Accessory chord of the left ventricle: is it dangerous?
There are several chords in the human heart that prevent the valve from bending during contraction of this organ.
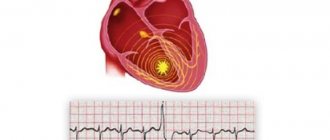
Thanks to their presence, it retains blood well and ensures adequate hemodynamics. The normal chord is a kind of spring with a muscular structure. Sometimes during intrauterine development, an additional chord appears in one of the ventricles of the heart, which is a thread-like cord of connective tissue. In some cases, this abnormal formation includes muscle or tendon fibers. In this article we will look at such a minor cardiac anomaly as an accessory chord of the left ventricle. In most cases, it is found in children under 18 years of age, but some people live with this diagnosis for many years and do not feel any changes in the functioning of the heart. Usually, an additional chord is detected by chance: during an examination for another disease or during a preventive examination. It is not detected either by listening to a heart murmur or by an ECG, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made after an ECHO-CG. Having heard a heart murmur, the doctor can only suspect the presence of this minor heart anomaly and recommend an ultrasound examination to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
In our article we will introduce you to the causes of development, types, symptoms, methods of observation, treatment and prevention of accessory chord of the left ventricle. This knowledge will help parents of children with such a heart anomaly choose the right tactics to approach the problem and save them from unnecessary worries.
An abnormal chord of the left ventricle is a hereditary anomaly, which in 92% of cases is inherited through the maternal line (in rare cases, through the paternal line), and develops in utero due to a failure in the development of connective tissue. That is why mothers who have previously been diagnosed with this disease are recommended to have their child examined.
It is possible that the following unfavorable factors may be the reasons for the appearance of an additional chord:
- bad ecology;
- smoking or drinking alcohol and drugs;
- nervous and physical stress.
The additional chord can be located in different parts of the left ventricle and have a different structure and structure. Cardiologists distinguish the following types of chords:
- by histological structure: fibrous, fibromuscular, muscular;
- in the direction of the connective tissue fibers: longitudinal, transverse, diagonal;
- by the number of threadlike strands: single, multiple;
- by place of attachment: apical, middle, basal.
In most cases, the additional chord of the left ventricle does not bear any functional load on the heart and does not interfere with its normal functioning. For many years, this minor anomaly may not be detected, because it is not accompanied by any special symptoms. A pediatrician can listen to a systolic heart murmur in a newborn, which is detected between the third and fourth ribs to the left of the sternum and does not in any way affect the functioning of the heart.
During intensive development, when the rapid growth of the musculoskeletal system significantly outstrips the growth rate of internal organs, the load on the heart increases, and the additional chord may make itself felt for the first time. Your child may experience the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- rapid or unmotivated fatigue;
- psycho-emotional lability;
- cardiopalmus;
- pain in the heart area;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
The same clinical manifestations can be observed with multiple abnormal chords of the left ventricle. Most often, such symptoms appear during adolescence. In the future, they can completely disappear on their own, but sometimes they remain in adulthood.
When symptoms appear, the child is required to undergo ECHO-CG, ECG and 24-hour Holter monitoring. These studies will allow the doctor to determine the presence or absence of hemodynamic disturbances. If the additional chord is “hemodynamically insignificant,” then the anomaly is considered safe, and the child only requires follow-up with a cardiologist. With a “hemodynamically significant” diagnosis, the patient is advised to observe, adhere to certain restrictions and, if necessary, treatment.
Symptoms
In 90–95% of cases, an additional chord in the heart is not clinically apparent and is an incidental finding. The doctor may suspect the presence of an anomaly already during an auscultatory examination. But there are also situations when false chords of the heart have clinical manifestations.
On what basis can one suspect a disease? If the additional chord in the heart is represented by a single thread, as is more often the case, then it does not manifest itself in any way, and the course of the disease is asymptomatic throughout life.
This developmental anomaly can be suspected immediately after birth based on the systolic murmur in the heart when listening to the child (in the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis is made during the neonatal period and early childhood, up to 3 years).
The increase in registration frequency, as mentioned above, is due to the fact that, according to recently adopted diagnostic and treatment standards, each child at the age of 1 month is prescribed ECHO-CG (ultrasound of the heart) to exclude congenital pathology of the cardiovascular system.
Heart rhythm disturbances may also occur. This symptomatology most often manifests itself in adolescence and can accompany the patient into adulthood.
Single chords in the left ventricle are generally not accompanied by any external manifestations. If the anomaly is located in the right ventricle or there are multiple formations in the heart, their presence can be suspected by the following symptoms:
- constant causeless weakness and fatigue;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased endurance;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- psycho-emotional instability;
- tingling in the heart;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
Most often, these symptoms are observed during adolescence, when intensive growth of muscles and bones occurs. If you do not pay attention to such signs, then the situation can only get worse with age.
Therefore, you need to be attentive to adolescent health complaints, and at the slightest suspicion of heart pathology, undergo a full examination by a cardiologist. If an additional chord is discovered in childhood and the child is already registered with a specialist, by the age of 11–12 years it is worth visiting a doctor more often for preventive purposes in order to prevent the development of undesirable consequences.
An abnormal chord of the left ventricle is detected in newborns almost immediately, at first, various studies are done, including ultrasound of the child’s heart. If this fact was missed, then there are symptoms that can be used to suspect falsehood:
- the emotional state is unstable, children are often capricious;
- dull chest pain;
- arrhythmia and interruptions are heard;
- the child gets tired very quickly, becomes lethargic, weak when performing simple movements.
At the doctor’s appointment, the mother is obliged to talk in detail not only about the issues related to the baby’s health, an abnormal chord of the left ventricle or ARV, a hereditary disease, of course, the mother may have no idea about the presence of this defect in her.
It would be right for each of the parents to undergo examinations; this will help diagnose abnormal chords in each, which will greatly facilitate the diagnosis. An ultrasound of the heart will show all changes, if any, in a few minutes.
An additional chord in the heart is an almost harmless phenomenon, but additional chords can already pose a serious threat to the entire body. Such cases make up 20% of the overall picture; they are detected by ultrasound examinations, ECG with stress for the patient, and heart murmurs are clearly and distinctly audible.
On what basis can one suspect a disease? If the additional chord in the heart is represented by a single thread, as is more often the case, then it does not manifest itself in any way, and the course of the disease is asymptomatic throughout life.
This developmental anomaly can be suspected immediately after birth based on the systolic murmur in the heart when listening to the child (in the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis is made during the neonatal period and early childhood, up to 3 years).
The increase in registration frequency, as mentioned above, is due to the fact that, according to recently adopted diagnostic and treatment standards, each child at the age of 1 month is prescribed ECHO-CG (ultrasound of the heart) to exclude congenital pathology of the cardiovascular system.
Is the accessory chord of the left ventricle dangerous?
Most cardiologists equate such a minor cardiac anomaly with a variant of the norm. The news of the presence of an additional chord in the left ventricle should not cause panic in the child’s parents, since this anomaly does not require surgical treatment and, in the absence of hemodynamic disturbances, does not require drug correction.
In some cases, the additional chord of the left ventricle may become a factor that contributes to the development of other diseases of the heart and blood vessels (infectious endocarditis, cardiac rhythm and conduction disorders, thrombophlebitis, etc.). It is impossible to predict in advance how likely the development of such pathologies is.
Possible complications
It is not always possible to predict in advance how any disease will develop. If there is an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle, the prognosis is positive. Most cases do not even require any treatment. But sometimes the heart's function is disrupted, which is quite rare. In such cases, drug treatment is required.
Complications are rarely observed. This mainly happens when patients ignore visiting the doctor in a timely manner or self-medicate.
Such a deviation is considered a minor anomaly. Doctors recommend not to panic if it is present. In most cases, the extra connective tissue does not affect the functioning of the heart and does not require treatment. In order to be confident in your health and protect yourself from negative consequences, you should undergo regular ultrasound examinations.
Observation of a child with an additional chord in the absence of hemodynamic disturbances
If an abnormal chord is detected that is not accompanied by symptoms, no special treatment is required. For such patients, it is enough to be regularly monitored by a cardiologist and undergo a control ECHO-CG once a year.
For children with such a minor heart abnormality, it is recommended:
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- Healthy food;
- engage in physical therapy;
- to harden;
- often be in the fresh air;
- prevent stress;
- ensure proper sleep;
- refuse heavy physical activity;
- do not take medications without doctor’s recommendations;
- make a decision about participating in a particular sport together with your doctor.
Parents of such children are not recommended to protect their child from everything and treat him as a disabled person, since this can significantly affect his further socialization. Communication with friends, visiting kindergarten and school, participating in clubs and feasible sports - all this will help the child adapt normally to society and feel complete.
If an additional chord is detected, which is accompanied by symptoms or hemodynamic disturbances, in addition to the recommendations described above and more stringent restrictions on physical activity, drug therapy is recommended.
These children may be prescribed the following medications:
- vitamins B1, B2, PP - prescribed to improve myocardial nutrition, taken for a month, the course of treatment is repeated twice a year;
- Magne B6, Magnerot, Potassium orotate, Panangin - are prescribed to improve the conduction of nerve impulses and prevent arrhythmias, drugs are selected depending on age and taken in courses for a month or more;
- L-carnitine, Cytochrome C, Ubiquinone - prescribed to normalize metabolic processes in the heart muscle;
- Nootropil, Piracetam - are prescribed when symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia appear.
Indications for immediate hospitalization in a cardiology hospital may include the following severe heart rhythm disturbances:
They can develop with multiple or transverse chordae and require detailed examination and subsequent treatment.
In rare cases, muscle fibers of the cardiac conduction system may be included in the structure of the accessory chord of the left ventricle. Such cardiac abnormalities can cause ventricular arrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation. To eliminate them, the following surgical interventions are indicated:
In most cases, an additional chord of the left ventricle appears due to a hereditary predisposition, and it is almost impossible to prevent its development in the prenatal period. Despite this, scientists do not exclude the possibility of the development of such a minor cardiac anomaly under the influence of certain unfavorable factors. That is why pregnant women are recommended:
- Eat properly.
- Stop smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
- Avoid heavy physical activity.
- Prevent stress.
- Walk in the fresh air and do gymnastics.
If an additional chord of the left ventricle is detected in a child, parents should pay close attention to his health, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, but not completely protect him from society. An important measure to prevent complications will be the timely treatment of chronic diseases that can be complicated by heart disease.
Children with an additional chord are recommended to regularly engage in physical therapy, which involves individual selection of the load. Wall bars exercises, dancing, gymnastics, sprinting, jumping rope - these activities will help strengthen the heart muscle and prevent the development of complications.
Physical activity should not be excessive, as it can aggravate the situation. Most cardiologists do not recommend that people with accessory chordae engage in professional sports. And such types of stress that occur during diving, snorkeling or parachute jumping are absolutely contraindicated.
Source: doctor-cardiologist.ru
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention for LVAD (left gastric accessory chord). This is especially true for pregnant women. If you have complaints or any suspicions regarding heart disease, you should contact a doctor and undergo an examination. Early diagnosis of diseases is the key to successful treatment.
To prevent possible heart pathologies, you should adhere to the following rules:
- no smoking;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- to walk outside;
- avoid stress;
- Avoid heavy physical activity.
Pregnant women are advised not to neglect special gymnastics, which is intended for women during this period.
Scientists have identified several physical activities that are beneficial for children with heart abnormalities:
- slow dancing (for example, ballroom);
- wall bars exercises;
- exercises with a skipping rope;
- massage;
- morning jogging.
Any physical activity is recommended for children, but excessive exercise is contraindicated. You can buy your child a hoop that he can spin in his free time. When walking in the summer, games with a ball or jump rope will be useful. In winter, you can take sleds or skis with you outside. Such activities are especially useful for children who are already aware of heart abnormalities.
However, not all exercise is recommended. You should not go diving, snorkeling or skydiving.
All chronic diseases should also be treated. They can cause heart complications.
Dr. Komarovsky also believes that children with an additional chord in the LV do not need treatment. The only limitation, in his opinion, is the inability to work as an astronaut or diver in the future.
serdechka.ru
As you know, the goals and objectives of cardiology are to study the human cardiovascular system, diagnose all sorts of disorders in its functioning and, accordingly, treat identified diseases (for example, if an additional chord of the left ventricle is detected). For a long time it was believed that heart problems mainly affected the older generation. However, today the situation has changed: heart disease is often diagnosed in middle-aged people, teenagers and even very young children. We will talk about the latter in more detail.
Pediatric cardiology
All cardiovascular diseases in children are usually divided into congenital and acquired. The first group of pathologies arises during the formation of the embryo. Doctors cite poor ecology, constant stress experienced by the expectant mother, hereditary predisposition and a number of infectious diseases as the main prerequisites for this. As for acquired heart problems, infections rank first on the list of possible causes. Complications usually result from improper treatment. What can be considered a reason to visit a cardiologist? Rapid heartbeat, pain in the sternum, swelling, swelling of the joints. In addition, it should be remembered that certain diseases, such as heart disease, develop completely asymptomatically at the initial stage. Therefore, it is advisable to conduct regular examinations. What to do if an additional chord is found in the left ventricle?
MARS
In the field of pediatric cardiology, there is such a direction as minor anomalies of cardiac development (abbreviated MARS). The accessory chord of the left ventricle belongs to this category. According to doctors, problems of this kind do not pose a great danger, since they do not pose a direct threat to the patient’s life. It should be noted, however, that all of them require constant medical supervision. The most common manifestation in this group is left ventricular accessory chord.
What it is?
This kind of chord is a thread-like structure. On one side it is attached to the wall of the heart muscle, and on the opposite side - to the valve leaflet. Diagnosis of pathology is complicated by the fact that it cannot be detected by ECG results or even listened to. A cardiologist may suspect that a patient has an accessory left ventricular chord if he hears a heart murmur. In this case, the doctor must refer the patient for an ultrasound to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Characteristic
This anomaly can have a different shape and structure. Often the additional chord of the left ventricle of the heart plays the role of an additional conducting element. This factor provokes the development of arrhythmia and ventricular fibrillation. Often the patient's complaints resemble symptoms of chronic heart disease. However, complications can only arise if the chord is of hemodynamic significance. Otherwise, you will not need any special treatment. The only thing you have to do is undergo a thorough examination before undertaking excessive physical activity.
fb.ru
Accessory chord (trabecula) of the left ventricle of the heart: concept, prognosis
The tendinous chords, or tendinous filaments in the cavity of the left ventricle, are connective tissue formations represented by a thin fiber attached on one side to the fleshy trabeculae in the wall of the left ventricle, and to the leaflets of the mitral or bicuspid valve, on the other.
The function of these threads is to provide a connective tissue framework inside the heart and to support the valve leaflets to prevent it from sagging into the cavity of the left ventricle (LV). When the ventricular myocardium relaxes, the chords tighten, the valve opens, allowing a portion of blood to pass from the atrium into the ventricle at the moment of diastole (relaxation) of the latter. When the ventricular myocardium contracts, the chords, like springs, relax, and the valve leaflets close, preventing the reverse flow of blood into the atrium and facilitating the correct release of a portion of blood into the aorta at the time of ventricular systole (contraction).
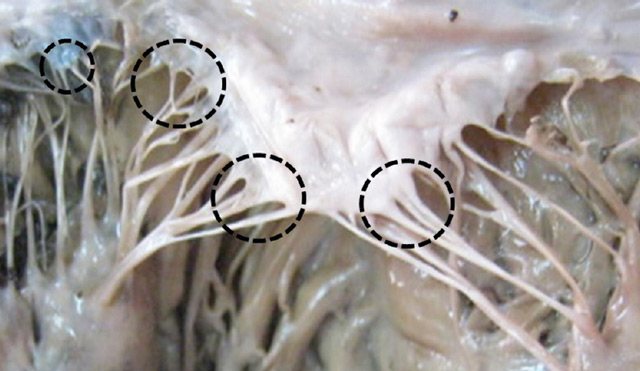
chords and trabeculae in the structure of the heart
Sometimes during the period of intrauterine development, for various reasons, not several chords are formed, as usual, but one or more additional threads.
If both ends of the thread are fixed, we are talking about a true chord, and if one end is not attached to the valve leaflet, but hangs freely in the cavity of the left ventricle, we are talking about a false additional or accessory chord of the left ventricle.
As a rule, one additional chord is found; multiple ones are less common. In relation to the longitudinal axis of the LV, longitudinally, diagonally and transversely located chords are distinguished. In most cases, such formations do not have a negative effect on the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart, and therefore are considered hemodynamically insignificant formations. However, in the case of a transverse location of the ectopic (that is, located in the wrong place) chord relative to the cavity of the left ventricle, its presence can provoke heart rhythm disturbances such as tachyarrhythmias.
Recently, the frequency of registration of additional chords in the heart has increased, mainly due to an increase in the number of echocardioscopy (ultrasound of the heart) performed in the newborn period, according to new standards for examining children under one month of age. That is, such chords do not appear clinically, and if the child had not undergone echocardioscopy, the parents might not have known that the child had an abnormally located chord in the heart.
The diagnosis “additional trabecula of the left ventricle” in the vocabulary of ultrasound diagnostic doctors is actually equivalent to the concept of an additional chord. Although, as mentioned above, from the point of view of anatomy, the trabecula is a separate formation that continues the chord.
Accessory chordae are classified as minor anomalies of the heart (MACD) - these are conditions that arise in the fetus during the prenatal period and are represented by a violation of the structure of the internal structures of the heart. In addition to the accessory chord, MARS includes a patent foramen ovale and mitral valve prolapse.
The development of an additional chord is caused, first of all, by heredity, especially on the mother’s side, as well as exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions, bad habits of the mother, stress, malnutrition and concomitant somatic pathology of the pregnant woman.
The occurrence of MARS can be caused by a disease such as connective tissue dysplasia - this is a hereditary pathology characterized by “weakness” of connective tissue in the heart, joints, skin and ligaments. Therefore, if a child has several heart abnormalities, the doctor should rule out dysplasia.
As a rule, the accessory chord does not manifest itself in any way throughout a person’s life. This is observed in most cases when the anomaly is not accompanied by connective tissue dysplasia and is represented by a single thread.
If a child has several chords identified by ultrasound of the heart, which also occupy a transverse position in the heart, it is quite possible that cardiac complaints may occur during periods of intensive growth of the child, as well as during puberty and pregnancy. These include weakness, fatigue with chest pain, accompanied by a feeling of palpitations and a feeling of lack of air, pallor. In some cases, such chords can provoke the occurrence of tachycardia or atrial fibrillation in the patient.
In the case when the occurrence of MARS is caused by dysplasia syndrome, the corresponding symptoms are characteristic - the child’s tall stature, thinness, joint hypermobility, frequent joint dislocations, deformation of the spine and ribs, structural disorders in other organs (prolapse of the kidney, dilation of the renal pelvis, deformation of the gallbladder, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and other anomalies in their various combinations).
Typically, an additional chord is an “incidental” finding during echocardioscopy of a child at one month of age or a little later. Currently, all babies at this age should undergo a cardiac ultrasound to identify heart defects that were not diagnosed immediately after birth and as a routine examination of the child. Therefore, even for parents of a healthy baby, a doctor’s conclusion about the presence of a chord in the heart may be a complete surprise. However, in the absence of other significant pathology, such children are considered practically healthy by pediatricians and do not require close monitoring by a cardiologist.
If the chord in the heart is combined with another pathology of the heart and blood vessels, the child should be observed by a pediatric cardiologist. In this case, the examination of the baby will include an ECG, and, if necessary, an ECG with physical activity at an older age, and 24-hour monitoring of ECG and blood pressure in the presence of heart rhythm disturbances. For adult patients with ectopic chord, the observation plan is the same with examinations performed once a year or more often if indicated.
Features of the pathology
The development of the anomaly occurs in the fetus during the prenatal period, and by the time of birth it is already formed. Due to the fact that it does not affect hemodynamics, it is almost always detected by chance. Only a small part (this applies to transversely located muscular and mixed chords) can have negative consequences for the work of the heart and all hemodynamics.
The peculiarity of the false chord in childhood is its incomplete development. But the situation should be constantly monitored by parents (they should not miss the first warning signs) and the local doctor. In the first year, a false chord of the left ventricle in a child cannot be eliminated without surgery, but its development can be influenced.
Only a hemodynamically significant abnormal chord can “make itself known.” This can be seen from the following signs:
- discomfort in the chest (but the newborn baby will not be able to report pain);
- high fatigue and poor exercise tolerance;
- frequent attacks of heartbeat;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- changes in psycho-emotional behavior (most often the baby becomes whiny and irritable, and the teenager may become withdrawn).
The doctor may suspect the presence of an abnormal chordae due to one more sign - a murmur upon auscultation of the heart.
Is treatment of additional chord required?
If a child has an abnormal chord in the heart, and the baby does not have other significant cardiac diseases, there is no need to treat this condition.
In cases where functional disorders of the cardiovascular system are observed at an older age, which do not cause hemodynamic disorders, the development of pulmonary hypertension due to the inability of the heart muscle to contract correctly, and also do not lead to heart failure, it is possible to prescribe medications that support and nourish the myocardium. The use of potassium and magnesium preparations (Magnerot, Magnevist, Panangin, Asparkam), B vitamins, antioxidants (Actovegin, Mildronate, Mexidol, etc.) is justified. The prescription of complex vitamin preparations is also indicated.
If the patient has significant cardiac dysfunction, taking medications such as diuretics, antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics and other groups of drugs is indicated. Fortunately, indications for this in the case of abnormal chordae in the heart are extremely rare.
There is no need to follow a specific lifestyle for a child with an additional chord. A balanced diet with fortified foods, long walks in the fresh air, as well as regular physical activity is enough. It makes no sense to limit a child’s participation in physical education or sports. A child can actively run, jump and perform all those physical activities acceptable for his age and practiced in the educational institution he attends. Swimming, figure skating and hockey are welcome.
Regarding preventive vaccinations according to the national calendar, we can say that an additional chord of honey. is not a diversion, and the baby can be vaccinated according to age.

As a child grows up and enters the difficult period of puberty, it is important to give up bad habits and adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle. In case of any age-related manifestations of the heart and blood vessels (sweating, fatigue, tachycardia, shortness of breath), the teenager should be shown to a cardiologist and, if necessary, take the above-mentioned drugs or inject them.
Pregnancy for girls with an additional chord is, of course, not contraindicated. In the case of the presence of several of the congenital heart anomalies, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound of the heart during gestation and observation by a cardiologist.
Serving in the army is not contraindicated for young men. A disqualification from the army is the presence of heart rhythm disturbances in the patient, the development of heart failure, which, again, is rare with an additional chord.
A few words should be given to the nutrition of children and adults with structural or functional disorders of the heart. If possible, you should avoid eating fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods. Preference should be given to fresh vegetables and fruits, natural juices, fermented milk products and low-fat fish. The consumption of red and black caviar, dried apricots, raisins, tomatoes, carrots, bananas and potatoes, rich in substances beneficial to the heart muscle, is encouraged. In addition, your daily diet should include cereal products, for example, various cereals for breakfast. Of course, you should protect your child from eating chips, canned soda and various fast food dishes, as this can lead to obesity, and excess weight will have an extremely adverse effect on the condition of the heart muscle and vascular walls in the future.
Complications with an abnormal chord, as a rule, do not develop. If for any reason the patient may experience heart rhythm disturbances, then thromboembolic complications (pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, etc.) may develop. Cardiac arrest may also occur due to fatal disturbances of ventricular conduction (ventricular fibrillation and paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia).
The prognosis if a child has additional chordae in the left ventricle is favorable both in childhood and in adulthood.
Source: sosudinfo.ru
What is an anomaly
First you need to figure out: what is an abnormal chord of the left ventricle?
This name refers to an anatomical feature of the structure of this organ, in which the chords (the so-called fibrous muscle connecting the opposite walls of the left ventricle) have an incorrect location. Of all the types of abnormalities found in the heart, this is the most common.
Irregular chords vary in number: both single (they account for 62%) and multiple (they account for 38%).
Impact on the quality of life and health of the accessory chord of the left ventricle in children and adults
In recent years, thanks to improved quality of examination of newborn children, especially by ultrasound examination of the heart, the number of cases of detection of cardiac anomalies has increased. Some doctors (ultrasound diagnostic specialists) regard concepts such as notochord and trabecula as synonyms. However, this is not entirely correct from the perspective of the physiological and anatomical structure of the body. And in the diagnosis, instead of “accessory chord”, “additional trabecula” is often indicated. To understand all the nuances of the pathological disorder, let’s consider the characteristics of the heart in children.
The human heart consists of chambers - there are four of them: two atria and two ventricles. In a properly functioning organ, blood flow is transferred to the ventricles from the atria. The uniform direction of blood flow is ensured by valves between the sections. The valves open and close depending on the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. To maintain the flexibility and functionality of the valve leaflets, their support is provided by threads of tendons - chords in the cavities of the ventricles. The threads are compressed alternately, causing tension on the valve and opening the way for blood flow into the ventricle. Then they unclench, ensuring the closure of the valve leaf, and the blood moves into the atrium.
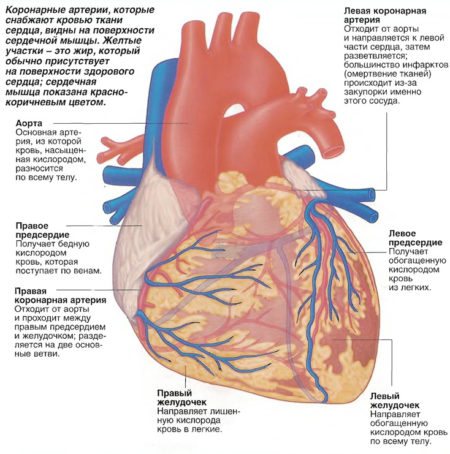
Cardiac sections
In some cases, when the baby's heart is in the developmental stage in the womb, another (and sometimes several) additional threads are laid in the ventricular section. Thus, the additional chord in the heart of a child is an additional connective tissue formation, which is most often located in the left ventricle of the heart.
What it is? The extra thread does not pose a hemodynamic threat to the functionality of the cardiac organ. Therefore, it is called a minor cardiac anomaly.
Taking into account the localization of the additional chord in the left ventricle of the heart, it is customary to identify diagonal, longitudinally or transversely located additional chords. Transverse chords are a rare phenomenon. The first two types of chords do not interfere with the normal passage of blood in the heart chambers, but the transverse one can become a serious obstacle to the advancement of blood flow, which affects the functionality of the heart muscle on the left. The longitudinal and diagonal chords are not hemodynamically influential, unlike the transverse chord. The latter can cause heart rhythm disturbances in a person in adulthood.
Diagnostics
At the doctor's appointment, a general examination will be performed, complaints will be listened to, and the heart will be listened to. Doctors sometimes detect murmurs when patients have extra connective tissue in the left ventricle.
Only ultrasound can provide reliable information. Having received its result, the doctor can already make a definite diagnosis.
If ultrasound is performed on children, then it is necessary to take into account some features of its implementation. A child is able to adequately perceive everything that happens from the age of 6. At an earlier age, his parents accompany him to the office, and it is also advisable to have toys with him. They will distract attention. Very young children are not completely undressed, their chests are simply exposed.
Ultrasound involves 2 procedures:
- Doppler examination;
- echocardiography.
Doppler examination is a study of hemodynamics. Echocardiography is intended for a general examination of the heart and its functions.
Such examinations are carried out in two-dimensional space, with patients taking a supine position. However, it is often difficult to persuade children to lie without moving for some time. This especially happens with very young children. In this case, it is possible to lay it on its side or even perform an ultrasound while standing or sitting. It is important that he arrives in a calm state.
But the position affects the result, so doctors then adjust them depending on the position of the child during the examination.
The heart is best viewed from the left side of the sternum. And also when placing the sensor, the age of the baby is taken into account. The older it is, the lower it is set. For newborns, the sensor is most often placed on the sternum itself. To detect an additional chord in the left ventricle, the four-chamber position is used. This allows it to be seen in the form of thin threads.
Reasons for the formation of an accessory chord
One of the main prerequisites for the formation of an additional chord in the cardiac ventricle (LVDC) is a genetic disposition. If the child's mother has heart pathologies, then the risk of developing congenital diseases or heart abnormalities in the fetus is high. Among the common pathologies of the children's heart are ARCH, false chord, prolapse of valve leaflets, etc.
There are a number of reasons for the formation of anomalies:
- Negative effects of air and drinking water pollution.
- The presence of mutagenic effects associated with drug use, alcohol, and smoking during pregnancy.

Attention! These factors are most dangerous during the formation of the connective structure of the fetus in the womb (before the sixth week of pregnancy) and throughout the entire period of gestation.
Consequences
Abnormal cords that did not cause hemodynamic disturbances in childhood and adolescence never lead to a worsening of the condition in adults. But the additional chords, which somehow made themselves felt in children, deserve close attention at any age. They can be the cause of a number of heart diseases. Any such chord requires lifelong monitoring with constant adherence to the following rules:
- Rational mode of labor activity. All loads must be well tolerated.
- Get proper rest at night and during the day (as fatigue appears).
- A periodic course of medications aimed at maintaining the functioning of the heart (pantogam, asparkam, cytochrome, magnesium preparations and vitamins PP, group B).
Full life activity can be possible in any situation if all recommendations were followed on time, according to Dr. Komarovsky. The accessory chord in the cavity of the left ventricle completes its development in the first 10 years of life.
Author of the article: Elena Vasilenko
mirkardio.ru