What is ferritin?
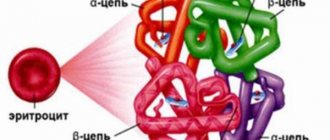
Ferritin is a special protein that stores iron. His responsibilities also include transporting this element to other internal organs. But in some situations it indicates the development of a malignant tumor - placental ferritin.
The protein complex is formed by two methods. Anabolic - ferritin is released from iron, which a person receives from food. Catabolic – the source of protein is the iron of hemolyzed red blood cells. The largest amounts of ferritin accumulate in the brain, liver, muscles, spleen and blood.
Causes of iron deficiency
The causes of iron deficiency can be divided into four groups:
- iron loss (blood loss)
- insufficient absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract
- insufficient intake of iron from food
- other reasons
Of course, a combination of all of the above causes of iron deficiency is possible.
Causes of blood loss:
- Obvious bleeding associated with injuries, surgical interventions
- Blood loss associated with diseases (peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum, hemorrhoidal bleeding)
- Menstrual bleeding
- Donation
Causes of insufficient iron absorption:
- Atrophic gastritis
- Helicobacter infection
- Celiac disease
Causes of insufficient iron intake:
- Vegetarianism, veganism
- Other unbalanced diets
- Poor socio-economic conditions
Other causes of iron deficiency:
- Intravascular hemolysis with iron loss through the urinary tract
- Hemolysis associated with implantation of artificial heart valves
- Nocturnal paroxysmal hemoglobinuria
- Surgical interventions for obesity (gastric bypass)
Biological significance and relationship with hemoglobin
Due to the low concentration of ferritin, the process of hemoglobin production, which is necessary for transporting oxygen to the internal organs, is disrupted. The end result is iron deficiency anemia. Pathological processes progress gradually.
In the early stages of iron deficiency, hemoglobin levels will be normal, and ferritin will decrease as the protein gives up its reserves to the body. Over time, if measures are not taken, all indicators will decrease.
Ferritin is important for the human body because it performs numerous functions:
- Protein provides iron, which is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, which is responsible for the transport of oxygen.
- Shows the level of reserve and total iron.
- A specific protein is responsible for transporting iron to other internal organs (liver, spleen, bone marrow).
Ferritin is also actively involved in the synthesis of certain radicals that contribute to the reduction of oxygen.
Reasons why high hemoglobin occurs in women
- Disturbances in the circulatory system and impaired blood clotting function;
- The predominance of a bluish tint of the skin along the periphery of the body: the tips of the fingers and toes, the lip area;
- Slowing down the working capacity of the brain.
Due to improper blood circulation, blood clots can form. They often cause the appearance of tumor formations, spontaneous numbness of various parts of the body, and are also involved in the loss of sensory organs such as hearing and vision.
As a result of poor circulation in the brain area, mental development delays occur. This happens due to a violation of the ability to understand and process information. A person experiences dizziness, confusion and clarity of consciousness.
High hemoglobin in women, as a rule, is a harbinger or already a consequence of various diseases. Based on this, specialists are in no hurry to lower the hemoglobin level, but are trying with all their might and using modern methods to determine exactly the reason that provoked such an imbalance in the entire metabolic system.
After eliminating the disease, the high hemoglobin level returns to normal.
What factors can increase hemoglobin in women?
Nothing happens on its own. Hemoglobin too, it just won’t increase in quantitative volume. All reasons can be divided into two groups:
- Physiologically normal deviation from the norm;
- Specific conditions.
Physiological deviations occur due to natural organismal changes, as a result of human adaptation to environmental conditions and their biological rhythms. Thus, the presence of a high level of hemoglobin in pregnant women is considered quite predictable and is not a signal indicating any disease.
Based on this, the following factors can be explained:
- People living in mountainous areas, or in areas where there is little oxygen, also have excessive amounts of hemoglobin. This is due to the fact that in order to ensure proper metabolism and enrich cells with oxygen, the body needs to increase the number of red blood cells, and therefore hemoglobin. Only due to this, a person will not suffer from oxygen starvation;
- A similar story can be observed in a person who smokes. Not only is too little oxygen supplied at this moment, but also due to inhaled nicotine, irreversible bonds are formed in the form of COHb - hemoglobin and carbon monoxide. Such hemoglobin becomes useless because it cannot carry oxygen. It only increases the total volume of red blood cells (RBC).
- If high hemoglobin in women is observed in the early morning hours, then this is also considered normal. Especially if, after checking the evening tests, good indicators are observed. This is explained by the fact that during sleep a person is at rest, and all energy resources accumulate and are consumed during the day.
- In the process of increasing the bonds of dissolved substances with water molecules, the total volume of blood increases, and therefore the red blood cells containing hemoglobin. This phenomenon is called hydration.
In all of the above cases, the amount of hemoglobin is normalized, without the use of any medications.
Causes of a specific nature appear as a result of developing pathological processes. These include the following:
- Diseases of tumor groups, since along with hemoglobin the level of leukocytes and platelets, which have the status of formed elements, increases. Symptoms of high hemoglobin in women will be the following: severe redness of skin pigment; the sclera of the eyes are covered with a red mesh; the appearance of blood clots and increased blood pressure.
- Heart disease, especially of the pulmonary circulation, so-called pulmonary. It has a significant impact on the entire transport of blood, and has a direct connection with the function of enriching cells with oxygen. Such people are easy to notice due to the predominance of a bluish tint to the skin, severe and frequent shortness of breath, which in the process turns into a cough. For this disease, only surgical treatment is performed.
- Many people ask the question: Why does high hemoglobin appear in women with kidney disease? The answer is simple. The kidneys are the point where the formation of red blood cells is regulated and, thanks to these organs, hemoglobin is synthesized in the bone marrow.
- Diseases of the pulmonary system, especially chronic forms, lead to an increase in hemoglobin in the blood. Such patients resemble patients suffering from heart disease.
- Other diseases also contribute to an increase in red blood cells: emphysema, dehydration, ailments in the liver organ, etc.
All diseases that arise as a result of pathological cases are very dangerous for their owner, since the blood becomes concentrated and prone to the formation of blood clots, and this can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Therapeutic measures
First of all, it is necessary to regulate the entire diet. It is not recommended to eat: berries, fruits and vegetables, especially red ones; cereals; meat and offal. Include in the menu: curd and fermented milk products, as well as legumes and raw non-red vegetables.
Drug treatment is unlikely to help here. But as an alternative, you can use the following methods:
- Drink water in moderation. Abuse of this resource will lead to excessive stress on the heart muscle.
- Lead a vegetarian lifestyle. Plant foods rarely contain the element iron. Some even slow down its absorption.
- You can donate blood to transfusion centers. By becoming a donor, a person saves not only his own life, but also someone else’s life. Even if the procedure is unlikely to be to your liking, the removal of blood clots or the consequences of a stroke or heart attack is a much more unpleasant moment.
If you have any suspicions or doubts, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Ferritin level in blood
Normal levels of ferritin in human blood depend on gender and age:
| Age, gender | Ferritin level (ng/ml = µg/l) |
| Baby | 25-200 |
| 1 month | 200-600 |
| Six months | 6-410 |
| 1 year | 6-80 |
| From 1 to 5 years | 6-60 |
| From 5 to 14 years | 6-320 |
| Men over 14 years old | 20-250 |
| Women over 14 years old | 10-120 |
| Menopause in women | 15-200 |
For a woman, low ferritin is a normal condition and is not a pathology.
During the period of bearing the baby, the indicators decrease, depending on the duration of pregnancy:
| Trimester | Ferritin concentration (ng/ml = µg/l) |
| I | <90 |
| II | <74 |
| III | <10-15 |
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin (reasons in some situations may indicate pathological changes) in a woman’s body is explained by the fact that it is taken by the fetus, which needs to develop.
A baby needs a large number of red blood cells and hemoglobin at birth in order to adapt to the world around him. Gradually, the hematopoietic system will begin to function independently and the level of ferritin in the small organism will stabilize.
Blood loss
Sometimes the cause of a decrease in hemoglobin is blood loss that exceeds physiological ones. In this case, nutrition may be sufficient, the production of red blood cells does not suffer, and the patient’s hemoglobin is reduced.
Posthemorrhagic anemia is of two types:
- Spicy. Develops with massive simultaneous blood loss - at the time of injury, surgery, during childbirth. When blood is lost, the body first restores its volume with tissue fluid. In this case, red blood cells become relatively smaller than normal, but the hemoglobin content in them is normal - they are normochromic. The hematocrit in the blood is reduced - the percentage of cellular elements and the liquid part. Then the red blood cell deficiency is replenished. If there is not enough iron and hemoglobin is poorly produced, then it remains reduced for some time.
- Chronic. It develops with constant small blood loss - with heavy menstruation, due to stomach or intestinal ulcers, with urolithiasis, hemorrhoids and other diseases. This anemia is usually hypochromic, since it is quite difficult for the body to replenish iron losses.
Posthemorrhagic anemia is usually accompanied by a decrease in serum iron levels and the appearance of a large number of immature red blood cells. With these anemias, hemoglobin will not rise unless the source of constant blood loss is found and eliminated.
Causes of iron protein deficiency with normal hemoglobin
The causes of low ferritin levels are numerous provoking factors, which are important to eliminate in a timely manner in order to prevent the occurrence of serious complications:
| Gender, age | Causes of low ferritin |
| Among women |
|
| In men | |
| In pregnant women |
|
| In children |
|
It is important to diagnose the causes of low ferritin with normal hemoglobin in a timely manner. It is necessary to start treatment at the early stages of emerging disorders and prevent dangerous consequences. These are hypoxia, a decrease in the body's defenses, heart disease, damage to the kidneys and genital organs.
Lack of iron with increased need
Normally, some part of the iron is constantly lost in feces, sweat, and is spent on hair and nail growth and epithelial renewal. If you get enough iron from your diet, iron deficiency will not develop.
In addition to situations where the body does not receive enough iron, there are conditions in which its loss is increased. Increased iron losses occur during heavy physical exertion, intense sports, and when working in hazardous industries.
During this period, the developing fetus requires a large amount of substances, including iron. He receives them from the mother's body. A woman needs more microelements, and if she does not get them from food, then her own resources are wasted. Iron deficiency anemia is the most common pathology in pregnant women.
The situation is similar for nursing mothers. In the first months, the baby receives essential substances from milk. The mother must provide these needs, so the diet of a nursing woman should be complete and varied. If she does not receive enough substances, this affects her health.
Symptoms of hidden anemia
In most cases, low ferritin levels can only be detected through laboratory tests; there are no pronounced clinical symptoms.
However, there are signs that you should pay attention to and visit a doctor:
- often feel dizzy;
- there is shortness of breath;
- the skin is pale, sometimes acquiring a bluish tint;
- a person gets tired quickly;
- bothered by headaches;
- heart rate increases;
- hair becomes dull and brittle;
- the skin on the face and body is dry;
- discomfort and pain periodically appear in the heart area;
- nails peel;
- pustules form in some places on the body;
- ulcers appear in the corners of the lips, which take a long time to heal;
- a person is worried about frequent colds.
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin (a doctor will help determine the reasons by prescribing a comprehensive examination) is also accompanied by severe irritability, depression, and sudden changes in mood. Sleep is disturbed, insomnia appears, taste habits change, and constipation occurs.
One of the signs of a specific protein deficiency is pain in the lower extremities, which cannot be explained. The same goes for hair loss. These symptoms are explained by the fact that the tissues do not have enough oxygen.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
Before understanding the reasons that can lead to hemoglobin deficiency, you need to pay attention to the symptoms:
- weakness not only during physical activity, but also in everyday life with a feeling of fatigue;
- labored breathing;
- tachycardia (lack of oxygen in tissues, the body tries to compensate by increasing heart rate);
- headache;
- dizziness;
- cold hands and feet;
- pale skin;
- irritability and nervousness;
- difficulty concentrating;
- lack of appetite;
- increased hair loss;
- brittle nails.
Often, a decrease in hemoglobin is not accompanied by any specific symptoms and is detected only after a blood test.
Stages
Hidden anemia is a consequence of the development of a certain disease or disorder in the human body. Sometimes they can be eliminated thanks to a properly formulated diet, but in some situations medical attention is required.
Hidden anemia is classified according to certain degrees of severity:
| Name | Description |
| I degree | The hemoglobin level drops to 90-120 g/l. In rare situations, minor symptoms and disorders occur, which can be eliminated with the help of a properly formulated diet. |
| II degree | Hemoglobin levels range from 70 to 90 g/l. The person's condition is satisfactory, hospitalization is not necessary, but medication is necessary. |
| III degree | Hemoglobin level is below 70 g/l. Complex therapy requires hospitalization of the person. The symptoms are severe; not only drug therapy, but also surgical intervention may be required, taking into account the cause of the pathological condition. |
As changes in a person's blood progress, internal organs suffer from a lack of oxygen. Their functioning is disrupted, against the background of which other pathological processes develop. Therefore, it is important to take action early on when iron deficiency occurs.
I have been taking iron for 2 months now, but my hemoglobin does not rise
Hello, dear Vadim Valerievich!
My son is 1 year old, height 78, weight 9500 kg.
At 10 months were in hospital 1 in the hematology department due to low hemoglobin - 81.
Treatment in the hospital: IM ferrum-lek + IM vitamin B2 alternating with vitamin B6.
We made 8 injections and, due to the fact that they caught ARVI, they went home (hemoglobin at that time became 99).
February and March we take actiferrin 18 drops 3 times a day, the first month we also take prescription vitamins (multivitamins in riboflavin-pyridoxine-glucose powders 3 times a day).
A month (March 3) after discharge we went for a consultation with a hematologist, hemoglobin was 107, the doctor said that it was necessary to take tests once every 3 weeks. and when hemoglobin reaches 120, take actiferrin for another 4 weeks at a dosage of 27 drops/1 r. in a day.
The child has been taking iron for so long, and we can’t even get to 110. The doctor allowed the measles-rubella-mumps vaccine to be given if the hemoglobin is more than 110.
Questions for you:
1. What to do? Is the medicine not suitable for us? 2. Does it make sense to order these vitamins again, since they increased hemoglobin by 8 units in less than a month? 3. Is there any deadline for taking iron supplements? Maybe it’s time for me to run to a hematologist? My teeth have already faded, there is a gray coating, although I give it through a syringe and then wash it down with water (I understand that healthy blood is more important than the beauty of teeth, but still.) 4. Can Aktiferrin be taken during meals or immediately after it? or between meals? I give it after meals, but maybe it’s not, the instructions don’t say anything about this. And can it be given with milk (the child, in addition to soup and vegetables with meat, eats milk porridge, fermented milk products and breastfeeding)
CLINICAL BLOOD ANALYSIS from 04/05/2014
Leukocytes (WBC) 8.5 10^9/l 6.0000 - 15.0000 Red blood cells (RBC) 4.02 10^12/l 3.8000 - 4.8000 Hemoglobin (Hb) 105 * g/l 109.0000 - 140.0000 Hematocrit (Ht) 32 * % 32. 5000 – 43.0000 MCH ( average Hb content in pg 22.0000 - 33.0000 erythrocytes) 26 Platelets (PLT) 253 10^9/l 180.0000 - 400.0000 Lymphocytes% (LR) 52% 37.0000 - 66.0000 Monocytes% (MR) 7% 3.0000 - 1 0.0000 Neutrophils.Myelocytes 0% 0.0000 — 0.0000 Neutrophils. Metamyelocytes 0% 0.0000 — 0.0000 Band neutrophils 8 * % 0.8000 — 3.2000 Segmented neutrophils 31% 23.0000 — 54.0000 Eosinophils 2% 1.0000 — 7.0000 Basophil s 0% 0.0000 - 1.0000 Plasma. cells 0% 0.0000 - 1.8000 ESR (according to Panchenkov) 8 mm/h 0.0000 - 15.0000
In the last analysis there are a lot of sticks, although the child is not sick with anything and feels well.
source
Conception and infertility with low ferritin
Conceiving a child with low levels of iron and ferritin in a woman’s body is impossible.
A deficiency of a specific protein negatively affects the functioning of the reproductive system:
- the viability of the egg decreases;
- there is no ovulation;
- when maturing, it is impossible to transport the egg to the uterine area;
- its process of attachment to the walls of the organ is also disrupted.
There is no complete guarantee of getting pregnant even with artificial fertilization of the egg. Therefore, low ferritin levels are one of the causes of infertility in women.
Causes of impaired production of hemoglobin and red blood cells
An erythrocyte has an average lifespan of about 3 months. After this period, it naturally breaks down. New ones are formed to replace destroyed red blood cells.
In order for them to be produced in sufficient quantities, several conditions must be met:
- The body must receive a sufficient amount of iron, B vitamins, folic acid, trace elements, proteins and amino acids. Hemoglobin does not increase if these substances are lacking. Their reduced intake occurs with dietary restrictions: vegetarians, especially strict ones, often suffer from iron and vitamin B12 deficiency; women who deliberately limit themselves in food for the sake of weight control, and not only women, may also suffer from a lack of necessary substances; monotonous unbalanced diet without enough meat, animal protein, vegetables, fruits.
- Substances received from food must be absorbed in the intestines. Sometimes, even with a sufficient amount of substances received, hemoglobin cannot rise. This happens for the following reasons: drinking large amounts of tea and coffee, which contain tannins that bind iron in the intestines and remove it; taking calcium supplements or large amounts of foods containing calcium (milk and dairy products), since calcium and iron are competitors; insufficient supply of acids and vitamin C necessary for the absorption of iron; intake of iron mainly from plant foods (“plant” iron is less easily absorbed); taking antacids that bind and remove iron; the presence of parasites in the intestines that take away vitamins (in particular B12); decreased gastric secretion as a result of illness or taking antisecretory drugs.
- Mechanisms regulating the production of red blood cells must work. There are pathological conditions that lead to a decrease in the production of red blood cells: kidney disease - the kidneys synthesize substances (erythropoietins) that stimulate the division of bone marrow cells, their deficiency is the reason that hemoglobin may not increase even with a sufficient supply of the necessary substances; aplastic and hypoplastic state of the bone marrow (with leukemia, autoimmune damage); ingestion of toxic substances into the body or taking medications that inhibit hematopoiesis.
To identify these diseases and conditions leading to the fact that hemoglobin does not rise, it is necessary to analyze the diet, examine the blood formula, the level of iron and vitamin B12 in the blood serum, conduct an FGDS, and take tests for helminthiasis.
Kidney pathology is detected by urine analysis, ultrasound and other more complex methods. Sometimes a bone marrow examination is required to assess the nature of hematopoiesis. In some chronic diseases, hemoglobin synthesis and red blood cell production are disrupted. In these diseases, several factors are involved in the mechanism of hemoglobin reduction. When anemia is detected and hemoglobin does not increase against the background of normalizing the diet and taking iron supplements, it is necessary to conduct examinations to exclude these diseases - infections (tuberculosis, brucellosis), foci of purulent inflammation (osteomyelitis, lung abscess, bronchiectasis). As well as systemic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus and others).
Indications for examination
The patient needs a comprehensive diagnosis so that the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and establish the provoking cause. It is important to consult a specialist if any clinical sign appears.
There are the following indications for laboratory tests to assess ferritin levels:
- suspicion of the development of iron deficiency anemia;
- high probability of developing malignant processes;
- chronic infectious or inflammatory pathologies;
- high probability of developing hemochromatosis.
Immune and visual disorders are also indications for examination. Constant weakness and frequent dizziness will allow you to suspect hidden anemia.
What does it affect?
The hemoglobin level indicates the nature of oxygen metabolism. Low hemoglobin leads to a deterioration in the supply of oxygen to tissues and disrupts the full functioning of the body.
Tissue hypoxia leads to the following:
- cellular metabolism is disrupted;
- the synthesis of hormones and enzymes decreases;
- hematopoiesis slows down.
There is no more precise answer to the question of what Hb affects: everything. With low hemoglobin protein levels, a woman experiences health problems, gets tired faster and is more susceptible to infections.
Diagnostic methods
A blood test will help determine your ferritin level.
But additional diagnostic methods will allow you to establish the cause of the pathological condition:
| Name | Description |
| Blood chemistry | The study helps to assess lipid levels, metabolism, and also identify the inflammatory process. |
| X-ray of the lungs | A diagnostic method with which a doctor evaluates the condition of the respiratory system. |
| Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) | The examination allows you to identify inflammatory foci or bleeding, against the background of which the iron level has decreased. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The specialist examines the internal organs for hidden bleeding, inflammation or developing disease. |
A stool test for occult blood, computed tomography (CT), and colonoscopy are also prescribed. Bone marrow puncture allows differentiation of iron deficiency anemia from other diseases. This is how the maturation index of neutrophils and erythroblasts is determined.
Folk remedies in the fight against low hemoglobin
If low hemoglobin is detected, treatment with folk remedies is an effective practice in combating this dangerous condition.
A decoction of rose hips and strawberry leaves strengthens the body as a whole and enriches it with vitamins. You can drink it instead of your usual tea during the day.
Fresh red beet juice, which you drink one glass a day, has a good effect. The peculiarity of beet juice is that it cannot be drunk immediately after squeezing; as soon as the juice is squeezed out of fresh beets, it should be put in the refrigerator for 3-4 hours so that toxic compounds evaporate, only after which the juice can be drunk.
Currant berry infusion is rich in vitamin C and is good for anemia.
Treatment for adults
Therapy for low iron levels depends on the triggering factor. Diagnosis and treatment is carried out by a hematologist. The specialist conducts an examination, prescribes an examination and, based on the established diagnosis, selects a treatment regimen.
In most cases, to restore the level of a specific protein, patients are given a special diet. In severe situations, drug therapy is selected.
Drugs
The doctor prescribes medications to patients, taking into account the results of complex diagnostics and the provoking factor, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. It is important to strictly adhere to dosages so as not to worsen your health condition.
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin (the causes will be determined by a hematologist using laboratory tests) is treated with the following drugs:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Feramid | The medicine is taken orally after meals. The adult dosage is 0.1 g 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 3-4 weeks. |
|
| Totema | The contents of the ampoule are first dissolved in water. Adults are prescribed 2-4 ampoules per day. The course of treatment lasts 3-6 months. |
|
| Ferroplex | The medicine is taken orally 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. |
|
If the patient's digestive reflex is impaired, medications are prescribed intravenously through a drip. The same goes for dehydration resulting from prolonged diarrhea. You should not take medications on your own; there is a high probability of side effects (liver enlargement, anaphylactic shock, allergic reaction).
Diet therapy
For most patients, proper nutrition helps restore ferritin deficiency.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
The patient's diet should include foods that contain large quantities of microelements that support the process of hematopoiesis.
Diet therapy provides certain principles that are important to adhere to:
- Meals should be frequent and small, so that all the necessary substances have time to be absorbed by the human body.
- All dishes are preferably baked, boiled, stewed or steamed.
- The food should be warm.
It is recommended that patients with latent anemia drink at least 2 liters of fluid every day.
I have been taking iron for 2 months now, but my hemoglobin does not rise
Hello, dear Vadim Valerievich!
My son is 1 year old, height 78, weight 9500 kg.
At 10 months were in hospital 1 in the hematology department due to low hemoglobin - 81.
Treatment in the hospital: IM ferrum-lek + IM vitamin B2 alternating with vitamin B6.
We made 8 injections and, due to the fact that they caught ARVI, they went home (hemoglobin at that time became 99).
February and March we take actiferrin 18 drops 3 times a day, the first month we also take prescription vitamins (multivitamins in riboflavin-pyridoxine-glucose powders 3 times a day).
A month (March 3) after discharge we went for a consultation with a hematologist, hemoglobin was 107, the doctor said that it was necessary to take tests once every 3 weeks. and when hemoglobin reaches 120, take actiferrin for another 4 weeks at a dosage of 27 drops/1 r. in a day.
The child has been taking iron for so long, and we can’t even get to 110. The doctor allowed the measles-rubella-mumps vaccine to be given if the hemoglobin is more than 110.
Questions for you:
1. What to do? Is the medicine not suitable for us? 2. Does it make sense to order these vitamins again, since they increased hemoglobin by 8 units in less than a month? 3. Is there any deadline for taking iron supplements? Maybe it’s time for me to run to a hematologist? My teeth have already faded, there is a gray coating, although I give it through a syringe and then wash it down with water (I understand that healthy blood is more important than the beauty of teeth, but still.) 4. Can Aktiferrin be taken during meals or immediately after it? or between meals? I give it after meals, but maybe it’s not, the instructions don’t say anything about this. And can it be given with milk (the child, in addition to soup and vegetables with meat, eats milk porridge, fermented milk products and breastfeeding)
CLINICAL BLOOD ANALYSIS from 04/05/2014
Leukocytes (WBC) 8.5 10^9/l 6.0000 - 15.0000 Red blood cells (RBC) 4.02 10^12/l 3.8000 - 4.8000 Hemoglobin (Hb) 105 * g/l 109.0000 - 140.0000 Hematocrit (Ht) 32 * % 32. 5000 – 43.0000 MCH ( average Hb content in pg 22.0000 - 33.0000 erythrocytes) 26 Platelets (PLT) 253 10^9/l 180.0000 - 400.0000 Lymphocytes% (LR) 52% 37.0000 - 66.0000 Monocytes% (MR) 7% 3.0000 - 1 0.0000 Neutrophils.Myelocytes 0% 0.0000 — 0.0000 Neutrophils. Metamyelocytes 0% 0.0000 — 0.0000 Band neutrophils 8 * % 0.8000 — 3.2000 Segmented neutrophils 31% 23.0000 — 54.0000 Eosinophils 2% 1.0000 — 7.0000 Basophil s 0% 0.0000 - 1.0000 Plasma. cells 0% 0.0000 - 1.8000 ESR (according to Panchenkov) 8 mm/h 0.0000 - 15.0000
Features of treatment for pregnant women
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin (a specialist will help identify the causes by prescribing the woman a comprehensive diagnosis) is often recorded in women during pregnancy. This is normal in some situations. But there are cases when the cause is a serious disorder, so examination and properly selected therapy are necessary.
While pregnant, a woman should not take medications as they can harm the fetus. Therefore, when doctors have low ferritin levels, they prescribe dietary supplements and dietary supplements to women. Biologically active supplements contain iron, vitamins, biostimulants and ascorbic acid.
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Teknofer | Adult patients are recommended to dissolve 1 tablet in a glass of water daily. The course of treatment lasts a month. It is recommended to give the medicine in drops to children. |
|
| Elevit pronatal | The medicine should be taken orally during meals with plenty of water. The recommended dosage is 1 tablet per day. |
|
| Medefer | The drug should be taken 1-2 tablets 1 time per day. |
|
Treatment during pregnancy is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the woman’s condition. You should not take medications on your own; they can harm the fetus. It is also important to strictly adhere to the prescribed dosages, since even dietary supplements can cause side effects.
Iron and hemoglobin
We remember the periodic table, or rather its individual components from the high school course. But now we will find out how the interaction occurs when iron and hemoglobin “meet” in the body and how this chemical element affects human health, as well as what is the difference between high and low hemoglobin.
The phrase “low hemoglobin” is familiar to many and it is directly related to the iron content in the body. Despite the fact that its quantity is measured in milligrams, it causes a lot of problems not only with human health, but also with appearance.
Iron is necessary for humans like air. Without iron, the oxygen entering the body is useless. When oxygen enters the blood, hemoglobin, an important component of which is iron, transports it from the lungs to the tissues.
There are a number of signs that indicate a lack of iron in the body. But these signs - nervousness, increased fatigue, shortness of breath during physical activity, memory impairment - are often ignored, explained by anything from age, to workload or existing chronic diseases.
Low hemoglobin is observed in almost every second woman and only in 1% of men. The fact is that the main provocateur of iron deficiency is menstrual bleeding, especially prolonged and heavy bleeding. Other reasons include increased physical activity and uncontrolled use of medications.
Our body absorbs no more than 2.5 mg of iron per day from food, so if the hemoglobin level is lower than 130 g/l, we need to think about the possible occurrence of anemia. Read the list of symptoms indicating iron deficiency in the body and think about whether you have something similar:
1. Fatigue, drowsiness, feeling “broken” after a sound eight-hour sleep; on weekends you can’t bring yourself to get up from the couch. Decreased endurance during physical activity. 2. Skin problems: pallor, dryness, flaking on the back of the hands, elbows, face, pockets in the corners of the mouth. Hair loss, loss of shine, gray hair. The nails begin to peel, break, and sometimes longitudinal striations and wavy appearance of the nails are observed. 3. Changes in taste preferences and sense of smell. There is an increased craving for meat, salty, sweet foods or, conversely, an aversion to boiled vegetables, fish, and alcohol. Someone may have a desire to eat chalk, and the smell of paint or whitewash will have an exciting effect, like valerian on a cat.
If you don’t experience anything from this list, you are a happy person, but I’m afraid there will be very few of them.
Pregnant women should pay special attention to iron deficiency, as this is a real threat of various pathologies for the child, who will be starved of oxygen in the womb.
Due to low hemoglobin during pregnancy, the functioning of the immune system and the growth of bone, nervous and connective tissues of the baby are disrupted. Statistics show that almost every woman suffers from a latent form of anemia by the end of pregnancy.
And what is the way out of the situation, you ask? Alternatively, this is a diet that includes foods high in iron, such as liver, legumes, apples, pomegranates, etc. These measures are good as a preventive measure, but in case of anemia this is clearly not enough, since, I repeat once again, the body receives no more than 2.5 mg of iron from food.
There are many folk recipes for anemia. Here are some of them:
— Pass a glass of walnuts, a glass of cranberries, 2 lemons through a meat grinder. Add a glass of black currants and 3 tablespoons of honey to this mixture. Take the resulting mixture 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
- In the evening, pour 1 tablespoon of raisins into a glass of water. In the morning, without getting out of bed, drink water and eat raisins.
Readers, I think, have their own recipes for combating anemia and increasing hemoglobin. I would like to introduce you to the product of the NSP company - Iron Chelate, which restores the normal level of iron in the blood without causing irritation to the gastrointestinal mucosa
When taking iron supplements, there are two factors to consider: absorption and tolerance. It is known that iron supplements can cause side effects in the form of irritation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Dietary supplement Iron Chelate contains ferrous digluconate (2-valent iron), which is usually well absorbed by the body and does not cause side effects. Vitamin C significantly improves the absorption of iron by the body.
By taking NSP's Iron Chelate dietary supplement, you will improve blood quality, enhance energy production and ensure normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Almost everyone knows that low hemoglobin is bad, but in its excess, as it turns out, there is nothing good either. Most processes in our body occur with the participation of iron, and it performs very important functions:
- regulates the functioning of the immune system
- takes part in the functioning of the thyroid gland
- helps remove toxins from the body
- participates in regeneration processes
- improves skin condition, hair and nail structure
Most of the iron in our body is part of hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen in the body, and when it is in excess, reactions similar to the formation of rust occur: iron molecules oxidize and damage living tissues. When a person lacks oxygen, the body tries to compensate by increasing the concentration of hemoglobin.
Excess iron is more common in men. It is especially necessary to pay attention to hemoglobin standards for smokers. Here, however, there is a possibility that the analysis will show the norm, but this will be a special form that does not have the ability to carry oxygen.
What are the consequences of the presence of this “extra” hemoglobin? Most iron accumulates in the liver, pancreas, and heart muscle, which ultimately causes changes in the organ itself. The following diseases can develop: hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the joints, nervous system, as well as cardiac pathologies, up to sudden cardiac arrest. Excess iron can cause cancer of the intestines, liver, and lungs.
Excess iron is even more difficult to eliminate than deficiency. Abroad, for example, donation is recommended for people over 40-50 years of age to prevent coronary heart disease. Sometimes this method allows you to achieve the desired results and sometimes even avoid medications during treatment.
To regulate iron levels in the blood, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition. However, there are some nuances here.
Iron from plant products is better absorbed when they are combined with products of animal origin, but if an apple in addition to meat is useful to eat for anemia, then this should not be done if you have high hemoglobin. Yes, by the way, regular consumption of celery can restore the balance of iron in the body in a few weeks.
If there is a lot of calcium and sugar in food, then iron will be poorly absorbed. And for those with high hemoglobin, it is better to avoid buckwheat porridge, which is useful for anemia. Vitamin C and B vitamins promote better absorption of iron.
At the beginning of the 20th century, scientists made the discovery that hemoglobin in the blood is similar in structure to chlorophyll, which later became known as the blood of green plants. Chlorophyll is the green pigment of plants that carries out photosynthesis, and photosynthesis is the process of absorbing carbon dioxide from the air, converting solar energy into chemical bonds and, above all, hydrocarbons. In simple terms, the process of photosynthesis releases oxygen.
Thanks to the scientific developments of NSP specialists, a product called Liquid Chlorophyll has appeared, which, by increasing the level of oxygen in the blood, has anti-anemic properties, and also accelerates tissue regeneration processes. Therefore, Liquid Chlorophyll is recommended primarily for high hemoglobin.
I hope that from this article it became clear to you how iron and hemoglobin are interconnected, as well as what low and high hemoglobin is. Now all that remains is to check the level of hemoglobin in your blood. Perhaps it's time to take preventive measures to avoid serious health problems.
If you want to purchase NSP products with a discount, please register for free using the link https://nsp25.com/signup.php?sid=1449440, in the “Service Center” column, indicate the service center number for Russia 300, Ukraine 333 , Belarus 307, Kazakhstan 118, Crimea 319, Armenia 148, Georgia 72, Moldova 280. For other countries, I can provide company contacts via e-mail. You will receive a discount card by email.
Features of treatment for children
Children with low ferritin, regardless of age, are also prescribed medications and diet to replenish iron deficiency. It is important to add legumes, meat, dried fruits and cocoa to your child’s diet. The vitamin C needed by the body is found in rose hips and kiwi. Seafood will also help increase hemoglobin levels and restore protein levels.
For children, iron-containing preparations are taken in syrups or sweet tablets:
Ferrum Lek tablets
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Ferrum lek | The dosage of the drug is determined taking into account the patient’s age and is 2.5-30 ml once a day. Chewable tablets may be given to children 12 years of age and older. Treatment lasts 3-5 months. |
|
| Hematogen | Depending on the age, it is recommended to give Hematogen to children 5-10 g 2-3 times a day. |
|
Medicines to restore iron levels for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. You should not give medications on your own, given the high likelihood of side effects.
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin can be successfully treated if a person is diagnosed in a timely manner. The causes of the pathological condition were also established and an effective treatment regimen was selected. Complications arise as a result of delayed medical care or improper treatment. It is important not to ignore the first symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, but to immediately go to the hospital.
Conditions leading to increased destruction of red blood cells
Red blood cells, having outlived their life, are destroyed in the spleen. Sometimes red blood cells die before they have lived their intended life. Then hemolytic anemia develops, with which hemoglobin cannot increase either.
This happens for several reasons:
- congenital, genetically determined defects of erythrocytes (changes in their shape, structure, enzyme composition), leading to a decrease in their stability;
- production of antibodies to one’s own red blood cells as a result of an autoimmune process;
- their increased death in the spleen due to its changes (for example, with cirrhosis of the liver);
- entry into the body of hemolytic poisons;
- destruction of red blood cells due to mechanical action (for example, with an artificial heart valve).
Red blood cells in hemolytic anemia can be destroyed constantly ahead of their time, then chronic anemia develops. This happens with pathology of the spleen or with the destruction of red blood cells on the heart valve. Taking iron supplements in this situation does not lead to an increase in hemoglobin, even when administered by injection.
Sometimes hemolytic anemia develops in the form of hemolytic crises. This course is characterized by a gradual increase in hemoglobin, sometimes to normal values, followed by a fairly rapid destruction of some of the red blood cells. After a crisis, hemoglobin decreases, and jaundice sometimes develops.
This type of anemia can be diagnosed by the characteristic course of the disease, as well as by studying the morphology of red blood cells (their appearance and structural features). It determines the normal level of iron in the blood serum and an increased level of indirect bilirubin (it is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin).
Correction of low hemoglobin levels should be carried out taking into account the underlying mechanism of anemia. If it is hypochromic iron deficiency anemia associated with iron deficiency in food, diet correction is mandatory. If there is a disease that leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels, it can be increased only by compensating for this disease. Metabolic disorders, autoimmune processes and other serious diseases may require complex treatment. Sometimes you have to resort to injections of vitamins and iron supplements, and even blood transfusions. A complete and high-quality examination will help to identify the cause of the decrease in hemoglobin and select adequate treatment.
source