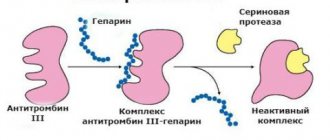
What is ECP?
The blood contains white blood cells - leukocytes, which are divided into several types. One of the varieties is eosinophilic granulocytes (or eosinophils). If you look at these cells under a microscope, you can see granules inside their cytoplasm. Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) is part of these granules. It is a protein with a positive charge.
During allergic reactions, ECP enters the bloodstream. The same phenomenon occurs during helminth invasion, since this protein has a toxic effect on parasite cells. And in allergies, ECP is intensively produced by eosinophils. This protein increases mucus production in the respiratory tract, affects blood clotting and the formation of immune cells. During allergies, an eosinophilic cationic protein is released from the cytoplasm. What does this reaction mean? This is the body's response to the interaction of the allergen and immunoglobulins.
Reasons for deviations
A deviation from the norm of the index occurs when a person has allergic and some other diseases or exhibits an allergic reaction.
Increased level
In an adult, the indicator increases with an allergic reaction. In asthma, the index is increased to 20 mg/l, and in atopic eczema or the presence of parasites in the body, the value reaches 70 mg/l. The highest value, up to 200 mcg/l, is manifested in diseases of the bone marrow, when increased production of blood cells is recorded. The higher the ESR, the more severe the patient's allergy. Doctors distinguish between mild, severe and moderate severity of the disease.
Important information: What is PDW or platelet population distribution width and deciphering the norm in a general blood test
Cationic protein is increased in patients with DRESS syndrome. Such patients exhibit increased sensitivity to medications.
This causes allergy symptoms:
- skin rashes;
- nausea;
- burning of the skin.
Most often, the cause of an allergic reaction can be drugs of the phenytoin group and antibiotics.
If the ecp value is increased, this means that the patient may be diagnosed with the following disorders:
- infectious and inflammatory pathology of the nasal mucosa;
- development of tumors in the kidneys;
- the presence of worms and other parasites;
- viral respiratory disease.
Reduced rate
A healthy person has a reduced ECP level in the blood. In the absence of an allergic reaction, inflammation, or helminthiasis, its concentration remains low. A decrease in the index is recorded during pathology monitoring due to the effectiveness of the treatment.
Why do you get tested for ECP?
Allergists and pulmonologists sometimes prescribe an eosinophil cationic protein test. What does this study show? The level of ECP in the blood indicates the severity of eosinophilic inflammation in allergies and helminth diseases. With bronchial asthma, you can notice a pattern: the more severe the symptoms of the disease, the higher the level of cationic eosinophilic protein. The higher the ECP indicator, the more severe the pathology. We can say that this protein is a marker of exacerbation of allergies.
This analysis is also necessary in cases where the patient is being treated for an allergic or helminthic disease. A decrease in ECP indicates the effectiveness of therapy.
Eosinophilic cationic protein - what is it?
Seeing the indicator eosinophilic cationic protein in the test results form, what kind of parameter it is, why it is set and in what cases are common questions that patients ask. This substance is one of the proteins that are part of the cytoplasmic granules of eosinophils (blood cells that appear at the site of inflammation, also during allergies and parasitic infections). In the mature state, eosinophils are found in tissues, but about 1% of the total number circulates in the bloodstream.
The eosinophilic cationic protein itself (designated ECP) is the result of eosinophil degranulation. By its concentration in biological fluids of the body one can judge the intensity of the inflammatory process and allergic reaction.
This protein is cytotoxic to a number of body cells and some microorganisms. Among them:
- epithelial cells;
- mast cells;
- smooth muscle cells;
- fibroblasts;
- helminths.
What does the eosinophil cationic protein test show?
In order to understand what eosinophilic cationic protein shows, it is necessary to highlight the main functions of this substance in the body. ECP has a direct connection with the mechanisms of antibacterial, antitumor and antiviral activity. An increase in the concentration of this protein in the bloodstream indicates the activation of anti-inflammatory processes.
An ECP blood test is prescribed if the following disorders are suspected:
- allergic reactions;
- inflammatory processes of various localizations;
- damage to the body by parasites;
- for bronchial asthma.
When is an eosinophil cationic protein test needed?
A referral for ECP analysis is issued by a doctor. If there are suspicions of pathology, corresponding symptoms are present, research results are used to make a diagnosis and confirm assumptions.
Among the indications for such an examination are:
- The presence of symptoms of atopic bronchial asthma: shortness of breath, suffocation after contact with animal hair, dust, pollen, and other allergens.
- Signs of atopic dermatitis: dry skin, itching, eczematous rash, changes in skin pattern.
- Suspicion of allergic rhinitis – runny nose, itchy nose, sneezing, headache, loss of smell due to exposure to an allergen.
- In case of reaction to food products - a rash after eating eggs, milk, fish, tree nuts, shellfish.
Analysis may be prescribed in a number of other cases:
- allergic otitis;
- parasitic and bacterial infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- in conditions accompanied by activation of eosinophils: malignant neoplasms, idiopathic eosinophilia.
In what cases is an examination prescribed?
A blood test for cationic eosinophil protein is prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing or attacks of suffocation upon contact with animal hair, plant pollen, dust;
- skin rashes accompanied by itching;
- runny nose or sneezing when in contact with allergens;
- skin rashes, swelling of the nasopharynx, sneezing and dyspepsia after eating certain types of food.
However, blood testing for ECP alone is not sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis. Additional tests are usually required.
Decoding the results
In what quantities should eosinophilic cationic protein be contained in blood serum? The norm is from 0 to 24 ng/l. Typically, the ECP content corresponds to the eosinophil count.
For some pathologies this figure can be significantly higher. Thus, in bronchial asthma, the ECP indicator can exceed the norm by 2-3 times.
Sometimes the analysis reveals very high levels (about 240 ng/l) of eosinophilic cationic protein. What does such a serious deviation from the norm mean? This indicates either infection with helminths (usually schistosomes) or an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis.
In some cases, ECP values exceed the norm by several tens of times (about 700 ng/l). Typically, such numbers occur in hypereosinophilic syndrome. This is a rather serious disease associated with impaired hematopoiesis.
Sometimes you can notice how eosinophil cationic protein begins to gradually decrease after treatment. What does this result show? This indicates the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy. Using the ECP study, the required dosage of drugs for patients with bronchial asthma is calculated.
What diseases does the analysis detect?
If the test result is no more than 24 ng/l, then this is considered normal. Only exceeding this figure is considered a deviation. This happens with the following diseases:
- acute upper respiratory tract infections (rhinitis);
- polyps in the sinuses;
- allergic form of bronchial asthma;
- bronchial asthma due to aspirin intolerance;
- food allergies;
- atopic dermatitis;
- allergic rhinitis with seasonal exacerbation;
- hypereosinophilic syndrome;
- helminthic infestation;
- allergic inflammation of the esophagus, stomach, intestines;
- eosinophilic pneumonia of autoimmune origin (Churg-Strauss syndrome);
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- taking certain medications (antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Carbamazepine, Phenobarbital, Co-trimoxazole, Phenytoin, Glimepiride).
Decreased protein levels are of little diagnostic value.
An increase in cationic protein in children under 1 year of age is not always associated with allergies. This can be caused by Rh conflict, pemphigus, infectious and fungal diseases.
Level exploration
Eosinophils are white blood cells that take part in the elimination of pathogenic elements in the body. Eosinophilic protein is their “weapon”. This index is designated ESR. It exhibits antibacterial, ribonucleose and antiparasitic activity. The blood test is carried out using the “sandwich” method. Eosinophils are present in the mucous membrane of organs, and their release can accompany various symptoms.
The ECP study is carried out for allergic diseases. When an allergen enters the body and causes an allergic reaction, the content of eosinophilic protein in the blood increases. This protein is considered an indicator of the development of allergies and is used to detect the progression of the disease or control during therapy.
Using this study, the doctor assesses the severity of asthma, prevents the development of attacks, selects the necessary medications and monitors treatment.
When to analyze
This test is prescribed to diagnose the following diseases:
- Allergic rhinitis, which is characterized by nasal congestion, loss of smell, runny nose when interacting with an allergen, sneezing, and headache.
- Atopic asthma - is expressed by signs of suffocation and the appearance of shortness of breath when a sick person comes into contact with an allergen.
- Allergy to foods, which is manifested by irregular heartbeat, pain in the abdominal area, vomiting, cough, skin rash, diarrhea, swelling of the oral mucosa and larynx after eating foods containing the allergen.
- Atopic dermatitis. The pathology is expressed by the rapid development of symptoms, the appearance of a rash, peeling of the skin, and irritation.
Important information: Norm of red blood cells in children by age (table)
Preparing for the study
Testing for this protein is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Before this, you should not eat food for 8 hours before the test. You should not smoke 3 hours before testing. In the morning you can only drink boiled water. 30 minutes before donating blood, you should not be nervous or physically tense.
On the eve of the test you should not: drink alcohol, eat fatty foods, take medications or nutritional supplements. Women should not have a laboratory test during their period because... at this time the number of eosinophils increases. The analysis cannot be carried out immediately after diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, such as ultrasound, fluorography and physiotherapeutic treatment.
How the analysis is done
To test for eosinophils, blood is taken from a patient's vein in the laboratory.
How to prepare for the examination?
A few days before the scheduled test, you should avoid taking medications that could affect the test results. Such drugs include:
- antibiotics;
- tranquilizers;
- interferon medications;
- laxatives containing psyllium;
- central nervous system stimulants.
It is also not recommended to eat fatty foods or drink alcohol a few days before the analysis. Before the study, you should not smoke, do heavy physical work, drink sweet tea, coffee, or juices.
The test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. You should stop eating 8-12 hours before the test. You can only drink clean water.
How is the analysis done?
To conduct a test for cationic eosinophil protein, blood is taken from a vein. Then the test tube with the material is sent to the laboratory. The blood is centrifuged to separate the red blood cells. The serum is studied using the immunochemiluminescent method.
This research method is based on the reaction of an antibody with an antigen. The protein contains arginine, an amino acid that is detected using monoclonal antibodies.
This is an informative research method that gives reliable results in 90% of cases. In diagnostic laboratories, the analysis is done quite quickly, usually the results are known within 1-2 days.
What to do if ECP is elevated?
The patient is always concerned when he learns that he has elevated eosinophil cationic protein. What to do in this case? It all depends on the reason that caused such a deviation.
If the patient has previously experienced signs of allergic reactions, then contact with substances that provoke an exacerbation of the disease should be avoided. The doctor will prescribe a course of treatment with antihistamines. If the allergen is unknown, skin testing will be required to determine the type of irritant.
If the patient has never shown signs of the disease before, then a slightly elevated ECP may indicate a tendency to allergies. In this case, they usually take an additional test for immunoglobulin and leukocyte formula.
It must be remembered that an increase in cationic protein can be associated not only with allergies, but also with helminth infestation or blood diseases. You may need to be tested for eggs of worms and protozoa, and consult a hematologist.
If the increase in ECP is associated with medication, then this phenomenon is usually temporary. After completing the course of treatment, all blood counts return to normal.
It is very difficult to understand on your own the reasons for the increase in cationic protein. First of all, you need to show the test result to your doctor. The treatment of such conditions is carried out by: an allergist, a pulmonologist and a dermatologist.
What is cationic eosinophil protein?
The word “cationic” means that the protein (protein) molecule is positively charged and has the properties of a weak base. The main properties are given to the protein by its high content of the amino acid arginine.
The diagnostic value of the analysis for the level of cationic protein of eosinophils is to assess the degree of eosinophilic inflammation in the body.
In test forms, the result of the study is designated as ECP or ECP - from the English name Eosinophil cationic protein, measured in ng/ml or μg/l. The study is carried out using the immunochemiluminescent method. It is based on the use of antigen-antibody immune reactions.
ECU functions
Eosinophils release cationic protein from granules in response to the interaction of their own surface receptors with the IgE immunoglobulin. Eosinophilic cationic protein:
- blocks the release of histamine by basophils and mast cells;
- stimulates T-lymphocytes;
- has an antimicrobial effect aimed at bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- acts as a neurotoxic compound on the nervous system of parasitic worms;
- destroys cancer cells, exhibiting antitumor properties.
ECB primarily serves as a marker of allergies. The determination of eosinophilic protein is also used in children and adults to diagnose DRESS (Drug Reaction with Eosiniphilia and Systemic Symptoms) syndrome.
DRESS syndrome is an allergic reaction to medications. The disorder is most often provoked by taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and anticonvulsants.
How does excess ECP affect a person?
Cationic protein in high concentrations is toxic to human nerve cells. When the level of eosinophilic cationic protein increases, cardiomycetes—special heart cells responsible for myocardial contractility—suffer, and the bronchial epithelium dies.
An increase in cationic protein can be assumed when:
- skin itching;
- cough;
- nausea, vomiting;
- swelling;
- frequent headaches;
- confused consciousness.