Diabetes provides many prerequisites for the development of secondary hypotension: fluctuations in glucose levels and its toxic effects with insufficient compensation, reduced levels of vitamins and minerals in the body, side effects of certain medications. These are only the most basic reasons that trigger the pathological mechanism. Also during hypoglycemia, a sharp decrease in blood pressure occurs.
Why is low blood pressure dangerous?
Low blood pressure is a condition in which the readings are 20% below the established norm. This is below 90/60.
During a decrease in pressure, symptoms such as general weakness and drowsiness, excessive irritability, and weather sensitivity appear. Possible memory deterioration or absent-mindedness, which is explained by a lack of oxygen supply to the brain. Thermoregulation is often impaired (cold extremities or a general decrease in temperature to 36 degrees). With a decrease in pressure, patients report headaches in the frontotemporal and frontoparietal regions. Dizziness and nausea may occur.
Hypotension is dangerous because it has an aggravating effect on the development of existing complications associated with
vascular system. First of all, as with hypertension, there is a danger of thrombosis and blood stagnation. The regeneration process is worse, which has a detrimental effect on the healing of diabetic ulcers and the development of diabetic foot syndrome. Also, the deterioration of oxygen supply to cells at low pressure affects the entire body as a whole and greatly affects the nervous system in particular.
What to do if hypotension occurs? Since we are talking about secondary hypotension, which develops against the background of the underlying disease - diabetes, the main attention in therapy should be directed to compensation. Improved compensation later
will lead to normalization of pressure.
Rarely does the fight against hypotension begin with drug therapy. Usually they start with changing their lifestyle: changing their diet and prescribing adequate physical activity. Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed. Herbal stimulants (tincture of eleutherococcus, aralia, lemongrass, ginseng) can also be used.
The doctor may also prescribe drug therapy based on individual indicators.
In any case, if you experience hypotension, be sure to consult a doctor. In the first stages it is much easier to deal with negative consequences. Track your blood pressure and keep a special diary; this will help you notice changes in time.
People who suffer from diabetes have to deal every day with various complications that arise due to their illness.
One of the most common complications is constant pressure surges. Blood acts on blood vessels through a force called blood pressure.
Due to an imbalance of glucose, diabetics have a peculiar blood viscosity, which is why their blood pressure “jumps.” As a result, heart disease and anomalies occur, sometimes even strokes (read what this means in this article). Therefore, patients should carefully monitor their blood pressure to avoid chronic heart disease.
Reasons for low blood pressure
There are many reasons for low blood pressure (hypotension) in diabetics, which do not always depend on the person’s lifestyle and behavior, so it is better to list each of them.
Disruption of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). As a rule, it is congenital. This is a big problem for diabetics, because without monitoring the ANS, they are at great risk to their health, not so much because of diabetes, but because of the impaired functioning of the ANS that affects it. For such people, low blood pressure is the norm, which means that constant heart pain due to diabetes also becomes normal.
Cardiac dysfunction (symptom of heart failure). This is one of the most serious problems - diabetes mellitus itself can have a detrimental effect on the heart, and if there are old problems with the latter, a vicious circle appears: a diseased heart lowers blood pressure - low blood pressure makes diabetes mellitus more difficult - diabetes worsens the functioning of the heart.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type. Here you should pay attention to the work of the kidneys - they produce stress hormones, which cause “jumps” in pressure.
Hypotension can also be caused by:
- Exacerbation of a stomach ulcer, an attack of pancreatitis or bleeding.
- Chronic fatigue, stress, depression.
- Heatstroke.
- Changes in atmospheric pressure.
- Lack of vitamins C, E and B.
If a diabetic does not have the above problems, and the blood pressure is constantly low, you need to pay attention to the medications you are taking.
It is possible that the patient has a personal intolerance to some component in the prescribed medication. You should consult a doctor to determine which element the diabetic is allergic to.
How to increase blood pressure?
You need to fight low blood pressure, because it also reduces blood pressure, and as a result, tissues are destroyed.
Ways to increase pressure:
- Drink tea in the morning on an empty stomach, green is best - it invigorates no worse than coffee and does not affect the functioning of the heart in any way.
- Take half a tablet of ascorbic acid + two tablets of extra green tea.
- Add ginseng in an amount of no more than 30-35 drops to a glass of juice (preferably grape juice) or water.
- Contrast shower in the morning.
- You can eat a small piece of salty cheese.
- Taking a natural tonic: Eleutherococcus, Leuzea, Schisandra, ginseng. 20 minutes before meals, 20-30 drops are taken 2-3 times a day. It is better to dissolve them in half a glass of water.
- Drink plenty of water (especially in hot weather) throughout the day.
- Massage, vigorous rubbing of the muscles of the legs, lower back and abdomen.
Low blood pressure in diabetes (hypotension)
The main problem that is associated with hypertension is the asymptomatic nature in the initial stages. For this reason, many people forget to control their blood pressure, which leads to serious problems in the future. But the most common signs of high blood pressure may include:
- Constant headaches;
- Dizziness;
- Vision problems.
However, in most cases there are no symptoms of hypertension.
A symptom of hypertension can be persistent headaches.
Low blood pressure due to diabetes mellitus most often occurs in the fairer sex. And if in ordinary life hypotension does not frighten a person too much, then for a diabetic this pathology hides real threats.
| Causes of low blood pressure in diabetes | Possible complications of hypotension |
|
Low blood pressure, like hypertension, is asymptomatic in most cases. Some patients closely monitor their health and notice the following problems:
- Constant feeling of weakness and drowsiness;
- Labored breathing;
- Coldness in the extremities;
- Heavy sweating;
- Dependence on weather conditions.
The problem of hypotension is mainly caused by a reluctance to lead a healthy lifestyle, so its solution lies not only in the hands of doctors, but also in the hands of the patient himself.
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking medications for hypotension, as many medications affect your blood sugar levels. As a rule, tonic drugs are prescribed, such as Leuzea, Eleutherococcus and others. Drug treatment can be combined with folk remedies:
- 2 tablets of green tea extract 1 tablet of ascorbic acid;
- 30 drops of ginseng in a glass of water or grape juice;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of blood-red hawthorn juice: take 30 minutes before each meal;
- Using essential oils of bergamot, orange, lemon, clove, spruce, eucalyptus (you can add 2-3 drops to an aroma lamp or 6-8 drops to a warm bath);
- Take 25 drops of hawthorn tincture an hour before each meal;
- Green tea with the addition of Chinese lemongrass juice;
- Pour 1 tablespoon of hare cabbage leaves into 300 ml of boiling water and leave for 4 hours. Take before meals 3 times a day.
Beta blockers
These drugs block beta-adrenergic receptors, preventing catecholamines from affecting cardiac activity. As a result, the number of myocardial contractions decreases. Prescribed to the patient for increased heart contractions and cardiac arrhythmias.
There are two groups:
- non-selective - affects all tissues in the body;
- selective - affect exclusively the receptors of the heart and blood vessels.
Non-selective beta blockers are contraindicated for diabetics as they increase blood sugar levels. Selective drugs are prescribed if high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are combined with other diseases: heart failure, heart attack, ischemia.
Such drugs are often used along with diuretics. Blockers cannot be used to treat high blood pressure in patients with asthma.
Antihypertensive drugs for diabetes mellitus should be selected by a doctor.
Increased blood pressure in diabetes
A metabolic disorder accompanied by chronic hyperglycemia is called diabetes mellitus. The pressure in this case, as a rule, exceeds normal levels. Due to a lack of insulin, the functioning of the circulatory system deteriorates, which leads to the occurrence of other diseases. For example, hypertension develops.
Hypertension and diabetes mellitus combine with each other and enhance their mutual negative impact on human organs and systems. More than half of patients suffering from type 2 diabetes have a history of high blood pressure.
First of all, the cardiovascular system suffers: the vessels of the brain, kidneys, and retina. They lose elasticity and flexibility, which leads to increased pressure and resulting complications.
Low blood pressure in diabetes is no less dangerous. Such phenomena are more typical for women. Hypotension is more difficult to diagnose, since there are no signs at the initial stage. People do not pay attention to general poor health. This leads to a gradual disruption of the blood supply to organs and tissue death.
Diuretics for patients with diabetes mellitus
Medicines such as diuretics remove excess fluid, thereby reducing vascular pressure.
There are four types of diuretics: potassium-sparing, loop, thiazide-like, thiazide.
Thiazide-like diuretics, which do not affect glucose levels, produce an excellent effect. Diabetes mellitus of both types requires the use of thiazide diuretics in quantities that do not exceed 12.5 milligrams. Both diuretic groups prevent the occurrence of renal complications and myocardium, but such drugs are prohibited for use in cases of renal failure.
Diuretic loop medications are rarely prescribed because the body loses potassium as a result. However, they are indicated for kidney failure, in which case additional medications with potassium are prescribed.
Potassium-sparing diuretics are also rarely used in diabetes, as they have a slight hypotensive effect.
Prevention of low blood pressure
An increase or decrease in blood pressure is a dangerous pathology that reduces the quality of life. If the disease develops against the background of diabetes, the likelihood of developing serious complications increases.
Therefore, it is important to prevent blood pressure disorders in diabetes. To do this, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Hypertension often occurs before diabetes develops, so nutrition and physical activity should be constantly monitored.
The basic rule for preventing the development of complications in diabetes, including surges in blood pressure, is to constantly monitor blood sugar levels. An increased concentration of glucose negatively affects the condition of blood vessels, which leads to impaired blood pressure.
- Take a contrast shower in the morning.
- Sleep at least 7 hours a night, go to bed at the same time every day.
- Remember to drink clean water in sufficient quantities.
- Massage your limbs every day for 10-15 minutes.
- Take vitamins and eat foods high in vitamins (such as fruits).
To urgently raise blood pressure, you can drink a glass of water with 25 drops of ginseng tincture or eat 0.5 tablets of ascorbic acid.
Stroke is an acute vascular accident in the brain. Every year, the disease affects up to half a million people in the country and often leads to death or disability of victims. High blood pressure after a stroke increases the likelihood of a recurrence of a vascular accident.
Statistics
Up to 24% of patients die in the first month after a stroke. During the first year, another 30% of patients die. Of the survivors, 20% of people are able to recover, the rest remain forever disabled of varying degrees of severity.
The disease is divided into 2 types: hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. They differ in the nature of the course and the causes of development. Hemorrhagic accounts for 20% of cases. The rest are caused by ischemia - acute oxygen starvation of cells.
Stroke
Ischemic. Occurs as a result of blockage of the vessel and disruption of the blood supply to the tissues. Acute hypoxia leads to the death of nerve cells and the death of part of the brain.
The brain is one of the most oxygen dependent. With a weight of no more than one and a half kg, the brain consumes 20% of the inhaled air. Therefore, without oxygen and glucose, which come with the blood, it cannot live and dies.
The high-risk group includes older and older people. Over the years, an increasing number of people suffer from atherosclerosis, hypertension, obesity, and heart pathologies - this provokes a stroke. As atherosclerosis progresses, excess cholesterol is deposited inside the vessel and atherosclerotic plaques form. Their sizes reach two centimeters. Over time, deposits can completely block the vessel.
Cause of high blood pressure in diabetics
In type 1 diabetes, the main cause of hypertension is nephropathy. This is a slowly developing complication in which, due to high glucose in the vessels, the renal glomeruli are damaged, which causes increased urination, protein begins to leak into the urine, and at the last stage, renal failure occurs. The more often a patient ignores prescribed diabetes treatment, the faster nephropathy progresses.
Damaged glomeruli begin to actively synthesize renin, a substance that enhances vascular tone. Pressure increases in the third stage of nephropathy, when the kidneys begin to filter urine 3 times slower. At this time, a two-way process starts: destroyed glomeruli cause hypertension, and this, in turn, aggravates vascular damage, including in the kidneys. This type of pressure is the most persistent and difficult to treat. With irreversible changes in the kidneys, it is observed in all patients with diabetes.
Diabetics with type 2 disease experience hypertension much earlier, even during prediabetes. High blood pressure is one of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome, a precursor to diabetes. Glucose begins to affect blood vessels even before its values become high. There is evidence that this process begins when glucose is above 6 mmol/l. The walls of blood vessels are damaged, plaques begin to form on them, and the lumen narrows. The onset of hypertension is accelerated by the faithful companions of diabetes - obesity and lack of exercise.
The relationship between the quality of diabetes treatment and the rate of progression of hypertension is direct; the higher the sugar, the higher the blood pressure in the vessels.
Reasons for increased blood pressure in diabetes:
| Disease | Characteristic | Frequency in diabetes, % | |
| 1 type | Type 2 | ||
| Diabetic nephropathy | Damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys. | 80 | 15-20 |
| Essential hypertension | A persistent increase in blood pressure without obvious reasons. | 10 | 30-35 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension | Increased upper pressure develops in old age. | 5-10 | 40-45 |
| Endocrine system diseases | Tumors, disorders of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland. | 1-3 | 1-3 |
| Diabetic angiopathy | Narrowing of a large vessel supplying the kidney. | no data | 5-10 |
Why does hypertension develop?
Even minor arterial hypertension in diabetes mellitus negatively affects the functioning of the body. Such patients are more susceptible than others to vascular atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
In the initial period, pressure in type 2 diabetes goes unnoticed due to the absence of symptoms. When two pathologies are combined - diabetes and high blood pressure - it is worth paying attention to factors that can aggravate hypertension:
- atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- endocrine disorders (thyroid gland, adrenal glands);
- disorders of the nervous system, stressful situations;
- increased physical activity;
- age-related changes in the body;
- errors in nutrition;
- excess body weight;
- breathing disorder, sleep apnea;
- lack of microelements, vitamins;
- influence of harmful chemicals;
- genetic predisposition;
- harmful stereotypes.
Some factors can be considered both as causes of high blood pressure in diabetes mellitus and as consequences of arterial hypertension. Hypertension often appears before diabetes mellitus occurs.
Blood pressure increases if antihypertensive drugs are abruptly stopped. Therefore, in order to exclude such phenomena, medications for blood pressure should be discontinued gradually. Blood pressure in type 2 diabetes mellitus tends to increase in the evening, which is taken into account during diagnosis.
Symptoms of hypertension
Patients with diabetes need to control their blood pressure to prevent it from becoming too high, which can cause a stroke. For this purpose, always keep a tonometer with you.
Symptoms directly depend on the level of pressure. The higher it is, the stronger the dizziness and chills. But headaches with minor deviations from the norm are stronger than with high blood pressure. Depending on the patient’s current blood pressure, there are three degrees of hypertension:
- Easy. The upper pressure does not exceed 160 mm. rt. Art., and the lower one - no more than 99.
- Moderate. Upper pressure no more than 179 mm. rt. Art., and the lower one - up to 109.
- Heavy. The top one is above 180, the bottom one is above 110.
In severe hypertension, the patient needs emergency medical care as this condition is life-threatening.
Main features
Risk factors
Hypertension in type 2 diabetics generally occurs without specific symptoms. And such manifestations as emerging headaches, a feeling of dizziness, and blurred vision are characteristic of many diseases.
It is common for a person to experience pressure fluctuations throughout the day - a decrease in levels at night and in the morning by up to 20%. A diabetic's blood pressure may be higher at night than during the day. This happens due to an increase in blood glucose, so-called diabetic neuropathy develops.
The vessels lack the ability to respond to stress, to narrow and expand in time. Patients are forced to frequently measure their blood pressure throughout the day. It is important to determine with great accuracy the required amount and hours when it is best to use high blood pressure pills.
Diabetes is characterized by orthostatic hypotension - a sharp decrease in blood pressure due to a change in the person’s body position. If the patient gets up after lying on his back, with low blood pressure, circles appear before the eyes, dizziness, and fainting is possible.
Complications
Complications from the combination of diabetes and hypertension increase the risk of disability and death in 80% of patients. Such complications are mainly caused by disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system. To reduce the risk of developing pathology, the attending physician’s task is not only to stabilize metabolism, but also to constantly monitor blood pressure.
Among the complications, diabetic kidney damage is the most common. This is a pathology of the vessels supplying these organs. Diffuse or nodular atherosclerotic changes appear, which leads to severe renal failure.
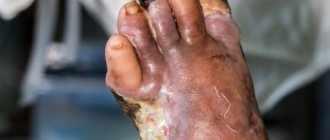
In diabetes, hyperkalemia causes disturbances in the functioning of the neuromuscular system and the peripheral circulatory system. Muscle weakness, paresthesia, flaccid paralysis of the arms and legs, diabetic foot, and gangrene occur.
The risk of atherosclerosis, coronary disease, heart failure increases, and heart attack and stroke develop 3 times more often. Damage to the blood vessels of the brain and retina leads to deterioration of vision and absolute blindness.
Therapeutic assistance
Treatment of hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus is carried out in parallel with therapy with drugs that lower sugar levels. The patient should understand that fighting two serious diseases at once is a long and complex process, and often lifelong.
- correction of body weight;
- rejection of bad habits;
- feasible regular physical exercise;
- healthy balanced diet.
Of course, you will have to use blood pressure medications. The appointment must be made by a doctor, taking into account many factors. Sometimes, to achieve an effect, you have to change blood pressure medications several times, selecting the right drug and the right dose.
In type 2 diabetes, treatment is often complicated. It must be carried out with caution. Many medications that lower blood pressure contain sucrose, which can affect glucose levels.
Diuretics are also used to lower blood pressure, and some antihypertensive drugs already contain them. If the patient has hyperkalemia, diuretic medications are used to reduce the accumulation of potassium.
Antihypertensive drugs
The traditional way to treat hypertension in diabetes is to take antihypertensive medications. There are different types of such funds. Their difference lies in the mechanism of action. The doctor may prescribe one medicine, i.e. monotherapy. More often, treatment is used in the form of combination therapy - a specific or several types of tablets. This helps reduce the dosage of active ingredients and reduce the number of side effects. Several tablets affect different mechanisms of hypertension development.
Beta blockers
These are drugs that lower the heart rate. For hypertension, they are prescribed in cases of persistent atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, after a heart attack, angina pectoris and chronic heart failure. The action of these medications is to block beta-adrenergic receptors located in various organs, including the heart and blood vessels.
A side effect of all beta blockers is the masking of signs of hypoglycemia. The recovery from this state is slower. For this reason, beta blockers are contraindicated in patients experiencing the onset of hypoglycemia. All active ingredients in beta blockers end in “-lol.” There are several groups of such drugs: lipophilic and hydrophilic, without or with internal sympathomimetic activity. According to the main classification, beta blockers are:
- Non-selective. They block beta1 and beta2 receptors and increase insulin resistance. Here the drug Anaprilin with propranolol is released.
- Selective. Blocking beta2 receptors causes undesirable effects, such as bronchospasms, which provoke asthma attacks, and vascular spasms. For this reason, selective beta blockers were created. They are called cardioselective and block only beta1 receptors. The active ingredients here are bisoprolol (Concor), metoprolol, atenolol, betaxolol (Lokren). They also increase insulin resistance.
- Beta blockers with a vasodilating effect. These are more modern and safer tablets for hypertension and diabetes. They are characterized by fewer side effects, have a beneficial effect on the carbohydrate and lipid profile, and reduce insulin resistance. The most suitable drugs in this group for diabetics are Dilatrend (carvedilol) and Nebilet (nebivolol).
Calcium channel blockers
These drugs are abbreviated as BBK. They block the slow channels in the blood vessels and heart muscle that open under the influence of norepinephrine and epinephrine. As a result, less calcium, a microelement that activates many bioenergetic processes in muscle cells, reaches these organs. This leads to vasodilation, which reduces the number of heart contractions.
Calcium antagonists sometimes cause headaches, hot flashes, swelling, and constipation. For this reason, they are replaced with magnesium preparations. They not only reduce blood pressure, but also improve intestinal function and calm the nerves. If you have diabetic nephropathy, you should first consult your doctor. Types of LBC are distinguished depending on which channels are blocked:
- Verapamil group. These medications affect the muscle cells of the blood vessels and heart. These include drugs from the group of non-dihydropyridines: phenylalkylamines (Verapamil), benzothiazepines (Dilziatem). They should not be used together with beta blockers due to the risk of rhythm disturbances. The result can be atrioventricular block and cardiac arrest. Verapamil and Dilziatem are good alternatives to beta blockers when they are contraindicated but necessary.
- Nifedipine group and dihydropyridine BBKs (ending in “-dipine”). These medications have virtually no effect on the functioning of the heart, so they are allowed to be combined with beta blockers. Their downside is the increased heart rate, which the heart tries to maintain pressure when it decreases. In addition, all LBCs do not have nephroprotective activity. Contraindications for use are hyperglycemia and unstable angina. In this category, there are several subtypes of drugs of the dihydropyridine group:
- nifedipine – Corinfar, Corinfar-Retard;
- felodipine – Adalat SL, nimodipine (Nimotop);
- lercanidipine (Lerkamen), lacidipine (Sakur), amlodipine (Norvasc), nicardipine (Barizin), isradipine (Lomir), nitrendipine (Bypress).
Diabetics have increased sensitivity to salt and increased circulating blood volume. As a result, blood pressure increases. To reduce it, diuretics (diuretics) are used. They remove excess fluid and salt from the body, reduce the volume of circulating blood, which helps reduce systolic and diastolic pressure.
Against the background of diabetes, diuretics are often combined with beta blockers or ACE inhibitors, since they are ineffective in the form of monotherapy. There are several groups of diuretics:
Diet
If previously hypertension aggravated by diabetes mellitus was treated only with antihypertensive drugs, now one of the main interventions is diet therapy. To stabilize blood sugar, it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods with easily digestible carbohydrates.
The development of hypertension is also associated with the fact that people gradually increase the amount of table salt in their food. It should be remembered that some products already contain hidden salt, so diabetics are prohibited from adding salt to their food.
A diet for hypertension should fill the body with microelements and vitamins. The menu contains vegetables and fruits, fish, and vegetable oil in sufficient quantities. It is advisable to eat at least five times a day; portions should be small.
Nutrition for hypotension should be strictly controlled by a nutritionist. On the one hand, a hypotensive person needs high-calorie, filling food, and on the other hand, such foods can increase the blood glucose level in a diabetic.
Diet food
If hypertension occurs against the background of diabetes, you need to be especially careful about your diet. A low-carbohydrate diet will effectively reduce sugar and normalize blood pressure. The patient should follow a number of recommendations:
- consume sufficient amounts of microelements and vitamins;
- reduce salt consumption: the norm during the day is one teaspoon maximum;
- Avoid sodium-rich foods;
- frequent meals - at least five times a day in small portions;
- It is forbidden to eat before bedtime, you need to eat two hours before and no later;
- eat low-fat foods, preferring complex carbohydrates;
- eat foods rich in potassium, as it lowers blood pressure and dilates vascular walls;
- include in your diet fruits and vegetables that are allowed for diabetics;
- bread baked from wholemeal flour;
- vegetable broths;
- lean fish and meat;
- low-fat fermented milk and dairy products;
- vegetable oils;
- dried fruits;
- eggs;
- seafood.
To improve the taste of dishes, you can use aromatic herbs, seasonings and lemon juice.
Contraindicated:
- smoked meats;
- alcohol;
- wheat flour products;
- drinks containing caffeine;
- fatty meat and fish;
- marinades;
- pickles;
- rich broths.
Excess weight greatly increases the likelihood of hypertension in patients with diabetes. To lose weight, it is advisable to reduce your daily caloric intake and move as much as possible.
Another option is to contact a nutritionist who can create a menu taking into account the clinical picture, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient. If the weight decreases by one kilogram, then the pressure decreases by 2-3 millimeters of mercury.
Now we know how diabetes affects blood pressure and what needs to be done about it.