the course of the disease - the situation is gradually getting worse.
- The patient begins to suffer from cerebral crises.
- The narrowing closed the vessel to 2/3 of its diameter.
- There is an aneurysm or mechanical damage to the artery.
- The lumen of the arterial pathway has visible irregularities.
- The vessel has pathology not on one side, but on both sides.
- Symptoms of pathology have an intensity of medium or higher.
- There is blockage or stenosis of nearby vessels.
Note that the risk of any negative consequences from the operation is much lower than the threat to health if you refuse the operation. In all cases, drug treatment is considered less effective.
The main goal: prevention of stroke, or prevention of recurrent stroke. In the second case, it is important to do the procedure before the second stroke occurs immediately after the first.
Carotid artery surgery lasts about 120 minutes. It is acceptable to use both local and general anesthesia.
If you suffer from any heart disease and are candidates for carotid artery surgery, be sure to visit an experienced cardiologist, as there is a high risk of complications and worsening heart problems.
This type of surgical intervention on the carotid artery has been used for six decades; the accumulated experience allows us to maintain fairly favorable statistics: the vast majority of patients tolerate the intervention normally and feel well immediately after it.
Carotid subclavian bypass and stenting are types of intervention with a minimum number of complications.
You can see how the operation takes place in the video; then we will briefly describe the process.
The process of surgery on the carotid artery depends on its type.
- Stenting is performed if it is necessary to restore the lumen of the vessel. In this case, the doctor does not remove the plaque, but simply presses it against the wall with a stent, thereby restoring normal blood flow;
- removal of plaque from the carotid artery by performing a classic open operation. Scientific name: carotid endarterectomy;
- prosthetics. It is used if there is a large area affected. In this case, the affected area is removed, and an endoprosthesis matching the diameter of the internal artery is placed in its place;
- if the plaque is small and located at the beginning of the internal carotid artery, eversion endarterectomy is used. Its technique is similar to conventional cutting, but at the same time the doctor performs the so-called eversion of the artery.
If there is stenosis of the cervical arteries (the subclavian region is affected), a slightly different type of intervention is used - carotid subclavian bypass.
The normal anastomosis between the carotid and subclavian arteries is restored using a shunt.
In which cases to perform an open operation, when it is necessary to install a stent or perform a bypass of the carotid artery, only the doctor decides, having assessed the characteristics of the course of the disease, as well as many other factors.
In some cases, the operation is prohibited; we list them:
- plaque mobility;
- incurable chronic diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- severe general health condition;
- intolerance to anesthesia;
- poor condition of the vascular network;
- deformation and thinning of the walls of the arteries in the complex;
- acute renal failure;
- abnormally complex structure of the vessel.
In addition, a contraindication for stent installation is an allergy to the substances from which it is made.
The operation is performed if stenosis (narrowing) spreads to the second segment of the subclavian artery. It is also indicated for patients with a hypersthenic physique, in cases where the isolation of the first segment is associated with some technical difficulties. Surgical treatment is indicated for patients with symptoms of subclavian artery stenosis, such as manifestations of vertebrobasilar insufficiency and ischemia of the upper limb.
Types of interventions on the carotid arteries and techniques for their implementation
The main types of operations on the carotid arteries are:
- Carotid endarterectomy (with patch, eversion).
- Stenting.
- Vessel prosthetics.
The type of surgical intervention depends not only on the type of damage to the vascular wall, the age and condition of the patient, but also on the technical capabilities of the clinic and the availability of experienced surgeons who are proficient in complex minimally invasive treatment methods.
The most common today is carotid endarterectomy, which is also the most radical, open, requiring the most visible incision. In the USA, more than 100 thousand such operations are performed per year, in Russia - an order of magnitude less, but still the coverage of those in need of treatment is gradually increasing.
Carotid artery stenting has many advantages over open surgery with the same operational risk. Its minimal invasiveness and aesthetics make it more attractive, but not all surgeons have sufficient experience in performing it, so not every patient has a choice, while the time to eliminate a vessel defect is limited. Due to this circumstance, alternative treatment with stenting is performed much less frequently than endarterectomy.
This is interesting: Heart medications: review of basic medications, indications, treatment examples
Prosthetics are indicated for those patients who have a significant lesion that does not allow for more gentle methods. For widespread atherosclerosis, prosthetics are considered the method of choice.
Carotid endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is the main operation to remove atherosclerotic plaque from the carotid artery, during which pathological contents are removed from the lumen of the artery and natural blood flow is restored. It is usually performed under general anesthesia, but local anesthesia with the simultaneous administration of sedatives is also possible.
Carotid endarterectomy is indicated for atherosclerosis, a thrombus in the carotid artery, which causes clinically significant hemodynamic disturbances in the brain, as well as for asymptomatic atherosclerosis, but with significant narrowing of the vessel.
The skin incision begins behind the ear, 2 cm away from the edge of the lower jaw downwards, parallel to it, then it goes along the sternocleidomastoid muscle and is about 10 cm in length. After dissecting the skin and underlying tissue, the surgeon finds the site of division of the common carotid artery, isolates both of its branches and penetrates to the internal one.
carotid endarterectomy (removal of plaque from the carotid artery)
When carrying out the described manipulations, great care is required, the nerves are carefully retracted to the side, and the facial vein is ligated. Having reached the internal carotid artery, the surgeon will try to make as little contact with it as possible with instruments, since careless handling of the vessels can cause damage to the integrity and fragmentation of the plaque, which is fraught with serious embolism, thrombosis and stroke right during the operation.
Heparin is injected into the vessels, they are sequentially clamped, then a longitudinal incision is made into the arterial wall until it penetrates into the lumen. To ensure blood flow to the brain throughout the intervention, a special silicone shunt is placed in the artery. It also prevents blood flow in the area of manipulation on the vessel.
The next stage is direct excision of the atherosclerotic plaque. It is started closer to the site of division of the common carotid artery, then the plaque is peeled off along the entire length from the common carotid artery to its internal branch until a clean and unchanged intima is obtained. If necessary, the inner lining can be fixed to the artery wall with a thread.
Removal of the plaque is completed by washing the lumen of the vessel with saline solution. Washing removes fatty fragments that can become a source of embolism. Restoring the integrity of the vessel is possible using a “patch” made from synthetic materials or the patient’s own tissue.
After all the manipulations on the vascular wall are done, the shunt is removed from its lumen, the surgeon checks the tightness of the sutures, sequentially removing the clamps from the internal and then the external carotid artery. The neck tissue is sutured in reverse order, and a silicone drainage is left in the lower part of the wound.
Eversion endarterectomy is a type of radical treatment of atherosclerosis, indicated for focal changes in the internal branch of the carotid artery in its initial section. After isolating the artery, it is cut off from the common arterial trunk, the plaque is separated, as if turning the vascular wall inside out. After cleansing the ICA, plaques are removed from the common and external branches of the artery, the intervention site is washed with saline and tissue integrity is restored, similar to what happens during a classic endarterectomy.
The advantage of the eversion technique can be considered to be less traumatic and faster, but limitations in its use are caused by the impossibility of removing large plaques (more than 2.5 cm) in this way.
Video: carotid endarterectomy for atherosclerosis
Carotid artery stenting
Stenting is one of the most modern methods of treating vascular pathologies of various locations. The method has undeniable advantages - minimally invasive and minor surgical trauma, the possibility of local anesthesia, a short rehabilitation period, limited to a few days.
However, stenting is not without its disadvantages. Firstly, there are not everywhere surgeons trained in this technique, and there is not enough data to study long-term results due to the novelty of the method. Secondly, after stenting it is difficult to achieve a long-term, lasting effect; sooner or later a re-intervention may be required, which will be much more complex and traumatic than if a classic endarterectomy had been performed initially. The risks of repeated operations increase many times over. The last circumstance concerns pronounced stages of atherosclerosis, at which the effectiveness of stenting is obviously in doubt.
Stenting is considered an excellent alternative to classical or eversion endarterectomy, which successfully removes blockage of the carotid artery by atherosclerotic masses with minimal risk to the patient. The operation is carried out under the control of X-ray angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessel.
The access for stenting is fundamentally different from that of the methods described above. This is a puncture instead of a wide incision, performed under local anesthesia, which gives a chance for treatment to elderly people and with concomitant pathologies that make radical operations contraindicated.
This is interesting: Lipidogram: the essence of the analysis, what it shows, the norm and deviations, how to take it
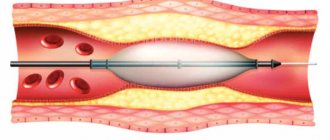
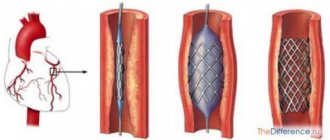
Surgery on the internal carotid artery through stenting begins with balloon angioplasty, that is, the introduction of a device (balloon) that expands the lumen of the artery at the site of its stenosis. Then a stent is inserted into the dilated vessel - a small tube resembling a spring or metal mesh, which expands and holds the lumen of the required diameter.
carotid artery stenting
When a balloon is inserted, there is a risk of destruction of the atherosclerotic plaque with embolic syndrome and the formation of a blood clot in the carotid artery, to prevent which special filters are placed above the intervention site to capture everything that can separate from the vessel wall and migrate into the blood going to the brain.
Arterial replacement
Arterial artery replacement is necessary for patients with widespread atherosclerosis, calcification of the vascular wall, when the pathology is combined with tortuosity, kinks of the artery. Such an operation is carried out when it is known that more gentle treatment will not bring results or will be unreasonably labor-intensive.
During prosthetics, the internal arterial trunk is cut off in the area of the mouth, the affected fragment is removed, the carotid arteries are cleared of atherosclerotic deposits, and then a connection is formed between the remaining part of the internal branch and the common artery with the help of a prosthesis. The prosthesis is a tube made of synthetic materials, the diameter of which is selected individually depending on the size of the connected arteries. The intervention is completed in the usual way with drainage installed in the wound.
How to treat atherosclerotic plaques of neck vessels?
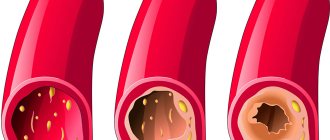
Atherosclerosis is a common pathology of the cardiovascular system. Cholesterol plaques can affect the vessels of the neck, head, aorta, and kidneys. They also distinguish obliterating atherosclerosis, in which low-density lipoproteins clog the vessels of the legs.
One of the most common forms is atherosclerosis of the vessels of the neck and head (ICD-10 code I70). The disease is extremely dangerous, since cholesterol plaques in these bloodstreams often cause cerebral disorders.
Characteristic signs of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head and neck are migraine, noise in the head, dizziness, speech and memory impairment. If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo a differential diagnosis.
Why does cervical vascular atherosclerosis develop?
Atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the neck can develop due to many reasons. According to doctors, the main provoking factor is an unbalanced diet.
If a person consumes an increased amount of animal fats and simple carbohydrates, then a violation of lipid metabolism occurs. Gradually, low-density lipoproteins accumulate in the walls of arteries and veins.
Plaques provoke the development of inflammatory processes. In advanced cases, calcium appears in lipoprotein tumors. As a result, atherosclerotic plaques become denser and significantly narrow the lumen of blood vessels.
Predisposing factors are also:
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Fibromuscular dysplasia and carotid aneurysm.
- Genetic predisposition to stenosis and atherosclerosis.
- Elderly age.
- Gender. What is the connection between atherosclerosis and gender? Men are more susceptible to atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels and arteries due to the fact that testosterone (male sex hormone), unlike estrogen (female sex hormone), does not help regulate lipid metabolism.
- The period of menopause in women. An increased amount of progesterone causes disruptions in metabolic processes.
- High blood pressure and pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Coronary artery lesions.
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2.
Predisposing factors also include obesity and physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of the neck and head
Atherosclerosis is a very dangerous disease, since in the initial stages it practically does not manifest itself at all. Often, the pathological process is detected in the later stages, when cholesterol plaques compress and greatly narrow the lumen of blood vessels.
A characteristic sign of atherosclerosis of the neck and head is headache. It has a paroxysmal dull character. The pain can “radiate” to the upper spine, jaw and back of the head. If blood clots form in the vessels of the neck and head, a person may develop a mini-stroke.
Hemodynamic disturbances in the brain and neck are also caused by:
- Dizziness.
- Decreased memory and mental activity.
- Speech disorders.
- General weakness, irritability.
- Decreased hearing and vision acuity.
- Noise in the head.
- Numbness in the arms or legs.
- In severe cases, plaques begin to stenose the bloodstream. As a result, the patient develops an ischemic stroke.
If timely treatment measures are not taken, compression of the arteries and vessels will lead to cerebral ischemia and even death.
Diagnosis of atherosclerotic lesions
Treatment will be successful at any stage if atherosclerosis is diagnosed in a timely manner. Initially, the patient should contact a neurologist. The doctor conducts an oral interview, studies the patient’s complaints and medical history.
For atherosclerosis of any degree, the patient should undergo a biochemical blood test for low and high density lipoproteins, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. The physician must also calculate the atherogenicity coefficient and draw a conclusion about how atherosclerosis proceeds. Normal values for LDL, HDL, total cholesterol and triglycerides are shown in the table below.
| Total cholesterol level. | Not more than 5.2 mmol/l. |
| Triglycerides. | No more than 1.7 mmol/l. |
| Low density lipoprotein cholesterol. | Not more than 2.6 mmol/l. |
| High density lipoprotein cholesterol. | No more than 1 mmol/l. |
| Atherogenic coefficient. | 3-3,5. |
For moderate or severe atherosclerotic lesions, the patient should undergo instrumental diagnostics. It is mandatory to appoint:
- Ultrasound examination with Doppler.
- Computed tomography with angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography.
- Angiography of the brain.
If necessary, diagnostics can be supplemented with other instrumental methods.
Treatment of atherosclerosis of neck vessels
The goal of treating atherosclerotic lesions is to prevent the development of stroke. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the patient may become disabled due to paralysis.
However, with timely and competent treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Atherosclerotic lesions can be cured in almost all cases with medication.
So, conservative therapy includes:
- The use of drugs that help improve metabolic processes in brain tissue and launch regeneration mechanisms. There are a lot of medicines in this segment. According to reviews from doctors and patients, the most effective medicine in this group is Actovegin.
- Taking pills that lower cholesterol levels reduces the risk of thrombosis and other complications. The most effective statins are Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Simvacard, Atoris, Crestor, Rosuvastatin.
- Using tablets for high blood pressure. Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, sartans can be used. It is advisable to take such tablets if atherosclerosis is accompanied by hypertension.
- Use of disaggregants. These medications prevent blood clots and thin the blood. The most effective antiplatelet agents are Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine.
- Moderate physical activity. It is advisable to do therapeutic exercises, walk more in the fresh air, visit the pool, and do yoga. It is better to refrain from heavy strength exercises.
- Dieting. This is a very significant aspect. If the patient does not eat properly, it will not be possible to normalize lipid metabolism. Fatty sauces, mayonnaise, ketchup, processed foods, fried foods, fatty meats, sweets, and fast food should be removed from the diet. It is also advisable to reduce the amount of salt consumed to 10 grams per day.
Is it possible to cure atherosclerosis of the cervical and head vessels at home? According to doctors, folk remedies will not help in this case. Any decoctions and tinctures can only play a supporting role. So, it is useful to take garlic-based tinctures, rosehip decoction, calendula decoction, potato juice, lemon-honey mixture.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery may be prescribed.
Surgical treatment of atherosclerosis of the brain and neck
For mild degrees of stenosis, drug therapy can be used. But in severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated. The operation is prescribed if atherosclerotic plaques have already provoked a mini-stroke.
The main goal of surgical intervention is to expand the lumen of blood vessels, improve cerebral circulation, prevent stroke and the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream.
There are several methods:
- Carotid angioplasty.
- Carotid endarterectomy.
- Carotid artery bypass.
All surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia. A contraindication to surgical procedures is decompensated diabetes mellitus.
Surgical treatment in 80% of cases helps prevent the development of stroke and normalize blood flow in the brain. After surgical interventions, the patient faces long-term rehabilitation.
TO THE DOCTOR
how can I call you?:
Email (not published)
Subject of the question:
Question:
Operations for tortuosity of the carotid arteries
Surgical treatment of tortuosity or kinking of the carotid artery is necessary when they cause hemodynamic disturbances with symptoms of cerebral ischemia. The operations are aimed at eliminating the changed area through resection with straightening of the arteries (redressing). In difficult cases, when the pathological tortuosity occupies a large area, it is completely removed and the vessel is prosthetic.
Surgery for carotid artery tortuosity can be performed under either general or local anesthesia. The same incision is used as for carotid endarterectomy. The intervention is usually well tolerated by patients and is considered safe.
Carotid endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is a classic open surgery on the carotid artery, the purpose of which is to remove cholesterol plaque. A widely used method of reconstruction is vascular patch repair. After administering a direct anticoagulant (most often, heparin is used) and closing the carotid arteries with a clamp, they are dissected along the anterior wall.
carotid endarterectomy (removal of plaque from the carotid artery)
The next stage is the separation of the sclerotic plaque from the walls of the vessel. After circular release of cholesterol formation, the final part of the plaque is crossed, then released upward. In the external and internal carotid arteries, the plaque is peeled off to the intimal layer, which is then sutured to the vessel wall with a special thread.
The third stage of the operation is washing the vessel with saline solution, along with which plaque fragments are removed - this manipulation prevents the formation of a migrating blood clot in the carotid artery.
The final stage is the closure of the surgical opening in the artery. To create a patch, artificial and biological materials (PTFE, xenopericardium or autogenous graft) are used. The type of patch is selected by the doctor, based on the condition of the vessel walls. The flap is sutured with prolene threads, then the shunt is removed, and the tightness of the patch junction is checked.
The clamps are removed and a clamp is installed at the mouth of the internal carotid artery to allow blood flow through the common vessel. After flushing out small thrombotic formations into the external artery, the clamp is removed. In the restored area, a drainage made of elastic silicone is installed in the area of the lower edge of the wound, after which the tissue is sutured layer-by-layer.
The carotid (carotid) artery is a paired large vessel, which, together with smaller vertebral arteries, is responsible for feeding the brain. Violation of its patency leads to cerebral circulatory insufficiency with the risk of subsequent stroke, and the presence of a protrusion of the wall (aneurysm) is dangerous for rupture.
The only treatment option for severe stenosis and carotid artery aneurysm is surgery. Let's consider the main types of operations on the carotid arteries, their advantages, disadvantages, features of preoperative preparation, rehabilitation period, and possible risks.
- stenosis of the internal carotid artery (ICA) more than 60% in patients who have experienced one or more mini-stroke or have symptoms of cerebral ischemia;
- ICA stenosis 70-99% with asymptomatic form of the disease.
Before plaque removal, all patients undergo a comprehensive medical examination, which includes:
- consultation with a neurologist, surgeon;
- blood test;
- allergy testing for local analgesics;
- angiography of the carotid artery.
To reduce the risk of complications, it is advisable to prepare your body for surgery:
- Quit smoking. Tobacco increases the likelihood of infection, blood clot formation, and slows healing.
- Get rid of extra pounds. This will reduce the load on the heart and facilitate recovery. Be sure to agree on a weight loss plan with your doctor: many well-known methods (certain types of physical activity, taking medications) are contraindicated in patients with cervical artery stenosis.
- Think positively. The psychological state of the patient is very important. After all, stress hormones negatively affect the course of the postoperative period.
There are several methods for performing CA:
- physiology (restoration of blood flow without changing the anatomy of the artery);
- preservation of small vessels with which the damaged area is connected;
- absence of foreign bodies.
- duration;
- narrow specialization: the only indication for performance is the presence of atherosclerotic plaques.
After surgery on the carotid artery, the patient spends several days in the hospital. Usually this period lasts 2-3 days. Patients with high blood pressure after surgery are placed in the intensive care unit. The sutures are removed after 7-10 days. If the postoperative period is favorable, you can return to work in 1-2 weeks.
During recovery it is recommended:
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor with discipline. This will speed up healing and prevent the development of complications.
- Keep the seam clean. For hygienic treatment, hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine are used. The bandage needs to be changed as soon as it gets dirty.
- Do not rub the seam. At first, patients experience a feeling of discomfort and numbness in the incision area. Painkillers can help manage symptoms.
- Stop smoking. Tobacco components create favorable conditions for the formation of blood clots, stroke or heart attack.
- Limit physical activity. For the first few days, try to refrain from even homework. Then gradually increase the load: start walking, working around the house. It is better to postpone sports, especially contact sports.
- Eat regularly and nutritiously. During the recovery period, the body is especially sensitive to a lack of energy, nutrients, and harmful foods. Try to limit your consumption of fatty foods, salt, sugar, flour, and snacks. Eat often, but in small portions. Give preference to plant foods, low-fat dairy products, and fish.
- Don't drive. For your own safety and the safety of others, wait until you start driving. A sudden deterioration in condition may cause loss of control over the machine. Most people begin driving 2-3 weeks after surgery. A longer break is recommended for patients who have had a stroke, a mini-stroke - at least a month.
Carotid endarterectomy is a routine operation that usually occurs without serious consequences. The most dangerous of them is ischemic stroke. The risk of stroke is only 2% and death is 1%.
Minor complications are more common but less dangerous. These include:
- pain, numbness in the suture area;
- bleeding from the wound;
- suture infection;
- nerve damage;
- repeated narrowing of the external or internal artery (restenosis).
Postoperative period and consequences of vascular operations
Usually the postoperative period proceeds favorably, complications are relatively rare. With carotid endarterectomy, the most likely complication is damage to the nerves passing near the arteries - the voice changes, swallowing is impaired, and facial asymmetry appears due to impaired innervation of the facial muscles.
From the side of the surgical incision, suppuration, bleeding, and suture failure are possible, but in the conditions of modern surgery, if all technical requirements for the operation are met, they are unlikely.
There are also some risks associated with stenting. These may be thromboembolism and blockage of cerebral vessels with fragments of atheromatous deposits, the likelihood of which is mitigated by the use of intraoperative filters. In the long term, there is a risk of thrombus formation in the stent area, for the prevention of which antiplatelet agents are prescribed for a long time.
Among the consequences of treating carotid artery pathology, the most dangerous are strokes, which can occur during or after surgery. Modern treatment methods reduce the risk to a minimum, so severe complications are observed in no more than 3% of cases with asymptomatic stenosis and 6% with signs of cerebral ischemia.
Rehabilitation after interventions on the carotid arteries is about three days if the postoperative period is uncomplicated. During this period, the patient is recommended to undergo strict bed rest, then activity gradually increases, but physical exertion and sudden movements should be avoided for at least 2 weeks so as not to cause suture dehiscence.
After treatment, you are allowed to take a shower; it is better to refuse a bath. Lifting heavy objects is prohibited, as are hazardous sports. After stenting, you should drink more fluids to speed up the removal of the contrast agent.
After the rehabilitation stage, the patient is sent home, and within a year will have to see a doctor at least twice. Blood pressure should be measured daily, an increase in which can cause serious consequences, including stroke. A therapist or cardiologist will definitely prescribe antihypertensive drugs for any degree of hypertension.
The need to change the lifestyle and diet of patients is dictated by the presence of atherosclerosis, which has already caused irreversible changes in large arteries. To prevent damage to blood vessels on the opposite side, as well as the arteries of the heart, brain, and kidneys, it is necessary to follow the recommendations that have been developed for patients with atherosclerosis
Operations on blood vessels are extremely complex, and therefore their cost cannot be low. The price for carotid endarterectomy averages 30-50 thousand rubles, in a private clinic it reaches 100-150 thousand. Resection of a vessel segment with tortuosity will require a payment of 30-60 thousand.
Stenting is a much more expensive procedure, the cost of which can approach 200-280 thousand rubles. The cost of the operation includes the costs of consumables, stents, which can be very expensive, and the equipment used.
Consequences and complications
The most common complication after surgery is stroke. The frequency of its development after treatment of atherosclerosis in Israel does not exceed 1%. If the patient complies with all recommendations for anticoagulant therapy, this risk is reduced even further.
Possible consequences of the operation:
- restenosis (repeated narrowing) of the vessel if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed;
- Hoarseness of voice, difficulty swallowing, numbness of part of the neck or face, which goes away on its own within 2 to 3 weeks.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a narrowed blood vessel may require one or more types of tests because the location of the narrowing is not always easy to find. For this purpose, our center uses:
- ultrasound - as the main method - since modern equipment provides maximum information not only about the presence of stenosis, but also the degree of deformation of the vessel, while being a non-invasive safe diagnostic method;
- MRI or CT;
- angiography - thanks to the introduction of a contrast agent, a complex diagnostic device monitors blood flow throughout the body, noting even minor deviations from the norm).
To diagnose atherosclerosis (which is the cause of narrowing), a laboratory method is also used - a blood test.
Risks and consequences of surgery
The risks of surgery are negligible if all precautions are followed and contraindications are carefully studied. So, the chance of death is less than one percent.
Considering the special sensitivity of the brain to ischemia and the complexity of the anatomical structure of the neck and chest, a number of specific complications occur during operations on the subclavian-vertebral segment.
- Stroke intraoperative or in the immediate postoperative period due to embolism, prolonged compression of the artery or acute thrombosis of the anastomosis.
- Damage to peripheral nerves (Horner's syndrome due to damage to the sympathetic trunk, plexitis due to damage to the brachial plexus, paresis of the dome of the diaphragm and impaired swallowing due to trauma to the phrenic and recurrent nerves).
- Reperfusion cerebral edema (the microvasculature, adapted to reduced blood flow, cannot immediately adapt to accept a large volume of blood).
- Other complications (bleeding, lymphorrhea, paresis of the diaphragm dome, pneumothorax, etc.).
- Myocardial infarction or stroke;
- Relapse of the disease (re-formation of plaque);
- Difficulty breathing;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Nerve damage;
- Wound infection.
internal bleeding, trauma in the area of catheter insertion, damage to the arterial wall, allergic reaction, displacement of the stent inside the vessel. In the first days, there is difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, “lump in the throat,” and rapid heartbeat. Gradually, the unpleasant symptoms disappear completely.