- 1 Fibrosis of the aortic valve
- 2 Aortic valve fibrosis 2.1 Clinical signs of the disease:
- 2.2 Diagnostics:
- 12.1 Popular articles:
Aortic valve fibrosis
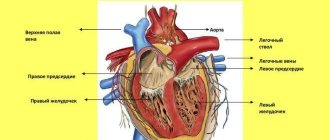
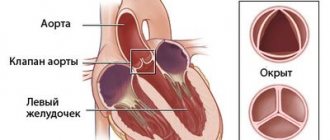
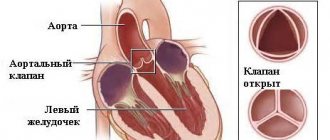
The aorta is the main artery of life, and its task is to conduct blood from the heart through the systemic circulation and it begins from the left ventricle of the heart. The aortic wall in a healthy heart is strong and elastic, but if the aortic walls become thickened, fibrosis of the aortic valve occurs. Pathologies reduce the elasticity of the aortic walls, and blood no longer flows normally, and this is fraught with many dangerous diseases.
- inflammatory process due to an infectious disease;
- injuries of various origins;
— allergic processes in the body;
- taking certain medications;
— addictions in the form of uncontrolled drinking and smoking;
- age-related changes and lack of calcium in the body;
- congenital stenosis of the aortic mouth. Let's take a closer look here. Congenital stenosis in humans is diagnosed from birth, but with age it worsens as fibrosis and calcification begin to progress. Those patients who were diagnosed with a congenital bicuspid aortic valve in childhood are especially susceptible to the occurrence of fibrosis, and in childhood this does not cause a significant narrowing of the aortic mouth, but with age everything changes.
You need to know that pathologies of this large blood-carrying arterial vessel cause serious circulatory disorders and if the disease progresses quickly, it can even lead to death.
Clinical signs of the disease:
— in the stage of compensation there are no unpleasant sensations. The patient learns about his illness either during an examination or by going to the hospital for another illness;
- the first complaint is shortness of breath. At first it appears during physical activity, then it becomes more and more and is already present even when walking slowly and at rest. Shortness of breath can also bother a person during sleep;
- heartache. They are similar to angina pectoris and most often appear after physical exertion. They can be both long-term and short-term;
- fainting and dizziness. They also most often appear during physical exertion, and fainting can last up to several minutes. Fainting is associated with the fact that during physical exertion there is a sharp drop in peripheral resistance and pressure in the aorta decreases, which leads to cerebral ischemia;
- heartbeat. The patient also complains that he feels interruptions in the work of the heart and as if it is “fading.” All this happens due to heart rhythm disturbances.
Diagnostics:
- surgical treatment.
This is a radical method of treatment and if there are no contraindications, then it is prescribed; - use of diuretics, cardiac glycosides, ACE inhibitors;
- with high blood pressure, medications for high blood pressure are selected according to a strict dosage, otherwise the pressure can be reduced very significantly;
- antiarrhythmic drugs that maintain heart rhythm.
Leaflet fibrosis: pathology of the aortic and mitral valves
Fibrosis of the aortic and mitral valve leaflets actually does not manifest itself in any way in the early stages of development. It is mostly discovered by chance during an annual examination.
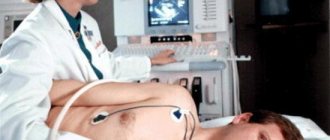
Echocardioscopy (ultrasound of the heart) helps to see the enlarged valves.
The doctor will assess the degree of pathological changes and prescribe the most effective course of treatment to stop the development of complications and improve the patient’s condition.
What it is?
You can understand what fibrosis of the mitral valve leaflets is by looking at the features of its structure and functioning. The essence of the operation of the valve apparatus is to allow blood to pass (in one direction) when a certain section contracts.
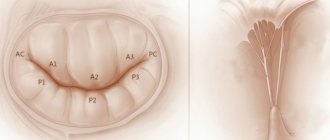
The main role is played by the valves, which are represented by loose connective tissue. Their nutrition is carried out through the smallest vessels. The aortic valve has three leaflets (right, left, posterior), and the mitral valve has two (posterior, anterior).
Under the influence of irritating factors, the connective tissue becomes coarser, which is why it ceases to fully perform its functions (maintain the flexibility of the valves).
Over time, the number of blood vessels supplying the valve is significantly reduced. The cells that make up it begin to die, being replaced by fibrous tissue.
It is one of the types of connective tissues, which is characterized by high strength.
Fibrosis classification
Each form of pathology has its own characteristics.
- The focal form is the basic one. It is characterized by moderate fragmented damage to the structure of the valve apparatus.
- The diffuse type is characterized by a large area of damage (cusps and subvalvular space). It is detected at advanced stages of fibrosis development.
- The cystic form is perceived as a separate pathology. It manifests itself as serious disruptions in metabolic processes and leads to the formation of cysts.
If the cusps of the mitral valve are sealed, then it is not at all necessary that this is a heart defect. Fibrosis is only a pathological change that occurs under the influence of other factors, and not a diagnosis. Because of it, stenosis and valve insufficiency can develop.
The appearance of voiced pathologies requires urgent medical intervention. The proliferation of fibrous tissue can be perceived as a substrate for the formation of cardiac muscle defects. However, it is unlikely to predict its development in advance.
The chances of timely identification of the problem increase through regular examination.
Causes
For the most part, the mitral valve leaflets become sealed. The problem can affect both a child and an adult due to the development of infection, inflammation, heart defects and other factors. It occurs for the following reasons:
- age-related changes;
- rheumatism;
- birth defects;
- atherosclerosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- inflammatory diseases.
Features of the manifestation of fibrosis of heart valves
The condition does not worsen immediately. It is possible to identify compaction of the valve wall from the clinical picture of a hemodynamic failure only with the development of severe regurgitation. It is characterized by reverse blood flow.
It returns to the atrium or ventricle depending on the affected valve. The essence of the problem lies in the incomplete closure of the valves. Sometimes it happens the other way around. Fibrosis leads to the fusion of the valves with each other.
In the first case, the pathological process provokes an enlargement of the atrium, and in the second, a narrowing of the valve opening.
The degree of regurgitation varies between mild and severe. The clinical picture will depend on the severity of the pathology.
Mitral valve damage
If the mitral valve leaflets are compacted, the patient may eventually develop the following symptoms of fibrosis:
- fast fatiguability;
- frequent shortness of breath;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- arrhythmia;
- feeling of shortness of breath;
- pain in the heart area;
- swelling of the legs.
Aortic valve damage
Fibrosis of the aortic valve contributes to the manifestation of cerebral hypoxia. The patient exhibits a pathological process with the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- pulmonary edema;
- loss of consciousness;
- angina pectoris.
Diagnostic methods
If a clinical picture characteristic of fibrosis develops, it is necessary to make an appointment with a cardiologist. The specialist will conduct a survey to find out the patient’s complaints and details (the presence of other pathologies and defects, hereditary predisposition). Then he will examine the patient and prescribe a series of examinations. Typically this is:
- Ultrasound (ultrasound) of the heart muscle makes it possible to see its structure in great detail in order to assess the degree of regurgitation or stenosis. With this test, the doctor will also see how well the left ventricle is working and whether the ejection fraction (the amount of blood entering the aorta) is sufficient.
- A chest X-ray is performed if venous stagnation of blood or enlargement of certain chambers of the heart is suspected.
- Coronary angiography in most cases is performed before surgical intervention for valve replacement.
As additional examination methods, blood and urine tests and electrocardiography are prescribed. They will help to identify associated complications and the causative factor of the changes that have arisen. Based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to accurately diagnose and create a treatment plan.
Experts' forecast
The prognosis directly depends on the presence of consequences and their severity. If they are absent, then fibrosis is not life-threatening for the patient.
The situation is different with the formation of congenital heart defects, due to which serious disruptions in hemodynamics occur. The prognosis in this case is extremely negative and the patient urgently needs surgery.
The degree of recovery and life expectancy of the patient will depend on its result.
Fibrosis usually affects the cusps of the mitral and aortic valves. Symptoms develop when disruptions occur in hemodynamics caused by regurgitation or stenosis of the valve ring. Surgery is used as treatment. The condition can be alleviated with medication. It is necessary to combine the basic treatment regimen with compliance with the rules of prevention.
Source: https://MirKardio.ru/bolezni/tyazhelye/fibroz-stvorok-aortalnogo-i-mitralnogo-klapana.html
Types and degrees of pathology
The initial stage of the formation of heart valve fibrosis is considered focal. It is characterized by the growth of fibers in a local area. This mechanism serves to limit the focus of inflammation or destruction of the myocardium, which is a compensatory-adaptive reaction.
Any formation of scar tissue in the myocardium is irreversible; muscle fibers lose their functional properties and inhibit the functioning of the entire organ.
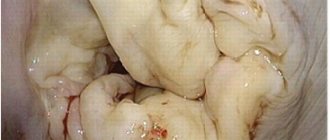
Heart valves
Cardiac fibrosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods
Cardiac fibrosis is a disease characterized by accelerated production of collagen and proliferation of connective tissue due to inflammation. This pathology leads to the fact that the tissues become denser and scars form in them.
What are the reasons for its appearance? What are the symptoms? How is fibrosis diagnosed and what methods are used to treat it? Read about it in the article.
In general cases, these include chronic diseases and inflammatory processes. Less commonly, the disease occurs after radiation exposure, trauma, severe allergic reactions, infections and weakened immunity.
However, if we talk about the causes of cardiac fibrosis (what it is is indicated above), it should be noted that in this case the main provoking factor is myocardial infarction, as well as age-related changes in the body.
But even here everything is ambiguous. If, for example, a person is diagnosed with aortic fibrosis, then there is a high probability that this was caused by injuries, infectious diseases and allergies. When it turns out that the mitral valve leaflets are affected, then most likely the prerequisites in this case are rheumatic processes. They negatively affect connective tissue.
Therefore, each case must be considered separately.
Focal cardiac fibrosis is a limited process. The initial stage of pathology, in other words. If treatment is not started on time, it will go into the diffuse stage. It is characterized by a large amount of damaged tissue.
The last stage is cystic fibrosis. A separate serious disease that affects metabolism and often leads to the appearance of cysts. They are known to also threaten human life and health.
Development of damage to the mitral and aortic valves
If the valve leaflets become rigid and inactive, this leads to either insufficient closure (insufficiency) or a reduction in the opening through which blood passes (stenosis).
With mitral or aortic insufficiency, part of the blood returns back to the atrium or ventricle of the left half of the heart. This creates an increased load on the myocardium, contributes to a decrease in the contractility of muscle tissue, which over time leads to circulatory decompensation.
How to treat fibrosis of the aorta of the heart
Fibrosis is a disease that is accompanied by thickening and scarring of connective tissue. Often, the disease is a consequence of inflammatory processes in the body. Aortic root fibrosis may be a consequence of trauma in some cases. There are several degrees of the disease.
- Focal. Benign process. The disease is accompanied by damage to tissues or organs.
- Diffuse. This type of fibrosis differs from focal fibrosis by serious lesions.
- Cystic. The most severe degree of the disease. The disease has a hereditary predisposition. The disease is accompanied by damage to the exocrine glands. Cystic fibrosis is accompanied by disruption of the exocrine glands. As a result of the disease, the functioning of the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract occurs.
- Local. The disease is a consequence of the injury received.
Some features of aortic root fibrosis:
— Due to a decrease in the pumping function of the heart, the blood vessels may be overloaded. As a result, the organs are filled with venous blood. This is the main cause of high pressure in venules and arterioles, which leads to pathological changes.
— Due to fibrosis of the aortic root, respiratory function is impaired. The blood is not enriched with oxygen. The patient exhibits signs of heart failure (blue lips, pale skin color, shortness of breath).
— Due to fibrosis, the patient develops symptoms that indicate stagnation of blood in the vessels of the liver and legs (heaviness in the right side of the body, swelling).
— The contractile function of the myocardium weakens as the disease progresses. As a result, in the atria and ventricle is formed
residual amount of blood that stretches the cavities of the heart. Because of this, the heart valves do not fit tightly together.
— Fibrosis of the aortic root is accompanied by the progression of heart failure. If the disease is not treated, the heart eventually loses its compensatory capabilities.
Some features of the treatment of aortic root fibrosis:
— The disease is treated only in a hospital setting. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes that led to fibrosis.
— The patient is prescribed beta blockers, B vitamins, hepatoprotectors, and other medications.
The aorta is the largest artery in the human body, which originates from the left ventricle of the heart. Its walls must have sufficient density and elasticity, because it is the aorta that receives blood flow under the highest possible pressure.
Disturbances in the structure or structure of the walls of the aorta, addictions, injuries and other factors can cause aortic disease. Pathologies of the largest conducting arterial vessel can cause serious circulatory disorders, and the rapid progression of the disease often leads to the death of patients. Any aortic disease has similar clinical manifestations, but different causes and etiologies.
The pathology is expressed in the gradual accumulation of calcified plaques on the walls of the aortic valve. The latter can accumulate due to:
- congenital or acquired heart disease;
- bad habits;
- unbalanced diet;
- emotional stress.
In this case, the lumen of the aorta gradually becomes excessively narrow, which impedes blood flow and provokes other dangerous pathologies. The problem is treated by correcting the diet, taking magnesium supplements, as well as organizing a healthy lifestyle. Calcification of the aortic walls can also develop due to the presence of a hereditary predisposition, which determines the leading role of rational nutrition in terms of ensuring the balance of ion-catalytic exchange in the body.
This aortic disease is characteristic of elderly patients who are plagued by age-related changes, vascular atherosclerosis, and high blood pressure. However, young heavy smokers are also at increased risk. The abundance of nicotine and tar in the blood contributes to the loss of elasticity of the walls of the aorta, which invariably leads to its hardening. The latter makes the vessel extremely vulnerable to various types of bruises and chest injuries.
The pathology has the common name of aneurysm. The disease is relatively rare, but represents an extreme danger. An increase in aortic dissection is a matter of time, since the constantly incoming blood flow will necessarily “undermine” the walls of the vessel. In the absence of medical care for a long time, rupture of the aortic walls and death are possible. When a disease is detected, surgery is considered the main method of eliminating the problem.
The pathology is one of the congenital heart defects, which is expressed in the abnormal partial departure of the aorta from the right ventricle. It is also possible that blood flow in the aorta is dominantly supported by the left ventricle. Enlargement of the right ventricular myocardium is often observed. Dextraposition of the aorta is mainly a component of tetralogy of Fallot, one of the complex heart defects.
A dangerous disease that is accompanied by the patient’s state of shock, severe acute hypoxia and ischemia, as well as blood flow disturbances with discirculation and the development of cerebral edema. The course of the disease is accompanied by sharp pain in the sternum, loss of pulse in the lower extremities with the development of paralysis of the legs and dysfunction of the abdominal organs. One of the operational diagnostic tools is to check the Achilles tendon and knee reflexes, which disappear. The main method of treatment is surgical thrombo- or embolectomy.
Inflammatory processes caused by infectious diseases, injuries of various natures, allergic processes, or taking certain medications can cause hardening of the aortic walls, called fibrosis. The pathological condition reduces elasticity, interferes with the normal passage of blood, and is also a risk factor for the development of dangerous diseases.
The pathology of the vessel structure often serves as a prerequisite for the further transition of this condition into an aneurysm. Accompanied by destructive and atrophic transformations of the middle tunic of the aorta.
It is strongly worth noting the need to immediately consult a doctor in case of problems with the cardiovascular system. Only precise diagnostic procedures can make a correct diagnosis. Auscultation of the aorta is considered one of such methods that can give accurate results. The procedure makes it possible to almost certainly detect the presence of an aortic aneurysm, making it possible to provide timely assistance to the patient. Pathology is detected by determining the systolic value above the vessel, which occurs in more than two thirds of patients. In addition, the study allows you to identify the presence of atherosclerotic deposits, determine the exact size of the aorta and the location of the pathological expansion (aneurysm), and recognize the presence of a tumor on the walls. Ultrasound scanning will complement the diagnostic picture. Notifying about the structure of the vessel, the presence of a rupture and its characteristics.
Damaged areas of the aorta can lead to complete rupture of the vessel walls and death of the patient. Modern medicine offers a gentle option for restoring blood flow - aortic replacement. In this case, the aneurysmal sac is removed from the bloodstream; the risk of rupture is eliminated.
Share with your friends:
Symptoms of fibrosis
A feature of mitral valve fibrosis is a long period of compensation. Therefore, the disease may not manifest itself for 3 to 5 years. Morphologically, this corresponds to the stage of focal changes. As the disease progresses, the following complaints appear:
- weakness and low exercise tolerance; difficulty breathing, feeling of lack of air, attacks of suffocation; frequent heartbeat, interruptions; pain in the heart area, including angina attacks; swelling in the legs.
Due to narrowing or incomplete closure of the aortic valve, blood flow into the systemic circulation is reduced. This is accompanied by oxygen starvation and a lack of nutrients in all internal organs. But the brain and myocardium are most sensitive to ischemia. Therefore, aortic fibrosis leads to dizziness, fainting, weakness, and attacks of heart pain.
Watch the video about heart valve fibrosis, symptoms and treatment:
Fibrosis, hardening of the aortic and mitral valve leaflets: what is it - Heart Health
Other cardiac pathologies
07.10.2016
12.6 thousand
8.5 thousand
3 min.
Mitral valve fibrosis is an extremely dangerous pathological condition that develops as a result of the negative influence of rheumatic processes, bacterial and viral infections and other phenomena. It is worth noting that the mitral valve is involved in pumping blood through the heart, so replacing the tissues that form this natural formation with fibrous tissue leads to disruption of the entire heart.
The causes of mitral valve fibrosis are extremely diverse. In the vast majority of cases, fibrous tissue changes appear against the background of a myocardial infarction, in which a certain number of heart muscle cells die and are replaced by connective tissue, which can spread to the walls of the mitral valve.
Another common cause of fibrosis is age-related changes, because heart tissue is also subject to wear and tear, suffers from hormonal changes, slower metabolism and many other adverse effects that occur as the body ages. Along with all this, other factors can provoke the appearance of fibrosis:
- rheumatoid processes;
- infectious damage to myocardial tissue;
- overload of the heart muscle;
- hypertension;
- lung diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- congenital heart defects.
It is now known that the causes of cardiac fibrosis may also be rooted in genetic predisposition.
It is known that there are many cases where this disease is observed in several generations of blood relatives at once, and characteristic tissue changes appear, as a rule, in relatives at the same age.
At the same time, defective genes that can be inherited and cause fibrotic changes have not yet been identified.
The mechanism of fibrosis development has now been studied quite well. Under the influence of various unfavorable conditions, the mitral valve leaflets first become significantly thicker.
Due to the existing compaction, a decrease in tissue elasticity occurs in the future. Next, mitral valve sections are formed at the edges of the mitral valve leaflets.
Fibrous changes then become more pronounced.
As the mitral valve leaflets are damaged, a gradual disruption of its obturator function is observed. Fibrous changes in the mitral valve lead to an increase in its dysfunction, which subsequently causes overload of the left heart and the appearance of symptoms characteristic of this pathological condition.
As the functioning of the mitral valve and left ventricle of the heart becomes impaired, there is an increase in the manifestations of heart failure, as well as pulmonary hypertension. As the valve leaflets are damaged by fibrosis, stagnant processes and symptoms characteristic of this condition occur. These may be symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- swelling of the legs;
- pain in the heart area;
- fainting conditions;
- noise in ears;
- pulsation in the heart area;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
The severity of symptomatic manifestations depends on how severe the compaction of the mitral or aortic valve leaflets is.
Typically, the development of this life-threatening condition is manifested by symptoms of heart failure, when the volume of blood thrown into the ventricle is reduced by 15-30%.
With an even greater decrease in the volume of thrown blood, pulmonary hypertension may develop.
Considering that many of the symptoms observed with mitral valve fibrosis are also characteristic of other diseases of the cardiovascular system, to confirm the diagnosis, the cardiologist first conducts a thorough medical history and conducts the necessary studies. Determining the problem may require the following procedures:
- EchoCG;
- ECG;
- radiography;
- dopplerography;
- auscultation;
- catheterization;
- MRI.
Along with all this, a clinical and biochemical analysis of blood and urine is often required. Deciphering the tests allows us to identify characteristic markers of fibrosis, and along with this, substances indicating the presence of a parasitic invasion of a bacterial or viral infection in the body. A comprehensive examination reveals the extent of damage to the walls of the mitral valve.
If the disease was detected at an early stage of development, treatment can be carried out using conservative methods.
As a rule, antiarrhythmic drugs, diuretics, and anticoagulants are used to improve the patient's condition.
If the doctor has prescribed a conservative method of treatment, the patient should try to avoid severe stress, physical overload, and at the same time maintain a gentle diet.
Your diet should include as many foods as possible that contain large amounts of potassium.
In the vast majority of cases, surgical treatment of mitral valve fibrosis is required. During surgery, either repair or complete replacement of the valve is performed. The choice of surgical intervention method depends entirely on the functionality of the damaged valve.
The higher the degree of damage to the valve, the greater the likelihood that complete replacement will be required. Thanks to the development of a technique for replacing the mitral valve, it has become possible to restore health even to seriously ill people.
After an operation to eliminate cardiac fibrosis, a person must follow a gentle diet, avoid increased physical activity and severe stress.
Source:
Fibrosis of the aortic valve leaflets: how it manifests itself, treatment and prevention
- Additional education:
- “Cardiology”, “Course on magnetic resonance imaging of the cardiovascular system”
Research Institute of Cardiology named after. A.L. Myasnikova
"Course on functional diagnostics"
NTsSSKh them. A. N. Bakuleva
- "Course in Clinical Pharmacology"
- Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education
- "Emergency Cardiology"
- Cantonal Hospital of Geneva, Geneva (Switzerland)
- "Therapy course"
- Russian State Medical Institute of Roszdrav
- Contacts
What is fibrosis of the aortic valve or mitral valve leaflets? Cardiac fibrosis belongs to a number of pathological diseases. It leads to rapid growth and increase in the volume of connective tissue. This, in turn, is fraught with the appearance of scars.
There are several types of cardiac fibrosis. The first of these is focal fibrosis. This form of the disease is initial. It leads to the formation of single scars. Timely diagnosis and treatment can stop the development of focal fibrosis. Otherwise, it will develop into other species.
The second type is diffuse fibrosis. It is one of the final stages of this disease. Diffuse cardiac fibrosis can damage a large amount of connective tissue and lead to much more dangerous and serious consequences.
Cystic fibrosis is a separate disease. It can lead to metabolic disorders and the formation of cysts in the human body. This is very life-threatening, so you should not neglect timely diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of fibrosis.
Fibrosis also varies according to the affected parts of the heart. It is worth considering each of these types in more detail.
Fibrosis of the mitral valve leaflets
Fibrosis of the mitral valve leaflets is a rather dangerous and serious condition. The reasons for its occurrence are very diverse. It is worth considering them in more detail.
Causes
Quite often, this disease appears after the patient has suffered a myocardial infarction. A common cause is age-related changes in the human body. Over the years, tissues and organs wear out. Heart tissue and urinary tract can be damaged due to hormonal changes, rapid slowdown of metabolism, etc.
Mitral valve fibrosis can also be caused by the following reasons:
- Hypertension.
- Lung dysfunction.
- Heart defects.
- Infectious or viral infection of the connective tissues of the heart.
- Strong physical activity, etc.
This disease, in the absence of timely intervention by specialists, can develop into myocardial fibrosis. Otherwise it is called myocardiofibrosis.
Aortic valve fibrosis
The aorta is an essential artery in the human body. It carries blood through a large circle of blood supply from the heart to all organs. But often it is affected by various diseases.
One of these is fibrosis of the aortic valve. What is it expressed in? The thickness of the aortic walls is rapidly increasing.
This negatively affects its elasticity, which significantly slows down blood circulation.
Fibrosis of the interventricular septum
Fibrosis of the interventricular septum is a fairly common heart defect. Its characteristic symptoms appear already in the first years of a person’s life.
Since this disease is congenital, the main reason for its occurrence is a genetic factor. IVS fibrosis is inherited.
Symptoms of fibrosis
Fibrosis of the heart valve apparatus can be identified by a number of specific symptoms. Among them are:
- Constant weakness.
- Shortness of breath during minor physical exertion and eating.
- Inoperability.
- Fatigue.
- Pallor.
- Light weight.
- Fainting
- Heartache.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Heaviness in the chest.
- Sudden changes in blood pressure.
- Tinnitus, etc.
If one or more of the above signs of this deviation appear, you should immediately contact a specialist. A cardiologist deals with diseases of this kind.
Diagnostics
Timely and competent diagnosis can correctly determine the necessary treatment and significantly reduce the risk of complications.
The first thing the doctor will do during your initial visit is an analysis of your medical history. The cardiologist will examine you and carefully review your medical history.
Next, the doctor can prescribe one of the modern types of diagnostics. It can be:
- Radiography. This diagnostic method can most accurately indicate the degree of changes in the heart and cardiovascular system as a whole.
- Echocardiography. It will help determine the exact location and degree of development of defects (scars).
- MRI. Traditional diagnostic method in cardiology.
- Catheterization. This method of diagnosing the disease uses a contrast agent. It is administered through the femoral artery. Catheterization can determine the condition and quality of the structures and parts of the heart.
- ECG, etc.
In addition to the diagnostic methods listed above, conventional blood and urine tests are also used. They are no less effective and efficient. These tests will help determine not only the degree of development of fibrosis, but also the presence of various viral infections and inflammatory reactions in the body.
Source:
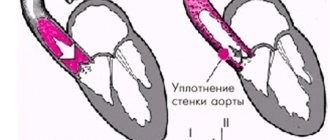
Sealing of the aortic walls of the aortic valve cusps
The aorta is the most important blood vessel of the human body, through which blood disperses to all internal organs through a system of blood vessels, with the exception of the lungs.
Compaction of the walls of the aorta is an extremely dangerous pathological process that leads to the development of diseases, leading to disruption of the functioning of internal organs and vital systems.
In some cases, compaction of the walls of the main vessel causes the death of the patient.
Etiology of the disease
The thickening of the walls of the aorta of the heart occurs as a result of certain processes in the human body.
The main reasons for thickening of the aortic walls:
- Development of hypertension.
- Vascular atherosclerosis.
- Previous diseases that are transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Past scarlet fever, measles.
- Smoking abuse.
- Foods with high cholesterol levels.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Viral infections.
- Genetic predisposition.
With the development of hypertension, when there is a constant increase in blood pressure, the vessels of the circulatory system experience excessive stress during blood flow, since blood passes through them under very high pressure.
The aorta, in turn, being the main conductor of blood, experiences pressure, which in case of hypertension unimaginably exceeds permissible norms.
Source: https://hospvet39.ru/serdechnaya-nedostatochnost/fibroz-uplotnenie-stvorok-aortalnogo-i-mitralnogo-klapana-chto-eto-takoe.html
Diagnostic methods
At the first stage of the examination, the patient is prescribed general clinical tests of blood, urine and ECG. But with their help, you can only detect an inflammatory or ischemic process in the myocardium, therefore, to make a diagnosis of heart valve fibrosis, instrumental methods are required:
- Ultrasound of the heart is the most reliable method; it helps to identify the degree of narrowing or insufficiency of the valve, assess the contractile function of the myocardium and the volume of blood entering the aorta during systole. X-ray reveals myocardial hypertrophy as a reaction to heart overload, congestion in the lungs, and calcium deposits on parts of the valves. CT and MRI are performed if differential diagnosis is necessary or before surgery.
Myocardial hypertrophy as a consequence of valve fibrosis
Fibrous dystrophy of the valve apparatus
An important role in the functioning of the valvular apparatus of the heart is played by the valves, which are represented by loose connective tissue consisting of dense collagen and continuously extending into the chordae tendineae (according to Wikipedia).
Under a number of circumstances, the number of blood vessels supplying the structure of the valves is reduced. As a result, elastic fibers are replaced by dense fibrous tissue, which is characterized by sufficient strength.
Having lost lability, the valves lose the ability to provide physiological hemodynamics. Most often, the mitral valve is affected by pathology, less often – the aortic valve.
Classification of pathology:
- focal. There is moderate damage to the structure of the valve apparatus;
- diffuse. The affected area covers the leaflets and subvalvular space;
- cystic. It is characteristic of an advanced stage and is considered a separate pathology with the formation of cavity formations.
Fibrosis of the aortic and mitral valve leaflets is explained by the following reasons:
- age-related changes with loss of natural collagen potential;
- rheumatic attack (especially repeated), for example, after oropharyngeal infections. The damage is attributed to antibody formation and cross-reactivity between group A streptococcal carbohydrates and heart valve glycoprotein. According to research, almost every five-year-old child has a history of a throat infection. It is possible to develop chronic rheumatic heart disease with damage in the form of post-inflammatory marginal fibrosis;
- Marfan syndrome, dysplasia, in which the anatomical and functional features of the connective tissue are genetically abnormal;
- atherosclerosis of the aorta. Calcification of plaques and subsequent thickening of its wall;
- foci of necrosis (with a heart attack) or inflammation (with myocarditis) near the valve ring.
Diagnosing fibrosis is not very difficult. Initially, clinical blood and urine tests are prescribed to detect the possible presence of inflammation. Biochemical research indicates changes in the levels of cholesterol, sugar, uric acid, total protein, and creatinine.
Ultrasound of the heart reveals the degree of narrowing, valve insufficiency, evaluates the contractile function of the myocardium, blood volume during systole.
X-ray examination reveals myocardial hypertrophy, pulmonary congestion, and calcification of valve fragments.
CT, MRI, CAG are performed if surgical intervention for prosthetic structures is necessary.
How does this process affect the patient’s quality of life?
The symptoms of the disease depend on which specific valve is affected by fibrosis, although some signs of pathologies may coincide. Most often, the patient does not show any complaints for a long time, his condition remains satisfactory. Deterioration in well-being is typical for an advanced process and the formation of complications.
If the mitral valve leaflets are sealed, it is noted:
- fatigue during routine physical activity and sports;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- episodes of heart rhythm disturbances in the form of extrasystole or atrial fibrillation;
- chest pain;
- periodic swelling.
If the thickening of the mitral valve leaflets continues to progress in the absence or ineffectiveness of treatment, MVP occurs with varying degrees of regurgitation or without.
Fibrosis of the aortic valve walls causes:
- progressive shortness of breath;
- pain in the heart during exercise;
- dizziness and fainting when playing sports;
- heartbeat disturbances.
Sometimes the life of a patient with cusp fibrosis is complicated by episodes of hemoptysis and asthmatic attacks due to hemodynamic disturbances.
For young patients, issues related to pregnancy and military service come to the fore. The first is decided individually depending on the stage of the fibrotic process, the presence of stenosis and hemodynamic disturbances. A woman carrying a child is observed, in addition to an obstetrician-gynecologist, by a cardiologist. Childbirth takes place by caesarean section.
The army and the opportunity to engage in professional sports depend on the decision of the medical commission. It is taken into account whether the pathology led to a pronounced defect and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Treatment and observation of a patient with fibrosis of the valve apparatus
Often on forums you can read the question of whether fibrosis can be treated using folk remedies. The answer is clear: there are no such recipes. This process is quite difficult in therapy even for modern medicine.
It is important to know that the prescription of medications is indicated only for the clinical picture of heart failure, in which the following are used:
- cardiac glycosides - Celanide, Digoxin, Strophanthin;
- diuretics - Trifas, Indap, Veroshpiron;
- if indicated, antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic drugs.
Medicines only minimize the symptoms caused by fibrosis without affecting the progression of the disease.
Radical treatment consists of the following methods:
- valve prosthetics to replace the diseased structure with a mechanical or biological analogue. As a rule, a median sternotomy using a heart-lung machine is used;
- mitral commissurotomy, closed or open, with the task of dissecting pathological connections between the valve leaflets;
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- endovascular prosthetics. The essence of the method is to insert a catheter with an implant through the femoral vessels without general anesthesia. Indicated for patients with severe chronic diseases;
- valve transplantation (a relatively new technique).
Indications for surgical intervention in fibrosis:
- neglect of the process;
- wrinkling of valves, tendon threads;
- the presence of pronounced calcification.
After the operation, the patient should be under medical supervision of a cardiologist. The patient is indicated for annual examinations and treatment in a cardio- or cardio-rheumatological sanatorium.
conclusions
Subjective symptoms indicating a change in the functioning of the heart always require consultation with a doctor. Preventive examinations are also important, allowing timely suspicion of the presence of pathological disorders in the structure of the myocardium.
Especially if the valves, due to fibrous degeneration, lose the ability to optimally perform their functions.
In terms of the prognosis of the disease, it directly depends on the severity of the process, the age of the patient, and the presence of other chronic diseases.
Source: //cardiograf.com/bolezni/patologii/fibroz-stvorok-aortalnogo-i-mitralnogo-klapana.html
Treatment of pathology
In asymptomatic cases of valvular fibrosis, treatment is not prescribed. Drug therapy is indicated for symptoms of heart failure:
Drugs for fibrosis can only act on the symptoms that it caused. Therefore, surgical intervention is recommended to radically improve the condition.
It is performed for cardiac decompensation. In addition to open-heart surgery with a heart-lung machine, intravascular access methods through large arteries and minimally invasive options are chosen.
In case of minor destruction of the valve leaflets, plastic surgery, suturing, and dissection of adhesions are used. Hemodynamically significant stenoses or insufficiencies are corrected by implantation of artificial valves. They can be mechanical or biological, made from donor or animal material.
Insufficiency or fibrosis of heart valves: causes and help for the patient
The replacement of elastic fibers of the connective tissue of the heart valve apparatus with rough ones is called fibrosis. It occurs under the influence of ischemia, inflammation or age-related changes. The mitral and aortic valves are most often affected. An acquired heart defect with circulatory failure is formed. Treatment requires cardiac surgery.
Causes of cardiac fibrosis
Fibrous fibers replace the focus of necrosis or inflammation in the myocardium. The structure of this tissue resembles a scar. The most common reasons for valves losing their flexibility and mobility are:
- age-related decrease in valve nutrition,
- rheumatic attack,
- tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media,
- scarlet fever,
- bacterial endocarditis or myocarditis,
- Marfan syndrome with mitral valve prolapse,
- atherosclerotic deposition of cholesterol on the aortic valves,
- myocardial infarction,
- autoimmune processes.
We recommend reading the article about mitral heart disease. From it you will learn about heart valve defects and their causes, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment, and prognosis for patients.
And here is more information about atherosclerosis of the aorta and valves.
Types and degrees of pathology
The initial stage of the formation of heart valve fibrosis is considered focal. It is characterized by the growth of fibers in a local area. This mechanism serves to limit the focus of inflammation or destruction of the myocardium, which is a compensatory-adaptive reaction.
With the progression of pathological processes in the body, the zones of sclerosis spread, and the second stage begins - diffuse changes.
Any formation of scar tissue in the myocardium is irreversible; muscle fibers lose their functional properties and inhibit the functioning of the entire organ.
Heart valves
Development of damage to the mitral and aortic valves
If the valve leaflets become rigid and inactive, this leads to either insufficient closure (insufficiency) or a reduction in the opening through which blood passes (stenosis).
Stenosis creates an obstacle to the ejection of blood into the aortic trunk or left ventricle. Because of this, internal organs are not provided with adequate nutrition.
With mitral or aortic insufficiency, part of the blood returns back to the atrium or ventricle of the left half of the heart. This creates an increased load on the myocardium, contributes to a decrease in the contractility of muscle tissue, which over time leads to circulatory decompensation.
Symptoms of fibrosis
A feature of mitral valve fibrosis is a long period of compensation. Therefore, the disease may not manifest itself for 3 to 5 years. Morphologically, this corresponds to the stage of focal changes. As the disease progresses, the following complaints appear:
- weakness and low exercise tolerance;
- difficulty breathing, feeling of lack of air, attacks of suffocation;
- frequent heartbeat, interruptions;
- pain in the heart area, including angina attacks;
- swelling in the legs.
Due to narrowing or incomplete closure of the aortic valve, blood flow into the systemic circulation is reduced.
This is accompanied by oxygen starvation and a lack of nutrients in all internal organs. But the brain and myocardium are most sensitive to ischemia.
Therefore, aortic fibrosis leads to dizziness, fainting, weakness, and attacks of heart pain.
Watch the video about heart valve fibrosis, symptoms and treatment:
Diagnostic methods
At the first stage of the examination, the patient is prescribed general clinical tests of blood, urine and ECG. But with their help, you can only detect an inflammatory or ischemic process in the myocardium, therefore, to make a diagnosis of heart valve fibrosis, instrumental methods are required:
- Ultrasound of the heart is the most reliable method; it helps to identify the degree of narrowing or insufficiency of the valve, assess the contractile function of the myocardium and the volume of blood entering the aorta during systole.
- X-ray reveals myocardial hypertrophy as a reaction to heart overload, congestion in the lungs, and calcium deposits on parts of the valves.
- CT and MRI are performed if differential diagnosis is necessary or before surgery.
Myocardial hypertrophy as a consequence of valve fibrosis
Treatment of pathology
In asymptomatic cases of valvular fibrosis, treatment is not prescribed. Drug therapy is indicated for symptoms of heart failure:
Medicines for fibrosis can only treat the symptoms that cause it. Therefore, surgical intervention is recommended to radically improve the condition. It is performed for cardiac decompensation.
In addition to open-heart surgery with a heart-lung machine, intravascular access methods through large arteries and minimally invasive options are chosen.
In case of minor destruction of the valve leaflets, plastic surgery, suturing, and dissection of adhesions are used. Hemodynamically significant stenoses or insufficiencies are corrected by implantation of artificial valves. They can be mechanical or biological, made from donor or animal material.
Consequences of fibrosis
The formation of stenosis of the opening or non-closure of the leaflets due to fibrosis most often occurs against the background of rheumatism, atherosclerosis, endocarditis of bacterial etiology. With heart attacks and myocarditis, changes in blood circulation are less pronounced.
In old age, in addition to insufficient blood flow, heart rhythm disturbances, swelling and shortness of breath, insufficient nutrition of the brain is difficult to tolerate. Therefore, if you have cerebral symptoms (without neurological causes), you need to undergo a heart examination.
Prognosis for patients
The course of the disease and its effect on life expectancy depends on the degree of stenosis or insufficiency of the valve apparatus. Minor changes have a favorable prognosis, and in case of severe, mature heart defects, the outcome of the disease depends on the timing and success of surgical treatment.
Prevention of pathology development
Since fibrosis leads to irreversible changes in cardiac hemodynamics, you need to know how to prevent its development. To do this, first of all, complete treatment of foci of infection in the body is required. Bacterial or viral diseases transmitted on the legs pose a particular danger.
If you suspect complications after them from the heart (aching pain, palpitations and shortness of breath with light exertion), you need to undergo a minimum diagnostic complex - a blood test, ECG, ultrasound of the heart.
It is also important to give up smoking, alcohol abuse, and limit fatty animal products, sugar and flour products in your diet. It is recommended to maintain a sufficient level of physical activity and control body weight.
We recommend reading the article about cardiac calcification. From it you will learn about the pathology and the reasons for its development, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment, and prognosis for patients.
Read more about restrictive cardiomyopathy here.
Fibrosis of the heart valves occurs against the background of age-related changes in the body, inflammatory or ischemic processes. The growth of coarse fibrous connective tissue disrupts the movement of the valves and leads to the formation of acquired heart defects.
Clinical manifestations depend on the degree of non-closure of parts of the valve or stenosis of the orifice, progression of circulatory failure. For treatment, medications are used only in the initial stages; radical relief from the disease is possible after surgery (plasty or valve replacement).
Source: https://CardioBook.ru/fibroz-klapanov-serdca/
Consequences of fibrosis
The formation of stenosis of the opening or non-closure of the leaflets due to fibrosis most often occurs against the background of rheumatism, atherosclerosis, endocarditis of bacterial etiology. With heart attacks and myocarditis, changes in blood circulation are less pronounced.
In old age, in addition to insufficient blood flow, heart rhythm disturbances, swelling and shortness of breath, insufficient nutrition of the brain is difficult to tolerate. Therefore, if you have cerebral symptoms (without neurological causes), you need to undergo a heart examination.
What are the symptoms of the disease
What are the symptoms of fibrosis of the cusps and aortic valve? The disease has several stages, so the symptoms of development are different for each of them. At the very beginning, the patient will suffer from shortness of breath and cough, but not strong and not particularly pronounced. Sometimes there may be blood in the cough, but it is extremely rare.
Passing a medical examination
When fibrosis of the leaflets progresses, then blood circulation is seriously impaired, although patients can still tolerate physical activity of varying intensity. Many continue to lead an active lifestyle and play sports. And only a medical examination helps detect fibrosis of the aortic valve.
With a decrease in myocardial contraction in the left ventricle, the pressure in the pulmonary circulation of the blood begins to rise, then the symptoms worsen. Shortness of breath interferes with vital functions, the heart rate constantly increases. Shortness of breath will appear even when a person is at rest, without engaging in sports or physical activity.
Often this condition is combined with asthmatic syndrome. The disease begins to manifest itself clinically when blood circulation is impaired, which is associated with the flow of blood from the left ventricle into the atrium. As a result, the myocardial contraction function is significantly reduced, and the condition may worsen if the blood volume is only 15 to 30%.
In this condition, the patient will develop and actively manifest symptoms such as increased heartbeat, increased pulsation in vessels located throughout the body, chest pain, noise and dizziness, fainting, swelling of the legs. Shortness of breath becomes a constant companion of a sick person, who begins to feel illness in the right hypochondrium. This indicates that blood stagnation has begun in another organ - the liver.
Echocardiography
How is the disease diagnosed? First, the doctor conducts a visual examination, and then sends the patient to undergo a two-dimensional cardiogram. This is necessary to determine how dilated the mitral valve is, which can become larger and reach 3-4 cm in size. A two-dimensional echocardiogram is reflected on the screen in the form of cross-sectional and longitudinal sections, which allows you to see the structure of the valve from all sides and evaluate what changes have occurred to it. The results most often indicate that the valve has begun to regurgitate.
Simultaneously with this method, another diagnostic method is performed, which is called chest radiography. It is needed to understand in which parts of the lungs congestion has occurred, whether there are pleural lines in the lungs along the costal and interlobar pleura. On a direct view, the heart will appear in a mitral configuration. Phonocardiography is performed separately to diagnose other pathologies associated with aortic valve fibrosis.
Prevention of pathology development
Since fibrosis leads to irreversible changes in cardiac hemodynamics, you need to know how to prevent its development. To do this, first of all, complete treatment of foci of infection in the body is required. Bacterial or viral diseases transmitted on the legs pose a particular danger.
It is also important to give up smoking, alcohol abuse, and limit fatty animal products, sugar and flour products in your diet. It is recommended to maintain a sufficient level of physical activity and control body weight.
We recommend reading the article about cardiac calcification. From it you will learn about the pathology and the reasons for its development, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment, and prognosis for patients.
Read more about restrictive cardiomyopathy here.
Fibrosis of the heart valves occurs against the background of age-related changes in the body, inflammatory or ischemic processes. The growth of coarse fibrous connective tissue disrupts the movement of the valves and leads to the formation of acquired heart defects.
Clinical manifestations depend on the degree of non-closure of parts of the valve or stenosis of the orifice, progression of circulatory failure. For treatment, medications are used only in the initial stages; radical relief from the disease is possible after surgery (plasty or valve replacement).
Due to deformation and disruption, regurgitation of the mitral valve may occur, which subsequently leads to thickening of the leaflets, dysfunction and insufficiency. There may be several degrees of progression of the pathology.
Heart valve insufficiency occurs at different ages. It has several degrees, starting from 1, as well as specific signs. Heart defects may include mitral or aortic valve insufficiency.
Valve leaflet calcification is quite difficult to detect. It can be either mitral or aortic, directly from the aorta and its root. There are two degrees of damage - 1 and 2.
Abnormal movement of blood in the left ventricle is called aortic regurgitation. The signs are invisible at first, only when the degree is already quite advanced, then severe symptoms appear. Valve defects occur even in children. Treatment is only surgery.
Such a formidable pathology as atherosclerosis of the aorta and valves manifests itself mainly in old age. Under the influence of certain reasons, the leaflets of the aortic and mitral valves are damaged, which will lead to serious consequences in the future.
Calcification of the heart and its individual parts (valves, cusps, vessels), the aorta is detected mainly after 60. The reasons may lie in poor nutrition and age-related changes. Treatment involves prescribing medications and following a diet. Folk remedies will also help.
Cicatricial changes in the myocardium (left ventricle, lower wall, septal region) appear after certain diseases. The presence can be assumed by signs on the ECG. Changes are not retroactive.
The disease restrictive cardiomyopathy is quite rare. The pathogenesis is asymptomatic, manifestations in children are more pronounced, but can be confused with other pathologies. What is special about endomyocardial fibrosis?
If mitral heart disease (stenosis) is detected, it can be of several types - rheumatic, combined, acquired, combined. In each case, mitral valve insufficiency can be treated, often with surgery.
Sources:
http://serdce-help. ru/%D1%84%D0%B8%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B7-%D0%B0%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%82%D0%B0%D0% BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE-%D0%BA%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BF%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B0 /
http://cardiobook. ru/fibroz-klapanov-serdca/
Fibrosis, thickening of the aortic and mitral valve leaflets: what is it?
Sazykina Oksana Yurievna, cardiologist
Due to the active introduction of echocardioscopy (ultrasound of the heart) into the examination of the general population, the majority of heart diseases do not have a single chance to remain undetected. This is because even minor changes in the internal structure of the heart can be detected using ultrasound.
Therefore, recently more and more patients are hearing from doctors that they have fibrosis of the heart valves, although there are still no clinical manifestations of the disease.
This is, of course, good, because the earlier fibrosis, for example, of the mitral or aortic valve is detected, the greater the chance of preventing the development of adverse consequences.
Fibrosis of the heart valves is nothing more than the formation of excess connective tissue in the place where thin, elastic and smooth valve leaflets should be located in a normal heart (each valve has its own number of leaflets). Fibrosis can affect not only the valves themselves, but also the valve ring, to which the valves are attached on one side, and even the muscle tissue around the valve ring.
Types of disease
The classification of fibrosis varies among specific organs. In the liver, the type of disease depends on the location of the scars in its lobules:
- focal;
- perihepatocellular;
- zonal;
- multibular;
- bridge-like;
- periductular;
- perivenular.
Local and focal fibrosis is the initial stage of the disease, when isolated areas of tissue are damaged. With a diffuse disease, the damage covers most of the organ. Cystic fibrosis is characterized by damage to the exocrine gland, the ducts become blocked and cysts form. This leads to the development of disorders in the respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract.
Among the sensory organs, epiretinal fibrosis of the eye occurs, when changes of varying degrees occur in the structures of the vitreous body and retina. Men may develop cavernous fibrosis of the penis. Women in some clinical situations may develop linear breast fibrosis.
Possible complications
With hypertension, the walls of the aorta can dissect; the same process will be triggered if the body is subjected to excessive physical stress.
If not treated promptly, peeling of the aortic walls will lead to protrusion of the blood vessel and its further rupture. In most cases this results in death.
The main method of therapy to prevent the development of these complications is surgery.
With improper treatment or without it at all, the patient may experience the following complications:
- Atrial fibrillation and other heart rhythm disorders.
- Atrioventricular block, when the movement of the impulse from the atrium to the ventricle is weakened.
- Secondary infective endocarditis.
- Heart failure.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
It is also possible that specific complications may arise, depending on the diseases accompanying the condition.
The essence of the disease
As the tissue grows, the number of blood capillaries inside it decreases significantly, therefore, it receives less nutrients, and as a result, some of the valve cells simply die off, turning into fibrous tissue.
This is a pathological condition because the rapid thickening of the walls and valves of the aorta significantly reduces its elasticity, and this, in turn, significantly slows down the speed of blood flow through the arteries and vessels and worsens the physical indicators of a person’s vital functions. That is, it has a detrimental effect on human health, and in advanced stages of the disease, even threatens his life.
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- serious disturbances in intestinal activity, accompanied by decreased calcium absorption;
- hereditary disposition;
- negative changes in the activity of the kidneys, which ensure the utilization of microelement salts;
- rheumatism of the heart;
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart muscle);
- hypertension;
- structural abnormalities of blood vessels;
- congenital heart defects (aortic stenosis, bicuspid aortic valve).
Additional risk factors that aggravate metabolic disorders and provoke the development of valve calcification are:
- bad habits;
- overweight;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- excess vitamin D;
- cancerous tumors;
- injuries of bones and soft tissues.
Often, calcification of the heart valves is combined with atherosclerosis.
Degree of development of calcification of heart valves
| Degree of disease | Signs of mitral valve pathology | Signs of aortic valve pathology |
| Compensated | An increase in the level of calcium in the blood, calcification of the valves. The tissues are compacted, there is a slight deterioration in hemodynamics | Difficulties arise with the opening of the valves, but the compensation mechanisms of the left ventricle keep the situation under control. During physical activity, minor heart pain is possible, which increases as the disease progresses. |
| Subcompensated | Shortness of breath during physical activity, tachycardia, arrhythmia, wet cough (sometimes with blood clots), hoarseness | Shortness of breath during physical activity, heart pain. Over time, signs of respiratory failure and aortic narrowing occur at rest |
| Decompensated | It develops rarely - with long-term ignoring of symptoms or an avalanche-like progression of the pathology. Pronounced weakness, shortness of breath with little physical activity. Cough with scarlet sputum, pale skin. Requires emergency medical attention | Signs of increased volume of both ventricles. Severe heart failure. The condition is extremely dangerous |
Severe shortness of breath and slight cough on exertion. Fast fatiguability. The appearance of hypertension.
If treatment is not started on time, the condition worsens with the addition of more significant symptoms:
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- Frequent dizziness and tinnitus.
- Heaviness and pain in the chest and right hypochondrium, due to stagnation of blood in the liver.
- Changes in blood pressure.
If fibrosis of the aortic valve progresses significantly, then surgery is prescribed to restore the valve or replace it. In this case, how dysfunctional the valve has become and how advanced its insufficiency is plays a big role. If it is severely affected, then prosthetics are mandatory.
The defect can also be corrected using the meterclip method, which is considered a type of mini-invasion.
This technique is considered quite innovative and advanced, allowing it to expand the possibilities of treating various heart defects, including fibrosis of the walls.
Metraclips allows you to operate on very seriously ill patients and those for whom surgery is contraindicated. As a result, the invasion helps patients return to a normal lifestyle, engage in usual activities, including sports.
Vitamin and mineral complexes
It is necessary to avoid in every possible way the penetration of infections into the human body, which negatively affect the state of health and the human body. In spring and winter, the doctor will prescribe additional vitamin and mineral complexes to increase the body's resistance to various viruses and harmful bacteria.
If the patient is ill with a viral or infectious disease, then when contacting a therapist, it is worth informing him about the development of fibrosis of the valves.
Course of therapy
In the absence of pronounced manifestations of fibrosis, treatment is not required. It is enough for the patient to be observed by a cardiologist and periodically undergo ultrasound of the heart. The exception is people who have concomitant diseases (arrhythmia, hypertension, ischemia). In their case, it will be necessary to use therapeutic agents, depending on the pathological process.
In case of severe fibrosis, which provoked the development of heart failure, diuretics (Indapamide, Veroshpiron) and cardiac glycosides (Digoxin, Strophanthin) are prescribed. Their role is to stimulate the heart and remove excess moisture from the body. Other medications are used depending on the manifestations of the pathological process and the causative factor.
Significant changes that provoked severe stenosis of the valve ring are eliminated surgically. Its essence is in valve prosthetics or plastic surgery. Most of the operations are full-scale, that is, on an open heart, using a cardiopulmonary bypass device.
The use of traditional medicine must be agreed with the attending physician. In fact, it cannot help in the treatment of fibrosis; it will only reduce nervous tension and saturate the body with useful substances.
Prevention measures
The appearance of fibrous tissue is easier to prevent than to stop or treat. The following tips will help with this:
- prevent rheumatism;
- eliminate infectious diseases without causing complications;
- make a proper diet;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- follow the recommendations of your doctor;
- undergo a full medical examination annually;
- strengthen the immune system;
- avoid physical overload;
- avoid stressful situations;
- exercise.
Moderate physical activity is especially beneficial for children. It’s better to forget about weightlifting and overly intense training on exercise machines. It is recommended to pay attention to running, swimming and other sports that strengthen the heart muscle.
Fibrosis of the valve apparatus is characterized by the appearance of negative consequences, for example, acquired heart disease (stenosis of the valve ring or insufficiency of its leaflets). If the changes are caused by rheumatism, then the chance of their development is higher than due to ischemia or heart attack.
Atherosclerosis of the aorta provokes non-rheumatic types of defects much more often than myocarditis. It is extremely difficult to predict the likelihood of their formation.
Doctors try to focus on the results of examinations and the course of the main pathological process that provokes changes in the heart in order to keep the situation under control.
Treatment and observation of a patient with fibrosis of the valve apparatus
Often on forums you can read the question of whether fibrosis can be treated using folk remedies. The answer is clear: there are no such recipes. This process is quite difficult in therapy even for modern medicine.
It is important to know that the prescription of medications is indicated only for the clinical picture of heart failure, in which the following are used:
Source: https://AptekaTamara.ru/bolezni/fibroz-aortalnogo-klapana.html
Causes of cardiac fibrosis
Fibrous fibers replace the focus of necrosis or inflammation in the myocardium. The structure of this tissue resembles a scar. The most common reasons for valves losing their flexibility and mobility are:
- age-related decrease in valve nutrition,
- rheumatic attack,
- tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media,
- scarlet fever,
- bacterial endocarditis or myocarditis,
- Marfan syndrome with mitral valve prolapse,
- atherosclerotic deposition of cholesterol on the aortic valves,
- myocardial infarction,
- autoimmune processes.
Types of pathology
In medicine, a special classification of fibrosis is used, which is based on factors such as the causes of formation, symptoms and rate of progression. The following types of pathology can be distinguished:
- Focal. This is the initial form of development of the disease. It is characterized by the formation of small and shallow scars on the connective tissue. Using modern diagnostic and treatment methods, you can quickly stop the development of the disease at this stage. This can prevent the formation of more complex stages of pathology.
- Diffuse. Its distinctive feature is that it can harm a fairly large area of connective tissue, which provokes the development of serious complications.
- Cystic. This stage is distinguished as a separate disease. At this stage, the patient experiences metabolic disturbances. It should also be noted that at this stage there is a high probability of the formation of cysts, which poses a danger to human life.
Answering the question “What is fibrosis of the aortic valve leaflets?”, we can say that this is a rather complex pathology that provokes the formation of dangerous complications and concomitant diseases.
Causes
Experts note that there is a fairly extensive list of reasons that can lead to the development of an anomaly:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system suffered by the patient;
- development of inflammatory processes of an allergic nature in the body;
- hereditary pathologies of aortic formation;
- excessive drinking or smoking;
- a reaction that may occur as a result of taking medications;
- changes in the body that occur with age;
- mechanical injuries of the chest, which are accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the heart or valves;
- frequent and intense physical activity;
- lack of calcium or other elements necessary for its normal functioning in the patient’s body;
- genetics.
Each or more of the above factors can lead to the inability of the aorta to perform its intended functions.