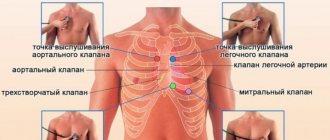
What is a “heart murmur”?
The reason for contacting a doctor, examination and treatment are extraneous sounds that are clearly heard during auscultation. A heart murmur in a newborn baby or at an older age is a specific phenomenon. Extra sounds are clearly audible when listening with a stethoscope. Noises occur during myocardial contraction and during the period of cardiac relaxation.
During the examination, it is possible to identify several variants of extraneous acoustics in the organ:
- organic;
- functional;
- systolic;
- diastolic.
Heart murmur associated with organic pathology is caused by dysfunction of the valve apparatus. This feature is explained by a narrowing of the hole where the valves are attached, or is associated with their inadequate closure.
The danger of the pathology is explained by anatomical features. They can also be observed in various diseases that have a negative effect on the cardiovascular system.
The functional appearance of pathological sounds in the organ occurs in both premature and full-term babies. Systolic murmur occurs when a portion of blood is pushed out of the ventricles into large vessels. Phenomena of diastolic origin appear in the heart when it relaxes. At this moment, the cavities fill with blood. Such sounds are most often considered pathological.
Types of heart murmurs
There are several types of murmurs that are detected in a child’s heart. They can be:
- Congenital and acquired.
- Congenital noises are observed in a baby from birth. Very often they are associated with the presence of heart disease, but can also be explained by the child’s transition to independent life.
Acquired murmurs may appear some time after the baby is born. They are caused by past infectious diseases or developing pathologies in the functioning of the heart.
Functional and pathological.
- Functional noises are usually associated with childhood development, so they are not worth worrying about. They will disappear as they grow older.
Pathological noises require treatment because they indicate illness. It is very important to conduct a thorough examination, identify the cause of the anomaly and choose a treatment method.
Causes of occurrence in children
Abnormal acoustic noises can appear normally or only when the functioning of any organ is disrupted. Their occurrence can be life-threatening if not detected in time. There are several types of causes of heart murmurs in newborns and older children:
- physiological;
- pathological.
The former do not exist throughout life, and under certain conditions they disappear on their own. Noises that appear in infants under the influence of various diseases can only be eliminated with the help of treatment.
Physiological noises
Normally, at a certain stage of life, sound phenomena always appear in a child. Both parents and the attending physician should be aware of this feature so as not to miss the problem. Almost half of the examined children exhibit these phenomena.
- A newborn baby immediately after birth adapts to dramatically changed conditions. His body begins to completely independently provide itself with the necessary beneficial compounds and oxygen. Noises appear especially often in infants of mothers who have had a caesarean section.
- At the age of 4 to 7 years, increased growth begins, and for this reason, cardiac activity becomes most active.
- The last period during which extraneous sounds occur is associated with adolescence. At this stage, this is the norm for a child. Additionally, the influence of excessive physical activity and the work of the vagus nerve are characteristic.
Functional changes are considered a minor problem that occurs in the baby. They reflect the work of the myocardium in systole and do not require medical assistance. During the process of adaptation of the body, they disappear without leaving any consequences.
Minor anomalies in the structure of the heart have a negative effect on the functioning of cardiomyocytes. Congenital changes do not pose a threat to the baby. Features of the anatomy of the respiratory system create conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the organ. Due to slight compression of the cavities, the process of moving blood into the vessels is somewhat disrupted.
Metabolic changes are accompanied by anemia. They manifest themselves by accelerating blood flow. Due to this feature, the body strives to enrich tissues with oxygen and nutritional compounds. When the cardiovascular system is activated, vortices are formed in the cavities of the muscle pump. This symptom in places of turbulence causes a malfunction of the valve apparatus, which is manifested by their inadequate closure.
Pathological noises
In small or adult children, in rare cases, foreign acoustic phenomena are detected in the organ. A more thorough diagnosis allows you to understand the problem. Examination methods make it easier to find the cause of heart murmurs in a child, which most often have a pathological origin.
Diseases and conditions that provoke extraneous sounds in the cavities of the heart include the following:
- cardiomyopathy;
- pericarditis of rheumatic origin;
- the presence of a heart defect;
- rickets;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- inflammation of the endocardium.
The cause of noise, which is of organic origin, is most often associated with rheumatism. The disease affects the valve apparatus with its own cells. They become aggressive, and in the event of an immune disorder, defense mechanisms are directed against the tissues of their own body.
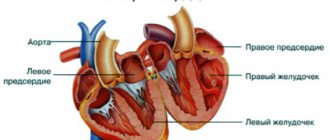
Normally, the left ventricle has a chord. It is a tissue whose task is to connect the opposite walls of the cavity. In rare cases, there is an increase in the number of such formations. They are not life-threatening, but in some children they cause abnormal noises.
A previous sore throat is considered the main disease that leads to the appearance of symptoms of rheumatism. For this reason, it is important to treat it promptly and completely.
Heart defects are always accompanied by extraneous noise. One of the most common is the open duct between the ventricles. The disease can be detected before the end of the baby’s second month of life. An oval window in the septum may not manifest itself for a long time. The main features are as follows:
- loss of consciousness;
- the infant does not eat well;
- weakness that does not go away with rest;
- excessive sweating.
Blood tests and instrumental studies can confirm the diagnosis.
Prognosis and consequences for the baby
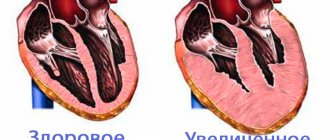
The main consequences for the child are:
- malformations in the development of the pulmonary artery;
- underdevelopment of the pulmonary valve;
- anomalies in the position of the main vessels;
- unclosed gaps in the partitions.
To eliminate these complications, operations are performed, as a result of which the child’s health is restored, he lives a full, long life. Untimely correction leads to the development of secondary immunodeficiency and significantly reduces life expectancy. Registration with a cardiologist, periodic examinations and examinations are required so as not to miss the time when the child will need medication correction.
Cardiologists make cautious forecasts for life and health. Many defects require long-term multi-stage treatment, including physical therapy. Such children are immediately assigned a disability group; their quality of life is often limited.
Methods and timing of diagnosis
If extraneous noise is detected during the examination, the baby is referred for consultation to a cardiologist. Diagnostics include the following:
- inspection;
- auscultation (listening with a stethoscope);
- ECG (Electrocardiography);
- EchoCG (Echocardiography);
- FCG (Phonocardiography);
- MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging).
During the external examination, the condition of the skin is assessed. If the child is one month old or several years old, then the mother is asked if the baby is short of breath. This is indicated by the blueness of the epidermis. During the examination, the boundaries of the heart are determined. This method of diagnosing early detection of pathology is carried out at the stage of the maternity hospital.
During auscultation, the tones and nature of noise in the cavities, which indicate pathology, are assessed. Recording an electrocardiogram gives a picture of the work of the myocardium. Echocardiography transmits sound phenomena that occur during the performance of all functions by the heart muscle.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed from 4-5 months of the baby’s life.
Extraneous sound vibrations disrupt the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. Turbulence in the bloodstream occurs when viscosity decreases, which is associated with the development of anemia. The mild stage of this condition does not pose a health hazard. Timely treatment quickly restores the baby’s body.
Prognosis for the disease
As we have already understood, the prognosis for the life and health of a small patient depends on many factors, including logistical ones. A number of defects are completely corrected after surgical treatment, and the child is cured.
Some defects are subject to multi-stage correction, including several heart surgeries and constant medication. Such children receive a disability group and most often have a severely limited quality of life.
Heart defects associated with severe genetic syndromes and combined with other developmental defects: anomalies of the limbs, brain, and genitourinary system are usually incurable. Most of these patients die in the first months of life or remain deeply disabled. Therefore, genetic counseling of a pregnant woman and high-quality ultrasound screening of the fetus, starting from the earliest stages of pregnancy, play a huge role in the prevention of such defects. In the CIS countries, genetic screening of pregnant women reveals about 76% of pathologies, which is a very good indicator.
Symptoms and signs
Pathological phenomena that are benign in origin, except for the characteristic picture, do not manifest themselves in any way during the examination. There are no negative consequences associated with functional noise in children. They carry organic changes that occur in the heart. They are characterized by the following symptoms:
- accelerated breathing;
- confusion;
- blue discoloration of fingertips, lips, earlobes;
- development slowdown;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- fast fatiguability.
Auscultation makes it possible to hear the main symptom of the disease - pathological sound effects. Normally they should not be in cavities. Over time they can grow. When they become severe, careful diagnosis and treatment are recommended.
Dr. Komarovsky advises that if the symptoms mentioned above appear, contact a pediatric cardiologist. Instrumental and laboratory tests will help to understand the problem. If the condition is functional, then the noise will disappear on its own without therapy.
Treatment
Correction of disorders is required for a child with moderate to severe severity of the disease. If necessary, several directions are used:
- medication assistance;
- surgery;
- traditional methods of therapy.
The first stage is considered to be drug support. At the beginning of the correction, a small dosage is prescribed. If the disease is severe, the patient skips this step and is immediately sent for surgery.
Medication assistance
It is important for children with a heart murmur to take vitamins. Group B is considered the most useful, as it normalizes metabolic processes in the heart muscle. For an infant, the best treatment is breast milk. It contains all the necessary compounds that are needed at this stage of development.
To stimulate contractile function, cardiotonics “Dopamine” or “Dobutamine” are prescribed. If endocarditis is present, antibiotics are recommended for the child. To remove excess fluid from tissues, diuretics are given. Additionally, the treatment regimen includes:
- Riboxin C – restores the heart muscle.
- Cocarboxylase - normalizes the rhythm, improving the tolerability of other medications.
- Cytochrome C – eliminates oxygen starvation of the myocardium.
- Panangin - replenishes the loss of potassium.
If therapy is ineffective, the patient is referred for surgical treatment.
Surgical assistance
When a child is referred for surgery, abnormalities in the structure of the heart are corrected. It is performed openly or using a minimally invasive option. After this, the function is completely restored. In difficult situations, the child requires several operations to solve the problem.
Heart murmurs that are benign in origin are not life-threatening. Organic pathological phenomena disrupt myocardial function, which creates difficulties when performing complex work. Timely treatment eliminates the problem and restores quality of life.
Parents should remember that routine examinations of the child are important for the early diagnosis of diseases. After birth, the body adapts to changed conditions. For this reason, strict control does not make it possible to miss pathologies that are dangerous to the baby’s health.
How to treat a baby
After a full examination, including tomography with contrast, radiography and angiography, doctors establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe targeted treatment. The choice of therapy depends on the identified cause of the pathology and the severity of its course.
To compensate for heart failure, newborns with congenital defects are provided with favorable conditions, placed in an incubator or special closed heated beds.
Such conditions make it possible to remove stagnation of blood in the veins. The initial stages of cardiac dysfunction require reducing the load on the heart muscle and correcting the water and electrolyte balance. The newborn is fed through a tube, removing the effort to suck. At the same time, oxygen therapy is carried out with monitoring the level of gases in the blood. If a serious defect is detected, surgical methods are resorted to.
The baby is prescribed a complex of vitamins B, A, E, glycosides, diuretics, and hormones. Drug therapy is always long-term; drug regimens and their choice for each baby are selected individually. At any stage of pathology development, drug therapy is used for treatment, aimed at improving myocardial nutrition and activating metabolism. These are enzymatic agents Capoten and Captopril, which babies tolerate well. Their interaction with antianginal and inotropic drugs is positive.
Infants are prescribed:
- Cocarboxylase, it normalizes heart rhythm, prevents blood acidification and the development of hypoxic encephalopathy. Improves the tolerance of cardiac glycosides.
- Riboxin, it activates the redox function of the heart muscle, improves its nutrition, and normalizes heart rate.
- Panangin, it normalizes the heart rhythm, upset due to potassium deficiency, improves the effect of oxygen, reduces cardiac hypoxia.
- Cytochrome C, it improves cell respiration and relieves myocardial hypoxia.
- Thiazides - Chlorothiazide, Cyclomethiazide, Veroshpiron are prescribed in long courses.
- Triamterene relieves potassium deficiency.
- Digoxin, it restores and maintains normal heart rhythm.
- Indomethacin, it relieves signs of intoxication due to oxygen starvation of tissues, calcium deficiency, and blood acidification. It is not advisable to combine Digoxin treatment with its use.
To remove excess fluid and relieve stress on the heart muscle, diuretics are prescribed. Their use is effective for symptoms of pulmonary edema. As an ambulance, in acute conditions, a single intravenous administration of Furosemide is used. Each drug is selected individually, especially for the dosage of cardiotonics of non-glycoside origin - Dobutamine, Dopamine, which increase contractions of the heart muscle. Such drugs are given to infants only under the supervision of a cardiologist, who, judging by the baby’s condition, adjusts the dosage of various medications.
Depending on the detected pathology, doctors urgently resort to surgical methods.
This is required in cases:
- valve replacement;
- stent installation;
- squeezing of blood vessels.
As a diagnosis and at the same time as a method of correcting defects of the heart valves, catheterization is performed; this is a minimally invasive intervention that solves two problems at once.
Structural congenital anomalies of the heart and main vessels are corrected using open surgery when it is not possible to use minimally invasive techniques. The result of the operations is complete normalization of the heart. Only complex pathologies require the staged implementation of several operations, but their result is improvement of heart function, stabilization of the baby’s condition, increase in the duration and quality of life.