What kind of disease is this?
Muscle hypotonia is a decrease in the tone of muscle fibers, as a result of which the response to nerve impulses becomes insufficient. This is not a separate disease, but a common syndrome that occurs in patients with additional problems in the brain, peripheral nerve bundles, muscles and spinal component. Often this pathology develops as a result of metabolic disorders. This disease develops when motor neurons are damaged and is often characterized by paresis (decreased muscle strength).
The normal functioning of the muscles of the body is determined by muscle tone, which means that any signals that the nervous system sends are an impulse to perform an action. With different degrees of hypotension, these actions are either performed with a slower response rate or are not possible at all. Such disorders are also manifested by increased flaccidity of muscle fibers, as well as the inability to keep the muscle in a tense state even for a short time.
The opposite condition is increased muscle tone, in which contractions of nerve fibers lead to overstrain. For example, if with hypotension it will be difficult to bend a limb, then with hypertonicity it will be difficult to return it to a relaxed state. These two phenomena are not mutually exclusive and can alternate.
What are the signs to recognize muscle hypotonia in a child?
Muscular hypotonia in infants leads to a change in appearance, so the symptoms of this disease are visible to the naked eye. A child with muscle hypotonia chooses elbows and knees spaced apart as support, while a child with normal muscle tone rests on his limbs at right angles. If the muscles of the back of the head are weak, the baby is not able to hold the head for a long time, but turns it to the sides, forward or backward.
When a baby with hypotension is taken under the arms, his arms involuntarily rise up parallel to the body. Children with normal muscle tone keep their arms and legs bent when they sleep. Their palms are open, and the child does not hold his hands in fists, like all other children with normal muscle tone. With muscular hypotonia, children's limbs involuntarily relax and droop. The muscles feel loose and soft to the touch. The limbs are spread apart far beyond the limits of physiological norms.
With hypotonia, a baby's legs can open almost 180 degrees. This position is called frog pose. A child with muscle weakness in this position experiences absolutely no pain or discomfort.
Kinds
The classification of this condition is made depending on the degree of damage and localization of the process. A congenital form of hypotension is distinguished when this symptom is part of the specificity of a genetic disease. Acquired types usually appear as a result of birth injuries, infectious diseases (meningitis, encephalitis), metabolic disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Classification of muscle hypotonia:
- According to the degree of damage, generalized or diffuse, as well as isolated (local) develops.
- According to the speed of spread: acute and slowly progressive.
- Based on their manifestations, they distinguish between episodic, progressive, recurrent and intermittent (characterized by periods of decline and rise).
- By level of origin: central level (graded into spinal and cerebral degrees), as well as peripheral, when there is a violation of the mobility of individual muscles. Peripheral hypotension, in turn, is divided into neuronal, neural, synoptic and muscle levels.
With diffuse hypotension, the central nervous system is mostly affected. When localized, the situation is somewhat different, because disturbances are observed in the work of peripheral centers of nerve endings. Most often this affects the functioning of the upper and lower extremities. There are also more severe cases when disruptions occur in two centers at once. Such pathologies are much more difficult to treat, and in the absence of sufficient medical care, the patient faces severe complications, including complete paralysis and death.
Types of arterial hypotension (hypotension)
Arterial hypotension is classified into the following types:
— Acute hypotension (acute arterial hypotension); — Chronic hypotension (chronic arterial hypotension); — — Primary chronic arterial hypotension; — — Secondary chronic arterial hypotension.
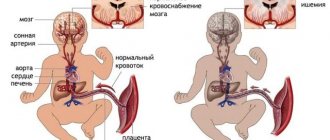
Acute hypotension (sharp drop in blood pressure). This type of hypotension is very dangerous because the level of oxygen supply to the brain sharply decreases (hypoxia), which after some time can cause a stroke. At the same time, a sharp decrease in blood pressure can be accompanied by diseases of internal organs such as myocardial infarction, severe arrhythmia, pulmonary embolism, allergic reactions, etc.
A sharp drop in blood pressure requires urgent medical attention!
The causes of a sharp drop in pressure can be poisoning (alcohol, food, drugs, medications), blood loss, acute infections, sepsis, dehydration, etc.
Chronic hypotension (constantly low blood pressure). This form of hypotension is often called physiological hypotension, because. in many cases, it is a constant companion in the lives of many people, for example, residents of high mountains, tropics, cold parts of the Earth or athletes, as an image of the body’s adaptation to the lifestyle. In these cases, persistently low blood pressure is not considered a disease.
The main danger of chronic hypotension is the risk of developing ischemic stroke in old age.
At the same time, chronic arterial hypotension is a serious opponent for many young people, because Frequent breakdowns of strength, in some cases developing into collapses, do not allow one to constantly work productively and achieve success in various areas of life.
Primary (idiopathic or essential) hypotension. This condition of the body is classified as an independent disease. The cause and etiology are currently the subject of debate and disagreement, but among the identified causes is prolonged psycho-emotional stress (depression, stress).
Read also Frostbite - signs, degrees and first aid for frostbite
It is very important to prevent this form of the disease from spilling over into a protracted period of oxygen deficiency throughout the body.
Secondary arterial hypotension. Unlike primary hypotension, secondary hypotension is a symptom of other diseases, including: arrhythmia, cardiovascular diseases, brain injuries, cervical osteochondrosis, diseases of the respiratory system and endocrine system, circulatory disorders, side effects of certain medications, gastrointestinal diseases, tumors, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, alcoholism, etc.
Orthostatic hypotension is a sharp decrease in blood pressure when a person suddenly stands up after prolonged squatting or lying down.
Causes
Most often, muscle hypotonia syndrome in a child is a congenital pathology and is diagnosed already in the maternity hospital. Upon examination, a decrease in muscle tone, the inability to perform flexion movements and other neurological signs are revealed. In most cases, it is a concomitant symptom of other neurological problems, developmental pathologies and genetic diseases.
Causes of congenital muscle hypotonia:
- Genetic diseases. These include Down syndrome, Aicardi syndrome, Martin-Bell syndrome, Leigh syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and deletions. Diseases of Dejerine-Sott, Crabbe, Menex, Niemann-Pick, Tay-Sachs. It can also be spinal muscular atrophy, septo-optic dysplasia, pituitary dwarfism, non-ketotic hyperglycinemia and others.
- Pathologies of intrauterine development. Most often this is a consequence of congenital cerebellar ataxia, dyspraxia, sensory integration dysfunction, hypotonic cerebral palsy, hypothyroidism and others.
- Birth trauma, asphyxia and intracranial hemorrhage.
The listed conditions and diseases are often accompanied by a decrease in muscle tone and other associated symptoms. In addition, hypotension may develop gradually, with varying rates of progression.
Causes of acquired hypotension:
- Genetic diseases: muscular dystrophy, Rett syndrome, metachromatic leukodystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy.
- Toxic mercury poisoning.
- Infectious diseases: encephalitis, meningitis, polio, sepsis, botulism and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Metabolic disorders: hypervitaminosis, rickets, kernicterus.
- Autoimmune diseases: myasthenia gravis, celiac disease and negative reaction of the body to vaccination.
- Neurological problems, which may include lower or upper motor neuron damage, as well as traumatic brain injury.
The causes of such disorders may be cerebral palsy, as well as pathologies of the cerebellum, hypothyroidism and Sandifer syndrome. All these diseases and pathologies have muscle hypotension in their symptoms, as well as additional signs that differ in the nature of the manifestations and the intensity of damage to the central nervous system. Once the disease is diagnosed, it is possible to accurately determine the cause of the development of muscle hypotonia, but in some cases this is simply impossible to do.
How to treat muscle hypotension in children?
The primary treatment for muscle hypotension in children is aimed at physical activity and massage. During the examination, the doctor will determine how weak the child’s muscles are and what specific treatment he needs.
With the help of massage and physical exercise, the muscles begin to actively strengthen and work. Such exercises can be done both in stationary conditions and at home.
The result is noticeable almost immediately: the child independently begins to move his legs and arms, take objects, hold his head, etc. If left untreated, muscle hypotonia leads to delayed development of the child. In the future, such children experience excessive plasticity and postural disorders. In case of advanced hypotension, the child may completely lag behind or stop developing. Therefore, caring parents should carefully monitor how their baby develops and contact a pediatrician if there are any alarming signs.
Let your baby be healthy!
Symptoms and complications
Depending on the cause of occurrence, the age of the patient and the severity of the pathologies, the clinical picture differs markedly. When examining newborns, without confirmation from a neurologist, such a diagnosis cannot be made, and in some cases, pathological changes appear much later.
Signs of muscle hypotension in children:
- When examined, the newborn reacts poorly to muscle irritation; reflexes do not work or are very weak.
- The child cannot hold his head, does not roll over from his back to his stomach, and cannot hold a toy in his hands.
- When lifting a child in your arms in a vertical position, the arms involuntarily rise up, and the baby may slip out of your hands.
- The sleeping position also “gives away” the disease: the child is fully straightened, the arms lie along the body, and are not bent at the elbows. When raised, the head tilts back, the limbs hang down.
- General delay in physical development; the child begins to hold his head up, sit, crawl, and perform other actions later than others.
Diffuse muscle hypotonia in children can be manifested by problems with respiratory function, absent or decreased reflexes, decreased activity and poor appetite due to difficulty sucking movements. Over time, such pathologies progress significantly, leading to retardation in mental and physical development, partial or complete muscle atrophy, curvature of the limbs and paralysis.
Pathologies of various types can progress for a long time without external manifestations. There are cases when a genetic deviation actively manifested itself only in adulthood, or during the period of hormonal changes in the body. The symptoms of hypotension are not so pronounced and for diagnosis it will be necessary to undergo a full examination of the body, including laboratory tests. In most cases, the diagnosis is made purely by chance, when visiting for another ailment.
Complaints from adult patients:
- Periodic or constant weakness throughout the body, regardless of working conditions.
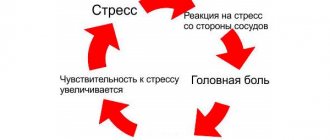
- Frequent headaches that do not go away after taking painkillers.
- Pain in the chest, slight tachycardia.
- Pathological sleep disorders, manifested not only by insomnia, but also by increased sleepiness.
- Increased sweating without external causes or changes in temperature environment.
- Behavioral changes: increased tearfulness or irritability, frequent periods of depression.
- Numbness of the limbs at an advanced stage of the disease.
Ignoring such alarming symptoms can lead to serious complications, including disability. Most often, we are accustomed to attribute such manifestations to tiring work, nervous stress and the inability to properly rest. At the same time, a timely examination will help determine the true cause of such ailments, as well as take the right measures.
How to diagnose muscle hypotonia in children?
To diagnose muscle hypotonia, carry out:
· Traction test;
· Passive muscle tone;
· Horizontal and vertical hanging;
· Assessment of muscle mass;
· Active muscle tone.
The most sensitive test for determining muscle tone is the traction test. To do this, the doctor takes the baby by the hands and pulls him into a sitting position. If the baby is healthy, then the head will immediately follow the body. In a sitting position, the child holds his head independently.
Passive muscle tone is determined by the sensation of resistance during passive extension and flexion of the limbs. The specialist measures the angle between the limb and the torso and studies the range of movements. With muscle passivity, a deviation from normal limits is observed.
The vertical suspension method is carried out as follows: the doctor holds the child under the arms and lifts him up into a vertical position. In normal condition, the child holds his head straight. With muscle hypotonia, the legs and head hang forward, and the child seems to slip out of the hands.
During horizontal hanging, the baby himself holds his head and back, bends his limbs at the joints. With hypotension, the baby bends through the doctor's hands like an upside-down U. The head and legs hang down like a doll.
When assessing muscle mass, the specialist pays attention to fascicularity, myokymia and other manifestations of muscle activity. Characteristic signs of muscle weakness include myopathy and myasthenia gravis. With chronic hypotension, joint contractures, scoliosis and tendon retraction are observed. Muscle atrophy is most easily established in the presence of asymmetry. This method is a little difficult due to the large variability of indicators in children with normal muscle function.
With the active muscle tone method, muscle activity indicators are studied. These include the child’s posture, the speed of movement of the limbs and their return to their original position, and the strength of the movements. When the baby lies on his back, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of any pathologies. With hypotension that developed in utero, arthrogryposis and dislocation in the hip joint are noted. Such a child, being in a sitting position, lowers his head and shoulders forward, his limbs hang.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a specialist - a neurologist. For this purpose, the child is examined already in the maternity hospital; if specific signs are identified, a consultation with a specialist is prescribed, as well as laboratory tests to identify possible genetic pathologies.
The following data is analyzed:
- Cases of hereditary diseases in parents and close relatives.
- Results of a physical examination, which determines muscle tone and checks basic reflexes.
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Genetic blood test.
- Biopsy of muscle or nerve tissue.
- Results of special comprehensive examinations: CT, MRI, EEG and electromyography.
- CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) studies.
Muscle hypotension is not classified as a separate diagnosis. Even in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) there is no special designation for this pathology. Based on the results of the above studies, the possible type of disease is determined, according to which further treatment is carried out. The closest diagnosis according to ICD-10 is congenital hypotonia in a newborn (nonspecific lethargy syndrome), coded P94.2.
Diagnosis of arterial hypotension
Hypotension is diagnosed using the following methods:
— questioning the patient for the presence of various symptoms in order to identify the cause of the disease; — identification of the type of hypotension: physiological or pathological type; — systematic measurement of blood pressure; — electrocardiography (ECG); — Doppler echocardiography; — cardiointervalography, etc.
Treatment
The main problem in the treatment of such deviations is the need for complex and long-term treatment. It is quite possible to normalize such a state, but it requires remarkable endurance and the application of strength and patience. At the moment, there is no cure for absolutely all diseases associated with the appearance of muscle hypotension, but it is possible to create conditions for the development of muscle tone and alleviation of symptoms. In addition, this will help avoid further progression of the disease and serious complications.
What methods are used in treatment:
- Physiological procedures. For a baby with suspected muscle hypotension, courses of therapeutic massage are required, which help strengthen motor activity and respiratory function. In addition, methods of therapeutic exercise and gymnastics are used, including regular exercises, therapeutic baths, aqua gymnastics and other procedures. Water activities will help strengthen your back and shoulder girdle, and also contribute to the overall health of the body.
- It is best for an older child to also develop fine motor skills. Modeling, drawing, finger games, assembling mosaics and other techniques are well suited for these purposes.
- Classes with a speech therapist will help to avoid pathologies of the speech apparatus, which are also often found with such decreases in muscle tone.
- Be sure to establish a balanced diet that includes all groups of nutrients, vitamins and mineral complexes.
- Special drugs are prescribed depending on the underlying disease and include groups of neurometabolic drugs, vascular and other drugs.
- If conservative treatment does not produce the expected results, there is a chance to improve the patient’s quality of life with implantable devices. They will transmit a nerve impulse to the problem area by electrical or pharmacological action.
In the treatment of this pathology, active recreation and walks in the fresh air are of great importance. You can master the technique of massage movements, for which specialists will show you key points and exercises. If a child is diagnosed with muscle hypotonia, special attention should be paid to correcting posture and gait, for which there are also special exercises. Correct adaptation of the baby will take a lot of time, because you shouldn’t even hope for quick results. At the same time, such events are vital and bring an unconditional positive effect, so you should not despair and give up.
Complications of hypotension
Particular attention should be paid to pregnant women with symptoms of hypotension, because Insufficient oxygen in the blood leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus, which can lead to poor growth or abnormal formation.
Sometimes, if hypotension is treated incorrectly, this disease can develop into another disease - hypertension (arterial hypertension, or high blood pressure), but with complex etiology and symptoms, which makes its treatment difficult.
With an exacerbation of arterial hypotension, a person may experience cardiogenic shock, in which the pulse is weakened, pressure is not determined, urination is suppressed, and fainting. First aid for this condition is to put the person in a horizontal position, provide an influx of fresh air and immediately call an ambulance.
The most important complication of hypotension is stroke and heart attack, which can be fatal.
Prevention
It is very important for parents to know the main symptoms of hypotension in infants and older children. If you suspect muscle dysfunction, you should definitely undergo examination by a neurologist. In addition, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations, undergo timely examinations and prevent rickets. Exceeding the permissible dosage of vitamin D can also lead to a similar pathology, so you should definitely find a middle ground when using pharmaceutical vitamin preparations.
Muscle hypotension often manifests itself as a result of genetic and metabolic disorders. This is a symptom of more than a hundred different diseases, in which manifestations of decreased muscle tone can be of varying intensity. With successful treatment, it is very important to regularly massage and use physical therapy exercises, as well as adhere to the doctor’s recommendations regarding taking medications. The prognosis for this pathology depends on the stage of progression and type of hypotension, as well as timely examination and treatment.
Did you like the article? Save it!
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments! Cardiologist Mariam Harutyunyan will answer them.
Ivan Grekhov
Graduated from the Ural State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. General practitioner
Hypotension in infants: symptoms
Dystonia in children is manifested by impaired muscle tone. This is a fairly common diagnosis. Dystonia can be associated with both hypertonicity and hypotension. Muscle hypotonia syndrome is often congenital. If its severity is weak or moderate, then the maternity hospital cannot always make a diagnosis. Attentive, caring parents are obliged to systematically monitor the condition of the muscle corset of their little child. This is how you can notice the symptoms of pathology at the earliest stages, which will allow you to both carry out effective treatment and avoid worsening the condition.
Treatment of hypotension with folk remedies
Important! Before using folk remedies for low and low blood pressure, be sure to consult your doctor!
Treatment of hypotension at home can be done by the following means:
Coffee with honey and lemon. Grind 50 g of roasted coffee beans, which can be done using a coffee grinder. Add ground coffee to 500 g of honey, and squeeze out the juice from 1 lemon. Mix everything thoroughly. The product should be taken 1 teaspoon 2 hours after meals. The product must be stored in the refrigerator.
Schisandra. Pour the crushed fruits of Schisandra chinensis with 40° alcohol in a ratio of 1:10. Leave the product in a dark place for 2 weeks. Take tincture 25-40 drops per 1 tbsp. spoon of cold water 30 minutes before meals.
Ginger. Dissolve half a teaspoon of ginger powder in 1 glass of sweet strong tea. Take the product 3 times a day for 1 week.
Rhodiola rosea (golden root). Drink Rhodiola rosea extract 5-10 drops 20 minutes before meals, 2-3 times a day for 10-20 days.
Low blood pressure charges
Note 1: parts – parts. Note 2: Take all the listed fees 1/3-¼ cup 3-4 times a day for 1-2 months. Then we take a break for a month and the course can be repeated. Note 3. To prepare the mixture, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of it into a thermos and pour 2 cups of boiling water, then let it brew for 12 hours.
Collection No. 1: St. John 's wort herb (3 parts), volodushka herb (2 parts), Echinops herb (2 parts), chicory herb (2 parts), Leuzea root (2 parts), licorice root (3 parts). ), dandelion root (2 tsp), juniper berries (1 tsp).
Collection No. 2: Veronica grass (2 parts), St. John's wort grass (5 parts), wormwood grass (1 part), sage grass (3 parts), watch leaves (4 parts), immortelle inflorescences (2 parts). ), tansy inflorescences (2 parts), chicory flowers (1 part), dandelion root (1 part), elecampane rhizome with roots (1 part).
Collection No. 3: St. John 's wort herb (4 parts), yarrow herb (4 parts), chicory grass (2 parts), strawberry leaf (2 parts), calamus rhizome (1 part), juniper fruits (1 part). ), rose hips 4 hours).
Collection No. 4: tartar grass (1 tsp.), nettle herb (2 tsp.), horsetail herb (2 tsp.), birch leaves (4 tsp.), mint leaves (1 tsp.), strawberry leaves (2 tsp. .), currant leaves (2 parts), dandelion root (4 parts), rhizome with elecampane roots (1 part), rose hips (6 parts).
Collection No. 5: yarrow herb (2 parts), Echinops herb (1 part), knotweed grass (2 parts), tansy flowers (1 part), licorice root (2 parts), Leuzea root (1 part. ), hawthorn fruits (3 parts), rowan fruits (2 parts).
Collection No. 6: St. John 's wort herb (4 parts), fireweed herb (4 parts), oregano herb (4 parts), knotweed herb (2 parts), plantain leaves (4 parts), mint leaves (2 parts). ), rose hips (6 parts), juniper fruits (1 part), calamus rhizome (1 part).
Collection No. 7: blueberry leaves (1 tsp.), lingonberry leaves (1 tsp.), black currant leaves (1 tsp.), thick-leaved bergenia (2 tsp.), forgotten kopeck (1 tsp.), golden root (1 tsp. .), angustifolia fireweed (1 tsp.), thyme (0.5 tsp.). Three tbsp. spoons of the collection are poured with a liter of water and boiled over low heat for 5-7 minutes. Next, the product is infused for 30 minutes and taken 2-3 glasses a day, like regular tea, with the addition of sugar or honey.
Causes of hypotension
Low blood pressure in a teenager is a rather abstract concept. Because the child’s body is designed in a special way. A decrease in indicators is perceived as an acceptable norm if the fluctuations are within certain limits. Simply put, low blood pressure is common in adolescents and is not considered a pathology.
Because children naturally have lower blood pressure than adults. But this phenomenon should not be ignored, because a decrease in blood pressure may indicate that the child has a serious illness.
Low blood pressure can be a consequence of physiological and pathological problems
There are several factors that can affect blood pressure levels:
- Incorrect, unbalanced nutrition (when the child lacks vitamins and nutrients).
- Emotional or physical fatigue (exhaustion).
- Passive lifestyle (lack of physical activity).
- Lack of sleep and rest.
Another decrease in indicators occurs:
- with hormonal imbalances in the body (which often worries both girls and boys during puberty)
- for problems with blood flow (this may be vegetative-vascular disorders)
- with high intracranial pressure
So, let's start with the fact that a decrease in blood pressure is not always considered a pathology. Since the level of pressure depends on many factors, the indicator is affected by:
- Child's age.
- His gender.
- Lifestyle and nutrition.
- Intensity of physical and emotional stress.
Attention! If a teenager’s nutrition is fine, he leads an active lifestyle and does not experience serious overload at school, then hormonal changes may be the cause.
During puberty, adolescents are subject to frequent changes in blood pressure.
The reason for this is hormonal instability. In a child’s blood, the concentration of sex hormones and growth hormone is simply off scale. Against the background of hormonal instability, blood pressure levels can either decrease or increase.
If we talk about vegetative-vascular disorders in the body, they lead to problems with blood flow. As a result of circulatory disorders, intracranial pressure increases.
Against this background, the teenager has a whole list of complaints.
Impaired blood flow to organs, including the brain, occurs against the background of a passive lifestyle.
Lack of physical activity leads to stagnation in the body, as a result of which the child’s blood pressure decreases. Improper or poor nutrition is another cause of problems with blood pressure.
If a growing body does not have enough nutrition, vitamins and microelements, then certain problems arise with blood pressure levels.
Extreme fatigue, drowsiness and dizziness may indicate low blood pressure
A drop in blood pressure is not asymptomatic. With a sharp decrease in indicators, a teenager may complain of:
- weakness
- decreased performance
- the appearance of headaches
- dizziness
- problems with information perception
If the cause of arterial hypotension is a pathological process, then the child experiences:
- Constant weakness, increased fatigue.
- Sensitivity to weather conditions and temperature changes.
- Lagging behind peers in development and learning.
First of all, the child becomes lethargic, nervousness, tearfulness, and frequent mood swings appear. Against the backdrop of problems with learning, the teenager has problems adapting to school.
Important: If the pressure is low, then it is difficult for the child to get out of bed, severe dizziness, pain in the head occurs, and “spots” appear before the eyes when changing position.
These symptoms should not be ignored, since they indicate not only a decrease in blood pressure, but also a disruption of blood flow to the brain. If such signs appear, you should consult a doctor.
There are several ways to stabilize the indicator, first you need to:
- consult a pediatrician
- do an ECG
- if necessary, ECHO or ultrasound of the heart
- visit a neurologist
- consult a cardiologist
If the doctor determines that the blood pressure has dropped due to the child having a particular disease, he will prescribe the necessary medicine.
But if no diseases or pathologies are found in the teenager, then you will have to stabilize the indicator yourself.
Proper nutrition and daily routine will help normalize blood pressure
To do this you will need:
- Organize your daily routine.
- Give the child's body the necessary physical activity.
- Provide him with adequate nutrition.
It's worth starting with your daily routine. A teenager should get up and go to bed at the same time, spending at least 8 hours in bed. Sleep will help the body recover and increase its resistance to stress.
Physical activity is necessary in order to avoid stagnation in the body. The child can:
- visit the pool 2-3 times a week
- walk before bed
- go for a morning jog
- do gymnastics daily
Help: Optimal physical activity on the body will help not only improve heart function, but also increase the elasticity of blood vessels. This will help avoid various diseases in the future.
Low blood pressure in a teenager is a phenomenon that many parents simply overlook and do not consider as a serious problem.
In recent years, this dangerous condition has been gradually gaining momentum. In the complete absence of adequate and competent treatment, after a certain time, this condition can develop into stable arterial hypertension.
Moreover, simultaneously with it, serious pathological diseases of a chronic nature can develop. This phenomenon is extremely dangerous for girls due to the likelihood of some complications occurring in the future during pregnancy and childbirth.
It is important to note that school-age children often complain to their parents about general weakness, malaise, headaches, dizziness, and memory loss. As a rule, such manifestations worsen in early spring and autumn. They may indicate a decrease in the child's blood pressure.
This condition should never be ignored as it can lead to more worrying complications. In order for the treatment of this pathology to be more effective, it is necessary to understand in advance why the child’s tonometer readings are decreasing. This article examines the main reasons for low blood pressure in a teenager.
The first step is to understand the general mechanism of pressure regulation. Generally, it can be divided into the following points:
- neurogenic. The level of pressure can be regulated through the autonomic nervous system. Mainly thanks to her sympathetic part. As is known, the introduction into the regulation of these mechanisms is carried out due to the so-called humoral factors;
- humoral. Thanks to the hormones of the sympathoadrenal system, blood pressure is regulated. Adrenergic neurons, as well as the adrenal medulla, take an active part in this process.
It turns out that low blood pressure in adolescents 14 years old can be observed in the following cases:
- poisoning by toxins. As a rule, it is most acutely observed precisely in the presence of areas of chronic infection;
- heavy bleeding;
- severe physical and psycho-emotional exhaustion;
- immediate drop in blood pressure;
- serious circulatory problems in the brain;
- organ or system pathology.
It should be noted right away that the pressure of a teenager, which has the following numbers - 110/65 - is far from normal. It is for this reason that you should immediately consult a doctor if such indicators are detected.
Symptoms
In order to promptly detect the first signs of a serious disease called hypotension, you should monitor the child very carefully.
The first and most obvious manifestations of low blood pressure include the following:
- chronic fatigue;
- increased drowsiness;
- complaints of constant dizziness;
- fainting conditions;
- feeling of aching muscles;
- chilliness;
- cramps and pain in the abdominal area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dyskinesia;
- decreased intellectual and physical activity;
- constant rapid breathing, which may indicate a lack of oxygen in the body, in particular in the brain.
All of the above symptoms do not always indicate low blood pressure in a teenager. Often, the causes of a similar condition may be a serious illness of an infectious nature or stress. In order to correctly determine the disease, you need to see a doctor for a detailed examination.
There are certain standards established by experts:
- 10 - 12 years: 110 - 126/71 - 81 mmHg. Art.
- 12 - 15 years: 110 - 135/71 - 85 mm Hg. Art.
As for the first group of children, who are from 10 to 12 years old, the initial period of puberty is characterized by the occurrence of obvious changes in blood pressure levels.
To a large extent, this applies specifically to girls, who are ahead of boys in the rate of physical development.
Despite the average values of the tonometer, experts consider the upper maximum to be the norm - 120 mmHg. Art. As a rule, the indicator directly depends on the body type: taller teenagers with a thin build have low blood pressure compared to their peers with an athletic type.
As you grow older, general ailments gradually disappear. But in order to completely eliminate the possibility of undesirable consequences, you should undergo an appropriate examination in a timely manner.
As for the norm, the pressure in adolescents should be approximately equal to the following values: 120/77 mm Hg. Art.
As you know, by the age of 12, a child’s vascular system has completely completed its formation.
With frequent changes in pressure, phenomena such as tachycardia, fainting, changes in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, pain in all parts of the head, and dizziness are likely.
Prevention of arterial hypotension
To prevent low and low blood pressure from bothering you throughout your life, try to adhere to the following recommendations:
— periodically measure your blood pressure, keep a log of measurements; — visit a cardiologist periodically; - try to lead an active lifestyle; - eat mainly foods enriched with vitamins, or take vitamin complexes; — maintain a day/night, work/rest routine; - get enough sleep; - avoid stress, think about changing jobs if necessary; — strengthen your body by hardening and moderate physical activity; — saturate your life with positive emotions. Remember, “A merry heart does good as medicine, but a broken spirit dries up the bones” (Bible, Proverbs 17:22).
Symptoms
Hypotonic disease, like hypertension, is characterized by characteristic symptoms that are easy to notice in children. Children with this diagnosis will constantly complain of the following signs of illness:
- Fast fatiguability;
- Drowsiness;
- Irritability;
- Pain in the heart area;
- Headache.
Also, a sick baby may have a tendency to faint. Parents will notice that his skin is pale and cold to the touch. The child himself will become dependent on weather conditions. They will begin to affect his well-being and behavior.
Hypotension that develops in a child can also lead to more serious symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Spasmodic pain in the abdomen;
- Accumulation of gases in the intestines;
- Aerophagia;
- Constipation;
- Interruptions in the heart.
After the child wakes up, he may show signs of cephalalgia. Since the morning he has been troubled by general weakness and malaise. Paroxysmal headaches can occur throughout the day. They arise due to changes in weather or the influence of an emotional factor.
A child with hypotension is lethargic and apathetic
What to do if your child has low blood pressure
Before raising your child's blood pressure, you need to be examined. To clarify the diagnosis and determine the possible cause of the drop in blood pressure you will need:
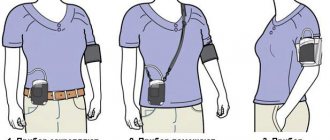
- Blood pressure measurement. Blood pressure is measured with a mechanical or automatic tonometer (the first option is preferable). The procedure is performed sitting or lying down. The cuff for the child is selected individually. It is placed on the forearm. Blood pressure is measured on both arms alternately with a short interval.
- Survey of the child and parents.
- Electrocardiography.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- General clinical blood tests.
- Blood chemistry.
- Orthostatic test.
- Load tests.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
Low blood pressure in a teenager or younger child requires complex treatment. It includes:
- The use of medications that increase vascular tone and blood pressure.
- Physiotherapy.
- Elimination of risk factors (treatment of existing pathology, normalization of nutrition and sleep, taking vitamins, changing lifestyle, eliminating stress).
- The use of folk remedies.
If hypotension is caused by neurocirculatory or vegetative-vascular dystonia, then exercise therapy, spa treatment, hydrotherapy, hardening, playing sports and normalizing the daily routine are indicated. Children should sleep 9-10 hours. In case of neuroendocrine disorders, it is important to limit the time a child spends on gadgets.
Physical activity
If hypotension is detected in school-age children, then physical activity needs to be increased. This helps to increase immunity, increase hemoglobin, increase blood flow and restore the functioning of the nervous system. If a teenager has low blood pressure, then swimming, jogging and working out in the gym will be useful. It is recommended to walk for at least 1 hour every day. It is possible to engage in physical therapy (physical therapy).
Important information: What to take for heart pain and low blood pressure
Diet
An important aspect of treatment for low blood pressure in a child is nutrition. Patients are recommended:
- Include pickles with moderate amounts of table salt in your menu. They help increase circulating blood volume and increase blood pressure. Salted seafood is healthy.
- Add extractive substances (spices, herbs) to dishes. This enhances the secretion of glands and promotes vasoconstriction.
- Enrich the menu with sources of vitamin C (citrus fruits, berries, cabbage).
- Eat fresh fruits, berries and vegetables every day.
- Eat red meat (beef, veal). This is important for hypotension due to anemia.
- Drink more fluids. The greater the volume of circulating blood, the higher the pressure.
- Eat in small, fractional portions.
- Include tonic drinks (strong tea, coffee, cocoa) in the menu.
Folk remedies
Raspberry leaves, eleutherococcus, lemongrass, parsley, currants, ginseng and honey are useful for low blood pressure in children. They allow you to increase blood pressure. For hypotension, herbal decoctions and infusions are useful. You can purchase ready-made preparations at the pharmacy. If you have low blood pressure, you can give your baby a mixture based on celery root and honey. From 3-4 years old you can use tincture of Eleutherococcus.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
If there is hypotension in children, the following physiotherapy procedures are useful:
- electrosonotherapy (therapeutic sleep);
- electrophoresis with caffeine, Mezaton or calcium;
- reflexology.
Drug treatment
For low blood pressure in adolescents, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Adaptogens and general tonics. These include tinctures of lemongrass, ginseng and aralia. Ginseng has a stimulating effect on nervous tissue, helps increase blood pressure, increases the overall tone of the body, improves performance and eliminates drowsiness. The substances contained in the root of this plant (glycosides, essential oils, phytoestrogens and pectins) have a therapeutic effect.
- Psychotropic drugs. These include Fevarin. The drug can be prescribed to children over 8 years of age. Fevarin helps with hypotension accompanied by depression.
- Nootropics (Pantogam, Calcium Gopanthenate, Pantotropil, Pantocalcin and Cerebrolysin). Drugs in this group improve brain function in conditions of arterial hypotension.
- Antioxidants.
Important information: Can ginger increase blood pressure?
If low blood pressure reaches critical values or is provoked by acute conditions (severe blood loss, shock), then the following medications can be used:
- Medicines that increase blood pressure (alpha-adrenergic agonists). These include: Mezaton, Stelfrin, Dopamine, Dobutamine. Mezaton is used in the form of a solution for injection. The mechanism of hypertensive action is associated with narrowing of arterioles due to stimulation of alpha1-adrenergic receptors. Mezaton is contraindicated in cases of pheochromocytoma, individual intolerance, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and ventricular fibrillation. According to indications, Adrenaline, Noradrenaline and Epiject can be prescribed.
- Systemic corticosteroids.
- Infusion agents (saline and crystalloid solutions).
All drugs are selected by the doctor taking into account the level of pressure, contraindications, individual tolerance and age of the child.
Treatment: correction of physical activity, regimen, nutrition, medications
For children, non-drug interventions play a special role in therapy; they provide more than half of the success of treatment. Non-medicinal methods include strict adherence to the daily routine, strict adherence to it, including on weekends. Sleep should last at least 9-10 hours, including daytime rest, and an elevated position of the head.
A set of morning exercises, hygiene procedures, a shower, preferably a contrast one, and avoidance of sun exposure and hot baths are required.
Physical activity, physical education and sports are important: cycling, swimming, tennis, dancing are suitable for hypotensive people, but without professional overload. Regular physical activity trains blood vessels. It is important to eat properly with enough protein, vitamins and minerals, and take tonic drinks.
The doctor prescribes massage of the collar area, feet, hands, calf muscles, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, electrosleep, tonic baths, showers), methods of systematic hardening. Psychological counseling is provided and a favorable emotional environment is created in the family and school.
Treatment methods
Therapy may be prescribed with or without medications. For long-term and persistent forms of the disease, a combination of two methods is often used.
Non-drug therapy involves lifestyle adjustments:
- good sleep;
- strict daily routine;
- walks in the air every day for about two hours;
- easy charging after waking up;
- eating small portions 4 to 6 times a day (unlike hypertension, with arterial hypotension there is no need to limit salt intake).
Physiotherapy, water procedures, psychotherapy, medicinal baths can be used.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes a massage course for the child. It can be general or one of the areas: calves, hands, neck-collar area.
If non-drug therapy does not demonstrate effectiveness, drugs are added to the treatment plan. In some cases, according to a specialist, drug treatment begins immediately. It includes a set of medications, their type and dosage are selected strictly individually.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for persistent low blood pressure in a child cannot always be established. Primary hypotension can be explained by hereditary predisposition, body type, puberty, the child’s character, unfavorable pregnancy and childbirth, as well as any social factors (daily routine, stress, etc.).
Hypotension can be a symptom of any disease: cardiovascular, mental, thyroid dysfunction, etc.