Execution technique
To carry out diagnostics, the patient visits a medical facility in the morning.
Before installing the device, it is necessary to do an electrocardiogram and measure blood pressure. If the values do not exceed the norm, then a specialist mounts the device. The cuff is fixed in the forearm area on the non-working arm in such a way that its position does not change during the entire period of the study. A mini-computer is attached to the belt, allowing you to read and write the necessary information.
The patient can also be fitted with electrodes of a Holter monitor, which allows parallel examination of the heart throughout the day.
The device operates continuously with periodic pumping of air into the cuff.
After the patient receives all the necessary recommendations, he goes home and goes about his usual activities.
What actions are needed when wearing the device?
When carrying out daily blood pressure monitoring, it is important to behave accordingly, as described by the doctor when installing the device, and to wear the device correctly. .
At the time when the next automatic blood pressure measurement occurs, the person must ensure that his muscles are in a relaxed state and his arm is located along the body.
It is important not to think that the indicators are being measured, as this may distort the validity of the results. Night sleep should also be restful. There should be no thoughts about the research process.
If the measurement began while moving, you need to stop and monitor the position of your hand.
Journaling
In addition to the fact that blood pressure is automatically measured at certain intervals throughout the day, it is also important to keep a patient diary, which records all the events performed by the patient during the day.
Experts recommend recording information regarding:
- depth and duration of sleep;
- number of awakenings;
- state of health;
- physical and emotional stress;
- eating food;
- taking medications;
- the presence of certain clinical symptoms, such as dizziness, fainting or a state foreshadowing them, pain in the heart, loss of vision, and others.
At the end of the examination, the doctor checks the monitoring data and records of complaints. This allows you to identify situations that provoke an increase in blood pressure and select the most optimal scheme of therapeutic measures.
History of the development of ABPM
The history of the use of ABPM begins with the use of a direct (invasive) method of automatic blood pressure monitoring. For the first time, an automatic device for long-term recording of blood pressure using the intra-arterial method was used by D. Shaw et al. in the mid-60s of the last century. With this technique, continuous recording of blood pressure was carried out through a catheter inserted into the brachial artery, which was flushed with heparinized saline solution through an infuser. Despite the high accuracy and continuity of recording, which made it possible to determine tens of thousands of blood pressure values during the day, this method of blood pressure monitoring had disadvantages that limited it widespread use in clinical practice and associated with invasiveness: the risk of complications (paresis of the median nerve, hematoma, infection), technical difficulties and the impossibility of frequent implementation. Already in the 70s, more advanced methods of instrumental monitoring of blood pressure were tested. Non-invasive automatic recording of blood pressure has become possible using portable devices that pump air into the cuff at specified intervals and record blood pressure throughout the day in an outpatient setting. Registration was carried out either by identifying the tones of N.S. Korotkov, when one or more microphones (piezoelectric sensors) were placed above the brachial artery under a classic cuff, inflated using a microcompressor (less often with gas cartridges) at predetermined intervals, or by the oscillometric method, when changes in air pressure (oscillations) in the cuff in phase were assessed decompression. The method is called 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM).
Preparation for the procedure
No special preparation is required. Taking or stopping medications on the eve and on the day of the study must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Daily blood pressure monitoring should never be carried out on the day of intensive diagnostic examinations, including drawing blood for various tests, X-ray examinations, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
In order for blood pressure monitoring to show an objective picture, it is very important to properly prepare for this procedure. To do this, you should strictly adhere to the recommendations listed below: . Ensure that the blood pressure recorder is properly charged during the procedure
When using batteries, consider whether they will be enough for 1 day of uninterrupted operation. Connect the recorder to a PC and program it with individual patient data. It is also necessary to set the functional mode of the device. For this purpose, determine the interval at which blood pressure will be measured. It is necessary to measure the circumference of the forearm. This is required to make the optimal selection of the appropriate air cuff that will suit the patient. Install a device designed for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. The cuff is fixed to the forearm. Accordingly, for right-handers, the left hand is used, and for left-handers, it is attached to the right. In order to avoid displacement during the procedure, it is necessary to securely fix it. Sometimes double-sided discs with a sticky surface are used for this. Proper and timely training is of great importance. This will help the patient choose the right behavior during the examination. When performing automatic blood pressure measurements, it is important to ensure that the arm is positioned exclusively along the body, and its muscles are as relaxed as possible. You should not think about the indicators or be interested in them during the test. This will help to avoid the influence of stress factors on the examination result. At night, a hypertensive patient definitely needs to sleep without focusing on the current measurement process, as this can lead to unreliable results. If a person suddenly hears a signal about the start of the next blood pressure measurement, he needs to stop, lower his arm with the cuff attached to it down and relax. It is in this position that you must wait until the measurement is completed.
- Ensure that the blood pressure recorder is properly charged during the procedure. When using batteries, consider whether they will be enough for 1 day of uninterrupted operation.
- Connect the recorder to a PC and program it with individual patient data. It is also necessary to set the functional mode of the device. For this purpose, determine the interval at which blood pressure will be measured.
- It is necessary to measure the circumference of the forearm. This is required to make the optimal selection of the appropriate air cuff that will suit the patient.
- Install a device designed for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring.
- The cuff is fixed to the forearm. Accordingly, for right-handers, the left hand is used, and for left-handers, it is attached to the right. In order to avoid displacement during the procedure, it is necessary to securely fix it. Sometimes double-sided discs with a sticky surface are used for this.
- Proper and timely training is of great importance. This will help the patient choose the right behavior during the examination.
- When performing automatic blood pressure measurements, it is important to ensure that the arm is positioned exclusively along the body, and its muscles are as relaxed as possible.
- You should not think about the indicators or be interested in them during the test. This will help to avoid the influence of stress factors on the examination result.
- At night, a hypertensive patient definitely needs to sleep without focusing on the current measurement process, as this can lead to unreliable results. If a person suddenly hears a signal about the start of the next blood pressure measurement, he needs to stop, lower his arm with the cuff attached to it down and relax. It is in this position that you must wait until the measurement is completed.
What's the use?
In addition to the fact that the device shows a picture of the patient’s health, it allows doctors to see the patient’s condition during periods of various stresses. For many, blood pressure monitoring is part of an additional examination. People are sometimes simply afraid of doctors in white coats, so they get nervous, which leads to increased blood pressure. This condition was given the name “white coat syndrome.”
When a person with this syndrome sees a doctor, he automatically panics and worries. The feeling of fear can be so great that it is difficult to see the picture of the disease. This portable diagnostic method allows the patient to relax and lead a normal lifestyle. It will not cause long-term inconvenience, so the method is considered one of the most popular.
Daily blood pressure monitoring is a diagnostic method that is used in the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular and central nervous system, thyroid gland, and kidneys.
Contraindications to the procedure
A safe procedure is not always prescribed by the treating specialist: the reason is poor tolerability of the study, conduction disturbances and increased systolic blood pressure (indicator more than 200). If preliminary daily blood pressure monitoring shows poor results, the procedure is not prescribed again. This type of diagnosis is contraindicated in patients with injuries to the shoulder, joints, or people with skin diseases on the forearm. Fixing the device can lead to deterioration of the skin condition (increased dermatitis).
A direct contraindication to the procedure is a decrease in platelet activity and a decrease in their number. Blood diseases during an exacerbation period are completely excluded by ABPM: other safe methods of studying blood pressure are prescribed. The technique is not used on patients with hand injuries, so as not to aggravate the condition of the upper extremities. Psychological reasons (phobias and fears) are a good reason for excluding ABPM as a procedure for a comprehensive study of blood pressure.
Are there any contraindications?
No matter how effective blood pressure monitoring is using automated equipment, there are several contraindications to the procedure:
- skin diseases (fungal diseases, lichen, eczema, etc.),
- petechial rash (appears with minimal pressure on the skin),
- blood diseases (thrombocytopenia),
- bruises, hand injuries,
- vascular lesions of the arteries and venous vessels of the hands,
- mental illness.
Wearing the device for a long time can worsen the course of the disease. You need to increase or decrease your blood pressure only after checking your blood pressure using a classic tonometer.
Reliability of the method
Is it possible to “deceive” ABPM so as not to serve in the army? Due to the fact that in recent years many young men, for one reason or another, do not want to serve in the army, they use many tricks to obtain a medical exemption from service. For example, many, while still in high school, begin to turn to therapists with complaints about “high blood pressure” and poor self-esteem, although this is not true. It is not difficult to increase blood pressure before seeing a doctor - physical activity (running, squats, etc.) is enough, but high blood pressure numbers in a conscript at an appointment will prompt the doctor to think about the need for further examination. In particular, about the use of ABPM.
Again, it is not difficult to achieve elevated blood pressure levels with ABPM, but it is almost impossible to deceive the doctor who performed or received the results. Firstly, this is due to the fact that many conscripts try to increase their blood pressure at night, and, as a rule, in young people, even those with hypertension, their blood pressure normalizes at night. Secondly, during exercise, the heart rate increases in proportion to the pressure, which in most cases is recorded on ECG monitoring. Therefore, the doctor, seeing sinus tachycardia coupled with increased blood pressure, will most likely think about the reliability of the technique and prescribe other research methods, perhaps even in a hospital.
Some people of military age use nicotine and caffeine-containing drinks in large quantities, and sometimes even alcohol on the day of the test. Such cocktails of caffeine and continuous exercise throughout the day will certainly affect the heart and blood vessels of a young person, and can lead to cardiovascular pathology in the future. Therefore, it is better not to take risks and carry out this examination as usual. In the end, military service is not as harmful as possible complications associated with increased blood pressure under the influence of caffeine, alcohol and excessive physical exertion, which young people unknowingly resort to in order to “dodge” the army.
There are cases when, on the contrary, the patient wants to “deceive” ABPM in order to hide hypertension and continue responsible work by passing an aptitude test. In this case, it is worth recommending that the subject, at least in general terms, reconsider his lifestyle and eliminate bad habits, such as poor nutrition and excessive consumption of salt, simple carbohydrates, animal fats and excess calories (not to mention alcohol, caffeine and nicotine). And at the same time normalize the level of physical activity, get rid of stress, lack of sleep and uneven loads. Moreover, for a good result, it is worth starting “perestroika” in advance, at least several months before the examination. And after it, “fix” a new lifestyle and improve your own health, at the same time slowing down the progression of hypertension.
How is ABPM performed?
1. Characteristics of ABPM monitors ABPM devices are currently lightweight portable automatic devices that use various methods of blood pressure recording: oscillometric, auscultatory, a combination of these methods and synchronization with ECG. Most monitors use an oscillometric method for determining blood pressure - recording vibrations of the wall of the brachial artery, transmitted through air vibrations in a compression cuff. The auscultatory method of recording blood pressure is based on identifying patterns of sound phenomena that occur during decompression of the brachial artery. In this case, phase I of Korotkoff sounds is associated with the moment of the appearance of compression noise, II - weakening, until disappearance (the so-called “auscultatory failure phenomenon”), III - intensification of tones, IV - sharp weakening, V - complete cessation (sometimes this phase is absent when the so-called “infinite tone phenomenon”). Each of the methods (oscillometer and auscultation) has its own advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of the auscultatory method: it is the official standard for non-invasive blood pressure measurement, high resistance to hand movements. Disadvantages of the auscultatory method: this method is sensitive to noise, to the accuracy of the location of microphones relative to the arteries, to the rotation of the cuff on the arm, and also requires direct contact of the cuff or microphone with the patient’s skin. The oscillometric method is resistant to noise loads, allows you to determine blood pressure in the presence of auscultatory phenomena, blood pressure values do not depend on the rotation of the cuff on the arm, and allows you to measure blood pressure through thin clothing. Among the disadvantages of the oscillometric method, low stability to hand movements can be noted. 2. Research program The standard method is in which automatic inflation of air into the cuff and decompression are carried out at intervals of 15 - 30 minutes* during the day and 30 minutes - 1 hour at night. The software of modern blood pressure monitors allows you to set several time periods with different recording intervals depending on the purpose of the study. The periods of day and night are set individually depending on the patient’s daily routine and correspond to periods of wakefulness and sleep. Air injection into the cuff can be done in a fixed mode, when a rigid maximum pressure limit in the cuff is set, or in a dynamic mode, i.e. to a blood pressure level of 30 mm Hg. exceeding the value of the previous measurement. 3. Installing the monitor on the patient Before starting each monitoring, it is necessary to carry out a control measurement of blood pressure with simultaneous determination of pressure by the monitor and tonometer. Control measurements are carried out in a sitting position with registration of phases I and V of Korotkoff sounds. In the absence of blood pressure asymmetry, ABPM is performed on the “non-dominant” arm. When asymmetry is more than 5 mm Hg. - on the arm with higher blood pressure readings. The size of the cuff should correspond to the circumference of the shoulder. The index finger should pass between the cuff and the surface of the shoulder. When using auscultatory devices, the cuff is placed on the bare shoulder. The oscillometric monitor cuff can be placed on the sleeve of a shirt or T-shirt, making the examination more comfortable and hygienic. The monitor is placed in a case and secured to the patient using two tapes: one goes over the shoulder, the other is located at the waist. All straps are carefully adjusted. 4. Instructing the patient Successful ABPM largely depends on the patient’s behavior and his desire to help the doctor identify his characteristic pattern of pressure changes during the day. It is important to explain to the patient the essence of the study, its significance for the selection and control of therapy, the operating features of the device, the precautions provided in the device to prevent excessive compression, and so on. During the study, the patient keeps a diary, which reflects the main points of life activity:
- What to write in your ABPM diary?
- physical, emotional and mental stress
- subjective sensations (headache, palpitations, etc.)
- time of eating, smoking (to detect postprandial hypotension)
- time of going to bed and waking up, quality of sleep
- taking medications
Analysis of the patient's diary makes it possible to clarify the reasons for fluctuations in blood pressure and adhere to a similar daily routine in order to standardize monitoring conditions for subsequent studies. During the study, it is recommended to lead a normal lifestyle, without excessive physical activity. When using oscillometric devices, the hand on which the cuff is applied must be completely motionless during inflation and deflation of air,
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Attention! Hypertension is a “cunning” disease and can be almost asymptomatic. The patient is experiencing serious discomfort, but one-time pressure measurements may not reveal the problem
How ABPM stands for
ABPM is 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. The shortened name of the method is most often used. It allows you to automatically record changes in blood pressure over a day or more using a special device. ABPM provides the doctor with the opportunity to identify hidden health threats, especially among apparently healthy people. Compared to conventional one-time methods for measuring ABPM pressure, the method gives a much more accurate picture. A key advantage of this study is the ability to record even small changes in pressure.
The undoubted advantages of the method of monitoring blood pressure and pulse include the fact that the patient does not need to undergo complex manipulations, does not need to change his usual lifestyle or go to the hospital.
The disadvantages include some discomfort from the fact that the device is on the body for a long time; the cuff on the arm, when measuring pressure, squeezes the arm quite strongly, this can especially bother the patient at night.
Nevertheless, this method has a very high diagnostic value. ABPM is extremely effective in diagnosing arterial hypertension.
Registrar
Indications for the procedure
Most often, such pressure monitoring is a decisive method in the diagnosis of many pathologies. There are many indications for its implementation:
- In some cases, it is necessary to exclude white coat hypertension. This syndrome is a specific psychological reaction - an increase in blood pressure, which manifests itself only at the time of visiting a medical facility. During a medical appointment, some patients’ blood pressure may suddenly drop or rise sharply (and quite strongly);
- To clarify the diagnosis of arterial hypertension, when the patient is diagnosed with high blood pressure for the first time, but the doctor wants to see additional data;
- The study is carried out for symptomatic hypertension, in cases where the increase in pressure is a consequence of stress or is associated with some other diseases, especially ischemia, heart failure, left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy, vascular problems in the brain, metabolic disorders;
- In older patients, hypertension is often observed due to age-related changes in body tissues;
- The study shows that if low pressure is suddenly replaced by high pressure, such changes over a long period of time can lead to serious complications;
- To clarify the diagnosis of hypotension if the patient has frequent fainting. It is carried out for patients with low blood pressure, especially with diagnoses of neurocirculatory asthenia, vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Examination during pregnancy if late toxicosis is suspected, and to exclude pathology and determine the process of labor management (if the woman in labor has hypertension);
Indications for use
The procedure is prescribed to patients who complain of:
- fatigue;
- headaches, dizziness;
- decreased vision, spots before the eyes;
- noise or ringing in the ears, stuffy ears.
ABPM can also be prescribed to a person who has no unpleasant symptoms, but when the doctor measures the blood pressure, it is elevated. The reason for this may be the “white coat” phenomenon: this is an individual characteristic that is expressed in a specific psychological reaction to doctors. A person with the “white coat” phenomenon begins to worry excessively during any medical procedures, so his blood pressure and heart rate increase. Measuring blood pressure and heart rate using daily monitoring allows us to exclude the influence of this phenomenon on the diagnosis.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The procedure allows you to identify arterial hypertension (hypertension), as well as preliminarily determine its cause - the underlying disease. It is confirmed during further examinations. This method can also be used to diagnose chronic hypotension (arterial hypotension) – low blood pressure.
ABPM allows:
- predict how dangerous arterial hypertension is for a particular patient;
- determine what complications it can lead to or has already led to;
- understand what level of physical activity is acceptable for a given person;
- determine whether blood pressure medications that have already been prescribed for treatment are effective.
Analysis of the results obtained
To develop further treatment tactics, the doctor studies the following monitoring data:
- average systolic and diastolic pressure per day;
- fluctuations in pulse blood pressure;
- increase frequency – the number of values is greater than normal;
- daily index - decrease in pressure at night.
The latter indicator, along with pulse pressure variability, is the most reliable predictor (prognostic sign) of the likelihood of developing coronary heart disease, stroke, sudden cardiac arrest, and the threat of fatal vascular accidents.
Depending on the type of graphic image obtained, the following groups of patients are distinguished:
- The daily index ranges from 10 to 19% – dippers (translated as “scoop”). The depression caused by a decrease in nighttime blood pressure resembles a bucket. Refers to a normal result.
- An index of up to 10% is an insufficient decrease in pressure during night sleep. Increased risk of heart disease, cerebral ischemia, nephropathy, and retinal damage.
- The daily index is negative, night pressure exceeds daytime pressure. Occurs in symptomatic renal hypertension. An unfavorable sign, the likelihood of heart failure and decreased renal function increases.
- An increase in the index of more than 20% is a group at high risk of heart attack and stroke in the morning.
We recommend reading the article on systolic hypertension.
From it you will learn about the pathology and the reasons for its development, symptoms of the disease, diagnosis and treatment. And here is more information about arterial hypertension and diabetes.
In order to study changes in blood pressure during normal physical activity, during sleep, and also to determine how much antihypertensive drugs prevent blood pressure surges, 24-hour monitoring is used. It is carried out using a special device; the patient must adhere to the rules of behavior during the period of blood pressure measurements and keep a self-monitoring diary.
After the data obtained, the treatment regimen is adjusted in such a way as to minimize the risks of acute vascular accidents.
ABPM
Dear Clients! All EMC clinics operate as usual – 24/7, 7 days a week . An enhanced disinfection regime has been introduced for your safety. Tests for COVID-19 and antibodies in the clinic and at home.
Certificate of absence of COVID-19 Computed tomography of the lungs of medical services at home (consultations, tests, procedures) is at your service consultations with doctors.
Please note: Inpatient visits have been suspended.
- What is ABPM
- Indications
- How is it carried out?
- Data analysis
First of all, ABPM results are assessed by calculated average values, including average systolic and diastolic pressure, as well as average blood pressure in general. Additionally, heart rate is taken into account.
Average indicators are calculated per day, for the period of wakefulness - usually the period from 7 to 23 hours is taken as the period of sleep, as well as the period of sleep - from 23 to 7 hours. Any drug therapy for arterial hypertension is aimed at changing the average values; they are also indicators of the effectiveness of treatment.
In this case, blood pressure should be normalized both during the day and at night.
Doctors and staff
Cardiologist, specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics
Head of the Heart and Vascular Clinic, Ph.D.
Cardiologist, doctor of the highest category
Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics
Cardiologist
Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, doctor of the highest category
Cardiologist
Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, Ph.D.
Cardiologist
Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, MD.
Functional diagnostics doctor
Doctor of the highest category
Pediatric cardiologist
Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, MD.
IGNATIEVA Oksana
Cardiologist, specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics. Head of the Heart and Vascular Clinic, Ph.D.
DYAGILEVA Maria
Cardiologist, doctor of the highest category. Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics
BURAKOVA Natalya
Cardiologist. Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, doctor of the highest category
BERDNIKOV Sergey
Cardiologist. Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, Ph.D.
KAMARDINOV Jamshed
Cardiologist. Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, MD.
PETROSYAN Anna
Functional diagnostics doctor. Doctor of the highest category
FILARETOVA Olga Pediatric cardiologist. Specialist in echocardiography and functional diagnostics, MD. More doctorsRemoval of blood vessels with Cutera XEO laser
28.06.2019
All videos
Good afternoon, my name is Lilia. I am 24 years old.
Since the age of 15, I have often been bothered by pain in the heart area, it increased when I was 18 years old, and now it is becoming more frequent and stronger (read more)
Good afternoon, my name is Lilia. I am 24 years old.
Since I was 15 years old, I have often been bothered by pain in the heart area, it increased when I was 18 years old, and now it is becoming more frequent and stronger, the nature of the attacks of pain has also changed (if previously there was simply a rapid heartbeat that prevented breathing normally, now at one moment, in a state of rest, the blood flows strongly into the heart so that it seems to jump out, then it becomes dark before the eyes, the blood seems to flow into the head and so on for 30-40 seconds, then as before - shortness of breath). During attacks, I feel a rapid heartbeat, some shortness of breath, chest pain, sometimes radiating to the left side of the neck and left arm, dizziness, and general weakness. I did an ECG, they said nothing except sinus tachycardia, I did an echo - they said that there is an additional chord, but this is a minor anomaly. She was also examined with a Holter apparatus, but on the day of the examination there was no attack and was given another similar device, which recorded attacks for 5 days, as a result they said that there was arrhythmia, acceleration of the heart rate from 85 to 160 at rest, of course, not Fine. But to identify the source, they also prescribed probing, which I refused at that time. We decided to postpone it until it got worse. Could these attacks be angina attacks? Or what is this even?? Is this related to the additional chord?? I note that neuralgia and spinal disorders have already been ruled out! Thank you in advance!
(Hide)
These symptoms do not relate to angina pectoris and additional chord. False chords are now not considered as a pathology; they are a normal and very common phenomenon. To do any (read more)
These symptoms do not relate to angina pectoris and additional chord. False chords are now not considered as a pathology; they are a normal and very common phenomenon. To draw any conclusions, ECG, echocardiography and ECG monitoring data are needed. You can send copies of the research to our email, but it is better to contact us in person.
(Hide) 02/08/2017
My child (4.5 years old) has a heart murmur and sometimes develops a strong cough during physical activity. What should we do?
( read more )
My child (4.5 years old) has a heart murmur and sometimes develops a strong cough during physical activity. What should we do?
( Hide ) Because of the murmur heard, your child is advised to have an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) to determine the cause of the murmur.
An examination by a cardiologist can determine the cause of cough after exercise, for (read more)
Because of the murmurs heard, your child is advised to have an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) to determine the cause of the murmurs.
An examination by a cardiologist can determine the cause of cough after exercise; for this, a regular ECG is performed and, if necessary, the ECG is recorded for a long time using a Holter monitor.
All examinations and consultations can be completed with a pediatric cardiologist at the European Medical Center. You can make an appointment by phone + (7.
(Hide) 10/14/2015
Please tell me how to stabilize sudden increases in pressure, accompanied by nausea and vomiting in a patient with chronic (read more)
Please tell me how to stabilize sudden increases in pressure, accompanied by nausea and vomiting in a patient with chronic hypertension (it is not always clear what comes first - the occurrence of nausea and vomiting and, as a consequence, an increase in pressure, or vice versa).
(Hide)
In order to stabilize sudden surges in pressure, it is necessary to correctly select continuous antihypertensive therapy.
It is best to make an appointment with a cardiologist, undergo an ultrasound of the heart, a daily test (read more)
In order to stabilize sudden surges in pressure, it is necessary to correctly select continuous antihypertensive therapy.
It is best to make an appointment with a cardiologist, undergo an ultrasound of the heart, 24-hour blood pressure and ECG monitoring - to diagnose cardiovascular diseases.
For more detailed information, you can schedule a consultation by phone. Specialists from the Cardiology Department will be happy to help you.
(Hide) 06/08/2015 All questions and answers Ask a question
Victor
Moscow
Thanks a lot! Health and all the best to the doctor who saves people. Thanks to the parents for their son. ( read more )
Thanks a lot! Health and all the best to the doctor who saves people. Thanks to the parents for their son. (Hide)
Maria
My husband was hospitalized at the clinic in serious condition, complicated by dangerous thrombosis. Many thanks from our family to all the staff of the clinic. Thanks to the attending physician Anikyeva for highly qualified assistance, constant attention, and prompt resolution of emerging problems.
All department staff are doctors (read more)
My husband was hospitalized at the clinic in serious condition, complicated by dangerous thrombosis. Many thanks from our family to all the staff of the clinic. Thanks to the attending physician Anikyeva for highly qualified assistance, constant attention, and prompt resolution of emerging problems.
The entire staff of the department - doctors, nurses, orderlies, catering workers - are extremely friendly. Thanks to their attitude, a long stay in the hospital does not become painful. Nurse Olga is a stunning example of high professionalism and human qualities.
We are also very grateful to the team of rehabilitation therapists Yulia Verbitskaya, Alexander and Dmitry for their professionalism and interest in achieving positive treatment results (Hide)
Andrey
Moscow
Dear Zaza Alexandrovich! Thank you for performing my operation to install a stent in the ICA. In the operating room, I realized that you are a magician and simply save people’s lives. Thank you for that! All reviews Leave a review
Source: https://www.emcmos.ru/services/sutochnoe-monitorirovanie-arterialnogo-davleniya-smad
Preparation for the procedure
Before ABPM, your doctor will sometimes stop certain blood pressure medications. Unless the doctor decides otherwise, you should take all medications. Wear light, short-sleeved clothing with looser clothing over the top. The device is usually attached to the belt, and sometimes hung from the neck. Before the study, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle; no additional preparation is required for this method of measuring pressure.
How is the procedure performed?
Let's consider daily blood pressure monitoring, how is this study carried out? To begin with, a pneumatic cuff is put on above the patient’s elbow, which is connected to the recorder using a tube. This small device, weighing about 300 grams, pumps air through programmed periods of time and then releases it. The doctor reads the results of pressure measurements from the device’s memory and analyzes them.
During the day, measurements are taken every quarter of an hour, and at night - every half hour. The pressure test lasts a day or more (as the doctor says), then the patient should turn off the recorder and visit the doctor again.
Taking measurements
A functional diagnostic specialist connects the device to a computer and programs it for a given patient.
The cuff is fixed on the “non-working” arm (for “right-handers” on the left hand, and for “left-handers” on the right hand). It is attached to the patient’s forearm two centimeters above the elbow, and is selected for each patient depending on the size of his hand. After this, the patient can go to work or home, the pressure will be measured automatically by the device. ABPM does not interfere with normal life, you can even continue to play sports.
Sports activities
How to behave during the procedure
Consultations on ABPM are provided by general practitioners and cardiologists.
Before the procedure, the doctor issues a special diary, where the patient should record everything that was done during the day, some types of mental and physical activity (sports, stress, emergency work), and note periods of sleep and wakefulness. You should record periods of feeling unwell (eg, dizziness, strong throbbing) and information about taking medications, that is, make notes about anything that can affect your blood pressure and heartbeat.
Daily blood pressure monitoring - who is prescribed and why, interpretation of results
What is it and how is it done?
Daily blood pressure monitoring is an instrumental study that monitors this indicator throughout the day. It is carried out like this: a cuff is placed on the patient’s shoulder to measure blood pressure. Using a special tube, the cuff is attached to the recorder. This small device pumps air into the cuff at regular intervals and then releases it. During the day, measurements are usually taken every 15 minutes, at night - after 30 minutes. A sensitive sensor determines the time of appearance and attenuation of pulse waves (as with conventional Korotkoff pressure measurement). The results are recorded in the device's memory. After reading them using a computer program, the functional diagnostics doctor analyzes the results and gives a conclusion.
What will this study show?
The study shows a number of important implications for human health.
- Maximum and minimum blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) during observation in the patient's natural environment, and not in the hospital.
- Average blood pressure during daytime and nighttime hours, which will determine whether the patient has hypertension. This is the main indicator for which the study is conducted.
- Circadian rhythm of blood pressure. Failure to lower blood pressure at night is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
All this data will help make a diagnosis of hypertension and select the right treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness.
About self-measurement of blood pressure
Constant self-measurement of blood pressure will provide much less valuable information. It cannot be carried out at night. If a person wakes up on purpose, this leads to an inevitable increase in pressure and distortion of the results.
You need to know that the most accurate results are obtained by measuring the traditional Korotkoff method (determination of tones using a phonendoscope). It is best to use semi-automatic devices with automatic air injection, since manual injection can cause a short-term increase in pressure. Devices that measure pressure on the wrist or finger are much less accurate. We recommend devices that operate on mains power rather than on batteries.
It should be taken into account that in approximately 5% of patients, pressure monitoring indicators differ significantly from self-monitoring data. Therefore, it is very important to carry out control measurements in the diagnostic room immediately after the start of the study.
How to prepare for research?
On the recommendation of the attending physician, certain medications for the treatment of hypertension may be discontinued before monitoring. If there are no special instructions, you must take all medications as usual. It is advisable to wear a light T-shirt with sleeves up to the elbow, and some loose clothing on top, since the recorder will be placed in a bag and hung around your neck, and there will be a cuff on your arm.
In some cases, it is recommended to bring batteries for the device. Alkaline (alkaline) batteries required.
Before the study, you can eat, drink, and lead a normal lifestyle.
How to behave during research?
Detailed instructions are given by the functional diagnostic nurse. She should give the patient a diary in which he will note his actions and sensations during each blood pressure measurement (except for sleep time), as well as taking medications and sleep time.
At the beginning of each measurement, the patient should stop and extend his arm down along the body, relaxing it. After completing the measurement, the subject must make an entry in the diary and continue the interrupted lesson. If the cuff slips, you need to carefully adjust it. The tube through which air is pumped must not be allowed to bend.
The increase in pressure in the cuff is often quite severe, resulting in pain when squeezing the arm. These feelings must be tolerated.
Indications for research
- “Borderline” blood pressure figures identified during repeated measurements using the Korotkov method.
- Monitoring of selected antihypertensive therapy, including to exclude episodes of severe hypotension after taking medications.
- Suspicion of “white coat hypertension”, when high blood pressure is recorded only when measured by medical staff. Suspicion of “workplace hypertension,” when increased blood pressure occurs at work.
- Severe hypertension resistant to treatment.
Who is recommended to undergo the study?
In the presence of the listed indications, especially valuable information can be obtained from the following groups of patients:
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- “White coat hypertension” and “workplace hypertension.”
- Episodes of hypotension.
- Young people with disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
- Older patients.
- Patients suffering from hypertension without treatment effect.
Contraindications for the study
- Exacerbation of skin disease at the site of application of the cuff.
- Disturbances in the blood coagulation system with a tendency to bleeding during exacerbation.
- Injuries to both upper extremities, excluding the possibility of compression by a cuff.
- Impaired patency of the brachial arteries, confirmed instrumentally.
- Patient refusal.
- The study may be useless if there are significant disturbances in heart rhythm, as well as very high blood pressure values (more than 200 mm Hg).
What is Holter?
During the examination, a special portable device is used - Holter. Its electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest; they record all changes in blood pressure and record an ECG throughout the day.
The diagnostic device is named after Norman Holter, a famous American biophysicist researcher. In 1961, he developed a monitoring technique and put it into practice for the first time. Thanks to the Holter method, today cardiologists can identify disturbances in the functioning of the heart and various hidden diseases that are not visible on a regular electrocardiogram.
Why do you need daily ECG monitoring (Holter)?
Holter monitoring can be prescribed by a cardiologist or a general practitioner in order to confirm the diagnosis, check the effectiveness of treatment, discontinue medications, clarify details, etc.
The Holter method allows you to identify:
- Ischemic ECG changes.
- Heart rate.
- Type of heart rhythm.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: pauses, ventricular extrasystoles and others.
A regular cardiogram is significantly less informative than 24-hour monitoring, since although it can detect heart disease, it is not capable of assessing the frequency of its occurrence and the severity of its course. It is easier for the doctor to select adequate therapy after analyzing the Holter ECG results.
Who is recommended for 24-hour ECG monitoring (Holter)?
Typically, the electrodes of the device are installed in patients for a day; if nothing could be recorded within 24 hours and no deterioration occurred, then the monitoring is extended (maximum period of 7 days).
Indications for use:
- Coronary heart disease of various forms: silent myocardial ischemia, Prinzmetal angina, etc.
- Studies of heart rhythm disorders: Parkinson's, Wolff's, White's syndrome, atrial fibrillation, as well as ventricular tachycardia and sinoatrial block.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Heart defects.
- Treatment control
- Scheduled preventive examination.
In addition, daily ECG monitoring is prescribed if there are patient complaints of discomfort in the left side of the chest, a feeling of a sinking heart, fainting, or a feeling of lack of air. Diagnostics for frequent dizziness is also indicated.
There are no contraindications for diagnosis, except perhaps skin lesions in the chest area, which will complicate the procedure for attaching electrodes.
How is the examination carried out?
In the diagnostic room, special disposable electrodes in the amount of 5-7 pieces are fixed to the patient’s chest with an adhesive plaster (depending on the Holter model). Using a wire, the sensors are connected to a recording device. The device is in a special case and is hung on the patient’s neck or belt.
The specialist will provide instructions on how to use Holter and give the patient an observation diary. It must indicate all the events that occurred with the person being examined: deterioration and improvement of the condition, taking medications, physical activity, nighttime, as well as daytime rest. Data must be recorded with precise time reference.
To see how the cardiovascular system reacts to stress, during the study the doctor may advise the patient to walk up the stairs. This will help find a connection between complaints and changes in the electrocardiogram.
Important! If the patient experiences any interruptions in the heart’s function within 24 hours, the rhythm increases for no reason, dizziness or other complaints appear, this must be recorded in the diary.
During diagnosis, you cannot undergo magnetic resonance imaging and x-rays of organs. A day later, the doctor removes the electrodes and deciphers the data obtained.
Monitoring - indications, installation, results, harm
Holter monitoring is a method of functional diagnostics that allows for daily monitoring of the electrocardiogram. ECG recording is carried out continuously from 24 hours to three days. To monitor the ECG, a Holter is used - a small portable recorder that records the round-the-clock work of the heart and records data on its work over the course of a day on a computer. These records are subsequently deciphered by a cardiologist.
Holter monitoring was named after researcher Norman J. Holter, who first put this device into practice in 1961.
When installing a Holter monitor, electrodes are attached to the patient's chest. The electrodes, in turn, are connected to a recording device. Of course, the patient experiences certain inconvenience while wearing the device, however, the study itself is very informative and accurate, which allows the cardiologist to determine an accurate diagnosis.
The data processing program provides analysis and determination of all types of heart disorders, in particular attacks of angina pectoris and arrhythmia, which can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Who is Holter monitoring indicated for?
With the help of a Holter, an ECG is prescribed primarily to determine heart rhythm disturbances - episodes of atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles, etc., which are quite difficult to detect during a short study - a regular electrocardiogram.
It happens that some atypical contractions for a healthy heart muscle appear only during periods of active physical activity, severe emotional shock, or in other situations. In these cases, such disturbances cannot be detected using a conventional electrocardiogram, whereas with Holter monitoring the patient can lead his usual lifestyle: engage in a certain sport, work, take any body position, etc.
Also, using a Holter study, you can determine various disorders of the blood supply to the heart muscle, in particular changes in the ST segment during sports or physical activity.
Can a Holter study negatively affect a patient's health?
Holter ECG does not pose any harm to health. There is also no risk of electric shock.
To avoid damage to the device, it is recommended not to take a bath or swim while wearing it to prevent water from getting inside. It is also not recommended to go through a metal detector while wearing a halter.
How is a Holter monitor installed?
Before the device is attached to the patient's body, he is advised to take a shower, since he will not be able to take a bath or remove the monitor for the next day or more.
The doctor attaches the electrodes to the patient’s chest and adjusts their position. Subsequently, the doctor connects the electrodes to the wiring of the recording device, which is attached to the patient’s body using special belts.
The doctor instructs the patient and teaches him to keep a diary. This is necessary for correct decryption of data received from the device. The patient records periods of sleep, wakefulness, physical activity, rest and all symptoms (chest pain, tachycardia, arrhythmia, etc.) with an exact indication of time.
After installing the device and receiving a list of instructions, the patient can return to his usual rhythm of life and daily routine.
Holter monitoring is an absolutely painless procedure. The patient experiences slight inconvenience only when wearing the device, when the wires and box of the device are hidden under clothing. During sleep, it is not recommended for the patient to turn over on his stomach, as the electrodes may become dislodged, which will disrupt data recording.
Holter study results
The holter is removed directly by a cardiologist or nurse. The patient provides the physician with a diary of activity and symptoms, which the physician examines along with device data.
Depending on the situation, the doctor makes a final diagnosis or sends the patient for additional examination. If the results of a Holter study within a day do not allow the doctor to form a definite picture, he can prescribe the patient to temporarily wear a heart rate recording device, which the patient himself will activate during the onset of alarming symptoms.
Why is ABPM necessary?
Blood pressure is an extremely unstable indicator. It can change during the day, depend on the emotional state, and differ during sleep and wakefulness.
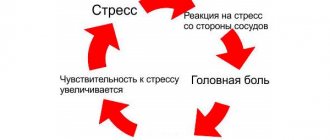
It is worth mentioning the term "EBH", the white coat effect, the essence of which is that some patients experience undue anxiety simply because they are in the doctor's office.
Their blood pressure rises, which does not correspond to the true blood pressure level. A lot of negative factors can influence measurement deviations: a cold stethoscope, crossed legs, excitement. To prescribe the “correct” doses of antihypertensive drugs, it is extremely important to know the exact blood pressure standards obtained in the patient’s usual environment outside the doctor’s office.
An objective picture is provided by 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) using a fully automated device mounted on the patient’s arm. The device records blood pressure values for 1-2 days under normal human conditions.
By analyzing the data obtained, the doctor confirms or denies the presence of hypertension. ABPM has a number of advantages over traditional studies.
The following disadvantages inherent in clinical measurements are excluded:
- the influence of an alarming reaction, which entails overdiagnosis of blood pressure and incorrect medical therapy for patients with EHD;
- rounding the measurement result, usually to tens;
- subjective assessment, when the researcher (doctor) is pre-set on a certain result, which he believes the patient “should have”;
- inability to take into account blood pressure fluctuations within 24 hours.
Daily monitoring is also useful for patients with already diagnosed arterial hypertension, when the study is combined with taking medications
Indications for use
The ABPM technique is indicated for:
- ineffectiveness of antihypertensive treatment;
- high blood pressure numbers in patients without signs of target organ damage (kidneys, myocardium, fundus, brain) and without identified risk factors for arterial hypertension (AH);
- normal blood pressure in patients with established risk factors for hypertension or existing target organ damage;
- high variability of blood pressure during self-measurement or during repeated visits to the doctor;
- frequent episodes of hypotension (low blood pressure) in older patients with type 1 diabetes;
- suspected preeclampsia.
ABPM is used in clinical practice not only in patients with hypertension, but also in patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Preparatory activities
The first step is to make an appointment with a cardiologist. At the Family Doctor Children's Center for ABPM, you can undergo an examination without a doctor's prescription, but it is better to stock up on a referral, since a specialist must evaluate the results of the examination.
ABPM requires a free machine, so pre-registration is required.
In our center you are accepted without a queue and by appointment, but in public medical institutions you will have to wait several weeks. No special preparation is needed. The device will be installed by a doctor. He will select the “correct” cuff depending on the circumference of the patient’s shoulder.
A cuff that is too short or, conversely, long will distort the readings. The bag with the monitor (reading mechanism) is attached to the patient’s belt. The cuff is placed on the non-working arm: for right-handers - on the left, for left-handers - on the right.
The doctor will check the device for accuracy by alternately measuring blood pressure on one arm with a monitor and on the other with a regular tonometer. If the numbers match, the patient is sent home.
From this moment on, the device will periodically measure your pressure and “remember” the data. ABPM allows you to obtain fairly accurate daily blood pressure dynamics, provided that the patient adheres to the doctor’s recommendations.
The result will be distorted if the patient does not inform the doctor about the medications currently taken.
Who is contraindicated for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring?
ABPM is a non-invasive technique that does not require serious intervention in the body. However, there are a number of contraindications for it.
Diagnosis is not possible if:
- upper limb injury;
- skin diseases localized in the arms and shoulders;
- rigidity of the vascular system, since the accuracy of the test is impaired;
- pregnancy;
- heart disease and other serious pathologies that interfere with diagnostics;
- high blood pressure levels;
- blood clotting disorders.
In these cases, the diagnosis of ABPM will have to be abandoned, turning to traditional blood pressure measurement.
How is it going?
Diagnostics are carried out for a day or two. The first 2 hours are not taken into account as this is the adaptation time. Your doctor will ask you to keep a diary to record your hours of exercise and periods of rest, times you sleep and wake up, medications you take, heart pain, and other symptoms of discomfort if they occur.
Blood pressure registration occurs once every half hour during the daytime and every hour at night, at least. At the appointed time, the patient comes to the clinic and the device is removed from him. The doctor processes the device readings. The results obtained are interpreted by a cardiologist, comparing them with entries in the diary.
During the examination, the patient should follow simple recommendations:
- monitor the position of the cuff. If it has slipped, correct it;
- at the moment of start, the device emits a sound signal and begins to pump air into the cuff. Try to relax your hand at this time. If possible, do not move, so the readings will be more accurate. At the end of the measurement, a repeat beep will sound;
- do not pinch the tubes connecting the monitor to the cuff;
- stay away from electromagnetic devices;
- Avoid stressful situations. Anxious reactions greatly distort the readings of the device;
- temporarily refrain from swimming;
- don't drink alcohol;
- Protect the device from moisture. If there is an urgent need to remove the cuff, carefully disconnect the tubes from the monitor. Otherwise, when air is pumped, they may burst;
- if you notice that the device has stopped working, inform your doctor;
- stop taking antihypertensive medications (with the consent of your doctor);
- don't forget to keep a diary.
The ABPM technique does not prevent the patient from living his normal life, although it does introduce minor discomfort.
The accuracy of the readings largely depends on the patient's behavior during diagnosis. Listen carefully to the doctor’s instructions before conducting the test and try to follow all recommendations.
Decoding the results
During the study, it was possible to obtain 14 reliable measurements during the daytime and at least 7 during the night. Based on them, the doctor calculates the average blood pressure and pulse rate.
Since the interpretation of average values today does not pose a problem and is carried out on the basis of generally accepted standards, the most important are the “additional” ABPM readings:
- circadian rhythm (CR). ABPM is the only non-invasive study that provides a complete picture of this characteristic. The main indicator of SR is the percentage decrease in blood pressure at night. Violation of this value signals dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (CVS) and damage to target organs by hypertension. A practical problem in using the indicator is its low reproducibility, therefore, to confirm the reliability of identified SR failures, repeated monitoring is required, which is not always convenient for the subject. However, this characteristic must be taken into account in the conclusion based on ABPM results, especially if the procedure is performed for diagnostic purposes;
- ambulatory pulse blood pressure. This indicator is directly related to myocardial and vascular problems. ABPM assesses this characteristic more accurately than clinical studies. The “critical” value of ambulatory pulse pressure is 53 mmHg. Higher values indicate a risk of CV complications;
- blood pressure variability. Elevated values of this indicator may indicate incorrect antihypertensive therapy and the need to change the treatment regimen;
- morning dynamics of blood pressure. It is known that at this time the greatest number of heart attacks, malignant arrhythmias and strokes occur, which can cause sudden death of the patient. The morning increase in blood pressure in hypertensive patients is consistently higher than in healthy people, which is fraught with cardiovascular complications;
- assessment of hypotension episodes in the daily blood pressure profile. For an objective quantitative assessment, it is sufficient to take into account only the minimum blood pressure values;
- smoothing index (SI). Since ABPM provides a large amount of information, it can be used to more accurately assess the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs. The indicator is calculated based on the hourly effects of the drug: the ratio of the average effect to the deviation from it. An IP of at least 1.2-1.5 is considered optimal.
The listed additional indicators of ABPM are very important. However, their practical use is still limited. The situation should change with the introduction of new generation drugs for hypertension into clinical practice and the widespread use of chronotherapy methods.
ABPM in childhood
ABPM can be done not only for adult patients, but also for children after seven years of age. This procedure is completely safe; it is performed on children with suspected hyper- and hypotension, with cardiac dysfunction, or with frequent fainting conditions. Often such a study is combined with ECG monitoring.
The study is carried out in exactly the same way as in adults, except that a different cuff size is selected. Before the procedure, the child needs to be told about the examination, why it is needed, and that it is painless. The cardiologist should give all the recommendations and tell you how to correctly fill out the diary during ABPM.
Important! The ABPM procedure is especially important for diagnosing vegetative-vascular dystonia. .
This pathology in children has recently happened quite often. Treatment requires accurate diagnosis, since VSD can easily be confused with arterial hypertension. The use of ABPM allows you to correctly give a medical opinion and determine the tactics of further treatment.
ABPM in children
Decoding the results
Modern ABPM devices themselves carry out the initial classification of the recorded data; pathologies are shown in tables and graphs. The doctor processes the records on a computer and this helps him make a diagnosis, choose the best treatment method and avoid possible complications.
ABPM - what kind of examination is it?
ABPM is a study of blood pressure (BP) using special equipment that does not stop for 24 hours. The diagnosis is prescribed by a doctor from the cardiology department.
The device for the procedure notes even the slightest changes in pressure and charts them. The data obtained as a result is sent to a specialist for decoding, on their basis a diagnosis is made, and treatment tactics are chosen.
Thanks to ABPM you can find out:
- pressure that is comfortable for the patient;
- how pressure changes under load;
- Blood pressure during sleep;
- pulse.
Holter heart monitoring is another method. Holter and ABPM are often confused, although they are different. The first method is intended only for measuring pulse and obtaining an electrocardiogram. However, Holter ECG monitoring and blood pressure monitoring are often recommended to be carried out in combination.
How the device works
The ABPM device measures blood pressure, as well as the characteristics of the subject’s heart rhythm by processing pulse phenomena in a pneumatic cuff. A recorder is attached to the patient’s belt, inflating the cuff with air and recording the readings. The cuff, similar to the usual part of a tonometer, is attached to it using a flexible tube. The ABPM recorder has higher accuracy than a conventional pressure measuring device. Using the device is easy.
The undoubted advantage of the method is that the recorder reacts to the smallest fluctuations in blood pressure, so the doctor has the opportunity to study the patient’s pressure in more detail.
Daily pressure monitoring: find and neutralize the hidden threat
Blood pressure (BP) is an extremely unstable indicator. Its meanings change not only depending on the time of day, sleep or wakefulness, but also in connection with the emotional state. The so-called white coat hypertension is not uncommon: when blood pressure changes made by the patient’s relatives at home show normal values, but the values measured in the clinic are far from ideal. In addition, various extraneous factors influence blood pressure measurements: a cold stethoscope, crossed legs, and even a full bladder cause deviations [2]. Meanwhile, knowing the level of blood pressure under normal conditions for the patient is extremely important for selecting appropriate doses of antihypertensive drugs, i.e., normalizing blood pressure. It is no coincidence that it is recommended to select treatment not in a hospital (as elderly patients mistakenly believe), but in an outpatient setting, when a person leads a normal life with appropriate activity, level of stress and other influences that affect blood pressure.
In order to accurately know the patient's blood pressure level outside the doctor's office, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, or ABPM, is used (see Table 1). A cuff is placed on the patient's shoulder, which measures blood pressure at least once every half hour during the day and once every hour at night. During this time, it is possible to obtain 14 of the most successful measurements during the day and at least 7 at night. Based on the results obtained, the average value of blood pressure and heart rate (HR) is calculated.
Table 1. Recommended blood pressure values based on ABPM.
Period
Optimal blood pressure
Normal blood pressure
Arterial hypertension
Wakefulness
50% indicates stable arterial hypertension.
The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure is called pulse pressure. Its increase above 53 mmHg. Art. - an independent risk factor for cardiovascular complications.
Indications and contraindications for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring
Indications for ABPM are:
- excessive variability in blood pressure during repeat visits to the doctor or according to self-measurements;
- high blood pressure values in patients without known risk factors for arterial hypertension and without signs of target organ damage (kidneys, brain, fundus, myocardium);
- normal blood pressure values in patients with existing risk factors for arterial hypertension or known target organ damage (microalbuminuria, left ventricular hypertrophy, changes in the fundus vessels);
- significant differences in blood pressure values measured by a doctor and independently;
- ineffectiveness of antihypertensive therapy;
- episodes of hypotension (low blood pressure), especially in the elderly and patients with diabetes;
- Blood pressure in pregnant women, suspected preeclampsia.
Absolute contraindications to ABPM:
- complications that arose during the previous study (swelling of the forearm and hand, pinpoint hemorrhages, contact dermatitis, extremely rarely - thrombosis of an atherosclerotic artery);
- skin diseases in the area where the cuff is applied;
- thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopathy and other bleeding disorders;
- blood diseases during exacerbation;
- vascular lesions of the upper extremities;
- upper limb injuries.
Among the disadvantages of ABPM, it is necessary to note the patient’s discomfort: many wake up when measuring blood pressure at night. Another possible problem is distortion of information if the examination was carried out on an uncharacteristic day for the patient (for example, on a weekend).
Procedure for carrying out ABPM
ABPM is usually prescribed by a cardiologist. Theoretically, in private clinics you can undergo this examination without a doctor’s prescription, but in practice it is better to get a referral, because in any case a specialist must evaluate the results and prescribe treatment.
Since the study requires a free apparatus, it is carried out by appointment. In public clinics, registration is usually several weeks (or even months) in advance; in commercial clinics, for obvious reasons, the queue is much shorter.
No special preparation is required. The device is installed by a doctor. The size of the cuff is selected depending on the circumference of the patient's shoulder: either a cuff that is too short or too long will distort the measurement results. The lower edge of the cuff should be 2 cm above the ulnar fossa, 2 fingers should pass between the cuff itself and the shoulder (in children and thin patients - 1 finger). The device is applied to the patient’s non-working hand (left for right-handers, right for left-handers). A special bag with a monitor, a device that records blood pressure, is attached to the body.