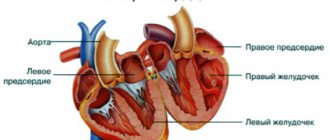
What happens in the child's body?
Tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat.
For adults, the normal heart rate is 80 beats per minute. Due to the higher speed of metabolic processes occurring in his body, a baby has a pulse of up to 140 beats. A heart rate over 170 can be considered abnormal for him. For various reasons, a child’s pulse may increase, and this does not always indicate pathology. Remember yourself - fear, physical activity, violent emotion - and your pulse quickens. You calmed down and everything went away. And the baby also reacts to some external stimuli - swaddling, examination by a doctor, loud sound, and so on. Such outbursts should not frighten parents.
The situation is much more serious if the attack is accompanied by additional symptoms and lasts longer than a few minutes. Tachycardia in newborns is divided into two types - sinus and paroxysmal. Sinus tachycardia is considered a functional disorder caused by a malfunction of certain body systems. Paroxysmal tachycardia is a more dangerous pathology because it is usually associated with organic damage to the heart.
What is bradycardia in newborns
With this disease, the functioning of the heart is disrupted, which can lead to loss of consciousness, and in rare cases, death.
Pulse rate
Factors influencing a child’s heart rate are the physiological characteristics of a growing organism, hormone levels, myocardial development and fitness. Depending on age, these indicators change, and along with them the heart rate decreases.
If the pulse is below the minimum normal values, bradycardia is diagnosed. The lower limit of the normal heart rate for infants in the first days of life is about 80 beats per minute, for premature babies - 90.
Causes of bradycardia in newborns
Bradycardia in a newborn can develop due to various pathologies. Sometimes it appears in the womb as a result of intoxication with certain medications that the mother took. For example, cardiac glycosides.
Age characteristics
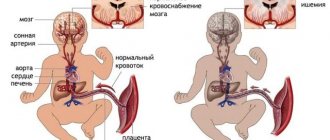
In most cases, the heart rate of infants decreases due to brain injuries during childbirth. Damage leads to obstruction of cerebral circulation and hypoxia. Bradycardia often develops in newborns due to hypothermia and malnutrition.
There are times when a baby's heart rate decreases due to severe fright or during sleep. In such cases, a reduced heart rate is not a symptom of the disease and should not cause concern.
As a child grows, his large vessels and heart may advance or lag behind each other in growth. There is also often an imbalance of hormones, especially those produced by the thyroid gland. As a result of these reasons, bradycardia develops.
When children start school, they are faced with increased stress.
Source
How to act
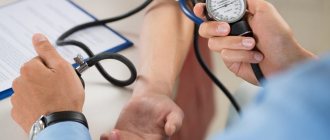
There is no need to regularly check your child's pulse. Moreover, you should not use tonometers (pressure measuring devices) designed for adults with a large cuff for this purpose.
When registering tachycardia on an ECG, you must show this ECG to the doctor who referred you for the study (pediatrician or cardiologist). Since tachycardia is not a disease, its identification requires a medical examination, and, if necessary, additional research to identify the cause of the accelerated heartbeat.
When to see a doctor and how often to get checked
If the child is feeling well and is developing normally, periodic palpitations are not a cause for concern. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- high body temperature, headache;
- dry skin and retraction of the fontanel in infants;
- shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty breathing;
- interruptions in heart function, dizziness or fainting;
- weakness, deterioration in school performance, pale skin and mucous membranes, drowsiness, swelling of the face or legs.
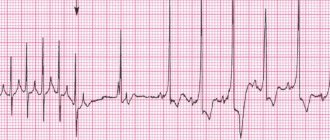
The first way to detect tachycardia in a child is electrocardiography. With sinus tachycardia, the following ECG signs are noted:
- increase in heart rate per minute compared to the age norm;
- all teeth are present;
- the RR interval is shortened due to the shortening of the diastolic pause - the TP segment.
With supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardias, the P wave is negative or not detected at all on the ECG. Ventricular tachycardia is manifested by regular widened QRS complexes without connection with P waves. An experienced functional diagnostics doctor will easily make a differential diagnosis between these conditions.
ECG in children with normal health and absence of heart murmurs is recorded during medical examinations at the age of 1 year, 6 years, 15 and 17 years. The doctor will refer you for a cardiogram if you have complaints of pain in the chest, shortness of breath, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, exercise intolerance, or if a heart murmur is detected.
If tachycardia is registered, the child may be prescribed 24-hour ECG monitoring. This study will provide information on the average daily, average night and average daily heart rate, compliance with age standards, rhythm disturbances, duration of the QT interval and other indicators.
If persistent tachycardia occurs, echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is prescribed. It provides information about the structural condition of the heart, such as minor malformations (patent foramen ovale) or congenital defects.
Pediatric tachycardia: why it is important to recognize the symptoms
Tachycardia in children is no less common than in adults.
This condition can be caused by various reasons, which should be clarified in order to cure the pathology. Cardiologists detect heart rhythm disturbances using certain indicators. In newborns, the heart rate normally does not exceed 110–170 beats per minute, at 1 year – up to 162, one to two years – 154, two to four years – 140, 4–6 years – 126, 6–8 years – 118 , 9–10 years – 108. Experts diagnose the disease if the heart rate exceeds the norm by 20–30 beats per minute.
The heart rate in children is faster than in adults, which is caused by a faster metabolism and increased oxygen requirements. The constant movement of children can also be considered as one of the causes of the disease. Rapid contraction of the heart can occur during processes such as:
- cardiopathy
- anemia
- Congenital heart defect
- thyrotoxicosis
- heart murmur in a child
- dehydration.
In addition to pathological disorders, such changes are often physiological in nature. There is a natural increase in heart rate during physical activity, emotional experiences, and overheating.
Types of tachycardia
In children, pathology can be of two types - sinus and paroxysmal. In the sinus form, there is a strong heartbeat, but the sinus rhythm remains normal. In newborns, this condition is often the norm, as it is caused by increased automaticity of the sinus node.
Sinus tachycardia in adolescents has its own characteristics; this process may have the following reasons:
- increased body growth
- stressful situations
- endocrine or cardiovascular disorders
- physical fatigue.
Paroxysmal tachycardia is a pathological process in which a sharp increase in heart rate is observed. The child’s condition returns to normal as suddenly as it deteriorated. Paroxysmal disorders occur in children of any age; they can occur in both newborns and adolescents. Children aged 5 years are most often susceptible to attacks.
Drugs for the treatment of tachycardia in children
Any type of pathology under consideration should not be deprived of the attention of medical specialists. Any changes in condition can cause extremely negative consequences
Therefore, the health of the baby depends entirely on the timeliness of visiting doctors.
In the case of sinus tachycardia, there may be no need for special therapy. Often it is enough to plan the daily routine, perhaps change the climate, bring the nervous system to a state of rest.
Paroxysmal tachycardia in a newborn must be treated without fail. At the same time, the most common drugs prescribed by doctors to children suffering from this disease are Amiodarone, Digoxin and Izolanide. In simple cases, Novocaine is prescribed in combination with sodium bromide and magnesium sulfate. If such a complex does not give the desired result, it is advisable to use Novocainamide.
Causes
The causes of tachycardia in an infant are different and depend on the form of rapid heartbeat.
The physiological form of sinus tachycardia develops due to the following factors:
- Severe fatigue;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Sharp fear;
- Stressful situations;
- Lack of oxygen (for example, in a stuffy room);
- High air temperature or sudden changes;
- Overheating;
- Increased body temperature.
Tachycardia caused by the above factors does not require special therapy and stops on its own after they are eliminated.
The following reasons contribute to the pathological form of sinus tachycardia in newborns:
- Dehydration of the body;
- Acidosis, hypoglycemia;
- Adrenal tumor;
- Pathology of the central nervous system (encephalopathy);
- Hereditary endocrine diseases (hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus).
Anemia or diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother can affect the development of sinus tachycardia.
The causes of the supraventricular form of paroxysmal tachycardia are:
- Congenital channelopathies are diseases characterized by the formation of additional conduction pathways in the heart; such pathology is observed in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome;
- Increased intracranial pressure due to excess production of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Birth trauma of the central nervous system, intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
Ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia in newborns develops due to the following factors:
- Myocarditis;
- Congenital heart defects;
- Electrolyte imbalance (changes in the level of potassium, magnesium, calcium and sodium in the body);
- Congenital hyperthyroidism;
- Autonomic dysfunction.
At a later age, ventricular tachycardia develops as a result of systemic diseases (rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus) and previous surgical interventions on the heart.
Prevention measures
The prognosis for this disease is favorable in most cases. By getting rid of the cause that causes tachycardia, it is possible to stabilize the heart rate of a newborn baby.
You can maintain heart health with moderate physical activity, proper exercise and nutrition. The baby should not experience strong emotional shocks. A newborn baby should not be overheated or hypothermic, and the risk of contracting viral infections should be avoided.
To prevent a child from getting sick, you need to harden him and strengthen his immune system, and conduct preventive medical examinations. If you suspect tachycardia, your baby should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible, and not try to get rid of it on your own.
Types of disease
| Sinus | Cardiac tachycardia in newborns is diagnosed if the heart rate goes beyond 170 beats per minute. In this case, the attack should be recorded for more than 10 seconds. In some cases, such an increase in heart rate may be the norm (approximately 40% of diagnosed tachycardia in newborns), due to the fact that the sinus node is overly active. For teenagers, sinus tachycardia is also an abnormality worth paying attention to. Basically, the automaticity of the sinus node increases with:
Doctors and parents need to carefully monitor the manifestations of possible concomitant diseases that may be accompanied by tachycardia to one degree or another. Prolonged attacks of sinus tachycardia are dangerous for myocardial metabolism, but if the attacks are physiological, this is a variant of the norm, that is, the body’s adaptation to external influences. |
| Paroxysmal | Disorders of myocardial function are also accompanied by tachycardia, which is called paroxysmal. Basically, this type of tachycardia is divided into ventricular and supraventricular. The main reasons for the development of paroxysmal tachycardia:
Paroxysmal tachycardia usually manifests itself very sharply, and the heart rate can be at around 180-250 beats per minute. The child may complain that he felt a blow to the chest. In some cases, there may be complaints of burning and pain in the chest. Paroxysmal tachycardia is considered, in comparison with sinus tachycardia, more dangerous, since the paroxysmal type of pathology can never be a normal variant. |
Often, two types of tachycardia are diagnosed in children: paroxysmal (ventricular or supraventricular) and sinus. With sinus tachycardia, the direction of the heartbeat wave is normal, but the heart rate increases. This type of disease is most common in newborns.
Immediately after birth, the tone of the sympathetic system prevails over the tone of the parasympathetic system, therefore there is physiological tachycardia.
Sinus tachycardia in older children can be provoked by a number of undesirable factors:
- stress;
- emotional fatigue;
- active growth of the body;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- problems with the cardiovascular system.
Paroxysmal tachycardia is characterized by a sharp increase in heart rate. It is worth noting that such an attack can occur spontaneously in children as young as 10 years old. It also ends quickly; after 15-20 minutes the baby’s condition returns to normal. Weakness and dizziness disappear.
The source of the impulse in paroxysmal tachycardia is any other part of the heart other than the normal pacemaker.
Sinus tachycardia in a child is a disease directly related to a sharp increase in heart rate. It should be noted that tachycardia is not considered pathological if it occurs in children aged 6-7 years. If the manifestations of the disease do not bother the baby, treatment is not required.
Doctors say that sinus tachycardia often occurs in children for the following reasons:
- congenital heart failure;
- hypoglycemia;
- deviations in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- anemia;
- myocarditis, etc.
How to recognize and treat sinus arrhythmia in a child
In children over 10 years of age, the manifestation of the disease is provoked by the following reasons:
- stressful situations;
- thyroid diseases;
- disproportionate physical activity;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and central nervous system.
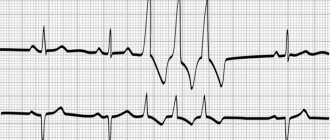
Sinus tachycardia in children is clearly visible on the ECG. The teeth and the distances between them allow the cardiologist to make an accurate diagnosis. Sinus tachycardia is characterized by the appearance of the following clinical symptoms:
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- pain without clear localization in the heart area;
- dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- darkening of the eyes.
Such symptoms are associated with insufficient enrichment of tissues with oxygen against the background of an accelerated heart rate.
It should be borne in mind that tachycardia often manifests itself with various symptoms, and treatment will differ depending on this. Selecting a drug for therapy on your own is prohibited; at best, the medication will not bring benefit, at worst, it will cause harm.
Paroxysmal tachycardia is a condition in which a child’s heart rate increases; such an attack can end after several hours or several minutes. In a 1-year-old child, the pulse during this period of time can reach 200 beats per minute. At the time of an attack, specific changes are monitored on the ECG.
There are two forms of paroxysmal tachycardia:
- ventricular;
- supraventricular
A supraventricular attack is characterized by a sudden onset. The baby feels a rapid heartbeat and weakness, and the following symptoms may also be present:
- pale skin;
- increased sweating;
- polyuria (increased amount of urine produced);
- swelling of the veins in the neck;
- nausea.
Prolonged attacks are accompanied by a significant decrease in blood pressure.
Ventricular tachycardia is more dangerous. It is quite difficult to determine the moment of the onset of the attack. At this moment, the baby is in serious condition, the veins in the neck are pulsating weaker than the veins in the wrist. Chronic ventricular tachycardia causes hemodynamic disturbances. This condition can be called life-threatening. Ventricular fibrillation and circulatory failure are possible.
It is worth noting that, regardless of the type of tachycardia in children, it is necessary to consult a doctor in all cases. Only a specialist who has assessed the state of the baby’s heart based on the ECG results will be able to determine the need for further therapy, as well as select a truly effective drug.
Treatment of pathology
Emergency help
During an attack, you must follow these recommendations:
- let fresh air into the room;
- cover the child's forehead with a cold towel;
- contact a specialist.
If tachycardia is of the paroxysmal type, then first aid depends on the location of the origin of the abnormal impulse. For the supraventricular form, the following steps must be taken:
To alleviate his condition, the baby should push with his nose closed.
- Child 3-4 years old: close the baby’s nose and ask him to push;
- massage the carotid artery.
- press on the root of the tongue;
If an attack of the ventricular form occurs, then help is provided with drugs:
- Intravenous administration of "Lidocaine 1%" approximately 1-1.5 mg/kg.
- If the attack does not subside, then you need to administer a solution of Gilurythmal 2.5%, diluted with 10-20 ml of sodium chloride 0.9% in an amount of 1 mg/kg.
- If the attack continues, Amiodarone 5% diluted with glucose 5% is administered - 10 ml.
Medicines
Treatment of tachycardia in children with medication is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor, who can adjust the dosage and course of therapy depending on the patient’s condition. Frequently prescribed drugs are presented in the table:
| Group | Drugs |
| Sedatives | "Seduxen" |
| "Luminal" | |
| "Valerian" | |
| "Asparkam" | |
| Potassium-containing | |
| Cardiac glycosides | "Digoxin" |
| "Verapamil" | |
| Beta blockers | "Pindolol" |
Surgery
Sometimes a patient's problem can be solved with the help of a pacemaker.
If other treatment options have not brought positive results, the attending physician may decide to perform surgery. Surgical procedures for tachycardia:
- Radiofrequency ablation. The method is based on the destruction of areas that supply the wrong impulse.
- Introduction of a pacemaker. An artificial pacemaker maintains the correct heart rate.
- Heart valve surgery. The operation is performed if there are certain congenital abnormalities.
Healers' recipes
Mild sinus tachycardia is treated with alternative medicine methods. Any influences can be carried out only after consultation with a specialist. Effective recipes:
- Motherwort infusion. One tbsp. l. dry herbs should be steamed with 1 cup of boiling water and left for 60 minutes. Strain the mixture, add 3 drops of peppermint oil, 1 tsp. honey The composition must be mixed and drunk. The course of therapy is 30 days.
- Valerian root decoction. Two tsp. The root is mixed with 1 teaspoon of dry dill, lemon balm, and hop cones. The mixture is poured with 350 ml of boiling water and left for half an hour. Drink 200 ml of the decoction before meals.
- Herbal collection. Mix 10 grams of horsetail, motherwort and hawthorn and add 0.5 liters of water. The mixture is heated in a water bath for 20 minutes and then cooled for 50 minutes. The strained tincture is taken 50 ml 4 times a day.
Classification of tachycardia
Considering the reasons that caused the increase in heart rate, tachycardia in children is divided into types.
Doctors divide childhood tachycardia into three types, depending on how much the baby’s heartbeat increases. Mild sinus tachycardia, when the heart rate increases up to 20%. With average, the myocardium contracts faster by 20-40%.
Severe tachycardia is recorded when the pulse becomes 50-60% higher than normal. At the same time, we note that the heart rate norms for children of different ages are different. The limit pulse for an infant is 170 beats per minute, for a 10-year-old child – 108 beats. Sinus tachycardia is divided into 2 subtypes:
- Adequate - possible in case of infectious diseases, exercise or stressful situations. It is not constant and short-lived.
- Inadequate - occurs at rest, does not depend on physical activity, use of medications or stress. Accompanied by a lack of air and a feeling of palpitations in the throat, weakness, and dizziness.
Features of the course of pathology in childhood
Like other diseases, tachycardia depends not only on the general condition of the body, but also on age-related characteristics. Parents need to know about the first signs of the disease in order to provide timely help to their child. These are common symptoms that occur regardless of age:
- pulsation of the veins located in the neck;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- moodiness;
- sleep disorders.
Normal heart rate in children
Newborns lose their appetite and may cry constantly. Also, the baby's lethargy should cause suspicion.
In newborns
In children of the first year of life, the heart rate is significantly higher than in an adult. A symptom of the disease is a pulse exceeding 160 beats per second. Since young children cannot tell their parents that they are feeling unwell, adults must be as observant as possible.
At this age, the most dangerous type of pathology is paroxysmal. In most cases, it is accompanied by geodynamic failures and serious conditions of the baby.
If seizures occur for a long time, newborns may develop heart failure. And sudden changes in heart rate can trigger cardiac arrest.
In young children
Episodic manifestations of the disorder in children under 5 years of age are considered normal. This is directly related to a lack of oxygen or accelerated metabolism. Since children cannot always describe symptoms and changes in their body, repeated attacks can be avoided through long walks in the fresh air and a properly balanced diet.
In preschoolers and children of primary school age, pathology can be triggered by worries, fear, stressful situations or infectious diseases.
Treatment of tachycardia attacks
Accompanied by the disease:
- dizziness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- attacks of angina pectoris;
- sudden mood swings.
In teenagers
An increased heart rate during puberty may indicate the presence of serious illnesses or be the result of a teenager’s increased temper. At this age they are too impressionable and take everything to heart. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after examining the child.
Experts identify a number of physiological reasons that can lead to the development of the disease in adolescents:
- age from 14 to 16 years. During this period, children grow quickly, the heart becomes larger, and the blood vessels do not have time to enlarge;
- sports, if the child pays a lot of attention and effort to physical activity;
- binge eating.
Elevated leukocytes in a newborn: symptoms and treatment of leukocytosis
A blood test is taken from children immediately after birth. This is done in order to find out exactly about the baby’s condition and, if necessary, take some measures. Unfortunately, it is now not uncommon for a newborn to have elevated levels of leukocytes in his blood. This is scary for new parents.
Leukocytes: description and functions
Before moving on to why a newborn baby may have elevated white blood cells in the blood, it is necessary to learn in more detail what these cells are and why they are so important.
Leukocytes, or as they are commonly called, white blood cells (which are actually transparent), protect the human body from external influences. A leukocyte can reach a size from 6 to 20 microns, and all of them can be of different shapes, both regular round and uneven.
There are many white blood cells in the human body, each of which can perform different functions. For example, some protect the body from antigens, others from bacteria and microbes, others from dead cells, etc.
But if bacteria or microbes enter the newborn’s body, or, for example, the child is injured during childbirth, then they will increase sharply, which can be seen from the results of a blood test taken from a finger.
Decoding: norms and deviations
If the birth went well and there were no injuries (or the possibility of infection), then most likely the newborn's white blood cells will be normal.
White blood cells in the blood are considered normal for a newborn child at a level of 9 to 30, which is much higher than that of an adult.
If we talk about deviations, then everything above 30 will be considered increased, and everything below 9 will be considered decreased. But if doctors rarely encounter a low level of leukocytes
Source
iserdce
Types of tachycardia in children and its causes
Tachycardia in a child can be of two types: sinus and paroxysmal. Sinus tachycardia is divided into physiological and pathological (extracardiac and cardiac).
Sinus tachycardia
Physiological tachycardia can occur with emotional stress, transition from a lying position to a standing position, changes in the microclimate, fear, or excessive intake of food and liquid. The causes of tachycardia in infants may be due to a violation of the automatism of the sinus node; it is the pacemaker - it sends an impulse and sets the frequency with which the heart muscle contracts. In a teenager, the cause may be accelerated growth of the body, overwork, chronic lack of sleep, and endocrine changes.
Pathological extracardial tachycardia occurs when the body changes: increased body temperature, toxicosis due to infectious agents, low blood sugar, hypoxemia (lack of oxygen in the blood), which manifests itself in anemia, respiratory failure. The cause may be acidosis - when taking certain medications, chemicals, poisoning, uncontrollable vomiting. Endocrine disorders - thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, tumor processes of the hypothalamus often cause this disorder.
Cardiac tachycardia appears as a signal of organic damage to the sinus node. This is the first sign of inflammatory processes in heart tissue - myocarditis, endocarditis and pericarditis, ischemic processes - ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, degenerative sclerotic changes - myocardial dystrophy, myocardiosclerosis. This type of accelerated heartbeat is characterized by a constant elevated heart rate at rest, independent of the state of the body and the environment.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
This type of pathology can affect both a one-year-old child and a 14-year-old teenager. It occurs equally often in different groups of children. More often than others, paroxysmal tachycardia is diagnosed in children aged 7 years.
Cardiac tachycardia is characterized by a sudden onset and an equally abrupt cessation. The reason for this is the appearance of a new impulse in addition to the sinus node.
The causes of paroxysmal tachycardia are:
- WPW syndrome
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia with sympatho-adrenal crises
- Neuroses due to damage to the central nervous system
- Organic disorders (see cardiac tachycardia)
Symptoms and treatment of tachycardia in children of different ages are somewhat different and depend on its type, which can be explained by physiological changes in the body that are characteristic of each age group.
First aid for a child
The sudden appearance of an attack of tachycardia in a child requires immediate action on the part of adults:
- provide access to fresh air - open the window, take the patient outside,
- place a cool wet towel on your forehead,
- call an ambulance.
Further actions will depend on the location of the tachycardia focus and the age of the child. The doctor will determine whether it is necessary to give any medications or whether it is enough to carry out special exercises to stop the attack.
Possible complications and consequences of the disease
- congenital pathologies;
- heart murmurs;
- anemia;
- dehydration;
- myocarditis;
- hypoglycemia;
- damage to the central nervous system (CNS).
Also, sinus tachycardia can appear for physiological reasons: the child’s anxiety during the examination, stress due to swaddling, severe pain, overheating. In most cases, sinus tachycardia in newborns is a completely normal condition that does not pose a threat to their life.
Sinus node tachycardia in newborns is divided into 3 types:
- moderate (heart rate up to 20% above normal);
- average (exceeding heart contractions by 20-40%);
- pronounced (increase in heart rate up to 60%).
The symptoms of sinus tachycardia in children are exactly the same as in adults:
- cardiopalmus;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- dyspnea;
- pallor.
Only a neonatologist can detect the disease in a newborn in the first days after birth. In an infant, sinus tachycardia is determined by a pediatrician during an examination. If such a suspicion arises, then the doctor will then prescribe a detailed study to confirm the diagnosis. The most informative is the electrocardiogram (ECG). This study allows you to accurately and quickly determine the frequency and rhythm of contraction of the heart muscle.
Infants may also be prescribed an echocardiogram or also called an ultrasound of the heart.
To identify the full picture of the disease, blood tests are often prescribed: a general blood test and an analysis for the presence of thyroid-stimulating hormones.
Sinus tachycardia during the newborn period, provided that it goes away within a few days, does not leave any consequences.
Despite the fact that sinus tachycardia in newborns in most cases is a completely normal and benign process, doctors still take the child under special control. Normally, the disease should go away within a few days after birth. If this does not happen, then the child is registered with a pediatrician and cardiologist.
If tachycardia is caused by temporary phenomena, for example, high body temperature, then it is necessary to urgently bring it down and prevent it from increasing in the future.
What will the doctor do?
Treatment of sinus tachycardia is primarily aimed at identifying the cause of the disease and its elimination. If this is a temporary phenomenon, for example, a child’s reaction to swaddling or stress during an examination by a pediatrician, then treatment is not required.
More serious causes of the disease (heart failure, diseases of the endocrine system) require treatment. To do this, the pediatrician gives a referral to specialized specialists (cardiologist or endocrinologist).
There is no way to prevent the occurrence of sinus tachycardia in newborns. And during the infant period, this can be done by carefully monitoring the child’s health. The best prevention of the disease is its early detection and treatment. It would also be a good idea to teach your child a healthy lifestyle from an early age.
The worst consequence of the disease can be death.
What is bradycardia in newborns
With this disease, the functioning of the heart is disrupted, which can lead to loss of consciousness, and in rare cases, death.
Pulse rate
Factors influencing a child’s heart rate are the physiological characteristics of a growing organism, hormone levels, myocardial development and fitness. Depending on age, these indicators change, and along with them the heart rate decreases.
If the pulse is below the minimum normal values, bradycardia is diagnosed. The lower limit of the normal heart rate for infants in the first days of life is about 80 beats per minute, for premature babies - 90.
Causes of bradycardia in newborns
Bradycardia in a newborn can develop due to various pathologies. Sometimes it appears in the womb as a result of intoxication with certain medications that the mother took. For example, cardiac glycosides.
Age characteristics
In most cases, the heart rate of infants decreases due to brain injuries during childbirth. Damage leads to obstruction of cerebral circulation and hypoxia. Bradycardia often develops in newborns due to hypothermia and malnutrition.
There are times when a baby's heart rate decreases due to severe fright or during sleep. In such cases, a reduced heart rate is not a symptom of the disease and should not cause concern.
As a child grows, his large vessels and heart may advance or lag behind each other in growth. There is also often an imbalance of hormones, especially those produced by the thyroid gland. As a result of these reasons, bradycardia develops.
When children start school, they are faced with increased stress.
Source
Why do you feel dizzy at normal blood pressure?
Many people who have experienced sudden onset of nausea and dizziness have measured their blood pressure and found that it is normal.
When dizziness and nausea may occur at normal blood pressure:
- with a sudden change in body position, tilting the head down;
- during severe psychophysical stress, sudden stress;
- during changes in atmospheric pressure, magnetic storms;
- when being in a stuffy, hot room, motion sickness in transport.
If attacks are repeated frequently and are accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness, you should urgently consult a neurologist. After you have been examined and diagnosed, your doctor will prescribe medication. This must be done, since nausea and dizziness can occur with very serious diseases that must be identified, and not just removed from the symptoms.
Possible causes of dizziness and nausea at normal blood pressure:
- spasm of cerebral vessels;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arthritis, cervical osteochondrosis;
- starvation;
- diabetes;
- oncological brain tumors;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- oxygen starvation, anemia.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. After examination and prescription of medical therapy, you need to complete the full treatment course and repeat it if necessary.
If you have been prescribed a special therapeutic diet, you may have to completely change your diet and engage in physical therapy.
How to help yourself or your family at home:
- lie on the bed in a cool room;
- place a small soft cushion under your head;
- do not move your head, look at one point;
- drink lemon, mint or chamomile tea;
- measure blood pressure and pulse rate;
- put “Glycine” or “Corvalment” under the tongue.
- If, in addition to dizziness and nausea, you feel numbness in your limbs, severe headache or heart pain, and the attack does not go away after 10–15 minutes, you need to call an ambulance to avoid serious complications.
What causes nausea and dizziness with low blood pressure?
There are cases when people with low blood pressure were never bothered by it, and they learned about their hypotension after purchasing a tonometer or undergoing a medical examination. This condition does not require drug therapy and is not considered a disease.
Unfortunately, some people with low blood pressure may experience sudden attacks of dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, coldness, or numbness in the extremities. Sometimes in severe cases, fainting may occur and coordination of movements may be impaired. Such symptoms cannot be ignored; they require a thorough examination.
What can cause nausea, vomiting and dizziness with low blood pressure:
- Inflammatory processes of the stomach, liver, pancreas, kidneys, large and small intestines.
- Prolonged malnutrition or fasting, low hemoglobin.
- Parasitic infection in internal organs or blood.
- Internal bleeding, stomach, uterine, intestinal.
- Food poisoning or chemical intoxication.
- Oncological diseases, leukemia and other blood diseases.
- Radiation exposure, heat or sunstroke.
Do not forget that a simple lack of sleep, watching news and traumatic films before bed, alcohol and nicotine intoxication can also cause dizziness and nausea.
When you feel sick and dizzy with high blood pressure
Nausea, vomiting and dizziness in hypertension are very alarming signs and require immediate medical attention. In the initial stage, patients with hypertension experience a dull, arching pain in the back of the head or temples, flashing spots before the eyes, and mild nausea without vomiting.
When the disease has progressed to the late, third stage, pain in the heart area and tachycardia occur. Vision may deteriorate sharply due to impaired blood supply to the retina, so you need to be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist.
If you suddenly feel dizzy, have nausea or vomiting, or severe weakness - these are clear signs of a hypertensive crisis, you need to quickly take the pills prescribed by the doctor to lower your blood pressure and call an ambulance.
Why does nausea and vomiting begin with a sharp rise in blood pressure?
With high blood pressure, a person sometimes experiences panic fear before an attack. This causes a sharp release of hormones - adrenaline and cortisol, which cause an increase in the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure also increases sharply, and the risk of vascular rupture and cerebral hemorrhage increases. Therefore, the body, through vomiting and frequent urination, tries to reduce the amount of fluid in the vascular system.
When to call an ambulance:
- If nausea and vomiting appear against the background of high blood pressure.
- There was severe weakness, coldness and numbness of the limbs.
- When you try to smile, you can see a curvature of the facial muscles to one side.
- Very severe headache, sharp deterioration of vision, unclear speech.
Such attacks should not be neglected under any circumstances; this is one of the symptoms of an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, in which any delay and attempts at self-medication can lead to death or disability. If a person is provided with first aid in a timely manner and quickly taken to the hospital, he can be saved!
What to do if you suspect a stroke before the ambulance arrives:
- be sure to check for breathing;
- Clean your mouth with a napkin to make breathing easier;
- in case of severe vomiting, put the patient to bed or sit down;
- turn your head to one side and slightly raise it; when sitting, tilt it slightly down;
- if possible, measure the pressure;
- put a cold compress on your forehead;
- put Nitroglycerin under your tongue;
- if there are no tablets, immerse your feet in hot water;
- Do not give anything to drink or eat under any circumstances!
Remember, these simple techniques could save your or someone else's life!
Diagnostic methods
In order to identify a possible disease as soon as possible, the doctor will try to find the root cause of the disorder in the functioning of the heart muscle and prescribe a series of diagnostic tests. First of all, this is the collection and analysis of the patient’s medical history in order to determine whether the child has chronic diseases that can affect the heart rhythm. The doctor also needs to be told about the medications that the little patient is taking. After this, the baby will need to undergo blood tests, this will help to find out if the baby has anemia and whether everything is in order with the hormones. It will be necessary to make an electrocardiogram of the heart in its normal state and undergo a stress ECG. If the cause is physiological, then treatment for tachycardia may not be required.