The Yusupov Hospital treats patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents. Almost 80% of patients after a stroke experience certain consequences of the disease. In order to overcome them, doctors use various rehabilitation methods, including exercise therapy for stroke. The set of exercises begins to be performed immediately after the patient regains consciousness. An earlier start of rehabilitation and an individual approach to the choice of means and methods of physical therapy allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to restore impaired functions even in those patients who were abandoned in other hospitals.
The rehabilitation clinic is equipped with modern equipment: computerized and mechanical simulators, verticalizers, Exart devices, Exoathlete. Professional rehabilitation therapists are proficient in the latest massage and exercise therapy techniques. Professors and doctors of the highest category use proprietary methods for restoring impaired functions after a stroke. Physiotherapists use modern physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetic therapy, therapeutic laser treatment, acupuncture, and transcranial stimulation. Every day, a multidisciplinary team of specialists works with patients who have suffered a stroke: occupational therapists, speech therapists, neuropsychologists, neurodefectologists. The decision on the choice of methods of physical therapy after severe strokes is made collectively at a meeting of the expert council.
Basic principles of exercise therapy after stroke
The early start of rehabilitation measures, which are carried out at the Yusupov Hospital, helps to speed up the pace and make the restoration of impaired functions more complete, and prevent the development of secondary complications. Exercise therapy for stroke (acute cerebrovascular accidents) begins in the neurology clinic and is subsequently carried out in the rehabilitation clinic. After discharge from the hospital, patients continue to perform physical therapy exercises at home under the supervision of rehabilitation specialists.
The patients themselves and their family members take an active part in the recovery of patients after a stroke. Rehabilitation specialists compile a set of exercise therapy exercises, teach methods of implementation, and teach how to monitor the functioning of the cardiovascular system during physical therapy exercises.
The very possibility of recovery is based on the general biological law of reorganization of functions - the ability to rearrange and participate in the restoration of the impaired function of those neuronal connections that were not previously involved in its implementation. The prognosis for recovery is determined by the volume and location of the lesion. The recovery of motor function is worse when the stroke is localized in the posterior thigh of the internal capsule, where the motor pathways converge into one bundle. Speech is restored more slowly when the pathological focus is located in both speech zones: in the posterior part of the left inferior frontal gyrus and the posterior part of the left superior temporal gyrus.
Active motor rehabilitation in most clinics is not carried out if the following contraindications are present:
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- chronic angina pectoris at rest and exertion;
- renal failure;
- acute inflammatory diseases.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the rehabilitation process after a stroke involves a multidisciplinary team of specialists who use innovative methods of rehabilitation therapy. This allows patients with severe concomitant pathologies to get back on their feet and restore self-care skills.
Speech and motor rehabilitation is impossible if patients have dementia and mental disorders. Physical therapy for brain stem stroke is performed lying down. The exercises are aimed at restoring motor functions of the limbs. Over time, exercise therapy is prescribed for facial muscles and restoration of speech functions.
What is a stroke?
You can hear the mysterious term “anaerobic gymnastics” from doctors. But behind the name lies only physical exercise after a stroke, during which oxygen consumption by tissues increases. In addition to the exercises prescribed by the doctor, patients are recommended the following types of anaerobic exercise:
- walking;
- cycling;
- swimming;
- dancing;
- moderate exercise in the fresh air (caring for flowers, decorating a personal plot, etc.).
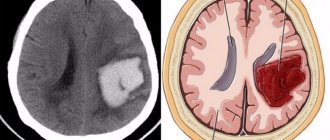
A stroke is an acute disorder of the blood circulation of brain structures, the symptoms of which appear suddenly and occur in individual foci or the general structure as a whole. This pathology often leads to death. According to statistics, after coronary heart disease, cerebral vascular diseases are in second place among the causes of mortality from pathologies of the circulatory system. Cerebral infarction and various cerebral hemorrhages are also a type of stroke.
If the manifestations of the disease can be detected in a timely manner and immediate treatment can be started, the patient has a chance to live. However, the pathology in most cases leads to disruption of the motor or sensory functions of the body, causing deterioration in brain activity - disturbances in speech, memory, orientation in space, and thinking.
Depending on what type of stroke is diagnosed in a patient, the patient’s chances of recovery and continuation of a full life vary. Thus, ischemic strokes, which make up 75-80% of the structure of the disease, are easier to treat. Hemorrhagic stroke has more severe consequences and is much more difficult to treat.
Motor rehabilitation after stroke
The main method of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke with movement disorders (paresis, impaired coordination and statics) is physical therapy. Its tasks include full or partial restoration of range of motion, strength and dexterity in paralyzed limbs, balance function in ataxia, and self-care skills.
In the rehabilitation clinic, in addition to exercise therapy, patients are prescribed electrical stimulation of the neuromuscular system of paralyzed limbs and are given classes using the biofeedback method. Physical therapy exercises begin as soon as the patient regains consciousness and improves his general condition. At first it is passive gymnastics. Movements in all joints of the limbs are performed not by the patient, but by the exercise therapy instructor or relatives instructed by him. The patient is taught breathing exercises. Exercises are carried out under the control of pulse and blood pressure with mandatory pauses for rest.
In the future, the exercises become more complicated, the patient begins to sit down, and then is taught to sit down independently and get out of bed. The timing of patient activation is determined by many factors:
- severity of stroke (size of infarction or hemorrhage, dislocation of brain structures, amount of edema);
- general condition of the patient;
- severity of paresis;
- hemodynamic state.
Some patients begin to get up from the 3-5th day after a stroke, in other cases they begin to become active after 2-3 weeks. An important stage of rehabilitation is learning to stand and walk. In patients with severe paresis of the lower limb, this stage is preceded by an imitation of walking while sitting in a chair or lying in bed. The patient learns to stand first with the support of a rehabilitation therapist, then independently, holding onto the headboard or bedside frame. At the same time, it evenly distributes body weight onto the healthy affected leg.
Subsequently, the patient learns to walk. Start by walking in place. Then the patient walks around the ward supported by a bedside frame, then learns to walk independently using a three-legged or four-legged cane. With good stability, the patient is immediately taught to walk using a stick.
Only with good balance and moderate or mild paresis of the leg can the patient begin to walk independently without relying on a stick. The volume of movements and distance gradually increase: the patient first walks around the ward or apartment, then along the corridor and up the stairs. After this, he can go outside and use transport.
Some patients with mild impairments “skip” many stages of rehabilitation and immediately begin to walk independently over relatively long distances, while others stop at certain stages. When a paralyzed foot drops, patients are recommended to wear shoes with high, rigid fastenings. To prevent stretching of the shoulder joint bursa in a patient with severe paresis of the arm while walking, it is recommended to fix the arm with a scarf, removing it during exercise therapy.
A set of exercise therapy exercises after a stroke
Immediately after the recovery of consciousness of a patient who has suffered a stroke, rehabilitation therapists begin performing passive exercise therapy. The exercise therapy instructor bends and straightens the patient’s paralyzed arm, moves it to the side and makes rotational movements with it. Such exercises are carried out daily. Their duration ranges from ten minutes to half an hour. At the same time, during one lesson they take 2-3 short breaks so that the muscles that have “forgot” how to work get a few minutes of rest.
The patient, lying on his back, is taken by both ankles, and his lower limbs are alternately flexed and straightened. The exercise resembles a “bicycle”, but the patient’s feet should not leave the bed. The patient, who is forced to maintain a horizontal position, can perform the following exercises independently.
Move your gaze up and down, from side to side, roll your eyes. These movements are performed first with closed, then with open eyes at an average pace. Each movement must be repeated 10 times. At the end of the exercises, you need to close your eyes and lightly stroke your eyelids with your fingers. Then you should open your eyes and blink vigorously several times.
The patient can squeeze and unclench his eyelids 10-15 times at an average pace. The patient can look at a certain point located directly in front of him, and, without looking away, turn his head to the right, then to the left. It is recommended to perform 5-6 turns in each direction.
To restore the function of the neck muscles, you need to carefully turn your head left and right, while fixing your gaze in front of you. Then it is recommended to bend and straighten your fingers 10 times.
To perform the following exercise, you need to hang a towel in the form of a loop over the bed. Thread a fixed upper or lower limb into a loop and simply swing it with different amplitudes.
Elbow joints need to be developed using the following exercise:
- the patient lies on his back, arms are located along the body;
- bend your right arm at the elbow and lower it onto the bed;
- Make similar movements with your left hand.
It is necessary to perform the exercise with each hand 10 times. Lying on your back, you can alternately bend and straighten your knees 10 times.
Once the neurologists allow the patient to sit up in bed, the exercise program becomes more complex. Now you need a set of exercises depending on the severity of the neurological dysfunction. Rehabilitation specialists, together with neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, draw up an individual rehabilitation plan aimed at maximizing the restoration of the existing defect.
In the early recovery period, exercises are prescribed aimed at:
- increased muscle strength;
- reduction and normalization of increased muscle tone;
- normalization and elimination of atactic disorders, including balance functions;
- restoration of muscle-joint sensation;
- restoration and automation of the most important motor skills (standing, walking, household self-care).
In the late recovery period, exercise therapy after a stroke is aimed at compensating for impaired functions, based on the inclusion of intact links and their functional restructuring.
Passive gymnastics.
The procedure for passive gymnastics for the limbs is simple: look at what movements an arm or leg can perform in a given joint, and perform these movements on your patient 10–15 times. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that passive gymnastics is performed slowly, smoothly, carefully; there is no need to make movements in the paralyzed limbs with the maximum possible amplitude, so as not to “loose” the joints. Start with the distal parts of the extremities: with the hands and feet, then move on to the medium and large joints.
Passive gymnastics for paralyzed limbs is carried out on all joints:
flexion and extension of fingers; flexion and extension of the hand, rotation of the hand; flexion and extension of the elbow joint; rotation of the arm in the shoulder joint, abduction and adduction of the arm, raising the arm up and down along the body.
Flexion and extension of the foot, rotation of the foot clockwise and counterclockwise, flexion and extension of the knee joint, rotation of the hip joint.
You can bend your legs bent at the knee joints to the sides with a limited amplitude. This is pleasant for a patient who has congestion in all organs and tissues due to lying for a long time and the inability to move. Movement is a vital need of the body. Therefore, treat the post-stroke patient with understanding and compassion. This exercise will help improve blood microcirculation in the tissues of the lower back.
It is important to note that the muscles of the paralyzed arm do not hold the shoulder joint in the shoulder joint capsule; it is held in place by the ligamentous apparatus, but the ligaments are capable of stretching. It is convenient to detect this when the patient is sitting on a chair: place your palms on the patient’s shoulders and feel the surface of both shoulder joints with your fingers, you will find a difference: on the sore side there is a gap between the head of the humerus and the joint capsule. Therefore, in order to prevent sprains and dislocation of the arm, the patient should not be pulled by the paralyzed arm, and if the patient is in an upright position (sitting or standing), the arm should be tied with a scarf or a special arm support bandage should be purchased.
Passive gymnastics is combined with elements of massage to improve blood circulation in the extremities. You can do stroking from the periphery to the center, light rubbing and gentle kneading. Vibration (effleurage) and deep kneading should not be done, as this contributes to increased tone in the muscles, which can lead to spasticity, since the nervous system is significantly activated by sending impulses and can “issue” pathological commands to the muscles. It is better to entrust therapeutic massage to experienced specialists.
Home exercise therapy complex for acute stroke
After discharge from the rehabilitation clinic, patients who have suffered an acute cerebrovascular accident receive recommendations from a physical therapy instructor. They need to continue to exercise at home.
You need to start exercise therapy after a stroke with simple physical exercises. The patient can do stretching:
- starting position “arms down, feet shoulder-width apart”;
- raise your arms up, while turning your palms outward;
- stretch in this position and take a breath;
- lower your hands down, trying to describe a circle with them, and exhale;
- return to the starting position.
Perform turns with feet shoulder-width apart and hands on waist. He turns his body to the right, spreads his arms to the side and inhales. Returns to the starting position and exhales. Also makes a left turn. Performs the exercise 5 times in each direction.
To perform squats, you need to lower your arms down and spread your legs apart. We do squats without lifting our heels from the floor, tilt our body slightly forward, and move our arms back. We inhale, slowly return to the starting position and exhale. The exercise should be performed slowly 6 times.
We do leg swings from the starting position “standing, hands on the belt.” One leg should be extended forward, swing the leg in a circular motion and return to the starting position. We fix our legs shoulder-width apart, and place our hands on the belt. We stretch our left hand forward, take a naked step forward with our right hand, clench our fists and place our hands to our shoulders. We get into the starting position and repeat the movements with our right limbs.
We perform 10 squats at any pace, alternately changing hands. At the moment of squatting, one hand should be on the belt, and the other behind the head. With your feet shoulder-width apart and your hands on your waist, we make 5 circular movements with your pelvis clockwise, then in the opposite direction. To speed up the rehabilitation process after strokes, rehabilitation experts recommend exercising at home on exercise bikes. Dosed walking, walks in the fresh air, Nordic walking with ski poles are useful.
If you or people close to you need rehabilitation after a stroke, call the Yusupov Hospital. Rehabilitation specialists will create an individual set of exercise therapy exercises. In the rehabilitation clinic, classes are taught by experienced physical therapy instructors who are fluent in modern methods of rehabilitation therapy after stroke.
Author
Alexey Markovich Moskvin
Recovery rules
A stroke and its consequences are quite serious, so it is important not to overdo it during recovery. It is imperative to consult a doctor, follow his recommendations and increase the intensity of exercise gradually. Remember the following rules:
- Any new exercise should be done gradually. If the patient can only sit independently, exercises in sitting and lying positions are suitable for him, which must be taught to do gradually and correctly. It is better if a doctor observes the process at first.
- Regularity is important. Only with constant exercise is progress in recovery possible. You can't stop doing the exercises. A smooth increase in the number of repetitions and intensity is welcomed as the patient’s condition improves.
- The best time for recovery exercises at home is in the morning. By evening, blood flow worsens, and the patient’s body becomes less susceptible to any influences. Morning exercises help you recover faster, this is a fact confirmed by doctors.
- The path to recovery should include not only exercise therapy, but also conservative therapy, massage and proper nutrition. Only an integrated approach will give good and quick results.
- If the condition worsens during exercise therapy, it is necessary to take a break from exercise. If a patient experiences dizziness during exercise, headaches after exercise, or blurred vision or loss of consciousness, this is an alarming sign that must be paid attention to.
By following all the rules, you can quickly and effectively restore the mobility of the patient’s limbs and return him to a full life, if this is possible with existing brain lesions.