Doesn't a false chord exempt you from military service?
Popular
Three pairs of names have been named that are destined for each other.
Which zodiac signs are prohibited from wearing gold jewelry?
The zodiac signs that will be covered by a money avalanche in 2020 have been named
? My grandson was diagnosed with false chord. What it is? Previously, no abnormalities in the functioning of the heart were observed. Cardiograms are normal. He's about to join the army. What should you be wary of?
Tatyana Vasilievna.
Dear Tatyana Vasilievna! According to the chief cardiologist of the Volgograd region, Vitaly Ivanenko, false chord is a fairly common abnormality of heart development.
– It cannot be said that false chord is a disease; it would be more correct to say that it is a minor anomaly in the development of the heart. It sometimes happens that during intrauterine development, one or several thread-like fibrous structures are formed, which are atypically attached to the walls, in most cases, of the left ventricle of the heart. That is, this is additional education, which ideally should not exist. Hence the name - additional or false chord.
? What could this be connected with, what is the cause of the anomaly?
– The proven fact of the formation of a false chord is heredity. If parents have similar growths, then with a high probability they will also be diagnosed in their children. Presumably, the occurrence of an anomaly can also be caused by factors such as adverse environmental influences, weak maternal immunity, unbalanced nutrition, smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy, infection of the fetus, and an unbalanced psycho-emotional state.
? How is a false chord diagnosed? Are there any external signs that can be used to determine that a child has extra fibers in the heart?
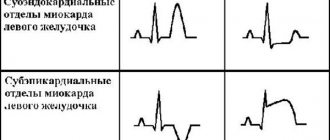
– There are no characteristic external symptoms. If there is only one anomaly (that is, one outgrowth and one notochord), then there is a high probability that it will not manifest itself in any way throughout life. Chords are classified into longitudinal, diagonal and transverse, depending on their location. Diagonal and longitudinal do not interfere with blood flow in the heart. But transverse chordae (mostly multiple) can sometimes complicate this process, which in adulthood in some cases can provoke heart rhythm disturbances.
Doctors' first suspicions about the presence of a false chord arise when systolic murmurs are detected when listening to the heart. In most cases, this is detected within a period of up to three years. If murmurs are detected, the pediatrician prescribes a consultation with a cardiologist, ECG, and ultrasound examination. If there is a need (some abnormalities, for example, according to the results of an ECG or ultrasound), stress tests and Holter ECG monitoring are also prescribed. Stress tests are a study of the cardiovascular system’s response to (physical) stress, and Holter monitoring is when the work of the heart is recorded during the day using special portable devices.
? Does the abnormality require treatment?
– False chord of the left ventricle in a child is almost always safe and does not require specific treatment.
? Is physical activity contraindicated for this diagnosis? Are there any restrictions or recommendations?
– There is no need to exclude physical activity, as it helps improve health, but it is very important to distribute it correctly. For example, it is not advisable to engage in weightlifting or boxing. Physical therapy classes are encouraged. It is also necessary to provide a complete, balanced diet with a maximum content of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is important to maintain a calm and balanced psycho-emotional state.
? Is the presence of a false chord in the heart an indication for exemption from military service?
– It all depends on the results of the medical study. If a cardiologist, after conducting a series of diagnostics, concludes that the anomaly is not accompanied by disturbances in heart rhythm and does not limit the functionality of the organ, then a false chord of the left ventricle in itself does not exempt one from performing military duty. And there is nothing to be afraid of.
Irina Marchenko. © Photo: Publishing House “Volgogradskaya Pravda” / archive.
Additional septum in the heart
The main reason for the formation of a defect in the heart cavity is genetic predisposition.
In other words, heredity is the etiological factor. The anomaly is transmitted from mother to child and quite often women are not aware of the existence of additional chordae.
The risk of developing abnormalities in the structure of the child’s heart increases if the mother has diseases of the cardiovascular system.
In addition to accessory valve muscles, other abnormalities can also be detected - mitral valve prolapse, open oval window.
An equally significant factor of adverse influence, against the background of which an extra chord may form in the heart, is an incorrect lifestyle. We are talking, in particular, about the abuse of bad habits.
If the expectant mother smokes and drinks alcoholic beverages during pregnancy, when the formation of connective tissue in the fetus occurs, then we should expect that the newborn will be diagnosed with abnormal defects in the structure of the heart!
Concept of chord in the heart
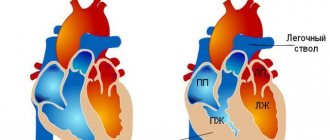
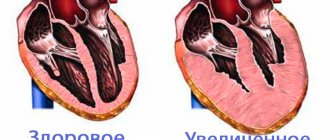
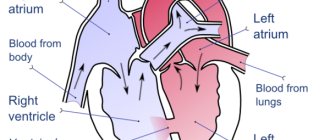
The heart is the main organ that maintains the vitality of the human body. It consists of four chambers, which contain 2 ventricles and an atrium. Between them there are valves that prevent blood from flowing in the opposite direction. Otherwise, mixing of venous and arterial blood would occur.
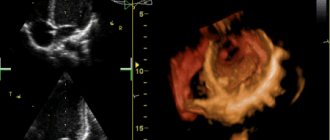
The heart contains several chords. They consist of muscle tissue and are strong threads. If the patient has an additional chord, it is easy to notice on an ultrasound examination - it will stand out due to its thickness. In most cases, an additional chord forms in the left ventricle.
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
The main etiological factor in the occurrence of such an anomaly as an additional chord in the heart of a child is genetic predisposition. The risk increases if the mother has cardiac pathology. But experts do not exclude other reasons for the development of small cardiac anomalies:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- malnutrition;
- environmental pollution;
- radiation.
An abnormality of connective tissue is closely related to its dysplasia. The formation of the fetal cardiovascular system ends by the eighth week of intrauterine development.
Obstetricians and gynecologists know that the blood of the unborn child circulates independently already on the 26th day of pregnancy, heart valves are formed at the 6th week, therefore it is in the first trimester that a woman needs to be especially careful about adverse effects.
An additional chord is formed in utero during the formation of the heart muscle. Doctors often detect left ventricular solitary chord (LVSD) on a routine ultrasound. At birth, the child is diagnosed with a congenital anomaly of the heart chambers. In infants, a false chord in the heart is often combined with other pathologies - the presence of excess trabecula or the opening of the oval window.
Is an extra chord dangerous for life? It depends on hemodynamics.
If the thread has no hemodynamic significance, then it can be argued that it will not affect the normal activity of the heart in any way, and therefore does not require treatment.
The effect on hemodynamics means the need for regular monitoring by a specialist. The table outlines the main types of accessory chord, as well as their effect on hemodynamics.
| Classification sign | Variety | Hemodynamic value |
| Direction | Transverse | Hemodynamically significant chord that impairs the functioning of the heart |
| Diagonal | Has no hemodynamic significance | |
| Longitudinal | Does not affect hemodynamics | |
| Location in departments | Right ventricular | Has hemodynamic significance, expressed by accelerated heartbeat, tingling in the heart |
| Left ventricular | Does not affect hemodynamics | |
| Quantity | Single | Has no hemodynamic significance |
| Plural | Hemodynamically significant chord, which is manifested by heart rhythm disturbances and deterioration of the child’s general well-being | |
| Location in the ventricles | Basal | Does not affect hemodynamics |
| Apical | Hemodynamically insignificant chord | |
| Middle | Has no hemodynamic significance |
LVDC develops in the womb. Why do children have this problem? The causes of pathology include:
- Genetic predisposition. False chord can be passed on to a child from parents. Most often, the anomaly is inherited through the female line if the mother has extra tendon threads in the heart.
- Abuse of bad habits. Smoking tobacco products, taking alcohol and drugs from 4-5 weeks of pregnancy can affect the intrauterine formation of the baby’s heart muscle.
- Poor environmental conditions. Polluted air and water are factors that can trigger the development of pathology.
- Nervous or physical stress. The formation of a false chord can occur due to severe stress or excessive physical exertion.
An abnormal chord of the left ventricle is a hereditary anomaly, which in 92% of cases is inherited through the maternal line (in rare cases, through the paternal line), and develops in utero due to a failure in the development of connective tissue. That is why mothers who have previously been diagnosed with this disease are recommended to have their child examined.
It is possible that the following unfavorable factors may be the reasons for the appearance of an additional chord:
- bad ecology;
- smoking or drinking alcohol and drugs;
- nervous and physical stress.
Additional chord in the heart of a child: types of chords, diagnosis and treatment
When the doctor tells you that your baby has a heart murmur, there is no reason to panic. The condition does not require emergency resuscitation measures or intensive treatment. The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. It will help clarify the location and number of additional strands. There are the following types of LVDC:
- according to location in the ventricle - apical, middle, basal;
- in relation to the axis of the heart - diagonal, longitudinal, transverse;
- by number - singular and plural.
If echocardiography has revealed an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle in a child of any age, I advise parents to undergo the following examinations:
- A general blood test is not important in terms of diagnosing LVHL, but it will reveal anemia or an existing inflammatory process in the body, which can aggravate the condition of a child with a minor cardiac anomaly.
- Electrocardiography. It is advisable to conduct Holter monitoring, which will exclude arrhythmia with greater diagnostic accuracy.
- ECG tests with physical activity will show how well the child’s heart “copes” with its function.
- Consultations with specialized specialists (orthopedist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist).
For a standard check-up for a minor cardiac anomaly, it is enough to undergo an echocardiography once a year. The examination is scheduled unscheduled if:
- the patient has complaints, including those not directly related to cardiology;
- you notice that the child is growing rapidly;
- there was a sharp weight loss;
- a chronic disease has been diagnosed, such as asthma, gastritis, nephritis;
- the child goes to kindergarten, school, university;
- there is a question about the sports section;
- stress occurred: an exam, the loss of one of the family members, conflict in the children's team and at home;
- pregnancy is planned or determined.
Single LVDC is not considered a pathology. Experts consider them as an anatomical feature of a person. The presence of an additional chord is not a contraindication to attending physical education classes.
Young men with abnormal cords can be drafted into the army if they do not have complications or concomitant pathologies.
It is only important to clearly tell the child about his condition and warn him that he needs to be attentive to his health.
Article last updated: 04/08/2018
According to research, an additional chord occurs in 22% of cases among the pediatric population. But this is only for individuals examined by echocardioscopy.
This additional chord is formed in the baby’s intrauterine heart at the 5th week of pregnancy.
Minor anomaly of cardiac development, or, as doctors like to write, MARS, is a group of anomalies in the development of cardiac structures with deviations from the normal structure, which do not lead to malfunctions. Consequently, there are no health complaints.
Our article will tell you about the features of cardiac structures, why an additional chord appears in a child’s heart and how to continue to live with it.
The heart consists of chambers - the atria and ventricles, between which there are valves. Valves are necessary to prevent blood from flowing in the opposite direction. The opening and closing of the valves is regulated by special strings, or chords.
The normal chord is attached to the valve at both edges and participates in its operation. The additional chord differs in thickness and structure from other chords and, as a rule, is not completely attached to the valve and may not participate in its operation.
How can such a chord be dangerous? It may contain additional pathways and cause heart rhythm disturbances such as atrial fibrillation or extrasystole. May change the speed of blood flow to the heart.
- The ultrasound specialist must indicate in his conclusion which chord is hemodynamically significant and how it affects the contraction of cardiac structures.
- If you do not perform ultrasound screening on your child, you may not even know about such a diagnosis.
- By location:
- right ventricular (found in 2 - 5% of cases);
- left ventricular (up to 95% of all cases).
By structure:
- fibrous;
- fibromuscular;
- muscular.
By placement in the heart:
- diagonal;
- longitudinal;
- transverse.
In count:
- single (in 70% of cases);
- multiple (in 30% of cases).
By participation in blood circulation in the chambers of the heart:
- hemodynamically significant. Affect blood flow and may interfere with heart function;
- hemodynamically insignificant. Usually considered as a variant of the norm, they do not harm the functioning of the heart.
At the reception there was a child, 7 years old, a boy. An ultrasound of the heart revealed a chord in the left ventricle. Mom said that she was also given this diagnosis, and her grandmother also has this heart anomaly.
The emergence of an additional chord also contributes to:
- smoking by mother during pregnancy;
- poor environmental situation;
- mother's poor diet;
- stress.
Usually, if there is an abnormal chord in the left ventricle, children do not show any complaints.
If there is a chord in the right ventricle, several signs are possible:
- fatigue;
- headaches, dizziness;
- there is a risk of heart rhythm disturbances;
- stitching pain in the region of the heart;
- emotional instability;
- intolerance to stuffy rooms.
It should also be borne in mind that these symptoms in most cases appear during physical activity.
Personal experience. As a rule, for every full consultation with a cardiologist, there is 1 child with an additional chord. In this case, no special complaints are presented, and the extra chord is an accidental finding.
There was even a boy hockey player who did 3-4 hours of daily physical activity with LVDC (accessory chord of the left ventricle) and tolerated such stress very well. But it should be borne in mind that this is a chord in the left ventricle.
I have never encountered an abnormal chord in the right ventricle in my practice.
Komarovsky E. O. about the “famous chords in the heart”: “In my practice, I have encountered children who were randomly identified with chords in the heart on an ultrasound. If not for the ultrasound, then clinically these are absolutely healthy children.
The only thing they are not recommended to do is jump with a parachute and work as divers.”
An additional chord is detected by ultrasound screening at 1 month of the child’s life.
Also, additional chords create a specific heart murmur, which, as a rule, can be heard well while lying down and disappears when the body position changes. In any case, if a murmur in the heart is detected, the doctor will refer the child for an ultrasound scan of this organ.
Also, if there is a risk of developing arrhythmia, it is necessary to conduct ECG monitoring annually. If changes are detected on the ECG, it is worth conducting a detailed examination - daily ECG monitoring.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment.
No surgical intervention is required for additional chord.
1. If the child complains, then treatment is symptomatic. Magnesium preparations; nootropics; drugs to improve blood circulation, which reduce the myocardium’s need for oxygen and normalize metabolic processes in heart cells.
2. Daily physical activity is necessary for normal heart function:
- walks in the air;
- cycling, rollerblading;
- jogging;
- hardening.
3. Nutrition should consist of saturating the diet with foods rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium:
- dried apricots;
- dairy products;
- baked potato;
- cheeses;
- raisins, dried fruits;
- bananas;
- nuts.
4. It is necessary to exclude prolonged contact with computers and phones.
5. A child’s healthy sleep of 8 hours a night is important.
Such a child should undergo an annual echocardioscopy, ECG and visit a pediatric cardiologist.
The additional chord of the left ventricle is a normal variant and, without any clinical manifestations, does not require drug correction. There is no need to panic if such a conclusion is written on the ultrasound, but it is better to contact a pediatric cardiologist who will tell you in detail what to do with the extra chord.
Source: https://bonbonufa.ru/zabolevaniya-serdtsa/dopolnitelnaya-peregorodka-serdtse/
Additional chord and army
It is impossible to say unambiguously whether the actions of the military commissariat sending a conscript diagnosed with “false chords of the left ventricle” to the army are legal. Sometimes such a call is unlawful, but more often the law is on the side of the state structure. The fact is that pathology rarely seriously affects the functioning of the heart and the entire human body.
The chord in the heart is the tissue that connects the walls of the left or right ventricles. When the organ contracts, these muscle connections do not allow the heart valves to bend and let blood back in, i.e. prevents regurgitation - reverse blood flow.
With an abnormal structure of the heart, additional chords are formed in the cavity of the left or right ventricles. Doctors say the main reason for their appearance is hereditary factors, the environment, as well as stress or bad habits of the mother during pregnancy.
Symptoms of the disease are often mild or do not appear throughout life. For this reason, the patient learns about the presence of formations by chance - during a routine examination or auscultation - listening to heart sounds, including murmurs.
Pathology in rare cases is accompanied by complications. The patient goes to a hospital or clinic with complaints of noises in the chest (most pronounced during coughing), pain in the left half of the chest, weakness, interruptions in heart rate and lack of air when breathing. Additional formations can also cause arrhythmia - disturbances in heartbeat rhythms. In this situation, the disease can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- headaches, dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- chest pain;
- interruptions in heart rhythm: the heartbeat slows down or increases in speed.
Symptoms and diagnosis
In early childhood, a chord in the heart may not manifest itself in any way and may be discovered completely by accident, during the examination of another disease. This rule also applies to single chords, which are located in the left ventricle.
If there are multiple or transverse abnormalities in the right ventricle, you may notice the following symptoms in the child:
- cardiopalmus;
- frequent and rapid fatigue;
- feeling of weakness in the body;
- the appearance of frequent dizziness;
- discomfort and tingling in the heart area;
- frequent mood changes;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
In the presence of formations in the right ventricle, these manifestations cannot always be noticed in early childhood. Most often they appear during the period of active growth of the child - in primary and secondary school age.
If you suspect the presence of a chord, you should contact a pediatrician who will conduct research and, if necessary, refer you to a cardiologist.
To diagnose the disease, the following measures are taken:
- the doctor asks the child in detail about the manifestations of pathology and general well-being;
- using a stethoscope, the heart rhythm is listened to; if there is a chord, extraneous noise will be heard;
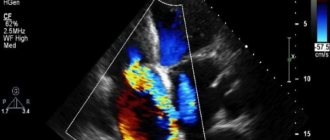
- Ultrasound examination of the heart muscle allows you to examine the pathology on the monitor, find out its location and determine the category (dangerous and non-dangerous);
- an electrocardiogram is prescribed to determine the heart rate in order to exclude pathology;
- daily recording of an electrocardiogram to determine the average indicator in different states of the child’s activity;
- If necessary, bicycle ergometry is performed - measuring cardiac activity during physical activity.
Today, all children at the age of 1 month have electrocardiogram readings taken to diagnose possible heart diseases for the purpose of prevention and timely treatment of pathologies.
Additional chord: is it taken into the army?
There is no article in the Schedule of Diseases indicating the fitness category for conscripts with chordae in the heart. Therefore, the likelihood of sending a citizen to a military unit depends on the clinical picture, the degree of dysfunction of the organ and concomitant diseases.
It is safe to say that with an additional chord, conscripts are recruited into the army, whose formation is represented by a single muscle thread. Members of the military medical commission believe that one extra chord in the heart in the army will not affect the well-being of a conscript during a year of army life.
Diagnostic methods
An abnormal left ventricular chord is diagnosed by neonatal echocardioscopy. At one month of age, babies must undergo a heart ultrasound to clarify the presence or absence of heart diseases that were not detected after their birth. This examination is routine for children. So, during an ultrasound examination, parents can find out that there is an extra chord in the heart of a healthy child. But if the child has no other pathology, then he is practically healthy and does not need to be observed by a cardiologist.
When an additional chord in the heart is combined with another pathology of the cardiovascular system, the child needs to be registered with cardiology. In addition to ultrasound, the baby is prescribed other types of diagnostics: ECG or Echo-CG. In adolescence, ECG diagnostics will be performed with additional loads. For adult patients diagnosed with ectopic chord, the monitoring scheme is the same: annual studies and listening to the heart on a cardiogram and ultrasound. How many studies to conduct per year depends on the course of the disease.
Do they take into the army with an additional chord?
Strong, healthy, self-confident men are the pride of our country, our army. The army turns a slender teenager, a “mama’s boy,” into a real man.
Have you noticed that some guys go into the army as thin, stooped teenagers, and after a year or two they return stronger not only in body, but also in spirit. Regime and physical activity strengthen the male body. But not everyone is ready to go through this school of life. Some guys, due to existing diseases, and some, simply put, “mow” - invent a non-existent pathology. Let's talk today about such a diagnosis as an accessory chord of the left ventricle. What kind of pathology is this? Serious illness or the possibility of being excused from service? Do they join the army with an extra chord in their heart?
Recommendations for anomalies - lifestyle, what not to do?
To maintain the normal functioning of a person with abnormalities in the development of the heart muscle, it is necessary to observe the following lifestyle:
- from childhood, harden the body , this is useful not only for strengthening the cardiovascular system, but also for the prevention of acute respiratory diseases, strengthening the overall endurance of the body;
- maintain proper nutrition high in vitamins, microelements and other beneficial contents. Reduce the amount of fatty, salty and spicy foods you consume;
- establish a daily routine - devote enough time to sleep (at least 8 hours a day, for children to take naps during the day), replace work with rest, alternate mental and physical work;
- start the day with morning exercises or engage in vigorous physical exercise throughout the day;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- completely give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- if possible, eliminate or reduce the number of stressful situations that affect a person’s psychological state;
- regularly take courses in relaxing therapeutic massage;
- engage in the prevention of infectious diseases;
With a mild degree of pathology, you can lead a normal life without denying yourself active hobbies and sports. However, an additional chord and an army are incompatible concepts, since they involve great physical activity, which is contraindicated for this pathology.
Experts classify the formation of an additional chord in the heart as a minor pathology, which in most cases does not require drug treatment or surgical intervention. In general, the forecast is quite positive. However, it is still necessary to monitor the development of the disease, sometimes visiting doctors and performing control diagnostic measures.
cardiohelp.com
Candy babies
08/30/2019 admin Comments No comments
Young people and their parents often wonder if they are being drafted into the army with grade 1 mitral valve prolapse. This pathology is one of the types of congenital heart defects. Doctors distinguish several degrees of the disease, each of which has its own characteristics of the course. Mitral valve prolapse and the army are not always compatible, so a special commission resolves this issue during diagnostic procedures for future military personnel.
Description of the disease
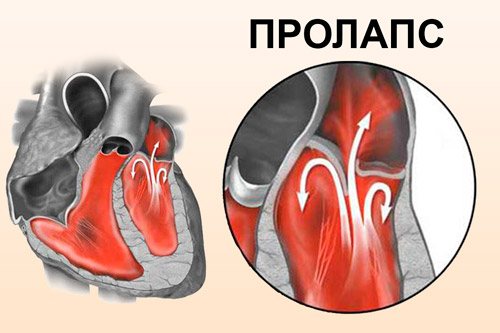
The disease is a disruption in the functioning of the main organ, which looks like this: blood is ejected by the left atrium, for which this area is compressed, during this period the valve flaps open, through them blood flows into the area of the left ventricle. Afterwards, the valves close, and the contractile activity of the ventricles moves the blood further. If mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is diagnosed, then this process changes. Part of the blood returns to the atrium during contraction of the ventricles, since the deflection (prolapse) does not allow the valves to close correctly and tightly. Therefore, a backflow of some part of the blood or regurgitation occurs, which causes the development of mitral regurgitation.
There are many reasons that provoke the development of such a deviation. Although people often do not know that they have this disease, when it is considered primary and is not accompanied by symptoms, doctors can detect it during examination. Usually, with this disease, doctors talk about a positive prognosis, which determines suitability for military service. However, the risk still exists, so it is necessary to understand each individual case. The danger of this pathology lies in the possibility of complications that are already deadly.
Prolapse of the mitral valve, its anterior leaflet, is of two types: with and without the presence of regurgitation. If the pathology is accompanied by large-volume regurgitation, then the patient’s condition is alarming and sometimes requires immediate surgical assistance. Such a diagnosis can be made by a doctor when examining a patient, listening to the work of his heart and identifying complaints. Usually the pathology is not accompanied by noise in the organ, so additional examination methods are necessary to clarify its presence.
Chords in the left ventricle: features
An additional chord manifested in the very left ventricle of the heart is a diagnosis that can only be established on the basis of a thorough ultrasound, and not by listening or an ECG. Of course, if a very young patient has a heart murmur and there is no suspicion of a serious defect, the doctor may suspect that it is a false chord or valve prolapse.
Quite often, not very honest specialists, especially various pediatricians, after carefully listening to the baby and pretending to be serious, say that your child has a certain murmur in the very heart and this is the notorious additional chord. A referral is issued for an urgent ultrasound. At the same time, not a single word about the detected noise is written in the outpatient card. If you go to a disinterested expert, it turns out that there was and is no dangerous noise. You need to know that a false chord cannot cause a heart murmur.
The additional chord itself is a certain cord, which is attached with one side to the cusp of a small valve, and, accordingly, the other to the wall of the heart itself. A person has several such chords, and their main function is to help the valve not bend too much all the time, but to retain blood during the period when the heart begins to contract. If one or more of these false chordae are thicker and denser, they become clearly visible on ultrasound. This is always and without fail written in the conclusion, adding the favorite phrase - hemodynamically insignificant. This means that the false chorda does not affect the heart in any way. It does not require any treatment.
If the additional chord discovered by the doctor is still hemodynamically significant, you need to go for a detailed consultation with an experienced cardiac surgeon. But don’t worry, because this doesn’t mean that it will have to be surgically excised, you just need to understand the current medical situation.
Diagnostics at the military registration and enlistment office
A heart disorder alarms doctors at the military registration and enlistment office, and they approach the examination procedure with all seriousness. Mitral valve prolapse has always been considered an ailment that can lead to serious consequences, so whether to enlist in the army is decided by a commission of doctors.
Every young man must undergo a medical examination before being drafted into military service. The list of specialists always includes a cardiologist, from which we can conclude that any abnormality in the heart will definitely be detected. If a violation of the functioning of an organ, its structure or hemodynamics is suspected, a number of diagnostic measures are prescribed. All doctor's reports must be retained to show the military medical commission. Despite the results of the examination, the military registration and enlistment office will carry out its own procedures to confirm or deny such a disease.
What is included in the complex:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound examination of the heart;
- chest x-ray;
- listening to the work of the organ through a phonendoscope;
- examining the guy and studying the symptoms of the disease.
If, after all the measures have been taken, the diagnosis is still confirmed, and grade 1 mitral valve prolapse is indeed recorded in the young man, then he will go into the army. The military way of life and the stress that will be given to the young man will not harm his health in any way.
In the document compiled by the doctors of the military commission, there is a section on the fitness of the young man, where there is no column about the condition of the heart valves. However, there is a part to fill that characterizes the valves of the organ. If we are talking about regurgitation, then the 1st degree of this deviation is almost never a reason for recognizing unfitness for service, but there are always exceptions to the rules.
Among other things, there is such a pathology as heart failure, which often accompanies grade 3 or 4 prolapse. This disease is also considered a contraindication for military service. Often it occurs in conjunction with other disorders and illnesses, which can become the basis for declaring a guy unfit for military duty.
Accessory chord (trabecula) of the left ventricle of the heart: concept, prognosis
© Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Chordae tendineae, or tendinous filaments in the cavity of the left ventricle, are connective tissue formations represented by a thin fiber attached on one side to the fleshy trabeculae in the wall of the left ventricle, and to the valves mitral, or bicuspid valve, on the other.
The function of these threads is to provide a connective tissue framework inside the heart and to support the valve leaflets to prevent it from sagging into the cavity of the left ventricle (LV).
When the ventricular myocardium relaxes, the chords tighten, the valve opens, allowing a portion of blood to pass from the atrium into the ventricle at the moment of diastole (relaxation) of the latter.
When the ventricular myocardium contracts, the chords, like springs, relax, and the valve leaflets close, preventing the reverse flow of blood into the atrium and facilitating the correct release of a portion of blood into the aorta at the time of ventricular systole (contraction).
chords and trabeculae in the structure of the heart
Sometimes during the period of intrauterine development, for various reasons, not several chords are formed, as usual, but one or more additional threads.
If both ends of the thread are fixed, we are talking about a true chord, and if one end is not attached to the valve leaflet, but hangs freely in the cavity of the left ventricle, we are talking about a false additional or accessory chord of the left ventricle.
As a rule, one additional chord is found; multiple ones are less common. In relation to the longitudinal axis of the LV, longitudinally, diagonally and transversely located chords are distinguished.
In most cases, such formations do not have a negative effect on the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart, and therefore are considered hemodynamically insignificant formations.
However, in the case of a transverse location of the ectopic (that is, located in the wrong place) chord relative to the cavity of the left ventricle, its presence can provoke heart rhythm disturbances such as tachyarrhythmias.
Recently, the frequency of registration of additional chords in the heart has increased, mainly due to an increase in the number of echocardioscopy (ultrasound of the heart) performed in the newborn period, according to new standards for examining children under one month of age. That is, such chords do not appear clinically, and if the child had not undergone echocardioscopy, the parents might not have known that the child had an abnormally located chord in the heart.
The diagnosis “additional trabecula of the left ventricle” in the vocabulary of ultrasound diagnostic doctors is actually equivalent to the concept of an additional chord. Although, as mentioned above, from the point of view of anatomy, the trabecula is a separate formation that continues the notochord.
Causes
Accessory chordae are classified as minor anomalies of the heart (MACD) - these are conditions that arise in the fetus during the prenatal period and are represented by a violation of the structure of the internal structures of the heart. In addition to the accessory chord, MARS includes a patent foramen ovale and mitral valve prolapse.
The development of an additional chord is caused, first of all, by heredity, especially on the mother’s side, as well as exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions, bad habits of the mother, stress, malnutrition and concomitant somatic pathology of the pregnant woman.
The occurrence of MARS can be caused by a disease such as connective tissue dysplasia - this is a hereditary pathology characterized by “weakness” of connective tissue in the heart, joints, skin and ligaments. Therefore, if a child has several heart abnormalities, the doctor should rule out dysplasia.
Symptoms of accessory chord
As a rule, the accessory chord does not manifest itself in any way throughout a person’s life. This is observed in most cases when the anomaly is not accompanied by connective tissue dysplasia and is represented by a single thread.
If a child has several chords identified by ultrasound of the heart, which also occupy a transverse position in the heart, it is quite possible that cardiac complaints may occur during periods of intensive growth of the child, as well as during puberty and pregnancy. These include weakness, fatigue with chest pain, accompanied by a feeling of palpitations and a feeling of lack of air, pallor. In some cases, such chords can provoke the occurrence of tachycardia or atrial fibrillation in the patient.
In the case when the occurrence of MARS is caused by dysplasia syndrome, the corresponding symptoms are characteristic - the child’s tall stature, thinness, joint hypermobility, frequent joint dislocations, deformation of the spine and ribs, structural disorders in other organs (prolapse of the kidney, dilation of the renal pelvis, deformation of the gallbladder, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and other anomalies in their various combinations).
Diagnostics
Typically, an additional chord is an “incidental” finding during echocardioscopy of a child at one month of age or a little later.
Currently, all babies at this age should undergo a cardiac ultrasound to identify heart defects that were not diagnosed immediately after birth and as a routine examination of the child. Therefore, even for parents of a healthy baby, a doctor’s conclusion about the presence of a chord in the heart may be a complete surprise.
However, in the absence of other significant pathology, such children are considered practically healthy by pediatricians and do not require close monitoring by a cardiologist.
If the chord in the heart is combined with another pathology of the heart and blood vessels, the child should be observed by a pediatric cardiologist.
In this case, the examination of the baby will include an ECG, and, if necessary, an ECG with physical activity at an older age, and 24-hour monitoring of ECG and blood pressure in the presence of heart rhythm disturbances.
For adult patients with ectopic chord, the observation plan is the same with examinations performed once a year or more often if indicated.
Is treatment of additional chord required?
If a child has an abnormal chord in the heart, and the baby does not have other significant cardiac diseases, there is no need to treat this condition.
In cases where functional disorders of the cardiovascular system are observed at an older age, which do not cause hemodynamic disorders, the development of pulmonary hypertension due to the inability of the heart muscle to contract correctly, and also do not lead to heart failure, it is possible to prescribe medications that support and nourish the myocardium. The use of potassium and magnesium preparations (Magnerot, Magnevist, Panangin, Asparkam), B vitamins, antioxidants (Actovegin, Mildronate, Mexidol, etc.) is justified. The prescription of complex vitamin preparations is also indicated.
If the patient has significant cardiac dysfunction, taking medications such as diuretics, antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics and other groups of drugs is indicated. Fortunately, indications for this in the case of abnormal chordae in the heart are extremely rare.
Lifestyle
There is no need to follow a specific lifestyle for a child with an additional chord. A balanced diet with fortified foods, long walks in the fresh air, as well as regular physical activity is enough.
It makes no sense to limit a child’s participation in physical education or sports. A child can actively run, jump and perform all those physical activities acceptable for his age and practiced in the educational institution he attends.
Swimming, figure skating and hockey are welcome.
Regarding preventive vaccinations according to the national calendar, we can say that an additional chord of honey. is not a diversion, and the baby can be vaccinated according to age.
As a child grows up and enters the difficult period of puberty, it is important to give up bad habits and adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
In case of any age-related manifestations of the heart and blood vessels (sweating, fatigue, tachycardia, shortness of breath), the teenager should be shown to a cardiologist and, if necessary, take the above-mentioned drugs or inject them.
Pregnancy for girls with an additional chord is, of course, not contraindicated. In the case of the presence of several of the congenital heart anomalies, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound of the heart during gestation and observation by a cardiologist.
Serving in the army is not contraindicated for young men. A disqualification from the army is the presence of heart rhythm disturbances in the patient, the development of heart failure, which, again, is rare with an additional chord.
A few words should be given to the nutrition of children and adults with structural or functional disorders of the heart. If possible, you should avoid eating fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods.
Preference should be given to fresh vegetables and fruits, natural juices, fermented milk products and low-fat fish. The consumption of red and black caviar, dried apricots, raisins, tomatoes, carrots, bananas and potatoes, rich in substances beneficial to the heart muscle, is encouraged.
In addition, your daily diet should include cereal products, for example, various cereals for breakfast.
Of course, you should protect your child from eating chips, canned soda and various fast food dishes, as this can lead to obesity, and excess weight will have an extremely adverse effect on the condition of the heart muscle and vascular walls in the future.
Are there any complications?
Complications with an abnormal chord, as a rule, do not develop.
If for any reason the patient may experience heart rhythm disturbances, then thromboembolic complications (pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, etc.) may develop.
Cardiac arrest may also occur due to fatal disturbances of ventricular conduction (ventricular fibrillation and paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia).
Forecast
The prognosis if a child has additional chordae in the left ventricle is favorable both in childhood and in adulthood.
Source: //sosudinfo.ru/serdce/dopolnitelnaya-xorda/
Features of suitability at 1st degree
The decision to enlist in the armed forces depends not only on the stage of the disease; additional factors are taken into account.
- serious heart rhythm disturbances;

- study of the total amount of blood return;
- determining how much the main organ has changed;
- calculation of the impact of heavy physical activity on the body.
Sometimes it happens that the pathology is revealed only at a medical commission already at the time of conscription, then the parents of the young man or he himself have the right to carry out additional diagnostic measures, during which the military registration and enlistment office is obliged to provide a deferment.
Whether someone with mitral valve prolapse is accepted into the army depends entirely on the severity of the pathology. If we are talking about stage 1, then we can say with 99% confidence that the guy will serve. It is also possible to sign a contract for further extension of service, especially if the person feels fine. Pathology of the 2nd and 3rd degrees is almost always a reason to go into reserve. One of the main pieces of advice is not to try to pretend when passing a medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office, otherwise such violations will be identified, and everything will end badly for the conscript.
Physical activity, which is necessarily present in the army, frightens all patients. But you shouldn’t worry about this, since sports are necessary for everyone without exception. The heart muscle is well strengthened during such training, especially when swimming, running, walking, skiing or skating, and performing physical exercises. Only serious loads are contraindicated, such as heavy lifting, strength and other exercises associated with lifting heavy weights. In any case, it is necessary to consult a doctor about classes.
4 With a false chord, are the symptoms true or false?
Many conscripts “want” to serve so much that they can come up with many colorful symptoms of a diseased heart with a false chord. In most cases, the developmental anomaly does not manifest itself clinically and does not actually bother the conscript. But is it worth it to downplay the veracity of the complaints, if any? Of course not. Any complaint in the heart is an indication for examination; in this case, it is better to “over-” than “under-”.
Moreover, sometimes a clinic can take place. This occurs in patients with false chorda during a period of intense physiological growth, when skeletal growth significantly outpaces the growth of internal organs, and the heart simply does not have time to grow, experiencing increased load. Complaints may include dizziness, weakness, palpitations, tingling or aching pain in the chest.