Causes
The causes of an enlarged heart in a child depend on the type of cardiomegaly. It can be primary or secondary. The secondary course of the disease occurs due to:
- severe toxic injuries;
- past infectious diseases that provoked various heart complications;
- respiratory failure of the lungs;
- acute viral infections.
If we are talking about the primary type of enlarged heart in a child, then the reasons for its occurrence are still not fully understood.
Reasons for the development of pathology
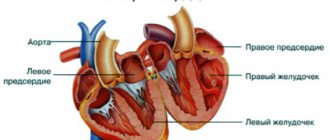
An enlarged heart in an adult is also called myocardial hypertrophy syndrome. Occurring against the background of an underlying cardiac disease, this condition can aggravate the overall clinical picture and worsen the prognosis of the underlying pathology. Enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart is less common than the left; in rare cases, there are changes in the size of both ventricles. According to statistics, against the background of concomitant cardiac pathologies, myocardial hypertrophy leads to mortality in 75-80% of cases. Therefore, timely detection and treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system will be the key to a stable state of health.
The average heart weight in adult men is about 330 grams, in women - about 250 grams; to determine the external size of your own heart, just look at your clenched fist - the volume of the heart is about the same.
This pathology can be detected both in childhood and in adulthood. Athletes are susceptible to myocardial hypertrophy, since during active training the heart is subjected to an inappropriately increasing load, actively pumping blood. The heart muscles become overstrained, an enlargement of the ventricle or even two occurs, and a state of myocardial hypertrophy occurs.
With coronary heart disease, reduced blood flow to the organ occurs. The cells of the main muscle do not receive sufficient nutrition, as a result of which they begin to actively contract, and the process of their degeneration into connective tissue begins. It no longer has the ability to stretch or contract, so only the cavities of the heart can be enlarged.
This phenomenon is most pronounced during myocardial infarction - a certain part of the muscle tissue of the wall becomes inactive, which leads to the formation of a scar in this place.
The most common factors leading to an increase in myocardial size are excessive stress on the heart during heavy physical work, too much activity during sports, bad habits, as well as concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system. To summarize, the main reasons can be identified:
- heart defects (both congenital, hereditary, and acquired during life);
- physical labor and various strenuous sports that place excessive stress on the heart;
- ischemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- abuse of tobacco products and alcoholic beverages;
- excess body weight;
- sudden, unexpected stress on the heart muscle, against the background of an inactive, sedentary lifestyle.
This condition may have a hereditary etiology, that is, transmitted through generations from relatives suffering from cardiovascular diseases. In the presence of such an acquired “inherited” disease as aortic stenosis, arterial hypertension, mitral valve stenosis, a large heart is not such a rare occurrence. Enlargement of the ventricle, or both, occurs under excessive loads, when the organ triggers a compensation mechanism in order to protect itself. As a result, the size of the myocardium is increased.
Carditis, rheumatic carditis are diseases of the heart, which can also lead to the fact that it becomes enlarged against the background of flabbiness of the myocardial muscles, while the ventricles grow in size, and the heart dilates transversely. There have been cases when such a hypertrophied organ occupied both sides of the chest.
Myocarditis is a heart pathology that occurs as a consequence of a severe viral infection. When the disease worsens, the patient feels shortness of breath, becomes lethargic, a picture of general malaise appears, and the heart beats at an accelerated pace. There is an enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart against the background of acute heart failure. This condition also causes myocardial hypertrophy.
Septic endocarditis is considered a dangerous disease because it occurs against the background of infection of the inner surface of the heart by the microbial environment. As a result of infection, the valves, muscles, and left and right ventricles undergo significant changes. The patient suffers from fever, aching joints, increased body temperature (which is often confused with cold symptoms), and the myocardium increases in size.
What symptoms should not be ignored
The following symptoms may indicate an enlarged heart in a child:
- increased heart rate;
- pallor or bluishness of the skin;
- rapid breathing;
- blueness of the nasolabial triangle;
- weak appetite.
Since the heart rate in children is always higher than in adults, it is impossible to say for sure whether your baby’s heart beats often or not. Only a doctor can determine this. But if the pulse is more than 160 beats per minute, then this is clearly not a good signal.
Breathing with cardiomegaly is not just rapid, but also shallow, uneven in inhalation and exhalation.
Pale skin occurs as a result of poor circulation due to poor functioning of the heart muscle and the organ itself.
Diagnostics
If a pathology is suspected, the baby is sent to a cardiologist.
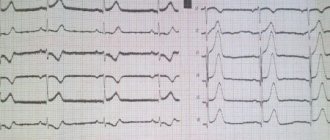
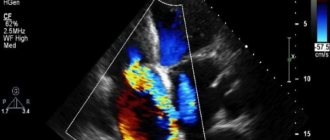
If a baby is suspected of having a pathology, he is sent to a cardiologist, and in difficult cases, even to a cardiac surgery center, where the symptoms will be examined in detail and the nature of the pulse and pressure, the condition of organs and systems will be assessed. For diagnosis, an ECG, ultrasound, phonocardiogram will be taken, and an x-ray of the heart will be performed. In severe and controversial cases, cardiac catheterization is performed, which involves inserting a probe into the heart cavity.
Why is it sometimes impossible to detect congenital heart disease in newborns? As a rule, the reason is the insufficient level of professionalism of the health worker, poor-quality equipment, and structural features of the fetal cardiovascular system, due to which it is impossible to diagnose a number of disorders.
Who diagnoses the disease and how
As a rule, pathology is diagnosed randomly. An enlarged heart in a child is usually detected on x-ray. The resulting image clearly shows the increased size of the main vital organ.
Some changes can also be seen on a cardiogram or echocardiogram. At the same time, the little patients themselves do not experience any unpleasant sensations or discomfort. Such a diagnosis is made against the background of sports activity or other diseases.
If complaints arise and the doctor purposefully orders an X-ray diagnosis of an enlarged heart in a child, then the prognosis is usually unfavorable. This indicates a deterioration of the condition, a severe course of the disease, which in a complicated form can be fatal.
You can perform timely diagnostics at JSC “Medicine”. The clinic is located in the center of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, 10. You can get to it from the metro stations: Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya.
Enlargement of the heart to the left
Hypertrophy of the ventricular walls means an increase in the heart muscle. The following reasons can lead to pathology:
- vices;
- diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- pregnancy period;
- anemia;
- alcohol consumption;
- renal failure;
- irregular training with enlarged heart muscle in athletes;
- rheumatism;
- myocardial infarction.
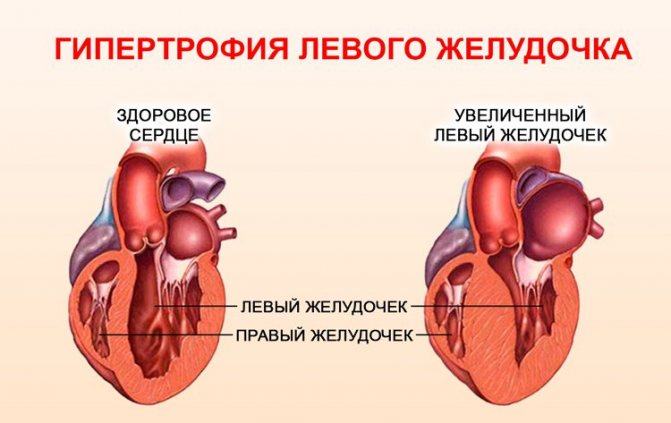
People who are constantly forced to do hard work, these include professional athletes, their main vital organ is forced to work more actively.
Regular increased exercise leads to the proliferation of muscle cells. Fluorography will definitely show that their heart is enlarged to the left in the picture.
Reducing the load to moderate will bring the enlarged organ back to normal. If the amount and strength of the load is not changed for a long time, complications and death may occur.
Changes begin to appear when the load increases regularly. The pathology has no clear signs, but it can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and fatigue;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- feeling of heaviness on the right side under the ribs;
- headache and tinnitus;
- high blood pressure;
- cough for no reason.
Enlargement of the organ to the left is more common, which may indicate diseases such as hypertension, stagnation of blood in the systemic circulation, and various defects. This condition is sometimes called "bull's heart."

What to do with an enlarged heart?
The first thing that worries parents if an X-ray reveals an enlarged heart in a child is the measures that can be taken.
- First you need to pull yourself together and put aside panic. If the disease is detected by chance, and not by diagnosis based on specific complaints and symptoms, then the baby is clearly not suffering, the organ copes with its task normally.
- It is necessary to contact a cardiologist who will prescribe additional studies and diagnostics to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
- Proceed with the intended treatment. The sooner this happens, the greater the chance of a favorable prognosis.
As for the treatment itself, it is prescribed individually, depending on the symptoms, the baby’s well-being, the severity and cause of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of the syndrome requires studying the patient's medical history. Chronic diseases, reasons for recent hospitalizations, medical records, test data, etc. are studied. This includes the appointment of a hardware examination using special equipment.
- Listening and heart rate monitoring.
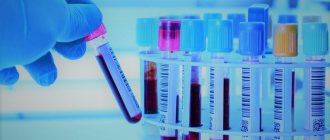
- Blood test for biochemistry.
- Biopsy examination.
- Chest X-ray. It is on x-rays that the boundaries of the expansion of the contours of the organ are clearly visible.
- ECHO KG, because the examination shows when the heart muscle has signs of necrosis or ischemic pathology.
- ECG.
- Ultrasonography.
- A CT scan or MRI will show an increase in the volume of the organ.
- Coronary angiography.
- It is necessary to study hormonal levels, work schedule, attitude to sports and the general condition of the body, since often a harmful lifestyle affects the course of the disease.
Treatment
- Diuretic medications to remove fluid retention.
- Antithrombotic drugs that affect blood clotting, acting against the formation of plaques and blood clots in blood vessels.
- “Heart” tablets (captopril, for example).
- Valve replacement if there is pathology.
- Installation of a pacemaker.
- Antihypertensive drugs for hypertension.
- Hormonal drugs.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in emergency cases, when serious consequences are predicted, in particular, the diagnosis of “bull’s heart”. To correct the situation, a transplant is needed, the operation is expensive and requires a donor organ.
As part of the treatment complex, the cardiologist prescribes compliance with the correct diet, work and rest. Together with drug treatment, this tactic gives a good result.
Correct mode
- Minimize salt and sugar in your diet.
- Avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Walk for 30 minutes a day.
- Measure blood pressure regularly.
- Perform special gymnastics.
Only timely diagnosis increases the chances of effective treatment. Every budget clinic offers methods for detecting the syndrome. This makes it possible to conduct the necessary examinations free of charge and at any time.
What does it show
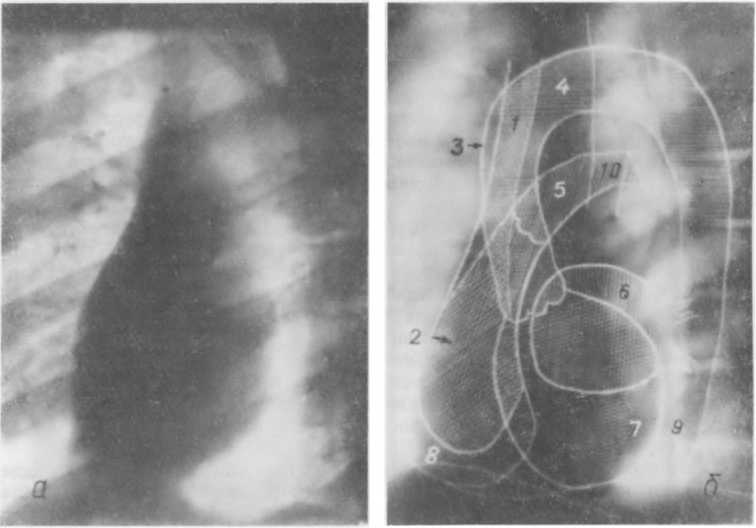
X-ray (a) and diagram (b) of the heart and large arteries (in the left anterior oblique projection)
As a rule, the heart is examined on x-ray in two projections (frontal and lateral), which makes it much easier to understand pathologies, visualize the size, contour of the organ and the vessels extending from it (their anomalies), cardiac arches, configuration and various deviations from the norm. Calcification is easily detected, and the condition of the lung tissue is also assessed.
The presence of scars in the pericardium indicates constrictive pericarditis. The technique makes it possible to detect stretching of the heart chambers, which are the cause of cardiomyopathy, congenital anatomical defects, valve deformations and other pathological conditions.
Note. An enlarged heart may be a sign of insufficiency or abnormal valve function.
Important information when making a cardiac diagnosis is provided by the study of large vessels located in the lung tissue. Quite often, the data obtained is more important than the size and condition of the organ itself.
For example, an increase in the right ventricle will be observed with an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, the latter will be changed in a characteristic way. If signs of edema are detected in the lung tissue, in which fluid accumulates, this inclines the clinician to make a diagnosis of congestive heart failure. The presence of this pathology can also be indicated by the formation of pericardial effusion, which is visible when describing a cardiac radiograph as an accumulation of fluid around the organ.
Visualization of the aorta and other large blood trunks makes it possible to diagnose aneurysms and other vascular pathologies (calcification, atherosclerosis), as well as detect congenital heart defects. The presence of calcium deposits in the lungs is a consequence of an infectious disease or may indicate the presence of carcinogenesis. As a rule, this coincides with dysfunction of the valves, narrowing of the lumen of the main arteries and pathological processes in the pericardium.
X-ray examination plays an important role in monitoring the patient’s condition after cardiac surgery. The doctor has the opportunity to monitor the condition of the implanted implants, whether there are any deviations, for example, accumulation of fluid or the formation of abnormal air spaces. It also monitors the position of the pacemakers, whether there has been any displacement, and so on.
How is diagnosis carried out?
A certain clinical picture, which haunts a person, pushes him to see a doctor.
Symptoms:
- increased atypical fatigue;
- arrhythmia, load on the aorta;
- soreness behind the sternum;
- fainting, dizziness;
- shortness of breath, even if light exertion predominates;
- swelling;
- cough.
Expanding dimensions to the right and left is fraught with dire consequences for the entire system. When the rhythm is disrupted, there is a risk of heart failure. When noise occurs, monitoring by the attending physician is important, because this indicates that the structure of the valves is changing. If the left and right ventricles of the heart are enlarged, the quality and productivity of the entire system decreases. This picture leads to the fact that at a certain point the organ will not be able to pump the required volumes of blood, which provokes failure. By ignoring the problem, you can get a “bull’s heart”.
According to medical practice, establishing an accurate diagnosis is quite problematic. The patient complains of feeling unwell, but the clinic signals other pathologies.
Diagnostic methods:
- radiography;
- auscultation, palpation;
- blood analysis;
- CT;
- caterization.
If the X-ray shows an enlarged heart, the doctor will be able to get his bearings and prescribe therapy in a timely manner. You can't hesitate for a minute.
Interestingly, the x-ray most often shows transformation of the left ventricle.