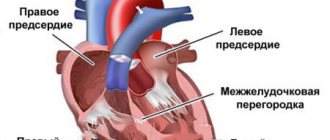
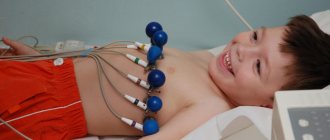
Ultrasound of a child’s heart (echocardiography) allows you to evaluate the functioning of this organ using ultrasound waves, diagnose diseases, and identify developmental defects. During the procedure, the size of the chambers, the thickness of the walls, the speed of blood movement, the study of the structure of the myocardium, the valve apparatus, the initial section of the coronary arteries, etc. are determined.
An ultrasound examination takes little time (15-30 minutes), allows you to obtain accurate information and does not harm your health.
You can have an ultrasound of your child’s heart at the Euro-Med clinic, where the procedure is carried out by specialists in the field of pediatric diagnostics.
Advantages of diagnostics at the Euro-Med clinic
- Our specialists build trusting relationships with young patients, and explain all research results to parents in understandable language, without complex medical terms.
- Ultrasounds are performed by pediatric specialists of the highest qualification category with over 10 years of experience.
- We use the most modern ultrasound machines: MEDISON SONOACE-X8; Philips HD9; VOLUSON 750. Their resolution allows you to obtain the most reliable results.
Ultrasound of the heart for a child
carried out according to the following indications:
- rapid fatigue, excessive sweating during physical activity
- pathological changes according to the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG)
- frequent colds, pneumonia
- unfavorable heredity
- pain in the heart area
- cold extremities
- heart murmur
- weight deficiency
- fainting
- cyanosis (blue) of the skin, especially around the mouth
- changes in heart rate (tachycardia, bradycardia)
Heart ultrasound (ECHO-CG, echocardiography) is one of the highly informative modern methods of instrumental diagnostics. With the help of the study, the doctor can evaluate the functioning of the heart and its individual structures - valves, atria and ventricles. Typically, echocardiography is prescribed for all children twice: in the first year of life and before starting school. The study allows you to exclude or diagnose various pathologies of the heart and nearby large vessels. As a rule, cardiologists prescribe treatment only after receiving the results of echocardiography and ECG.
Execution technique
An ultrasound of the child’s heart is performed without special preparation. Some experts recommend not pre-feeding the baby, so as not to encounter interfering contractions of the diaphragm. But, as practice shows, hungry children behave restlessly, which makes scanning even more difficult. To carry out the manipulation correctly and obtain reliable results, the following conditions must be met:
- you can fix the child or distract him for 5-15 minutes;
- the sonologist has experience examining young children;
- The ultrasound diagnostic device is equipped with a special children's (small) sensor.
When going for an ultrasound, take care of all the baby’s needs so that during the procedure you don’t have to suddenly change a wet diaper or urgently feed the baby. Bring a bottle of water or juice with you, and don’t forget your favorite toy. Dress your baby in comfortable clothes that can be removed quickly. Stock up on napkins to wipe the little patient’s chest later. Ultrasound scanning is performed in the following sequence:
- the child is undressed, exposing the upper part of the chest, placed on the couch (on the back);
- a special hypoallergenic gel that improves the conductivity of the ultrasonic signal is lubricated on the skin in the heart area;
- Using sliding movements, the sonologist fixes the desired areas on the monitor, measuring them and studying the blood flow in the vessels;
- While the specialist makes a conclusion, the mother can dress the child.
The conclusion is issued immediately. You should see a doctor about this.
Indications for ECHO-CG
An ultrasound of the child’s heart should be performed in the following cases:
- presence of heart murmurs on auscultation;
- ECG changes;
- child's complaints of stabbing, pulling, aching pain in the heart area;
- chest deformation;
- high blood pressure;
- prolonged dry cough;
- sensation of vibration or “trembling” over the heart area or in the subclavian fossa;
- frequent coldness, pallor, blueness of the limbs, nasolabial triangle (in small children when crying, sucking the breast);
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- repeated fainting in the child;
- frequent pneumonia;
- heart disease in close relatives;
- excessive sweating, swelling of the extremities;
- retardation in physical development, etc.
Specialists at the PreAmbula Clinic recommend undergoing a heart ultrasound, regardless of the presence of complaints. Many diseases can be asymptomatic for a long time until decompensation occurs. For example, some congenital heart defects can only be detected by echocardiography. The outcome of the disease largely depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment.
Indications for heart examination
Ultrasound of the heart is indicated for newborn children, starting from 5 days of age.
Diagnosis is carried out on the direction of a pediatrician or cardiologist, if there is a need to clarify whether there is a defect or other diseases, or as planned - when the baby turns 1 month, 1 year, 2 years old.
Urgent ultrasound diagnostics is carried out for the following indications:
- drop in blood pressure;
- severe shortness of breath;
- severe pain in the heart area;
- arrhythmia.
Such diagnostics are done in clinics or special centers.
What heart pathologies are diagnosed using ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the heart is a fundamental method for diagnosing the following cardiovascular pathologies:
- various congenital and acquired heart defects (ventricular and atrial septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, mitral stenosis and mitral insufficiency, tricuspid and aortic valve defects, etc.);
- aortic aneurysm;
- hypertrophy of the myocardium of the ventricles or atria (often develops secondary to defects);
- various types of cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic, dilated);
- blood clots in the chambers of the heart;
- myocarditis (inflammation of the middle layer of the heart muscle);
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner layer of the heart muscle);
- changes in the myocardium (presence of scars, sclerotic processes);
- additional chords in the chambers of the heart;
- ischemic disease, etc.
Timely diagnosis of these heart diseases is necessary for proper treatment. If any heart defect is detected in a small child, the issue of the need for surgical intervention is decided. Early stages of diseases that can be detected by ultrasound of the heart are more treatable than advanced forms. In addition, the examination is necessary to determine the child’s physical fitness group. If you have any cardiac pathology, some sports may be contraindicated.
Therefore, before enrolling in the sports section, it is better to conduct an ultrasound of the heart.
When performing an ultrasound of the heart, a small child is often diagnosed with a patent foramen ovale. This is a small opening that connects the right and left atria. Normally, it heals after some time, so there is no need to worry if your baby is found to have an atrial septal defect. In this case, you need to consult a cardiologist and come for a repeat echocardiogram after some time. It is believed that the interatrial window closes normally before the age of 5 years. If after this moment it remains, then they already talk about congenital heart disease and decide on the choice of optimal treatment.
How are birth defects diagnosed?
In medicine, congenital defects are understood as such anatomical defects of the heart that disrupt its normal development and arose during pregnancy or during childbirth.
READ How is ultrasound of renal vessels performed?
There are several dozen types of such anomalies known - all of them are the main cause of impaired blood flow and subsequent overload of the heart muscle.
In infants, the structure of the heart is not the same as in older children - between the atria there is an open oval window.
In the very center of the interatrial septum there is a hole, which is the connecting link between the left and right atrium.
Video:
From the point of view of physiological expediency, an open oval window is necessary for the normal development of the fetus.
At the intrauterine stage, the baby's lungs are not yet functioning, and the blood flow communicates with the systemic circulation through the open foramen ovale.
If the oval open window closes, pathological processes will begin in the right ventricle, resulting in the death of the fetus.
After birth, as the lungs expand, pulmonary circulation gradually improves in children, the body receives oxygen from the lungs, and the oval open window becomes irrelevant.
In addition, the level of pressure in the left atrium in children rises with age, so the oval open window closes after some time - the valve adheres to the interatrial septum.
This usually happens during the first year of life, but can happen later. It is within normal limits if the patent foramen ovale ceases to function by the age of 5.
Newborn babies often become more active—screams and crying associated with anxiety cause increased pressure in the right atrium.
As a result, the open oval window begins to function again, which is accompanied by a direct flow of blood through the atria.
Video:
Visually, the functionality of the oval window is manifested in the blueness of the child’s nasolabial fold.
If the oval foramen remains functional for a long time, then this is considered a violation of the norm and is diagnosed as a congenital defect.
READ What does ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities show?
Preparing for echocardiography
No special preparation is required before performing echocardiography. Experts do not recommend engaging in sports training before the procedure. If your child is taking any sedative or stimulant medications, you should consult your doctor. Some medications may need to be stopped for 1-2 days before the ultrasound so that they do not affect the picture of the heart muscle. Immediately before the test, you should try to calm the child so that his pulse is within normal values.
Preparing for a pediatric heart ultrasound
Children's cardiac ultrasound is a non-invasive and absolutely safe method for examining the heart for your child, which does not require special preliminary preparation.
At the Miracle Doctor clinic, ultrasound is performed using modern imported expert-level ultrasound systems with the ability to conduct duplex and triplex scanning.
The specialists of our clinic are fluent in performing ultrasound examinations. Doctors at the Miracle Doctor clinic will conduct diagnostics, interpret the results of the study, and, if necessary, give recommendations or prescribe treatment. The procedure is carried out within 15-20 minutes, small patients tolerate it comfortably and easily.
An ultrasound of the heart is often prescribed if a child regularly suffers from pneumonia. Echocardiography may also be necessary for shortness of breath, developmental delays, and pathologies seen on an x-ray. It is worth doing an ultrasound if your child is often diagnosed with colds and high blood pressure. It is mandatory to do an ultrasound of the heart to monitor the child’s condition after cardiac surgery.
There are certain recommendations regarding at what age a child should have an ultrasound. It is first performed at one month of age to identify congenital defects. Further, you need to undergo the procedure at the age of 6-7, before entering school. The next time is at age 14, when puberty begins. If a boy or girl is going to attend sports clubs, then diagnostics will also not be superfluous.
How is the procedure done?
In the cardiac ultrasound room, the child should undress to the waist and lie down on the couch. If the baby is very small, then one of the parents helps the specialist by holding and calming the child. A gel is applied to the chest, which is necessary for better contact of the sensor with the skin. From the ultrasound sensor, the image of the internal structures of the heart is transmitted to the monitor, where the doctor records the parameters being studied. The ultrasound diagnostic procedure usually takes no more than 15-20 minutes.
All indicators obtained using ultrasound are entered into a special form. The results are given to the patient along with the doctor’s report. If necessary, the ultrasound technician may refer you to a cardiologist or other doctor.
Indications for the procedure
The need to perform an ultrasound of the child’s heart may arise for various reasons. Usually, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the heart when a child develops ailments that may be symptoms of cardiac diseases.
Such ailments include:
- loss of consciousness;
- fast fatiguability;
- breast refusal for no apparent reason;
- elevated temperature for no apparent reason;
- shortness of breath in the absence of fever;
- sweating;
- cold fingers and toes;
- chest pain on the left side;
- periodic blue lips, especially during physical activity;
- pneumonia with relapse;
- changes in the cardiogram;
- visually noticeable pulsation in the neck or right hypochondrium;
- poor physical development;
- dry cough for no apparent reason;
- genetic predisposition to cardiac diseases.
According to medical indications, a heart ultrasound is prescribed if a heart murmur is detected during examination with a phonendoscope; if there are signs of heart failure; with an increase in the size of the liver and swelling of the legs; for ischemic diseases; for chest injuries; after cardiac surgery; for oncological diseases; if there is a suspicion of an aortic aneurysm.
Cardiac ultrasound is also prescribed for children during a routine examination.
Echocardiography at the Preambula Clinic
To schedule an ultrasound of your child’s heart in Moscow, just call the PreAmbula clinic.
We employ highly qualified specialists with more than 20 years of experience in ultrasound diagnostics. Our doctors specialize in cardiac ultrasound in children, taking into account their age characteristics. At the clinic, you can also visit a cardiologist who will interpret the results of the ultrasound examination and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
The quality and information content of ultrasound diagnostics largely depend on the equipment used. The PreAmbula network of clinics has the most modern equipment for performing ultrasound.
If your child has any heart complaints or you just want to make sure there is no heart pathology, sign up for the PreAmbula clinic. Echocardiography is an absolutely safe, quick and painless procedure that does not require special preparation.
Echocardiography with spectral analysis and color circulation
— 2900 rub.
A heart echo for a child is a modern non-invasive procedure that allows you to diagnose both congenital and acquired diseases of the cardiovascular system in children at any age. Read more about the diagnostic capabilities of the examination, its conduct, and indications.
Is it dangerous to perform an ultrasound on a baby?
Many parents are concerned that manipulation is prescribed to their children. Moms and dads, supported by the incorrect opinion of grandmothers, assume that scanning irradiates the baby and causes harm to the growing body. Why then do doctors recommend heart ultrasound to be performed on all children? Perhaps this is not as dangerous as many people think? Let's figure it out!
An ultrasound examination is performed by a sonologist using a special device. At one end, the device is equipped with a sensor that sends and then receives sound pulses. Don't try to listen - you won't hear anything. These sound waves are inaccessible to the human ear, but the device understands and interprets them perfectly. On the other side, the device is equipped with a monitor and many buttons. With their help, the specialist measures the parts he needs.
The study does not bring any learning, harm, or anything else invented by patients. You don’t have to worry: an ultrasound of the child’s heart will not cause any inconvenience. The procedure is painless and completely harmless.
During pregnancy
To confirm all the above arguments and finally convince parents of the safety of the manipulation, it should be said that ultrasound of the baby’s heart muscle is carried out during pregnancy. You probably haven't thought about this if you're apprehensive about doing research now.
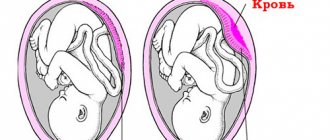
Color Doppler mapping shows blood flow in the heart
Performed in the second and third trimesters, ultrasounds are designed to detect congenital defects in the baby, including heart defects. The doctor carefully examines this organ, studies the chambers, ventricles, and examines the functioning of the blood vessels. Pathologies identified at this stage become the reason for an immediate ultrasound after birth.
Echo CG of a child’s heart – what is it?
Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is a study of the functioning of an organ in real time, allowing one to determine both the static characteristics of the heart (size, wall thickness, condition of the myocardium and valves) and dynamic (the volume of blood ejected during contraction, the direction of blood flow, valve function) . Knowledge of these parameters allows you to assess the state of the child’s cardiovascular system with minimal time and effort.
During the Echo CG process, the scanner receives information from the organ in three different modes:
Possible pathologies
A cardiologist who has received the transcript of the echocardiogram of the child’s heart and compared them with the above standards is able to establish an accurate prognosis. Sometimes this requires additional diagnostic methods. The most common pathological disorders that ultrasound can detect in children and adolescents are:
- The presence of open holes in the interventricular septum, in which the study shows an increase in the thickness of the walls of the heart muscle, as well as the volume of the hollow parts of the heart.
- Violation of the integrity of the septum on the cardiogram shows thickening of the walls of the atria, the presence of holes in which should not exist.
- Valve defects, after undergoing ECHO CG, show a change in the size of the window, which serves for blood circulation between the ventricles.
- Deformation of the aorta. With this pathology, a decrease in the diameter of the blood vessel is observed, as well as a change in the thickness of its walls.
In the presence of inflammation of the cardiovascular system in newborns, dysfunction of blood ejection or its reversion may occur. There is also an increase in the volume of all hollow parts of the motor organ.
If the baby is suspected of developing or having pathological diseases of the heart muscle, such diagnostic methods will promptly and accurately identify them. This will make it possible to quickly correct problems that arise. The obtained data from ECHO CG can not only confirm the presence of the disease, but also refute it.
Before you register your baby for an ultrasound, you need to carefully prepare, taking into account his character, manners and habits. It is advisable not to feed him before the procedure itself, as this may be a hindrance. It is better if the mother feeds the baby 2-3 hours before the start. There are no contraindications or side effects from echocardiography, but the outcome and time of the baby’s stay in cardiology depends on the preparation of the parents.
Echocardiography (ECHOCG)
- the safest and most painless, non-invasive (without compromising the integrity of the skin), accessible method of studying the cardiac activity of a child from the first hours of his life.
The essence of the procedure is to register ultrasonic waves that reflect tissues of different densities: the myocardium, great vessels, and surrounding anatomical formations. Thus, the structure and functional state of the baby’s cardiovascular system is determined with a high degree of information and in real time.
When is a child's heart ultrasound performed?
As a child grows, his heart undergoes significant changes. There are certain age periods when the risk of manifestations of disturbances in the functioning of the organ is greatest:
- The moment of birth. When a person takes his first breath, the blood circulation pattern changes - as the lungs begin to work, the pulmonary vessels open and the pulmonary circulation begins to work. This leads to closure of the interventricular foramen and complete separation of the right and left parts of the heart. In addition, the load on the left ventricle increases sharply due to increased vascular resistance.
- Puberty period. The sharp growth of the child and the increase in the concentration of hormones in the blood during this period leads to an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system. The myocardium does not always have time to cope with the increased needs of the body.
In the absence of complaints, cardiac ultrasound is mandatory for children aged 1 month, 7 years and 14 years.
Fetal echocardiography
Ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy is prescribed if there are signs of developmental disorders of this organ identified during standard ultrasound screening of pregnant women. In addition, the study is planned to be carried out in the following cases:
- burdened family history - the presence in the family of close relatives with congenital heart defects;
- deviation from the norm in the amount of amniotic fluid - high or low water;
- chronic systemic diseases of the mother - diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- congenital heart defects in previously born children;
- detection of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, accompanied by impaired heart development;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (flu in the first trimester, rubella).
The optimal period for performing the examination is considered to be 20–22 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, the organ is already fully formed and its size allows for an accurate diagnosis of pathologies.
Echo CG for newborns
Cardiac ultrasound is performed at the age of 1 month during a routine medical examination. A heart examination during this age period can reveal congenital heart defects (narrowing of the aorta, intracardiac septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus). The reasons for conducting an EchoCG are the following symptoms:
Indications for echocardiography in older children
In the absence of complaints, echocardiography is performed when passing a school commission at 7 years old, as well as at 14 years old. Echo CG is prescribed at any age with the following symptoms:
- frequent prolonged pneumonia;
- complaints of shortness of breath during physical activity;
- retardation in height and body weight;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- murmurs heard by the pediatrician.
Particular attention should be paid to the state of the cardiovascular system during the recovery process after streptococcal tonsillitis and scarlet fever. Streptococci that cause these diseases can damage the endocardium, causing disruption of the valves and myocardium, leading to the development of myocarditis.
Decoding cardiac ultrasound data
At the end of the ultrasound procedure, the doctor issues a report indicating the results. But for people who do not know medical terminology, this information is incomprehensible - they need a specialist to decipher it.
Heart ultrasound indicators in children of different genders and ages differ, and in a 14-year-old child they completely correspond to the indicators of an adult.
Deciphering the obtained research results will not add information if norm indicators are not used as a guideline for comparative analysis.
If the transcript of the ultrasound report of the heart indicates a decrease in the size of the opening in the left atrium and right ventricle, this indicates a thickening of their walls and mitral leaflets.
The diagnosis is mitral valve stenosis.
If the transcript contains information about an increase in the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle, it means that the closure of the mitral valve leaflets is impaired. The diagnosis is mitral valve insufficiency.
A transcript indicating thickening of the walls of the left ventricle and right atrium, as well as the narrowness of the aortic mouth, indicates stenosis of the aortic mouth.
Whereas thickening of the left ventricle and right atrium against the background of non-closure of the aortic valve leaflets is a clear symptom of its insufficiency.
Video:
If the transcript does not contain confirmation of the functioning of any part of the heart muscle, then doctors determine myocardial infarction.
If there is an expansion of all the cavities of the heart against the background of a decrease in the ejection fraction, myocarditis is diagnosed.
Despite popular belief, cardiac threats can be detected not only in older people, but also in infants.
You should not tempt fate - it is better to show the child to specialists in time, undergo an examination and have an ultrasound of the heart, before a minor pathology has time to become a serious threat to his life.
moydiagnos.ru
Features of preparing and carrying out the procedure in a child
No special preparation is required for the examination. You need to pay attention to the following points:
- A cardiac echo is performed in a calm state, with a normal heart rate, since when they increase, the parameters of cardiac activity also change, which will complicate the diagnosis. Therefore, it is advisable that the child does not undergo physical activity before the study, and also does not cry and lies quietly during it.
- It is advisable to come to the examination with a fresh (done more than a month before) electrocardiogram. This will help the doctor to suggest possible problem areas in the organ and pay close attention to them during the procedure.
- If the hospital does not have disposable supplies (sheets, napkins), then you need to take a towel with you to lay it on the couch, and then wipe off the remaining gel applied to the skin.
- For children under three years of age, ultrasound is performed with special children's sensors. Therefore, before performing the procedure, it is necessary to find out their presence from the doctor.
Cardiac ultrasound is performed by a pediatric cardiologist specializing in echocardiography. One of the main disadvantages of ultrasound examinations is the strong dependence of diagnostic accuracy on the experience and qualifications of the doctor conducting the examination.
During echocardiography, the child lies on the couch. Immediately before the examination, a special gel is applied to the skin of the chest in the area where the heart is projected. Its functions are to reduce the layer of air between the sensor and the surface of the chest and ensure free movement of the scanner over the skin.
Different parts of the heart are better visualized in different body positions. Therefore, during the examination, the doctor may ask you to lie on your left side, on your stomach, and hold your breath while inhaling or exhaling. Ultrasound diagnostics is absolutely safe and painless; the only thing the child will feel is a slight tickle. The duration of the examination ranges from 10 minutes to half an hour.
How is heart ultrasound performed for children?
Private clinics in Moscow perform cardiac ultrasound for children of all ages, starting from infancy. The methods of economic activity of paid clinics make it possible to diagnose heart diseases in children using modern, high-quality equipment from well-known imported manufacturers of medical equipment.
Diagnostic doctors at private clinics specialize in performing hardware diagnostics in children and are fluent in the technique of performing cardiac ultrasound (ECHO CG) and interpreting the data obtained during the examination.
The ultrasound examination method in children is performed using the ability of the soft tissues of the human body to reflect the waves received during the diagnostic process. These reflected signals are captured by the scanner and transformed by a special converter into electrical signals, which make it possible to obtain an image of the heart structures on the monitor.
Heart ultrasound for children is performed in a warm, ventilated room, in which the necessary sanitary measures are carried out several times a day.
Before the ECHO CG procedure, the child’s outer clothing is removed and the chest is exposed. A hypoallergenic, chemically non-aggressive gel is applied to the skin of the chest in the area of the mediastinum, which improves the conduction of the ultrasonic wave. After the examination, the doctor will remove this gel with a disposable paper napkin.
After applying the gel to the skin, the doctor runs a special sensor across the chest, while talking to the child, trying to distract him or, if necessary, calm him down. The examination procedure takes 15-30 minutes, depending on the pathology and age of the child.
What the study shows - deciphering the results
After conducting an Echo CG, the specialist fills out a special ultrasound protocol, which indicates the registered parameters of the organ’s functioning and the size of its departments. The norms for interpreting cardiac echocardiography in children are indicated in special tables and the doctor compares the obtained indicators with them, since each age group has its own parameters.
After 14 years, the data obtained are compared with normal values for adult men and women. It should be noted that the diagnosis is made not by an ultrasound diagnostic doctor, but by a pediatric cardiologist based on the results obtained.
Let's summarize
Ultrasound examination of the heart muscle in children is one of the most accurate diagnostics. There is no need to be afraid of it; pathologies not identified in a timely manner can be much more dangerous. As a rule, young children behave restlessly during scanning. Don't worry: this will not affect the results of the study in any way. Pathology either exists (and it will be revealed) or it does not (which the study will show). Do not attempt to decrypt the data yourself. Your only assistant is a cardiologist.
Echocardiography price
You can get a heart echo for a child in Moscow both in private clinics and in public hospitals. The cost of an Echo CG for a child is on average 2,600 rubles. The exact cost depends on the prestige of the medical center, the type of device used and the qualifications of the doctor performing the procedure.
It is important to know:
The diagnostic capabilities of echocardiography in children make it possible to quickly and cost-effectively identify congenital and acquired heart defects, myocardial lesions and other cardiac disorders. Timely diagnosis allows for surgical correction of developmental defects and prescribing optimal treatment for diseases before complications and heart failure develop.
Today, ultrasound examination of the heart is prescribed for every baby. The procedure allows timely detection of deviations in the functioning of the organ. Unlike an ECG, an ultrasound shows the process of the heart: the speed and quality of blood flow, the functioning of each department. This makes it possible to identify even minor pathologies, but many mothers are frightened by the study, so let’s take a comprehensive look at the procedure.
Ultrasound of the heart makes it possible to timely identify and prevent the development of various pathologies of the organ.
Possible results
Cardiac ultrasound in children is interpreted by the diagnostician who conducted the study. He describes everything he saw in the conclusion, which is transmitted to the attending physician.
The conclusion is not yet a diagnosis, it only indicates the changes in the heart seen by the specialist. The final interpretation of the child’s results and determination of the diagnosis is carried out by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist.
Norm
Normal ultrasound readings of the heart of a baby at 1 month and older children differ. The table shows the average indicators of ultrasound examination standards in children of different ages.
Table. Normal cardiac ultrasound findings in children:
In addition to these indicators, ultrasound evaluates the condition of the valves, which normally should close tightly and open completely during contractions and relaxations of the heart.
Possible pathologies
What does an ultrasound of the heart show in a child in case of any pathology?
Using ultrasound, you can identify congenital and acquired heart defects, infectious lesions, tumors, cardiomyopathies:
- Open oval window.
This is the opening between the right and left atria, which is necessary for the fetus during intrauterine development. For a newborn, an open oval window is normal; it should close by the first year of life. If this does not happen, they talk about congenital heart disease. - Mitral valve stenosis
. A common congenital defect that is associated with a narrowing of the opening between the left chambers of the heart. As a result, hemodynamics suffer. The opposite condition is mitral regurgitation, when the valve leaflets do not close completely. - Aortic valve stenosis.
In this case, the opening leading from the left ventricle to the aorta is narrowed. This leads to an increase in the myocardium of the left ventricle. - Endocarditis
. Infection of the inner lining of the heart, most often the valves are affected. On ultrasound it looks like a warty thickening of the valve leaflets. - Myocarditis.
Myocardial inflammation in newborns on ultrasound looks like a uniform thickening of all the walls of the heart, usually associated with infection or an autoimmune process.
These are the most common pathologies that can be diagnosed using ultrasound. A specialist will talk about other diseases in the video in this article.
Heart ultrasound is a high-quality and affordable method for diagnosing various diseases. It has an advantage in children because it is absolutely safe, does not require special training, and is non-invasive.
Using the method, you can detect various defects, tumors, and infections. An ultrasound is performed taking into account the indications determined by the pediatrician. Interpretation of newborns and older children is carried out by several specialists.
When should a child have a heart ultrasound and is it safe?
Ultrasound examination of the heart can be performed from the first days of life; there are no contraindications for it, since the method involves the use of only ultrasound rays, which are absolutely safe for the body. Echocardiogram is an ultrasound aimed at studying morphological and functional changes in the functioning of the heart.
How many times are children tested? If the birth went well and no pathologies were observed in the fetus during pregnancy, then a referral for the first examination is given at the age of one month. Together with it, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, pelvis and head is performed. The next visit is scheduled at 6 months of age, although in some clinics this is replaced by an ECG. It is recommended to conduct an echocardiography at the age of 14, during the period of formation of hormonal levels and an active pace of development.
There are many reasons for performing an ultrasound, and if the doctor insists on the procedure, you should not refuse
The doctor may also prescribe the procedure if:
- the newborn refuses to breastfeed and has a weak sucking reflex;
- the child periodically loses consciousness;
- gets tired quickly;
- suffers from shortness of breath;
- the baby's nasolabial area or lips turn blue;
- limbs are cold even in a warm room;
- the patient has been diagnosed with pneumonia;
- the pediatrician heard a murmur in the heart muscle;
- irregularities were detected in the cardiogram;
- The baby complains of pain or pressure in the left side of the chest.
Do not refuse the procedure if your baby has been diagnosed with a sore throat or other respiratory diseases. They often cause heart complications, so if the clinic is ready to conduct an examination, it is better to agree.
If the parents have heart pathologies that are inherited, the mother suffered an infectious disease during pregnancy, or the baby’s first appointment with a specialist revealed some abnormalities, the doctor may prescribe a scheduled re-examination. There is no need to be scared; an ultrasound of the heart will not harm the child, even if it is performed frequently.
Do all children need research?
From the first minutes of life, every newborn undergoes a thorough examination and examination by specialists. If the neonatologist sees the need, then ECHO CG is performed even then. If there is no need for such a diagnosis, then the first ultrasound examination of the heart muscle will be performed when the child is one year old. We can conclude that ultrasound scanning is performed on children at any age. The technique has no contraindications. But there are many indications for its implementation. An ultrasound of the child’s heart is prescribed if:
- during the next examination, the pediatrician heard a heart murmur or an abnormal rhythm of a muscle organ was noted;
- cyanosis was detected - the appearance of a blue stripe above the lip (in young children it is observed after sucking or crying, and in older children - during physical activity);
- the doctor suspects cardiac pathologies due to insufficient weight gain and poor appetite;
- the child gets tired quickly, is too apathetic, has increased sweating and shortness of breath;
- the child has cold hands and feet that do not change their temperature even in a warm room;
- there is swelling of the extremities (legs, fingers).
Some pediatricians believe that there is no need to wait twelve months. Even if the baby does not have any indications, the diagnosis must be performed at 1 month of age. In the future, scans are carried out as planned: per year, 14 and 18 years.
Do not forget about emergency situations when an ultrasound examination for a child turns out to be unplanned. This manipulation is necessary when:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- sudden severe shortness of breath that does not go away even at rest;
- cutting, pressing, burning pain in the area where the heart muscle is located;
- arrhythmias, tachycardia and other heart rhythm disturbances detected during electrocardiography.
If any abnormalities are detected in a child during an ultrasound, then subsequent diagnostics are scheduled after a few days or months (depending on the condition of the little patient).
How is diagnosis carried out?
Echocardiography is always performed in the presence of parents. The mother must hold and calm the baby, as he will have to lie motionless on his back for some time. It is allowed to hold the baby in your arms if he behaves calmly.
Make sure to take your favorite toys; the procedure will take about 15 minutes. The patient is undressed to the waist, the doctor applies contact gel to the chest and begins the examination using a special sensor. The specialist will evaluate:
- parameters of the heart and its parts;
- myocardial wall thickness;
- heart rate;
- change of phase of excitation and relaxation;
- blood circulation algorithm;
- will check the operation of each valve.
The duration of an ultrasound examination, as a rule, does not exceed 15 minutes.
How is an ultrasound of the heart done?
An ultrasound examination of the heart and blood vessels is performed on the child in a lying position, on his back (an adult is usually placed on his left side).
The baby's chest is exposed and lubricated with an antiallergic agent in the form of a cream or gel (for better sliding of the sensor over the body).
A specialist performing diagnostics of the baby’s heart vessels moves a sensor across the chest, the device sends ultrasounds that are reflected from the muscles and cavities encountered along the way with different wavelengths (depending on the density of the tissues).
The device records reflected waves and obtains the dimensions of the chambers and ventricles of the heart, blood vessels, automatically generating a diagnostic report.
The infant should not be hungry, then he will behave more calmly.
The mother needs to take with her a bottle of water for drinking, a couple of napkins to remove the gel from the baby’s body, and also a favorite toy to distract her from what is happening, which is incomprehensible to the child, although the diagnosis is performed without causing any inconvenience at all.
Crying will not affect the results (either the disease is present or not), but everyone will be more comfortable if the child behaves calmly.
No preparation is required for a cardiac ultrasound.
Decoding the results
The study is deciphered immediately; today, all readings are automatically entered into a protocol, which is pasted into the card. The doctor checks all parameters with the norms according to age tables. In the protocol, mom will find a large number of contractions; they correspond to the size of a certain part of the heart: for example, the left ventricle - LV, the right atrium - RA.
Standards for children of different ages
The norms will differ depending on the age and gender of the baby. Rates vary even among newborn babies and children as young as one month old. Patients over 14 years of age are assessed according to the adult norm table.
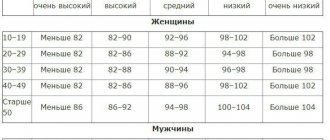
For newborns weighing up to 3.5 kg, the norms look like this:
| Index | Female | Male |
| LV EDC | 16-21 | 17-22 |
| LV ESR | 11-15 | 11-15 |
| Left atrium diameter | 11-16 | 12-17 |
| Right ventricular diameter | 5-13 | 6-14 |
| TZSLZH | 2-4 | 3-4 |
| MZhP | 2-5 | 3-6 |
| 2-3 | 2-3 | |
| Ejection fraction | 65-75% | 65-75% |
| 1.42-1.6 m/s | 1.42-1.6 m/s |
The study is deciphered immediately - all readings are entered into the protocol automatically.
Children over 1 month old and weighing up to 4.5 kg must meet the following parameters:
| Index | Female | Male |
| LV EDC | 18-24 | 19-25 |
| LV ESR | 12-17 | 12-17 |
| Left atrium diameter | 12-17 | 13-18 |
| Left ventricular diameter | 5-13 | 6-14 |
| TZSLZH | 3-5 | 3-5 |
| MZhP | 3-6 | 3-6 |
| Right ventricular free wall | 2-3 | 2-3 |
| Pulmonary valve blood flow velocity | Approximately 1.3 m/s | Approximately 1.3 m/s |
The doctor will decipher the results immediately after the appointment. If deviations from the norm are detected, he will refer the baby to a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist.
Pathologies shown by ultrasound of the heart
An ultrasound of the heart in a newborn shows the organ from many sides, therefore it allows one to identify many pathologies in the early stages. Among them:
- Mitral valve stenosis. In this case, they talk about reducing the diameter of the hole between the parts of the heart due to thickening of its walls.
- Heart defects in any manifestation - possible changes in the structure of valves or septa, their displacement, absence or presence of additional chords.
- Narrowing of the aortic opening, blood cannot fully pass from the left ventricle to the aorta.
- Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle, myocardium.
- Inflammation of the endocardium - the inner lining of the heart.
- Myocardial infarction. Manifests itself in the death of a significant part of the muscle tissue of the heart and myocardium.
- The presence of blood clots inside or outside the chambers.
- Accumulation of fluid in the heart sac.
Many diagnoses are typical for adults and older people, but this does not mean that such a disease cannot be diagnosed in young children. You should be attentive to the child’s complaints, monitor his condition in order to consult a doctor in time.
There are a lot of heart pathologies, so if your child complains, you should consult a pediatrician
How is cardiac ultrasound performed in children?
Technically, cardiac ultrasound in children is no different from the procedure for adults.
The only difference is the lack of preliminary preparation - there is no need to refuse food before the procedure.
The cardiac ultrasound procedure is completely painless and does not cause any discomfort in children. The child is undressed to the waist and placed on the couch.
Photo:
If the child is very small, then parents must ensure his peace of mind. Therefore, often the baby’s parents are next to him during the procedure, distracting his attention with the help of toys.
In the chest area, the sonologist applies a gel to the baby's skin and then moves a sensor over its surface. As the scan progresses, the doctor may ask the child to hold their breath for a few seconds.
The youngest patients should be seen by a specialist experienced in examining children using ultrasound.
It is important that the ultrasound laboratory is equipped with appropriately sized sensors.
The first scan of the baby's heartbeat takes place before birth - at 20 weeks of the mother's pregnancy.
The first planned ultrasound of the heart is done when the baby is one month old. The next planned ultrasound is performed after a year of life.
During routine examinations, doctors evaluate the heart and blood vessels, determine its parameters and check for abnormalities.
In proportion to body weight, a child's heart is much larger than that of an adult. Its anatomy is also different.
Video:
Primary studies and correct interpretation of the results make it possible to recognize congenital pathologies, as well as timely detect potential threats to the child’s health:
- all types of heart defects;
- the presence of parietal or intracavitary thrombi;
- deviation from the norm in the parameters of the heart chambers;
- inflammatory processes in the myocardium;
- changes in the volume of the heart muscle;
- ischemic manifestations;
- fluid in the pericardium;
- changing valve parameters;
- inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the heart;
- myocardial infarction.
Contraindications to the examination
There are no contraindications for the study, but it is recommended to follow some rules related to the emotional state of the subject. It is better to feed infants shortly before the ultrasound, then there is a high probability that the infant will sleep and allow the doctor to carry out all the manipulations.
On the contrary, it is recommended not to feed children over 3 years old 2 hours before the examination. At this age, it is extremely important to psychologically prepare the child so that he is not afraid of the doctor and does not worry. When the baby is nervous, an error appears in the measurements, and the pulse will increase.
What should you not do before the examination?
First of all, patients should not worry, be exposed to stress, or worry too much about the examination itself and the possible results.
All this can negatively affect the information received and distort subsequent therapy. You should not eat too much or drink a lot of liquid even before a classic ultrasound performed through the chest.
The best result in this case is to adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and lead a calm, normal lifestyle.
If you have to undergo an examination through the esophagus, you will have to pull yourself together and refuse food and water so as not to encounter unpleasant phenomena during the ultrasound procedure.
And, of course, if the patient has any health problems, the attending physician must be warned about this in advance, because both the conduct and results of the examination may depend on them.
If a patient has tachyarrhythmia or high blood pressure, he should definitely visit a cardiologist before going for any ultrasound, especially an exercise procedure.
If the patient's pulse is more than ninety beats per minute, and the pressure is higher than 170 to 99 mm Hg, only a cardiologist will be able to say whether it will be necessary to reduce the pulse with pressure or not, and how best to conduct an examination in order to obtain the most reliable and detailed results.
Cost of the procedure
An ultrasound of a child’s heart can be done free of charge at regional children’s clinics. The referral is given by the pediatrician as part of routine examinations or as indicated. If the clinic does not have such equipment in its arsenal, then it must cooperate with other medical institutions where referral will be given.
In order not to wait for an appointment or to undergo an examination unscheduled, you can use a paid service. It is usually provided in multidisciplinary centers. When examining a small child, it is necessary to clarify his age: the specialist must have experience working with infants, in addition, a small attachment for the device may be required.
The cost of the examination will vary depending on the region of the country. In the capital, the procedure costs 2500-3000 rubles. In St. Petersburg and other large cities, the price is reduced to 1500-2000 rubles. However, some clinics charge for transcription or additional research. These aspects should be clarified when registering for the procedure.
Ultrasound examination of the heart is a safe and effective method for diagnosing diseases. It can be carried out from the first days of life, has no contraindications or restrictions on the number of studies. Mothers should not neglect routine examinations; they can be vital.
An ultrasound of the child’s heart is a study that will help find out whether everything is in order with the structure and chambers of the heart, its contractility and the condition of the valves. It has no contraindications, does not require preliminary preparation, and can be performed from the first day of life.
Questions for the doctor
Good afternoon. I recently had a child, we are registered with a pediatric cardiologist, since during pregnancy there was a suspicion of a heart defect. When should a child have an ultrasound to confirm or rule out pathology?
Irina, 28 years old, Ivanovo
Good afternoon, Irina. Your doctor knows how often to examine your heart if a defect is suspected. This is usually done immediately after the baby is born, then every three months until the baby is one year old. After ultrasound, they do it every six months to five years. Usually at this age, suspicion of a congenital defect is removed.
Hello. My child and I are not being discharged from the hospital because there is a suspicion of a heart infection. The doctors did an ultrasound and ordered several more studies. What should be the interpretation of an ultrasound scan in a newborn to suggest an infection?
Maria, 34 years old, Tver
Good afternoon, Maria. Ultrasound is the very first method to detect infection in the heart. As a rule, the endocardium or myocardium is affected. In the first case, doctors will see thickening of the valves, which prevent them from closing fully. If the myocardium is damaged, its increase will be observed in all departments.
These and other questions inevitably arise before all parents who decide to take their child for a heart ultrasound. Cardiologists at the Miracle Doctor clinic are convinced that diagnosis is best done earlier in order to exclude possible pathology of the heart muscle and the vessels that supply the myocardium.
Perhaps the most important question that mothers and fathers ask is whether it is worth doing an ultrasound of the child’s heart if nothing is bothering him? Diagnostics will prevent possible disorders in the development of the heart, help identify congenital defects, and assess the rhythm of the heart and the activity of the cardiovascular system. It is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the child’s heart for the purpose of prevention, even when the child does not complain of heart pain, increased heart rate, or other symptoms that may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
When should you do an ultrasound of your child’s heart?
This study is indicated in the following cases:
- the child lost consciousness
- baby gets tired quickly
- refusal to breastfeed in the absence of signs of acute illness
- there is a slight body temperature, but the throat is not red, there are no other signs of ARVI, the baby does not complain of anything
- shortness of breath without fever
- pediatrician listened to a heart murmur
- you notice that your limbs sometimes become cool
- the child complains of pain in the left side of the chest
- blueness of the lips and the area above them is observed (nasolabial triangle), even if this is observed only during physical activity (in infants - during sucking)
- gets tired quickly at the slightest exertion, this is accompanied by shortness of breath
- there have already been more than 2 inflammations of the lung (in this case, ask for an ultrasound of the thymus in children, since the cause of frequent diseases may be hidden in it)
- fingers feel a tremor over the lower left half of the chest or “in the pit of the stomach”
- changes were recorded on the electrocardiogram
- the pulsation of the veins in the neck or area in the right hypochondrium is noticeable to the eye, even if this does not always appear
- retardation in physical development
- dry cough in the absence of signs of acute respiratory infections and red throat.
A routine heart examination, like an ultrasound of the baby’s head, should be done at 1 month of age if the mother has had rubella or other infectious diseases during pregnancy. This is also necessary if there were congenital malformations of internal organs in the family (especially heart defects and hypertension).
What the study can show
Children's heart ultrasound (echocardioscopy) reveals the following diseases:
- heart defects (violations of the structure of valves, septa, additional chords, etc.)
- parietal or intracavitary thrombi
- dilatation or narrowing of the chambers of the heart
- myocardial inflammation
- increase or decrease in heart muscle volume
- fluid in the pericardial cavity (heart sac)
- cardiac ischemia
- increase in the volume of the valve apparatus
- inflammation of the lining of the heart (endocarditis)
- myocardial infarction
Moreover, the last two diseases may well be detected by ultrasound in a child, and not just in older people. You need to remember this in order to take it seriously if your baby complains of heart pain.
Preparing for diagnosis
An ultrasound of the child’s heart is performed without any preliminary preparation. If the baby is less than a year old, you can feed him before the examination so that he can sleep peacefully during the diagnosis.
Children of any age also do not need to adhere to a special diet.
How the research is carried out
In order to perform an ultrasound of the child’s heart, he does not need to be put under anesthesia, but it is necessary for him to lie quietly for 15 minutes. To do this, parents come into the office to calm the baby and distract him from exploring with toys.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
A pediatric heart ultrasound will help the doctor make or confirm a suspected diagnosis because the results show:
- are there any blood clots in the cavities of the heart or blood vessels on their internal surfaces;
- the presence of congenital defects;
- neoplasms;
- deviations in the size of the heart or its parts from the norm;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the heart;
- ischemia;
- myocardial infarction, etc.
An echocardiogram will show quite accurately whether there is cause for concern and how serious the situation is.
Record
Not only adults, but also children have to undergo such a procedure as an ultrasound examination of the heart. Very often, in addition to the conclusion, parents are interested in all the normal indicators in the functioning of their child’s heart. Let's talk about heart ultrasound standards together.
What can be seen on an ultrasound
A diagnostic method such as cardiac ultrasound (cardiac ultrasound) is an accessible and informative study in pediatric practice. With the help of a sensor and a device, there is an excellent opportunity to “look” at the heart without violating the integrity of the body.
Using cardiac ultrasound, not only anatomical but also physiological parameters of the heart are assessed: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), left atrium diameter (LA diameter), right atrium (RA) thickness, right ventricle (RV), interventricular septum thickness (thickness of the IVS), ejection fraction (EF), blood flow velocity in the valve (blood flow velocity in the PA valve), etc.
Normal indicators differ depending on the age and body weight of the child. Using this method, a pathology can be diagnosed that the doctor suspected or could not notice using an electrocardiogram, auscultation, palpation, percussion and general examination.
Cardiac ultrasound can diagnose:
- (CHD): patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), IVS defect, mitral valve defects, aortic valve (AV);
- acquired heart defects;
- nature of noise;
- rhythm disturbances;
- minor cardiac anomalies: open foramen ovale, abnormally located chord of the left ventricle, etc.;
- enlargement of the heart chambers;
- hyper-, hypotrophy of the heart;
- blood clots in the cavities of the heart chambers;
- myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis;
- neoplasms.