What to do if you have recurring heartbeat problems
If you have a history of heart disease, when it begins to beat louder or quieter, there is no reason to rush to the doctor. Likewise, if it is acute and occurs no more than once a week, it becomes more frequent or is accompanied by confusion or dizziness. You should talk to your doctor when abnormal heart rhythms occur frequently and there are also warning symptoms such as signs of an enlarged thyroid gland, weight loss, fatigue or insomnia. Attention : if you begin to faint or a sudden heaviness in your chest is accompanied by nausea and sweating, call an ambulance immediately, you may need emergency help. It could be a heart attack.
What is arrhythmia?
Cardiac arrhythmia is a failure in the correct contractions of the heart muscle (frequency, rhythm, sequence). The disease occurs due to damage to the heart muscle. This is facilitated by a previous heart attack, changes in the balance of water and salt in the body, and a nervous state. Arrhythmia also appears as a consequence of previous diseases in the body. Many experts suggest that arrhythmia does not pose a serious danger to the patient. But there are cases when strong and frequent arrhythmia causes severe damage to health. With prolonged attacks, the heart muscle is depleted, dysfunction of the organ valves occurs, and changes in the size of parts of the heart organ occur.
Folk remedies and emergency care
- As soon as you notice the irregular beating of your “flame motor”, sit down and raise your legs up (placing them on something suitable). Breathe slowly and deeply, allowing your belly to expand with each breath. By focusing on slow, steady breathing, your heart rate will likely quickly return to its normal rhythm.
- If you can’t get back to normal, do the Valsalva maneuver (experience, test). Pinch your nose, close your mouth and try to exhale. Since you will not be able to exhale - your nose and mouth are closed - you will tense up. The brief increase in blood pressure that occurs as a result of such activities should help calm the heart.
- Cough with force. Like the Valsalva maneuver, it increases the pressure inside the chest. Sometimes that's all it takes to restore your normal rhythm. Another way is to pop a balloon, which has a similar effect.
- Take a few sips of cold water. No one knows exactly why this helps, but it often gives immediate results. According to one version, swallowing water causes the esophagus to put pressure on the heart and this “push” restores the rhythm.
- On the other hand, you can not drink, but splash ice water on your face. Such a shock may be enough to perform a healing trick.
How to prevent an attack of arrhythmia?
To prevent paroxysm of atrial fibrillation, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of the cardiologist, follow all instructions and take prescribed medications. Another measure is to eliminate the causes of the disease:
- If a person drinks alcohol, he needs to give up this bad habit;
- When the pathology is caused by other abnormalities in the functioning of the heart muscle, concomitant diseases should be treated - an accurate diagnosis is made by a doctor;
- In case of disturbances due to overload, it is recommended to adhere to a gentle regime, exclude exhausting sports and refuse a work schedule that makes you very tired;
- If deviations are provoked by constant stress and prolonged depression, you will have to take sedatives, protect yourself from negativity, enlist the moral support of relatives, and perhaps visit a psychologist.
The main preventive measure to prevent new attacks is to eliminate the primary source of fibrillations. Most likely, you will have to reconsider your lifestyle and give up bad habits, but without such measures it is impossible to talk about the effectiveness of treatment.
Emergency care for paroxysmal arrhythmia should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor; until the ambulance arrives, the patient is at rest. To avoid complications, the symptoms of an attack cannot be ignored, otherwise there is a risk of even death.
Relaxation techniques to normalize heartbeat
- If there is a problem in question, then it is likely that stress is to blame. In fact, it may be your body's way of telling you that your stress levels have exceeded a safe level. In this case, meditation helps to get back to normal. Take 30 minutes a day to allow your mind and body to relax.
- You can also calm your mind with aromatherapy. Apply a few drops of lavender oil to a handkerchief and inhale its pleasant aroma. Or try rubbing 2 drops of bitter orange oil (also called Seville) into your chest or adding it to water when you take a bath.
- Be sure to get at least 7 hours of sleep every night. Fatigue is another trigger for abnormal heart rhythms.
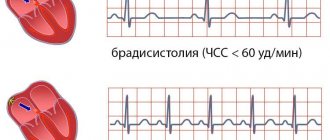
Types and symptoms
| Name | Variety | Characteristic |
| Tachycardia | Sinus tachycardia |
|
| Paroxysmal tachycardia |
| |
| Bradycardia | Sinus bradycardia |
|
| Heart block |
| |
| Extrasystole | Ventricular |
|
| Atrioventricular |
| |
| Atrial |
| |
| Sinus extrasystole |
| |
| Atrial fibrillation | Paroxysmal |
|
| Persistent |
| |
| Chronic |
|
Medicines that may cause the problem
- Many prescription and over-the-counter medications can cause heart palpitations, so always read the package insert before using any product. It may say something like, “do not use this product if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.” Or a specific warning about a drug's side effect may be given. Pay special attention to cold and allergy medications that contain decongestant ingredients. The ingredient that is often implicated in the problem is pseudoephedrine.
- Some bronchodilators for asthma, such as salbutamol (Ventolin), also increase the risk of abnormal heart rhythms. Also look into antihistamines such as loratadine (Claratyne). If you are taking these drugs, ask your doctor about switching to alternative drug options.
- Avoid any diet, product or supplement containing ephedra (also called ma-huang). Products containing ephedra are used to promote weight loss and increase energy levels. However, ephedra can dramatically increase the risk of spikes in blood pressure and heart rate—sometimes with dangerous consequences.
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia
In case of cardiac arrhythmia, the patient is referred for examination to a cardiologist. During the initial examination, the doctor, using hardware examination, confirms or refutes the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist develops a treatment algorithm, which includes medication and traditional methods of treatment. Treatment with drugs is based on the individual diagnosis. Medicines are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease and complex indicators of the body. In mild forms, sedative medications are taken for cardiac arrhythmia. Treatment of more complex forms of arrhythmia takes place under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
Lifestyle changes - how to prevent heart rhythm disturbances
- Practice at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise 3 or 4 times a week. Walking, running and active sports are all excellent choices. Just don't focus too much on improving your previous results or beating your opponent - this will only increase stress. Do the exercises at a pace that allows you to comfortably carry on a conversation.
- Warm up for 10 minutes before each workout and remember to gradually reduce activity within 10 minutes after the main program.
- Any food that causes sudden fluctuations in blood sugar levels can cause your heart to race. If you go crazy over sweet foods, like a drug addict and your engine is racing, try cutting back on sugar and sweets in your diet.
Complications: what happens if help is not provided in a timely manner?
Not in all cases, the attack can be stopped effectively and quickly - for example, according to doctors, in 10% of cases only electric pulses help, and drugs are powerless. What consequences can result from failure to provide assistance to a patient? In case of atrial fibrillation, emergency assistance must be provided urgently, otherwise a change in the intensity of blood flow will occur, and with it an embolism in the atrium.
Negative consequences also develop, such as:
- Pulmonary edema and acute heart failure - the course of the disease is significantly aggravated;
- Hypoxic shock - it is caused by a sharp decrease in pressure and a disruption in the supply of oxygen to organs. Most often, this consequence provokes too frequent muscle contraction;
- Fainting;
- Heart attack or angina - caused by disturbances in coronary blood flow;
- Formation of blood clots - when urgent medication is ignored, and more than 2 days have passed since the onset of the attack, clots form in the blood. They clog blood vessels, leading to death of limbs, gangrene, and stroke.
However, such severe complications are not a reason to panic. It is quite possible to stop an attack without consequences for your health, you just need to not ignore the signs of an attack that has begun.
Supplements to help cope with illness
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Many people with irregular heart rhythms are deficient in magnesium, so try to eat more foods rich in it. These include whole grains, beans and legumes, dark green leafy vegetables and shellfish. If you choose to supplement with this mineral, you will need 300 mg per day. Caution : Do not take magnesium if you have kidney disease.
- Coenzyme Q10. This natural substance is sold over the counter in tablet form. It helps keep the heart rhythm correct. It must be taken in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. The effect does not occur immediately, but after several months.
- Drink 2-3 g of fish oil every day, unless you eat a lot of fish. It is rich in healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Taurine, an amino acid available at pharmacies and health food stores, helps suppress irregular electrical impulses in the heart.
Read other related articles
Causes of atrial flutter
The reasons that cause atrial flutter can be very different, but, as a rule, it develops due to damage to the heart tissue. Anatomical changes are more pronounced in older people, so they are diagnosed more often. Young people suffer from arrhythmia for functional reasons or due to a metabolic disorder.
The difference between atrial flutter and fibrillation (AF) is that they affect the impulse differently
The causes of atrial flutter or AF may include the following heart diseases:
- heart valve disease;
- IHD;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocardial inflammation;
- high blood pressure.
TP also occurs in patients with lung pathologies. Chronic lung diseases (asthma, bronchitis) and pulmonary embolism can cause flutter.
In addition, people with diabetes are also at risk of developing TP. This is also possible if there is an imbalance of electrolytes in the body or if there is an excessive content of thyroid hormones.
If it is ari, for no apparent reason, then we can talk about the idiopathic form of TP, which can be hereditary.
Why does atrial flutter occur? The reason is repeated excitation of the fibers, which should relax after the passage of the impulse, but instead they are subjected to a repeated impulse.
The so-called “repeated circle” occurs due to structural changes and pathologies (inflamed areas, necrosis and scars) that interfere with the normal propagation of the impulse through the heart muscle.
In this case, frequent impulses causing contractions of the atria are not completely transmitted to the ventricles, because the atrioventricular node is incapable of transmitting such frequent impulses. Due to the occurrence of an obstruction, about 1/2 of the impulses are transmitted through the AV node.
This ratio of impulses in the atria and ventricles allows the patient to live, because when all impulses are transmitted through the atrioventricular node, the pulse can reach 250-300. This is fraught with circulatory disorders and severe heart failure.
AFL can also become AF, which is not known to have the ability to transmit atrial contractions to the ventricles in an exact ratio.
The difference in the course of TP depends on the form of blood circulation
Cardiologists divide TP into two types:
- Typical. In this version of TP, the electrical impulse is sent through the right atrium, and contractions reach 340 times per minute. In most cases, the atrium contracts around the tricuspid valve in a counterclockwise direction.
- Atypical. AFL is so called because the impulse travels along an atypical path - through the right or left atrium. In this case, the pulse can reach 340-440.