Sustavin.ru » Osteochondrosis » Cervical osteochondrosis » Pressure surges with cervical osteochondrosis
0
3767
Article rating
Today, chronic hypertension occurs in a third of the world's population. According to doctors, most of them are susceptible to degenerative changes in the spine. That is, cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure are interrelated.
Pressure surges in cervical osteochondrosis
The neck area is anatomically adapted to the structural content of nerve centers that influence the activity of the cardiovascular system. Any changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs lead to changes in blood pressure (blood pressure).
Osteochondrosis and blood pressure
How does high blood pressure occur in osteochondrosis? Hypertension affects 40% of people, cervical chondrosis – 70% of the population. Consequently, the likelihood of a combination of diseases is quite high, and the incidence rate increases with age.
The cervical region is associated with the cardiovascular system, therefore, its disorders are related to hypertension. The parasympathetic center in the back, which provides nutrition to the nerves, is located in the area of the 8th–6th thoracic vertebrae. This largely explains the connection between high blood pressure and cervical spine disorders.
The nerves located in the 3rd cervical and 6th thoracic regions innervate the heart muscle, which suggests the influence of osteochondrosis on blood flow in the spinal cord and brain.
A number of studies have found that osteochondrosis affects blood pressure and often leads to heart rhythm disturbances. High blood pressure is a common problem for patients with herniated and protruded discs.
Low pressure with osteochondrosis in the cervical spine
The autonomic part of the nervous system has features that may be associated with low blood pressure in osteochondrosis of the neck. Low blood pressure most often occurs due to poor conduction in the nerves when the vertebrae are compressed. Symptoms of low blood pressure are more often expressed with the following results:
- With pressure on the spinal cord and arteries that provide it with nutrition;
- When the nerves that are responsible for regulating blood pressure are damaged;
- A disturbance in the autonomic nervous system, when the departments responsible for lowering blood pressure become active;
- When areas of the brain are “switched off” due to poor delivery of nutrition supplied with the blood to its tissues.
Hypotension is expressed by the following symptoms:
- Headache in the back of the head and temples;
- Frequent attacks of nausea, especially when walking, bending and turning the head sharply;
- Vomiting often occurs;
- Due to irritation of the nerve responsible for breathing, a lack of air may occur;
- Sharp and active sweating;
- Pain behind the sternum and in the region of the heart;
- Numbness of the limbs and their severe coldness;
- Hearing loss, noise and ringing in the auditory organs.
Clinical picture of a combination of diseases
The first manifestations that characterize high blood pressure in osteochondrosis:
- headache;
- blood pressure changes;
- dizziness.
Against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, along with high blood pressure, visual disturbances and heart pain often occur.
Important! Similar signs also occur under the influence of thoracic disorders (thoracic osteochondrosis).
Blood pressure surges in osteochondrosis
A person’s blood pressure may fluctuate slightly during the day (after sleep, the levels are lowest; in the evening they increase). This is a normal condition that is influenced by psychological and physical factors.
In the case of the influence of osteochondrosis on blood pressure, the jumps are more expressive and are accompanied by the above-mentioned manifestations.
Pressure surges with cervical osteochondrosis are a good reason to undergo a specialized examination, since the spine and pressure are a combination that can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life.
Symptoms and relationships
Studies have shown that diseases such as hypertension and cervical osteochondrosis are interrelated.
The cause of hypertension is structural changes in the 7th or 5th disc of the spinal column, which bear the maximum load.
Symptomatic hypertension occurs due to compression of not only the nerves, but also the blood vessels passing through the spine. Patients who complain of malaise, pain, arterial hypertension, headache, ringing or noise in the ears cannot imagine that these problems are directly related to cervical osteochondrosis.
If you do not understand the causes of hypertension, it can smoothly move from one stage to another. At the beginning, a person does not pay attention to a short-term rise in blood pressure (and this is the first stage of the disease).
After some time, weakness, headaches and a stable increase in pulse and systolic pressure to 150-160 mm Hg appear. Art.
The risk zone is the blood vessels and heart muscle. And very quickly the second degree turns into the third, the pressure continues to rise, reaching 180 mm Hg. Art. It becomes difficult to control even with medication.
Hypertension in the second stage is dangerous due to its hypertensive crises. One of the reasons for the appearance of such a complication lies in the compression of the nerve ending or carotid artery during cervical osteochondrosis. And the consequence of increased pressure in the third stage of hypertension is a heart attack or stroke.
Causes of high blood pressure
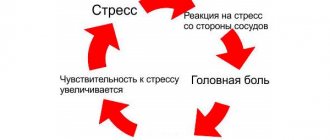
There are many factors that can increase blood pressure. In particular, in a stressful situation, its increase is a natural response of the body, ensuring the body's stability by increasing the supply of blood to the organs. But modern life is full of various stressors, under the influence of which a predisposed person often experiences disorders in the function of defense mechanisms. As a consequence, an increase in pressure (with or without osteochondrosis) occurs even with moderate irritation.
With stress and physical overexertion, the cervical spine is affected, osteochondrosis and hypertension develop. Therefore, in the case of diagnosing hypertension from cervical osteochondrosis, it is necessary to conduct a wide specialized examination aimed at identifying the first cause of the disease.
Diagnostic measures
During the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis and hypertension, the location, nature, and degree of vertebral disorder are determined. For this purpose, imaging methods are used - X-ray, CT, MRI. To assess the current state of blood flow, Doppler or duplex scanning is used:
- The X-ray image provides information about the condition and position of the cervical vertebrae and discs, the displacement of the vertebrae in relation to each other, and the degree of change in the joints.
- MRI provides information not only about the condition of the vertebrae and discs, but also reveals changes in muscle and nervous tissue, and determines structural changes in the spinal canal, which cannot be achieved using x-rays.
- CT scan displays vertebral disorders, placement, shows the state of spinal and vertebral processes, the spinal canal, and intervertebral discs. This method is used to determine the degree of inflammatory processes in the cervical region and the presence of a hernia.
- Doppler examination reveals disturbances in blood flow. This method helps to indirectly determine the condition of the vascular walls.
Hypertension with cervical osteochondrosis
In order to correctly diagnose a patient with cervical osteochondrosis and high blood pressure and prescribe the necessary treatment, it is imperative to conduct a full examination.
Diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head;
- MRI of the head;
- Doppler ultrasound of blood flow in cerebral vessels;
- appointment with a neurologist (vertebrologist), cardiologist.
Head MRI procedure
It is also necessary to take a general blood test, primarily to study the blood coagulation function, since the tendency to form blood clots in combination with cervical osteochondrosis can lead to thrombosis and stroke in a short time.
A blood test for lipid concentrations is mandatory to exclude atherosclerosis.
Treatment
During therapy, pharmacological methods and physiotherapy are used. As an auxiliary method of eliminating high blood pressure in cervical osteochondrosis, it is advisable to use traditional medicine methods.
Medicines
Pharmacological treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure outside the normal range is determined in accordance with the causative factor in the occurrence of the disorder. If the cause is an inflammatory process, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed; if the disease is caused by a disorder of bone tissue, another technique is used - restoring the structure of bone tissue, taking drugs that improve blood flow.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, it is important to eliminate severe pain. For these purposes, local drugs are prescribed. Local agents such as Voltaren, Phenylbutazone, Menovazin have a good analgesic effect; for cervical osteochondrosis and arterial hypertension, these medications not only relieve pain, but also relieve swelling of the tissue.
Physiotherapy
To reduce high blood pressure due to neck osteochondrosis and strengthen the back muscles, electrical stimulation is often recommended, which can significantly reduce the load on the spine. Mud and water procedures (therapeutic showers, healing baths) have a good effect, which is to accelerate metabolic tissue processes and blood circulation.
Important! Electrophoresis is recommended for an analgesic effect, and magnetic therapy is recommended to accelerate tissue recovery.
Cervical chondrosis and pressure respond well to special training that strengthens the neck muscles and relaxes pinched nerves. Exercises are carried out slowly, with light effort. Do them 10 times:
- Pull your neck up. Do not tilt your head, chin parallel to the floor, gaze directed forward. Hold for a few seconds, relax.
- Turn your head to the left. You shouldn't feel pain! Hold for a few seconds, relax.
- Repeat the above exercise to the right side (10 times).
- Lower your head until your chin touches your chest. Hold for a few seconds, relax.
- Tilt your head as far back as possible. Hold for a few seconds, relax.
- “Write” with your head the numbers from 1 to 10 and in reverse order.
Perform exercises every time the pressure rises due to osteochondrosis.
First aid for cervical osteochondrosis and high blood pressure
In this case, the patient needs to be correctly diagnosed, and only then prescribed pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs. Among the numerous medications offered in pharmacies today, we can recommend: Nimesulide, Dicofenac, Rofecoxib, Xefocam, Cilecoxib. However, do not forget that effective treatment can only begin after consultation with a doctor, and not with a pharmacy employee.
Nimesulide
Dicofenac Xefocam
Cilecoxib
Prevention
The best treatment for any disease is preventive measures. They can both prevent illness and alleviate the manifestations of an already present illness.
Preventive methods:
- Suitable physical activity (try not to overload the body).
- Healthy eating to prevent metabolic disorders.
- Fresh indoor air. Lack of oxygen in the air causes oxygen deficiency in the blood, which leads to vasospasm.
- To give up smoking. Nicotine causes blood vessels to contract, so stopping smoking is an important step in alleviating the disease.
Cervical osteochondrosis should not be ignored. Although this part of the spine is small, problems with it can lead to serious problems that can be fatal.