Causes of leg damage in diabetics
- Diabetic nerve damage - neuropathy. Over time, under the influence of high sugar, the nerve endings of the feet are damaged. This leads to a disruption of sensitivity in them. A diabetic loses the ability to feel pain, pressure, temperature. The ability to feel pain is very important for a person, since pain warns of illness and danger. When this ability is lost, it is very easy to miss wounds or even ulcers on the legs. This is why diabetics’ legs do not hurt due to neuropathy, and they come to them late for treatment;
- Diabetic vascular damage - angiopathy. With diabetes, the function of blood vessels throughout the body deteriorates. The small (peripheral) vessels of the legs are especially affected, this leads to impaired microcirculation and cell hypoxia. As a result, the skin of the legs of diabetics is very dry and inelastic. This pathological dryness is not relieved by moisturizing cream and causes cracks to appear, which can become infected. Wounds develop, which take a very long time to heal due to lack of microcirculation;
- Diabetic joint damage is arthropathy. Impaired protein glucose metabolism leads to disruption of cartilage tissue and the development of hyperostosis. Therefore, diabetics often experience pain in the joints of their lower extremities, especially when walking. Arthropathy begins with swelling and redness of the foot. Over the years, deformation of the fingers appears, and pronounced swelling of the foot is observed. In severe cases, dislocations, subluxations, and fractures occur, as a result of which the foot shortens and widens.
In modern medicine, the entire variety of diabetic lesions is usually referred to by a single term – “diabetic foot”.
Manifestation of symptoms
There are many manifestations of diabetic foot damage. The patient may not attribute some of them to complications of diabetes, or even notice them. In view of this, every diabetic should know the symptoms of diabetic foot damage.
They are as follows:
- dry skin that cannot be overcome with cream;
- peeling and itching of the skin of the legs;
- hyperpigmentation and depigmentation of the skin of the lower leg;
- excessive callus formation (hyperkeratosis);
- hair loss on the lower legs in men;
- change in shape and thickening of nails;
- swelling of the ankles;
- the skin of the legs is pale and cold to the touch (rarely, on the contrary, bluish and warm);
- fungal infection of the skin of the feet and nails;
- numbness of the lower extremities;
- leg pain;
- violation of thermal, tactile and other types of sensitivity.
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms listed above in time, then severe consequences of diabetic foot damage occur.
Namely:
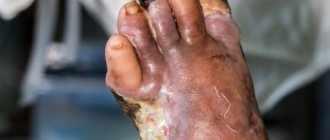
- non-healing painless ulcers and wounds;
- abscesses, phlegmons;
- arthropathy;
- osteomyelitis (bone suppuration);
- gengrene.
Foot diseases, main symptoms
Leg disease in people with diabetes manifests itself with different symptoms and appears due to certain reasons. The most common is diabetic foot syndrome (diabetic neuropathy).
- Diabetic neuropathy is when the peripheral nervous system, due to large amounts of glucose, stops transmitting nerve impulses, cells die, and the person stops feeling anything. As a result of this disease, ulcers may appear on the legs, which take quite a long time to heal. With this disease, the patient completely ceases to feel any pain. It is very important to consult a doctor, since the wounds that appear may not heal, bacteria will begin to develop in them, as a result of which the limb may simply be amputated.
- Problems with peripheral arteries, which manifest themselves in the fact that the patency of the blood vessels decreases, the tissues of the legs stop receiving oxygen, which causes pain in the patient. Starving the tissues of the lower extremities can also lead to amputation, so at the first sensation of pain or cramps you should consult a doctor.
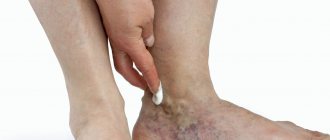
- Swelling of the lower extremities. Appear due to nephrotic syndrome or atherosclerosis. To reduce swelling, the patient needs to balance the diet and monitor physical activity.
- Leg ulcers. They appear when tissue is damaged, due to neuropathy or vascular pathology. Ulcers are formed as a result of calluses, burns, cracks, and bruises. If there is the slightest hint of the formation of an ulcer, you should consult a doctor to prevent the appearance of pus.
Diabetic neuropathy of the lower extremities
There are 3 stages of ulcer formation:
- Previous (fever, swelling, pain in the lower leg, tooth).
- Expanded (skin defects appear, bloody spots appear, the volume of the wound increases).
- Progressive (a purulent ulcer appears, body weakness, temperature, and pain increase).
Characteristics of leg pain due to neuropathy
Legs with diabetes mellitus hurt both when walking and at rest, especially bothering the patient at night. As a rule, they are of medium intensity, but over time they intensify and prevent the diabetic from leading his usual lifestyle. Pain is localized in the feet and legs, less often large joints hurt (with diabetic arthropathy). With this disease, in addition to the fact that the diabetic’s legs hurt, symptoms are also observed: cramps, tingling, numbness, weakness in the legs, decreased sensitivity, swelling of the legs.
The reasons for the symptoms described above can be different and are not always caused by the development of diabetes - this includes joint pathology, damage to nerves or blood vessels, venous disease, and osteochondrosis. To make a correct diagnosis and identify the true cause, the doctor necessarily recommends undergoing an examination.
Treatment for leg pain varies and depends on the primary disease. For example, drugs that are used to treat joint disease do not help relieve pain in the legs in diabetes.
Swelling of the legs in diabetes also has different causes. Diabetics often have concomitant heart disease, and, as is known, with heart failure, swelling of the feet and legs appears in the evening. Swelling can also be due to varicose veins of the lower extremities. Diabetic kidney damage is characterized by morning swelling of the legs.
Current approaches to the treatment of angiopathy
Angiopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that requires medical attention. It is important that the examination and treatment of the patient is carried out not only by an endocrinologist, but also by other specialized specialists - a cardiologist, neurologist, angiologist, ophthalmologist, nephrologist, etc.
How to treat blood vessels in diabetes mellitus and avoid the development of serious health consequences: let's figure it out.
Treatment of the underlying disease
Treatment of diabetic angiopathy is primarily based on correcting impaired metabolism and normalizing blood glucose levels.
The main drugs that lower blood sugar include:
- Metformin (Siofor, Glycon);
- Glibenclamide (Maninil);
- Gliclazide (Diabeton);
- Miglitol (Diastabol);
- Glimpiride (Amaril).
The doctor selects the dosage, frequency and duration of taking the drug individually based on the characteristics of the course of the disease and the initial blood sugar level. If tablet drugs do not have the desired effect, or the patient is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, he is indicated for subcutaneous injections of long-acting and short-acting insulin.
Daily insulin injections should become a habit
Important! The target blood glucose level in patients with diabetes is considered to be 3.3-6.5 mmol/l.
Features of lifestyle and diet
Also, cleansing blood vessels in diabetes mellitus is achieved by maintaining a correct lifestyle and following a therapeutic diet.
Medical instructions for diabetics include the following recommendations:
- Categorical refusal of bad habits.
- Getting rid of extra pounds, maintaining a normal BMI.
- Compliance with the drinking regime: drink at least 1.5 liters of water daily.
- Regular physical activity, agreed with your doctor. Hiking, swimming, and therapeutic exercises are useful: almost any regular activity has a positive effect on blood vessels in diabetes.
- Walks in the open air.
- Clinical observation by an endocrinologist and other specialists, careful implementation of their prescriptions.
A healthy lifestyle will help you cope with the disease
In addition, effective restoration of blood vessels in diabetes is impossible without following the rules of a therapeutic diet. Patients should eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day.
Can be used:
- soups with vegetable and weak meat (chicken) broths;
- lean meat and fish;
- cereals (buckwheat, rice, millet, pearl barley);
- bran bread - in limited quantities;
- vegetables - cabbage, all types of lettuce, zucchini, cucumbers;
- eggs – up to 1 pc. in a day;
- berries and fruits (except for sweet varieties);
- dairy products.
Vegetables and cereals should form the basis of a diabetic's diet
“Fast” carbohydrates (sugar, sweets and confectionery, fast food, baked goods) and sources of cholesterol (fatty meat, lard, offal) are contraindicated for diabetes and angiopathy. In addition, patients are advised to limit table salt to 2.5-3 g/day.
Sweets are prohibited
Important! The main rule of the diet for patients with type 1 diabetes remains the daily calculation of the energy value (including carbohydrate content) of the food consumed. This is necessary to adjust the dosage of administered insulin.
Foot examinations for diabetes
It is very important to see a doctor on time to diagnose complications of diabetes. The patient can specifically examine the lower extremities in the “Diabetic Foot Room”. Where specially trained endocrinologists, vascular surgeons and nurses work.
Doctors diagnose the degree of damage to the legs, adjust the treatment of diabetes, and also prescribe specific treatment for neuro- and angiopathy. The nurses in this office teach patients proper foot care, perform hygienic treatment of the feet (cut off calluses, apply medicinal creams, etc.).
Be examined in the “Diabetic Foot Office” upon initial diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, then at least once a year if you feel normal.
Research carried out in the office:
- examination, with mandatory checking of the pulse in the lower extremities;
- checking neurological reflexes;
- ultrasound examination of leg vessels;
- testing pain, tactile, temperature and vibration sensitivity;
- electroneuromyography.
Even a slight change in condition (the appearance of new symptoms) or slight inflammation on the skin of the legs is a reason to consult a doctor within 24 hours.