What is extravasal compression of the vertebral artery?
To answer the question of what extravasal compression of the vertebral artery is, you should understand this complex term step by step.
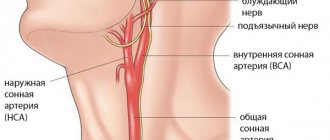
“Compression” in medicine means “squeezing something,” in this case the vertebral artery. The vertebral arteries pass through the intervertebral foramina of the cervical vertebrae towards the spinal canal, where they supply the spinal cord. Compression of the vertebral artery is not an independent disease, but rather a consequence of the development of another pathology.
Most often, this pathology is an intervertebral hernia. It is the resulting hernia that can compress the vertebral artery, thereby disrupting the blood supply to the spinal cord. Extravasal compression of the vertebral arteries is usually localized in the area of the 4th-5th vertebrae.
How to determine the syndrome
The disease, which occurs as a result of extravasal compression of the vertebral artery, requires careful diagnosis to identify the causes of its development and the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the vessels. During diagnosis, doctors use the following modern research methods, which allow them to determine the exact location of the problem, assess its extent and the patient’s chances of a full recovery:
- magnetic resonance therapy, which makes it possible to diagnose anomalies and defects in the structure of the spinal column, which provoke vasoconstriction;
- radiography of the cervical spine in different projections, with the help of which it is possible to identify intervertebral hernias and tumors;
- duplex scanning, which allows you to assess the degree of narrowing and determine the exact location of extravasal compression of the left and right paravertebral arteries;
- Spiral computed tomography is a method that allows you to detect the location of compression and its features.
Causes of the disease
As mentioned above, an intervertebral hernia can lead to extravasal compression of the right, left, or simultaneously two vertebral arteries. In turn, a hernia can occur due to developed osteochondrosis or physical overload. Other provoking factors may be:
- benign or malignant tumors in the neck;
- incorrect, abnormal structure of the spine, its curvature (congenital, acquired, traumatic).
Causes of impaired blood circulation in the vertebral arteries
The disease can be either congenital or acquired. The first include: arterial kinks and pathological tortuosity.
What diseases can lead to extravasal compression:
- Atherosclerosis;
- Embolism;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Scoliosis;
- Thrombosis;
- Injuries affecting the spine;
- Tumors in the neck area;
- Intervertebral hernia;
Most often, the causes of the development of the syndrome occur in combination. For example, refusal to treat atherosclerosis leads to the formation of blood clots, and already against this background, symptoms and signs of VAS (vertebral artery syndrome) appear.
Signs of extravasal compression of the vertebral artery
Signs of extravasal compression of the right, left, or both vertebral arteries are most often temporary. This pathology manifests itself as pain. Pain appears when turning the head sharply or in the morning after waking up (since during sleep a person can remain in one position for a long time). In addition to neck pain, compression is manifested by headache (aching, throbbing), dizziness, indigestion, difficulty moving, impaired vision or hearing, and lacrimation. Also, compression of the vertebral arteries can lead to the development of neurological diseases.
Extravasal compression of the left vertebral artery
You can understand the signs of compression in more detail by the type of its localization. For example, if this pathology affects the left vertebral artery, then the symptoms may be as follows:
- frequent headache;
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- increased blood pressure;
- nausea.
With pronounced compression of the left vertebral artery, a person may even faint.
Extravasal compression of the right vertebral artery
The same symptoms may occur in patients with compression of the right vertebral artery. During exacerbations of the disease, a person may from time to time lose a sense of balance and fall, but remain conscious.
Bilateral – compression of both vertebral arteries
When both vertebral arteries are compressed, all of the above symptoms persist, but gain double strength. Moreover, all these symptoms are not specific, that is, they can accompany other diseases. This is why compression is so difficult to diagnose and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Therapy methods
The goal of treatment is to relieve swelling and inflammation. At the site of compression of the artery, congestion forms, which leads to the formation of swelling and the development of the inflammatory process. An important step in the treatment of VA compression is the correct selection of medications. The neurologist prescribes medications that should restore hemodynamics.
Extravasal compression of the left or right vertebral artery is amenable to both drug and physical treatment.
Doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Sleeping on a therapeutic orthopedic pillow is often used as a physical treatment method. It helps to stretch the cervical vertebrae. In addition, the pillow contains magnetic particles. Thanks to its composition, it heats up and maintains the temperature throughout the night.
The use of an orthopedic pillow is one of the methods of treating the disease
With the help of such a pillow, a hernia of the cervical vertebrae is treated. Instead of a pillow, it is recommended to use a wool roller. It is placed under the neck so that the head is suspended.
If the patient is bothered by very severe headaches, he is prescribed novocaine blockade of PA. In cases where conservative treatment does not bring results and the disease is in an advanced stage, surgical intervention is prescribed. After it is carried out, preventive measures are prescribed:
- physiotherapy;
- massage of the collar area;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture.
Massage must be performed only by specialists. It is carried out carefully, without effort or jerking. The procedure takes 20 minutes.
Diagnostic methods
At the first examination, the therapist
,
a neurologist
or other specialist can only suspect the presence of compression of the vertebral artery by asking the patient about all the symptoms, as well as examining him and palpating him. To clarify, confirm (or refute) the diagnosis, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound with Doppler. It is the Doppler study that allows us to evaluate the speed of blood flow in the arteries. On the screen, the doctor can see the lesions and identify the degree of development of the disease.
- MRI
. - CT scan
. - X-ray
.
The last three studies on the list help evaluate the structure of soft and bone tissues, identify fractures, dislocations, foci of inflammation, vascular pathologies, and tumors of various origins.
Treatment of spinal artery syndrome
In severe cases, treatment of vertebral artery syndrome is possible through neurosurgery
Mechanical compression of a blood vessel is manifested by edema and inflammation. Therefore, treatment should primarily be aimed at eliminating them. The attending physician should not forget that the existing symptoms are also accompanied by impaired blood flow in the veins.
To restore hemodynamics, the patient needs an integrated approach, which consists of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs. Paroxysmal pain is relieved with novocaine blockade of the vertebral artery and sympathetic plexus.
How to treat?
Treatment of extravasal compression of both vertebral arteries is primarily to eliminate the main factor in its occurrence. That is, treatment of compression occurs in parallel and simultaneously with the treatment of intervertebral disc herniation, tumor, compression fracture, and so on.
Treatment may be medication. Patients are often prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain and restore normal well-being. Drugs aimed at restoring blood flow and oxygen supply to the blood may also be prescribed. All medications should be prescribed only by your doctor. The dosage and frequency of use are very important. Self-medication can only harm and worsen the situation.
Treatment of compression can take place in other directions:
- physiotherapy;
- massage and manual therapy;
- physical therapy and special gymnastics.
When all of the above treatment methods do not produce an effect for a long time, the doctor considers the possibility and advisability of surgery. Surgeons, by making small incisions, can remove discs and tumors that are compressing the arteries. Treatment of compression should be carried out by doctors of several specializations: surgeons, therapists, neurologists, oncologists and others. You will find specialists in these and other areas at the Energo clinic. Our team consists of experienced professionals who, in their practice, have encountered various cases of compression of the vertebral artery and have positive experience in eliminating it.
Modern approaches to treatment
The main goal of therapy for extravasal compression of the VA is the restoration of normal blood flow through the vessels of the neck and restoration of damaged areas of nervous tissue. Treatment of the disease in practice is carried out using conservative and surgical methods.
Drug treatment of pathology has the following goals:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- elimination of local tissue edema;
- restoration of adequate blood circulation through the vertebral vessels;
- normalization of the functioning of brain structures.
After a detailed examination, the doctor can prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and decongestants, as well as analgesic dosage forms to a patient with extravasal bilateral compression of the vertebral arteries, and, if necessary, a novocaine blockade. After stopping an acute attack, as a rule, the patient is recommended a course of therapy aimed at restoring brain cells, normalizing the functioning of neurons and preventing their death.
The decision on the need for surgical correction of the pathological condition is made solely by the doctor. Indications for surgical treatment of VA compression are large herniated intervertebral discs, tumors in the cervical spine, traumatic lesions with disruption of the integrity of the vertebrae.
Upon completion of treatment in a hospital setting, patients with extravasal compression of the vertebral arteries are recommended to undergo a course of rehabilitation therapy in a sanatorium or at a specialized resort, which will enable the sick person to improve their general condition and recover faster from the disease.
Vessels
Small Diameter of Vertebral Arteries: Normal, What It Is
Feb 03, 2020 Kokh V. A.
61818
Vessels
Duplex Scanning of Brachiocephalic Arteries: What is BCA, Explanation
Feb 03, 2020 Kokh V. A.
8313
Vessels
Disease prevention
Extravasal compression of the vertebral artery is such a serious disorder that it is easier and better to prevent it than to treat it later. Treatment usually takes a long time, while prevention consists of simple things:
- active lifestyle and giving up bad habits;
- regular exercise (you don’t have to go to the gym for this, you can just do morning jogging or light exercise);
- massage aimed at improving blood flow, strengthening muscles, restoring their tone.
All of the listed preventive measures, observed in combination, will certainly give a positive result and will help to avoid not only compression of the vertebral arteries, but also other problems with the musculoskeletal system, nervous system, heart and vascular system, and so on.
Prevention measures
Unfortunately, this diagnosis is made quite often not only to older people, but also to young people. In order to prevent the occurrence of this disease, certain preventive measures should be taken to prevent the disease from progressing.
Among these manipulations, the following techniques should be highlighted:
- physical therapy to strengthen the muscle corset,
- special exercises to relieve muscle tone,
- blood flow stimulating massage.
Comprehensive actions will benefit not only those at risk, but also those who suffer from osteochondrosis and hernias.
If a person is prone to developing this pathology, he is registered with a medical institution. This involves undergoing a systematic examination. At the discretion of the specialist, diagnostics of cerebral vessels may also be included. Often, the patient is recommended to take prophylactic medications.
Diagnostic measures
Magnetic resonance examination
To clarify the correct diagnosis, you need to contact your doctor to prescribe an additional examination, which necessarily includes the following measures:
- Magnetic resonance examination.
- Radiography.
- Duplex scanning.
- Dopplerography.
- Antiography.
The use of all these measures in combination makes it possible to identify the exact cause and spread of the pathological process, as well as prescribe appropriate therapeutic measures.
The main causes of the disease
Vertebral artery syndrome occurs when these vessels are compressed by extravasal elements.
The most common causes of this pathological condition in medical practice are:
- compression of the left and right vertebral arteries by a tumor of various etiologies, which is localized in the neck and puts pressure on the vessels, thereby causing a narrowing of their lumen;
- compression of vertebral vessels by intervertebral hernia;
- narrowing of the internal lumen of the vertebral arteries, caused by the abnormal structure of the spinal column, which contributes to unnatural bends and bends of the vessel, their spasm in certain areas and disruption of blood transport.
Most often, this pathological narrowing is diagnosed at the level of the fourth and fifth cervical vertebrae. The disease occurs in patients of different age groups, but most often among the elderly and with changes in posture and degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the cervical spine.
Prevention of the development of PA syndrome
The manifestation of extravasal compression of the right or left vertebral artery is easy to prevent. There are a number of preventive measures for this. If the patient has already suffered extravasal compression of the VA once, he should be registered with a neurologist and undergo preventive vascular treatment annually.
Physical therapy plays a major role in disease prevention. It must help strengthen the spine and cervical regions. The exercises must be performed under the supervision of specialists. To keep your spine healthy, you need to regularly perform simple exercises.
Hypothermia and heavy physical activity negatively affect the condition of the vertebral arteries. People who have had this disease are contraindicated:
- work at height;
- playing sports;
- starvation;
- lifting weights.
They are required to undergo a medical examination annually. If necessary, such patients are prescribed a preventive course of medications.
To prevent the development of complications it is necessary:
- monitor your health;
- follow all doctors' recommendations;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- follow all prevention methods.
If extravasal compression of both vertebral arteries occurs, you must immediately seek medical help, conduct all the necessary studies and review your diet.
Very important for effective treatment is not only timely diagnosis, but also prevention of such a disease as compression of one or both vertebral arteries. Therefore, a preventive examination of people at risk of vertebral pathology will not be superfluous. Ultrasound diagnostics and other additional procedures are considered the most effective.
Patients who have more than once suffered manifestations of extravasal compression syndrome of the vertebral artery must be followed up with a neurologist and undergo preventive treatment of blood vessels. In addition, it is useful to conduct exercises to strengthen the shoulder girdle, spinal and cervical muscles.
Hypothermia and all kinds of injuries that can cause the development of this disease or cause its relapse also have a negative impact on the body. Patients with PA syndrome are prohibited from working at heights, transport, performing heavy physical activity, playing sports and interacting with moving mechanisms.
The information on the site is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. Consult your healthcare provider.
Early and correct diagnosis of the disease is of great importance for effective treatment. Given that this vascular pathology is a fairly common phenomenon, it would not be superfluous to carry out a preventive examination of children at risk of vertebral pathology, starting from the neonatal period. Ultrasound diagnostic methods are very effective at the general stage, and when deviations from the norm are detected, various additional diagnostic procedures are performed.
Patients who have suffered acute manifestations of PA syndrome must be constantly monitored by a neurologist and regularly undergo courses of preventive vascular treatment. Exercises to strengthen the shoulder girdle, back and neck muscles are very useful. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia and various injuries that can trigger a relapse of the disease. Work in transport, at heights, heavy loads, sports and work with moving mechanisms are not allowed.
Copying site materials is possible without prior approval if you install an active indexed link to our site.
Attention! The information published on the site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation for use. Be sure to consult with your doctor!
How does the disease manifest itself?
Extravasal compression of both vertebral arteries is manifested by a number of pathological symptoms that are temporary and usually occur suddenly, with sudden movements of the head or after sleep. One-sided narrowing is often diagnosed: compression of the left vertebral artery provokes left-sided changes, while compression of the right vertebral artery provokes disturbances on the right side.
The main signs of extravasal compression of both vertebral arteries:
- the main symptom is intense headaches of aching, throbbing or bursting nature, mainly in the frontal region, which are periodic and accompanied by dizziness;
- nausea during an attack of pain, sometimes vomiting;
- disorders of the vestibular system, falls without loss of consciousness;
- hearing loss;
- disorders of the visual analyzer: blurred vision, increased eye fatigue, feeling of a foreign body in the eyes, lacrimation, pain, sensation of flies before the eyes;
- Another manifestation is rare attacks of transient ischemic attacks with characteristic symptoms.
Short description
Extravasal effects on the vertebral arteries can manifest as left- or right-sided lesions. However, both of these conditions do not have any significant features, apart from the area of distribution of the pathological process. This is due to impaired blood supply, resulting in severe abnormalities.
In medical circles you often hear the term vertebral artery syndrome. The rate of bleeding is significantly reduced, resulting in much less oxygen reaching the brain.
Patients with this diagnosis usually complain of nausea, headaches, and dizziness.
Compression of the vertebral artery
In addition, the symptoms include decreased visual acuity and hearing problems. This condition is characterized by soreness in the eyes with redness and the formation of tears.