From this article you will learn:
- causes of bleeding gums,
- bleeding gums - treatment at home and at the dentist.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Bleeding gums is one of the symptoms of their inflammation, indicating that the patient has one of two inflammatory gum diseases - either gingivitis or periodontitis. Most often, it occurs while brushing your teeth or when chewing hard food, and is due to the fact that the gums, weakened by inflammation, are more easily injured in response to mechanical stress.
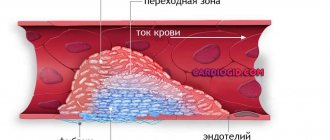
The cause of gum inflammation and bleeding is irregular oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of soft microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Plaque and tartar bacteria produce various toxins and pathogens, which trigger inflammation in the gums. In Fig. 1-3 please note that inflammation is expressed precisely in those areas of the gum where it is in direct contact with plaque.
Sometimes you may not find accumulations of microbial plaque at the necks of teeth. And at the same time, for some reason, the gums still bleed when brushing your teeth, and also have a pronounced bluish color. This is due to the presence of subgingival dental deposits, which form in patients with long-term chronic inflammation of the gums (i.e., chronic periodontitis). Such dental deposits can only be detected and removed at a dentist’s appointment.
When trying to stop or cure bleeding gums at home, patients make 2 main mistakes that only lead to the progression of inflammation. Some patients stop brushing their teeth altogether. Others begin to uncontrollably use antiseptic rinses, as well as special toothpastes and gels for gums (which can only lead to a temporary subsidence of symptoms). In this article we will tell you how to properly treat bleeding in order to avoid the development of chronic gum inflammation.
Causes of bleeding gums –
If you are interested in the mechanism of how poor hygiene and gum inflammation lead to bleeding, it looks like this. Plaque and tartar bacteria produce a large number of toxins and various pathogens that trigger a chain of inflammatory reactions in the gums. In particular, this leads to increased permeability and fragility of capillaries (which is due to the fact that blood appears precisely when brushing teeth), as well as to swelling, redness or cyanosis of the gingival papillae.
In parallel with this, the process of desquamation (squamation) of epithelial cells of the gum mucosa intensifies, which leads to thinning of the epithelium. The latter further reduces the resistance of gums weakened by inflammation to mechanical stress, for example, when brushing teeth or chewing hard food. Therefore, when together: 1) fragility and increased permeability of capillaries, 2) thinning of the epithelium + 3) even completely normal mechanical stress, it ends in bleeding when brushing your teeth.
By the way, a very common symptom that accompanies bleeding gums is pain when brushing your teeth. The mechanism of its development is also associated with thinning of the epithelium of the gum mucosa and a decrease in the latter’s resistance to mechanical stress. And the conclusion that needs to be drawn from all of the above is that treatment should not be tied to the fight against a separate symptom of bleeding; it should consist in eliminating the main cause of gum inflammation, i.e. removal of microbial plaque and tartar.
Factors predisposing to bleeding gums –
If this is not the first time that you have experienced bleeding, this indicates that your gum inflammation is chronic and has been going on for quite a long time. In this case, when brushing your teeth, blood may appear and then disappear again (24stoma.ru). Typically, gums bleed only during exacerbations of chronic inflammation. Exacerbation of the inflammatory process most often occurs in the off-season and is associated with a decrease in immunity or the development of vitamin deficiency.
But we don’t want you to think that poor immunity or vitamin deficiency are the causes of exacerbations of gum inflammation and bleeding. The cause is still plaque bacteria. It’s just that local protective factors in the oral cavity (against the background of decreased immunity) no longer cope with the previous volume of toxins and pathogens released by microbial plaque on your teeth. Other predisposing factors may include mouth breathing and xerostomia, which contribute to an increase in the amount of plaque in the mouth.
When bleeding is not associated with gum inflammation -
Sometimes the appearance of blood when brushing your teeth may not be associated with plaque and gum inflammation. For example, an exception may be local bleeding in the area of 1-2 teeth, which occurs as a result of trauma to the gums by the overhanging edge of a filling or crown. In this case, the elimination of the traumatic factor immediately leads to the elimination of symptoms.
Hormonal changes in women during pregnancy can also cause bleeding gums. According to statistics, approximately up to 50% of pregnant women suffer from an edematous form of hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a persistent increase in the volume of the gingival papillae + bleeding when touched. However, bleeding gums during pregnancy is not solely hormonal in nature.
In particular, an increase in the volume/height of the gingival papillae leads to a “purely mechanical” increase in the depth of the periodontal pockets. Usually they are no more than 2-3 mm, but as the size of the gingival papillae increases, the depth of the gingival pockets also increases, which prevents their natural self-cleaning and creates conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, in pregnant women, as a rule, there are two causes of bleeding, and in order to exclude the microbial factor, it is necessary to carry out additional cleansing of the periodontal pockets with an irrigator.
Why do my gums bleed?
A dentist can tell you why your gums bleed. There is an opinion that bleeding gums occurs due to the use of hard toothbrushes or abrasive pastes. Indeed, frequent trauma to mucous tissue leads to the appearance of microcracks and bleeding. But improper brushing technique is not the main cause of gum inflammation.
Other equally important causes of periodontal disease include:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- allergic reactions to certain medications;
- errors in dental treatment;
- diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- disorders of the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- decreased immunity and infectious diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels.
The causes and treatment of bleeding gums are closely related, since treatment tactics depend on the factor that provokes the disease.
Poor oral hygiene
Failure to comply with hygienic rules of oral care is the main cause of periodontal bleeding. Bacterial plaque layers on top of each other, forming a microbial plaque.
Numerous accumulations of bacteria, under the influence of gingival fluid and saliva, harden and take the form of small stones. Due to mechanical compression of the gingival margin, as well as toxic substances released by bacteria, periodontal tissue is irritated. Such conditions serve as a favorable factor for inflammation and bleeding of the gums.
Use of medications
The use of certain medications may cause bleeding when pressure is applied to the gums. Typically, drugs that cause such effects include:
- blood thinning medications (“Aspirin”, “Warfarin”, “Curantil”);
- antibiotics used for a long time;
- drugs for the treatment of endocrine disorders, including hormonal contraceptives.
Each medication comes with instructions indicating possible side effects. Among them you can find bleeding from the gums. As a rule, after stopping the use of the above drugs, signs of inflammation in the oral cavity are eliminated on their own.
If refusing prescribed medications can harm your health and life, and your gums are bleeding precisely because of drug treatment, you need to consult a dentist and a specialist.
Dental procedures
During dental treatment, the dentist may accidentally make mistakes that lead to signs of gum inflammation. Such errors include:
- contact with the mucous membrane of aggressive chemicals (phosphoric acid, sodium hypochlorite);
- accidental damage to the gums by dental instruments used in treatment (bur, probe, matrix, retraction threads);
- poor-quality treatment of dental canals (leaving nerve bundles and blood vessels in the pulp, root perforation, filling material extending beyond the apex, preservation of an overhanging filling).
If the cause of bleeding in the mouth is a chemical burn or mechanical damage, the gums heal in 25 days. With improper dental treatment in adults, symptoms of inflammatory disease continue for 2–3 weeks. In 70% of such cases, repeat dental care is required.
Blood diseases
Bleeding from the gums can appear due to the following diseases:
- hemophilia;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- thrombasthenia;
- hemoblastoses.
With pathologies of blood cells, the permeability of blood vessels is impaired, the walls of capillaries and veins become fragile. Increased blood pressure, stress and other factors can cause the gums to bleed very heavily.
Chronic diseases
The reasons for the appearance of blood when spitting saliva do not always come from the oral cavity. Diabetes mellitus, VSD, oncology of the hematopoietic organs, hypothyroidism, cirrhosis of the liver, viral hepatitis, HIV and AIDS disrupt the functioning of blood and lymphatic vessels, causing bleeding from the gums. To eliminate dental problems, comprehensive treatment is necessary.
Vitamin deficiency
When the body lacks vitamins and minerals, resistance to pathogens decreases, resulting in inflammatory periodontal diseases. Ignoring the signs of vitamin deficiency and lack of oral sanitation can lead to partial or complete adentia.
Hormonal disorders
Any hormonal changes cause bleeding when accidentally pressing on the mucous tissue. Often such changes are provoked by hormonal contraceptives containing a large amount of biologically active substances. Proper selection of the dose of the drug or complete cessation of taking OCs will help eliminate the dental problem.
Why do gums bleed during pregnancy?
In 50% of cases, bleeding in the mouth occurs due to hormonal changes during fetal embroidery. A decrease in the amount of vitamins A, E, K and C changes the composition of saliva, which leads to increased accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth and gums. In addition, signs of pregnancy such as toxicosis, changes in pressure and a decrease in hemoglobin change the condition of periodontal tissues.
Professional oral hygiene and other preventive measures will prevent periodontal inflammation and the addition of additional infections in the oral cavity during pregnancy.
How to make the correct diagnosis -
If you have bleeding gums, the causes and treatment will be interrelated, meaning that the amount of treatment needed will greatly depend on the type of gum inflammation (gingivitis or periodontitis) of which it is a symptom. Your doctor will give you the final diagnosis, but in most cases, distinguishing between these 2 forms of gum inflammation is quite simple.
For example, with gingivitis, in addition to pain and bleeding of the gums when brushing your teeth, there is swelling, redness or cyanosis of the gingival margin, and accumulation of soft plaque and/or tartar at the necks of the teeth (Fig. 1-3). What cannot happen with gingivitis is tooth mobility, periodontal pockets with purulent discharge, and severe exposure of tooth roots. If you have such symptoms, this already indicates the presence of chronic periodontitis, i.e. much more serious gum disease.
What do gums and teeth look like with periodontitis?
Important: gingivitis is the very initial stage of gum inflammation, and if not treated correctly, it inevitably turns into periodontitis (in which the bone tissue around the teeth begins to gradually dissolve, which leads to their mobility). The transformation of gingivitis into periodontitis always occurs in those patients who have been treating bleeding gums at home for years - exclusively with the help of various rinses, ointments and anti-inflammatory toothpastes.
Without removing the causative factor of gum inflammation (i.e., dental plaque), all these remedies can only temporarily suppress the symptoms of inflammation. In this case, the inflammation will not go away, and will be more asymptomatic until the destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth becomes so great that their mobility appears. Therefore, if you want to cure bleeding gums only with means from advertising on TV - without removing dental plaque and normalizing oral hygiene, then pay attention to the photos of such patients in Fig. 4-6.
What causes bleeding?
Treatment of almost any disease should begin with identifying and eliminating the root cause.
Bleeding gums are no exception. Factors provocateurs:
- The most common cause of bleeding gums is poor oral hygiene . This may be using an unsuitable toothbrush, insufficiently or incorrectly brushing your teeth, using toothpicks, etc.
- Tartar formation . Without preventive measures, over time it grows and begins to separate the gums from the teeth, thereby causing bleeding.
- Lack of vitamins in the body . Of course, vitamin deficiency affects all human organs, including the gums;
- Incorrect installation of dental crowns and implants.
- Gum diseases : periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis and others.
There may be other reasons for this problem. Only a dentist can identify the nature of such a disease.
The dentist will tell you about the causes of bleeding gums and how to solve the problem:
Bleeding gums: treatment
As we said above, the causes and treatment of bleeding gums are interconnected, and the most important thing you should do is remove dental plaque. The second important step is a course of anti-inflammatory therapy. And if such therapy, especially for gingivitis, can be successfully carried out at home, then in order to remove dental plaque, you will still have to see a dentist. Below we will talk in detail about the drugs and procedures...
Removal of dental plaque –
To remove plaque from teeth that are bleeding, it is optimal to use ultrasonic teeth cleaning. If you have gingivitis or if there are not too many deposits, one visit lasting 40-60 minutes is usually enough. The most difficult thing to remove is subgingival dental plaque during periodontitis, because... in this case, they are localized in periodontal pockets below the gum level. The lack of good visual control makes them laborious to find and remove, and will require several visits to the doctor.
I’ll tell you right away that very rarely will a dentist bother with you and look for subgingival dental deposits. And therefore, if with gingivitis (in which there are only supragingival deposits) you can get quality service by contacting a regular dentist or hygienist, then with periodontitis it is best to contact a periodontist. This is what dentists who specialize in gum disease are called.
How to remove dental plaque with ultrasound: video
Anti-inflammatory therapy –
The standard course of anti-inflammatory therapy for gingivitis usually lasts up to 8 days, for periodontitis – exactly 10 days. There is nothing complicated about it, and it can be easily done at home. An exception may be cases of exacerbation of severe chronic periodontitis, when in addition to antiseptic rinses and applications of anti-inflammatory gels, it is advisable to also rinse deep periodontal pockets (only a dentist can do this).
TREATMENT SCHEME –
Gum treatment is carried out 2 times a day, morning and evening, and it is advisable to carry it out only after meals and subsequent brushing of teeth. Thus, 1) had breakfast, 2) brushed your teeth, then you need to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. With slight inflammation and slight bleeding, the usual 0.05% chlorhexidine solution, which is sold in pharmacies for 40 rubles per 100 ml bottle, may be enough for you. But in case of severe inflammation, it is better to choose solutions of this antiseptic of 0.2-0.25% concentration (examples of such agents are below).
- Rinse aid LACALUT Aktiv –
in our opinion, this is the most effective rinse for bleeding gums. It contains a 0.25% concentration of chlorhexidine, sodium fluoride, but also, which is very important, aluminum lactate. This last component very quickly reduces bleeding from gum inflammation. It costs about 300 rubles for a 300 ml bottle.
- Rinse aid PRESIDENT Antibacterial –
contains a 0.2% concentration of chlorhexidine, as well as high concentrations of mallow, chamomile and echinacea extracts, which have an anti-inflammatory effect. This is also a very good rinse, but due to the absence of aluminum lactate, bleeding will decrease a little more slowly (compared to Lakalut Active). The price for a 250 ml bottle is from 200 to 300 rubles.
What to do next: to rinse the mouth with any of the above antiseptics, just take 10-15 ml of solution into your mouth and, without spitting, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. They spat, and then you need to apply a special anti-inflammatory gel to your gums. For severe inflammation of the gums, we recommend only Cholisal gel, but if the inflammation is moderate, then another drug, for example, Parodontocide gel, is also suitable.
In order for the gel to adhere well to the moist mucous membrane of the oral cavity, it is advisable to dry the gums in the areas where the gel is applied with a dry gauze swab. You need to apply the gel in front of a mirror, with your teeth bared properly, so that your gums are clearly visible. The gel is applied with a finger to the marginal part of the gum around the necks of the teeth. As a rule, the gel is applied only to the front of the teeth. During and after treatment, saliva is usually actively released; it does not need to be accumulated or spat, but swallowed as usual.
After treatment, it is important not to drink or rinse your mouth for 30 minutes, and not to eat for 2 hours. In the evening, repeat the treatment: first rinse your mouth for a minute with an antiseptic, then apply the gel to your gums (again, it is advisable to do this only after eating and subsequent oral hygiene). You may also find the following links useful -
→ Rating of rinses for gums, → The best gels for gum inflammation.
Toothpastes for bleeding gums -
If you want to achieve an even faster effect from anti-inflammatory therapy, in addition to rinses and gels for gums, you can use special medicated toothpastes. But still keep in mind that using such pastes without removing dental plaque will only temporarily suppress the symptoms and turn the inflammation into a chronic form.
- Parodontax toothpaste –
If you listened to our advice and chose Lakalut Active rinse + Cholisal gel for a course of anti-inflammatory therapy, then Parodontax or Parodontax-F toothpaste will go well with such products (they are distinguished only by the absence or presence of fluoride, and the option with fluoride would be preferable).
Parodontax pastes contain very high concentrations of medicinal plant extracts - echinacea, peppermint, sage, myrrh, chamomile, ratania, mineral salts, zinc citrate. This composition allows you to very quickly relieve swelling and bleeding gums. In addition, Parodontax-F also contains 1400 ppm of fluorine. Price from 150 rubles per 75 ml tube.
Important : if you choose not Lakalut Active for mouth rinsing, but any other antiseptic rinse (without aluminum lactate), then it is best if at least the toothpaste contains aluminum lactate. These pastes include: “PRESIDENT Extra Active”, “LACALUT Aktiv Herbal” or “LACALUT Aktiv”. We recommend such combinations of products so that the products you use have different mechanisms of action on bleeding and inflammation of the gums, and in this case the treatment will be faster and more effective.
→ Rating of toothpastes for gum inflammation
Toothbrush for bleeding gums –
If brushing your teeth causes severe bleeding, pain and a desire to give up hygiene altogether, it is best to use a special gentle toothbrush with soft bristles (labeled Soft) for the duration of treatment. But remember that it is not advisable to use such a toothbrush all the time, because... Soft bristles are somewhat less effective at removing plaque. And therefore, after the inflammation subsides, it is advisable to start brushing your teeth again with a medium-hard brush labeled Medium.
Examples of soft bristle brushes:
Oral hygiene training –
After removing all dental plaque, the doctor should teach you how to brush your teeth correctly. Otherwise, dental plaque will appear again within a few weeks, and you will again suffer from the same symptoms. Remember that the best remedy for bleeding gums is good oral hygiene, including regular flossing after every meal.
During my time as a periodontist, I have seen thousands of patients with severe gum disease (each time the result of years of self-medication). These patients were ready to spend hours doing various rinses, lotions, brewing infusions, etc., but despite all this, they were not able to find 3-5 minutes 3 times a day to brush their teeth after each meal. Although this is precisely the most important thing. Follow the link below for a comprehensive list of recommendations for brushing your teeth.
→ Proper oral hygiene
Taking vitamins –
If you have a strict diet or are fasting, then your body simply will have nowhere to get the vitamins necessary for metabolism. A lack of certain vitamins can lead to poor blood clotting and capillary fragility, which, together with insufficient hygiene, can stimulate the development of bleeding symptoms. Thus, vitamin C somewhat prevents gum bleeding. It is best taken as part of a multivitamin preparation.
Let us draw your attention to a very important point - under no circumstances and never take vitamin C in a daily dosage of 1 g (1000 mg) or higher. In such concentrations it leads to directly opposite effects in the body, which was revealed in scientific research at the University of Chicago Medicine. Under normal conditions, the daily requirement for men is about 90 mg, for women – 75 mg. In case of a cold (sharp decrease in immunity), daily consumption can be increased to no more than 500-800 mg, and for a not too long period of time.