There are many diseases that cause congestion in the lungs. This pathological process is characterized by a violation of the outflow of blood from the venous vessels of the lungs to the heart. Thus, oxygenation of the entire body is disrupted due to insufficient supply of oxygen-enriched blood to the systemic circulation.
In order to compensate for the pathological condition, the body increases blood flow through the pulmonary arteries, which leads to worsening congestion. Such mechanisms are a consequence of pathologies accompanied by heart failure.
How does blood stagnation manifest in the pulmonary system?
Few people know that pulmonary congestion is such a dangerous condition that can progress to pulmonary edema at any time.
Liquid accumulates in the venous network, interfering with gas exchange and gradually leaking into the interstitial space.
The patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- 1. Shortness of breath (depending on the severity of the process, it is determined after physical exertion or even at rest);
- 2. Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, fingertips, which gradually spreads throughout the body;
- 3. Cough and moist wheezing without sputum (or with sputum, but difficult to separate);
- 4. Blood pressure disorders;
- 5. Problems with heart rhythm;
- 6. Constant weakness (during stagnation of the lungs, the organs are not sufficiently supplied with oxygen, which is why the whole body suffers);
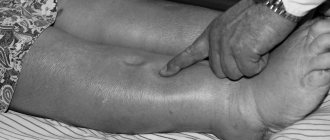
- 7. The formation of swelling in the legs, which gradually rises higher.
The patient has a history of pathology of the cardiovascular system, which goes into the stage of decompensation, causing complications. In the absence of timely treatment, edema of the pulmonary tissue begins to develop, which is accompanied by suffocation, severe cyanosis , abnormal pressure and other life-threatening symptoms.
Lung congestion in the elderly: symptoms and treatment
The forced recumbent state of elderly patients, cardiac pathology leads to stagnation of blood in the small pulmonary circle in the circulatory system, in the venous outflow. If treatment is not started in time, pulmonary edema may occur, which can result in death.
Pulmonary congestion is a life-threatening condition that is associated with insufficient ventilation of the lung tissue as a result of stagnation of blood in the lungs. Often stagnation is caused by forced inactivity of older people, chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Causes of congestion
Along with elderly people over 60 years of age, those at risk for pulmonary pathology include patients who have undergone operations, injuries, and those in the terminal stage of oncology. According to statistics, death occurs from stagnation in more than half of cases. Especially if the stagnation is caused by a condition such as pulmonary embolism.
The forced recumbent state of elderly patients and concomitant cardiac pathology leads to the development of cardiopulmonary failure, i.e. Blood stagnation occurs in the small pulmonary circle in the circulatory system and venous outflow is disrupted.
The physiological mechanism is that first the venules expand, which causes compression of the pulmonary structures, then the transudate finds its way into the intercellular space and edema occurs.
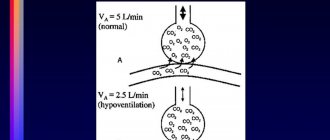
All this disrupts gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen cannot enter the blood in sufficient quantities, and carbon dioxide cannot be removed from the body.
Thus, impaired pulmonary ventilation and physical inactivity in the elderly are the main factors in the development and progression of stagnation.
Under the influence of microorganisms, for which stagnation is a favorable environment for reproduction, pneumonia (pneumonia) begins.
At the sites of fibrous tissue formation, pneumosclerosis occurs, affecting the structure of the pulmonary alveoli and bronchi. If treatment is not started in time, pulmonary edema may occur, which can result in death.
The disease may also be associated with heart failure, under the influence of the following factors:
- cardiomyopathy, pathology of the heart structure;
- hypertensive crisis;
- renal failure and vascular sclerosis;
- poisoning with chemicals through the respiratory system, taking medications, injuries.
Symptoms of stagnation
Initially, symptoms are similar to pneumonia. In many cases, early diagnosis is difficult. Along with the examination and listening to breathing, body temperature is measured, blood tests are taken and an x-ray of the lungs is taken.
Both diagnosis and treatment, as well as the prognosis of stagnation, depend on how the body is able to cope with pathogenic microflora.
In cases with reduced functions of the immune status, the disease can occur as early as the 3rd day.
Elderly people are susceptible to congestion after a few weeks and its symptoms are as follows:
- the temperature background is stable, rarely outside the normal range;
- rapid breathing with symptoms of tachycardia;
- the sick person speaks intermittently, feels anxious, and breaks out in a cold sweat;
- a cough appears with exudate, then with blood, bloody foam;
- patients complain of increased fatigue and weakness, it is difficult for them to lie on a low pillow (when sitting, the symptoms of shortness of breath gradually disappear);
- upon examination, the skin is pale, the nasolabial triangle is bluish in color, there are signs of swelling of the lower extremities;
- Pleurisy and pericarditis may occur against the background of hypoxia and pathological processes of insufficiency.
If the first symptoms of respiratory failure associated with the lungs appear, then urgent medical attention is needed.
Treatment approaches
At any stage of the disease, treatment is best done in an inpatient setting. In difficult cases - in the intensive care ward or in the intensive care unit. To increase breathing volume, an oxygen mask or artificial respiration apparatus is prescribed.
During hospitalization, the patient is prescribed an X-ray of the lungs, an ECG, and an ultrasound of the heart. A clinical blood test and biochemistry show signs of an inflammatory process: an increase in ESR, leukocytes, a positive C-reactive protein reaction.
Establishing the cause of stagnation should be the main focus of therapy. If the symptoms are caused by problems with heart failure, then the attacks are stopped and a complex of cardiotherapy is prescribed.
Regardless of the source of the disease in the lungs, a group of antibacterial therapy is prescribed to suppress the pathogenic effects of microbes on the lung tissue. To these are added agents that reduce the thickness of sputum.
It is important to treat a cough, not suppress it. Treatment is carried out using mucolytics, herbal preparations, extracts of coltsfoot, plantain, thyme, which are recognized as the most effective phytotherapeutic agents. Diuretics and vitamins are required to enhance the immune response to pathogenic microflora in an elderly person.
How to deal with the problem
At the first symptoms of congestion in the lungs, you should contact your local physician to prescribe intensive treatment. The best option is to treat the underlying disease before the onset of decompensated complications, but patients often ignore the problem and pulmonary edema.
Attempts at self-medication and uncontrolled use of diuretics pose a direct threat to the patient’s life, as they can provoke acute coronary insufficiency.
Treatment of congestion in the lung tissue should be carried out by a professional doctor.
Congestion in the lungs is treated conservatively, trying to bring the patient’s body into a compensated state. For this purpose, drugs are used that correct heart rate, blood pressure and increase myocardial contractility. Diuretics are also used to remove excess fluid, but they are prescribed very carefully and are not used for low blood pressure.
It is much easier to combat pulmonary congestion in the initial stages of its development. In addition, some populations are more difficult to treat. For example, in older people, congestion in the lungs develops more rapidly and takes much longer to go away.
In severe cases, doctors must use resuscitation protocols to maintain adequate blood oxygenation and cardiac function. Unfortunately, often stagnation of blood in the lungs quickly transforms into edema and ends in death.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Pulmonary congestion is a severe pathological disorder in which fluid accumulates in the alveolar region. Regardless of the causes and nuances of the occurrence of the disorder, such changes pose an increased danger to the life and health of the patient, due to a violation of the general gas exchange, that is, breathing.
The occurrence of such a failure may indicate the development of many pathological processes that carry increased risks.
Treatment and prevention
As noted earlier, it is imperative to treat pulmonary congestion immediately after diagnosis.
Regardless of the stage of the disease, it is best to use hospital treatment, and in case of any complications, resuscitation measures are used, in particular, using an artificial respiration apparatus and oxygen masks. The patient is obliged:
- undergo an ECG;
- take an x-ray of the lungs;
- undergo an ultrasound of the heart.
Inflammation is determined by biochemistry or a local blood test.
Therapy
If the nature of the disease is infectious, then a complex of antibacterial therapy is used. It effectively reduces the influence of microbes on lung tissue, reducing inflammation and thereby relieving congestion.

In addition, drugs are prescribed to thin sputum clots (Bromhexine, ACC). Treatment of congestion in the lungs is carried out, in addition to the use of mucolytics, with the use of herbal extracts (plantain, coltsfoot, thyme), which ensure normalization of blood flow in the lungs and reduction of inflammation.
It is also necessary to include vitamins that increase immunity in the treatment regimen (Vitrum, Supradin). Therapy is often supplemented by the prescription of diuretics to relieve swelling and normalize fluid metabolism in the body. They ensure the removal of toxins and pathogenic organisms from the body that cause stagnation.
If a person suffers from congestion in the lungs, which results in weakening of the heart muscles, then it is imperative to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and undergo the full course of treatment prescribed by a cardiologist or pulmonologist. After all, the result of untreated congestion in the lungs can be cardiac arrest.
Warning
In addition to medicinal methods, dietary nutrition based on the exclusion of salt from the diet will help to reduce the risk of developing further complications. This will help reduce swelling and normalize the flow of blood and lymph in the lung tissue
It is very important to include foods with plenty of carbohydrates, vitamins and protein in your diet. This will provide the necessary vital energy to the cells
This helps stop the development of stagnation processes. If a person does not have the strength to do the exercises himself, then he needs to turn to loved ones for help. The patient should not be in one position for a long time, because this will only complicate breathing and the functioning of the chest organs.
Basic exercises can be taught by a specialist in physical therapy and breathing exercises.
It is very important to breathe correctly; to develop respiratory function, you can periodically inflate a balloon, breathe into a glass of liquid using a cocktail straw
The listed exercises help enrich the respiratory system with the required amount of oxygen. Another benefit is the increased movement of the chest, which prevents congestion. The patient is recommended to be as active as possible to combat pulmonary congestion at any stage of the disease.
Treatment may also include:
- mustard plasters;
- medical banks;
- physiotherapy;
- tapping massage.
It is also recommended to add hot tea with honey or lemon to the course of therapy. It perfectly expands and strengthens the walls of blood vessels
Another important property of this drink is to counteract the appearance of phlegm.
Congestion in the lungs is not a death sentence. Drug therapy, as well as increased breathing and minor physical exercises can improve blood flow in problem areas of the lungs and relieve symptoms of congestion.
Sources of development of pathology
Congestive processes in the alveolar part of the pulmonary system can be a consequence of various pathological conditions of the human body. However, the result of this state of the pulmonary system is serious oxygen deficiency and a general decrease in respiratory function with the gradual development of complications and chronic disease.
Important! What is pulmonary congestion? This is an extremely dangerous condition associated with a violation of the ventilation process of the lung tissue against the background of blood stagnation.
The most common diseases that cause congestion in the lungs include:
- presence of extensive traumatic injuries;
- inhalation of volatile toxic compounds;
- kidney disease (narrowing of the arteries or failure);
- use of certain medications;
- staying at high altitude for a long period;
- ischemic heart disease;
- stenosis of the mitral or aortic heart valve;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocardial infarction.
In this case, the most likely of them are disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Separately, it should be noted that an increased likelihood of developing such a pathological condition is present in those individuals who, for one reason or another, are limited in their own mobility.
Due to the lack of regular physical activity, venous stagnation of blood occurs throughout the body, which further leads to a decrease in the level of blood circulation in general and gradually destroys most organs and systems. Stagnant blood in the pulmonary circulation leads to the leakage of its plasmatic component into the alveolar part and the gradual accumulation of fluid.
How to treat
If any symptoms appear, you need to go to the hospital. Which doctor should I see? Phlebologists, urologists and surgeons are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of such ailments.
After the examination, tests are prescribed, as well as instrumental examination - ultrasound, CT, MRI, phlebography with a contrast agent.
Often, it may be necessary to undergo several studies to obtain a more reliable picture of the disease.
Sometimes it happens that the cause of the pathology is not related to neoplasms or other diseases, in which case preventive measures and treatment with medications that help improve blood supply are sufficient.
Options for other reasons:
- Hormone therapy, surgery - if the cause is tumors.
- Physical activity, antibacterial or antiviral therapy - if the cause is a sedentary lifestyle.
- Exercise therapy – due to physical inactivity or wearing clothes that cause discomfort.
- Treatment methods for venous stagnation in different organs depend on the location of the anomaly. Therapy includes several methods.
- Pelvic plethora. Mostly medications (drugs, suppositories) are used, but sometimes surgical intervention is still necessary.
- Congestion of the brain is eliminated by lowering pressure and reducing swelling. They use pills, injections, neck massage, and electrical stimulation.
- Pulmonary stasis is mostly treated with medication; in case of serious complications, surgery is performed. Disability may be assigned.
- Kidney hyperemia requires the prevention of infectious complications and pain relief. In this regard, it is imperative to take antibacterial drugs that have the ability to relieve pain. Blood flow is restored by surgery.
- Stasis of the lower extremities is treated with diuretics, venotonics, and ointments. When treating leg stasis, it is important to use compression stockings, or tights. A contrast shower and daily walking come to the rescue. To alleviate the condition, you can raise your legs.
The best prevention of venous blood stagnation is a healthy lifestyle. Namely: moderate, regular exercise, healthy eating, giving up bad habits.
Signs of pathological disorders and their symptomatic indicators
Symptomatic indicators of congestive changes in the pulmonary system may vary depending on the characteristics of the condition that has arisen and its root cause. The presence of mild congestion, the main manifestation of the pathology is the presence of shortness of breath.
Attention! In the case of deeper lesions, an unproductive cough with a possible admixture of blood and a lack of air in the lungs to pronounce complete sentences appear - shortness of breath and coughing may occur after voicing a couple of words.
Among the general manifestations of fluid stagnation in the pulmonary system, it is possible to distinguish the following number of signs:
- increased swelling of the lower extremities, regardless of the degree of load.
- general pallor of the skin.
- increased anxiety and restless behavior.
Also, stagnant processes are characterized by difficulty breathing in a supine position. As a result, it is difficult for a person to fall asleep on a flat surface - a significant elevation of the upper body is required, for example, several pillows or raising the top of a medical bed.

Important! Increased oxygen deficiency, leading to frequent loss of consciousness, cannot be ruled out.
In addition, there may be a symptom such as gurgling and wheezing when breathing, which are clearly expressed and audible without the use of a stethoscope.
Elderly patients may experience other manifestations of pathological disorders:
- Increased fatigue and weakness, the symptoms of which gradually decrease in a sitting position.
- General pallor of the skin with severe hyperemia in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
- Broken sentences, cold sweat and constant anxiety.
- The presence of tachycardia in combination with increased respiratory rate.
- Manifestations of pleurisy and pericarditis due to oxygen deficiency.
- Stable body temperature, often within normal limits.
The manifestation of such symptoms requires qualified diagnostics to determine the pathological condition and prescribe the optimal treatment method. Reduced immunity is the main reason for visiting a specialist, since the disease in this case can develop rapidly.
At the initial stage of development, diagnosing pulmonary congestion is complicated by the fact that the symptomatic indications are very similar to pneumonia. For this reason, patients with such symptoms require in-depth diagnosis using laboratory tests and instrumental studies to differentiate the diagnosis.
The video in this article will introduce readers to the main causes and possible complications of the development of pathology.
Types of blood stagnation: classification
Pathology can occur in the pelvis, brain, lungs, kidneys or lower extremities.
Specification of the disease by place of development:
- Pelvic plethora. Happens quite often. Manifestations can appear in both sexes. Involves problems with the genital organs, infertility, painful sensations in the lower abdomen. In pregnant women, it provokes premature birth, which can become a factor in the underdevelopment of the child or his death.
- Congestion of the brain. Develops due to disorders outside the skull or inside it. The chronic form of stasis provokes edema and increased intracranial pressure due to oxygen starvation.
- Lung stasis. The lung tissues become denser and take on a brown tint, and swelling appears. Complications such as tissue sclerosis are possible.
- Kidney hyperemia. The disease causes hardening of the kidneys and changes in their size (enlargement). Kidney spasm is likely due to poor blood flow.
- Stasis of the lower extremities. It progresses slowly, causing deformation of blood vessels, the consequences of which are problems in the circulatory system.
Degrees of the disease:
- Chronic degree. At the beginning of development, the pathology cannot be detected; it is a rather sluggish process. The patient’s well-being worsens over time: severe fatigue, swelling, and soreness occur.
- Acute degree. Promotes blockage of blood vessels, serious condition of the patient. The affected area begins to hurt and swell, the temperature of the skin there quickly drops, and the skin turns blue. Also, due to hemorrhage, spots and blisters are possible. If you do not provide help, negative changes become irreversible.
Generalized diagnostic methods
Even with partial manifestation of symptomatic indicators of congestive processes in the pulmonary system, you should contact a medical institution for qualified help. The issue of this disease is primarily dealt with by a therapist, who can subsequently refer you for consultation and treatment to another specialist, depending on the results of the diagnostic procedures performed.
During the initial examination, the doctor conducts a general examination and collects anamnesis from the patient. At this stage of the examination, general signs of a disorder are immediately revealed - pale skin, the presence of wheezing in the pulmonary cavity, and others.
After the specialist makes a primary diagnosis, the patient is sent to undergo a series of hardware studies and tests:
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiogram and echocardiogram;
- blood chemistry;
- oximetric blood test;
- general blood analysis.
It is necessary to undergo all the indicated procedures as soon as possible, since changes in the lungs can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases and a decrease in the overall resistance of the immune system. The consequences can be irreversible, the cost of which is the patient’s life.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor can determine the general condition of the patient, identify the disease that led to stagnant processes and prescribe the optimal treatment option.
Features of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients
The occurrence of pneumonia in bedridden patients is usually caused by bed rest, when a person is forced to remain motionless for a long time. At risk are people who have suffered a stroke, traumatic brain injury, those suffering from cardiovascular pathology and those who, due to their incapacity, are forced to stay in bed for a long time.
In the category of elderly patients, the stagnant form can be detected even with active movement, and this is due to the fact that in old, weakened people the diaphragm stops contracting, and breathing becomes shallow. And this is already fraught with congestion in the lungs.
Symptoms of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients
At first, the disease develops without any characteristic signs. Chills, cough and fever, characteristic of focal and lobar forms, are absent. At the same time, the patient may complain of weakness, a feeling of incomplete inspiration and shortness of breath.
All this makes it extremely difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, since malaise in bedridden patients is not a rare deviation. Therefore, if the listed symptoms persist for a long time, the patient should undergo an X-ray examination, because often recognition of the disease occurs already at the stage of the appearance of sputum and wheezing in the lungs. Untimely attention to congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients leads to a long-term struggle with it.
Treatment of pneumonia in bedridden patients with medications
In order to prevent the development of complications, treatment of congestive pneumonia should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician. Complication means the penetration of a bacterial infection.
For the treatment of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients, a specialist prescribes antibiotics and procedures for pumping out accumulated water. Complex action drugs have a beneficial effect on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and diuretics accelerate the removal of fluid from the body.
Fluid that has accumulated in large quantities in the lungs is pumped out through a puncture made in the chest. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not cause pain, since the muscle layer between the ribs is very thin.
Relief occurs almost immediately - the patient begins to breathe deeply. If it is impossible to transport the patient to a medical facility, the puncture can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Remember that when the disease is congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients, the treatment prognosis is favorable if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
How is the treatment carried out?

The main method of eliminating congestive processes in the pulmonary system should be aimed at treating the primary disease, especially for cardiovascular pathologies. The duration of such therapy can take a fairly long period of time and require a large number of procedures.
To treat a congestive process in the lungs that has arisen against the background of cardiovascular pathologies, the following series of drugs are used as part of a therapeutic course:
| Treatment of pulmonary congestion | |
| Drugs | Action |
| Loop diuretics | This series of drugs allows you to reduce the total amount of physiological fluids in the body, which reduces the load on the heart muscle and vascular walls. The result of use is not only easier blood circulation, but also a decrease in the amount of fluid in the pulmonary cavity. |
| Beta blockers | They allow you to reduce the heart rate, increase the resistance of blood vessels to stretching and increase the tone in the pulmonary system. As a result of use, the general condition of the circulatory system improves and the alveolar part of the lungs is cleansed. |
| Nitrate drugs | These drugs help reduce the overall load on the heart in case of myocardial damage and coronary artery disease, and also reduce the body’s system-wide need for oxygen. This allows you to level out oxygen deficiency. |
| ACE inhibitors | This series of medications is used for manifestations of heart and kidney failure, and also as an antihypertensive agent, which reduces the load on blood vessels and prevents the filling of the pulmonary alveoli with blood plasma. |
Causes of venous congestion
As we know, the reverse outflow of blood ensures heart contractions, an impulse arises with the help of which blood moves throughout the body. But there is additional stimulation of the outflow of venous blood, namely the contraction of the calf muscles, abdominal muscles, it is worth noting that pressure on the foot also helps to stimulate the outflow of blood and eliminate blood stagnation.
Thus, if your muscles are not developed enough or you lead a sedentary lifestyle, then the risk of developing this pathology increases.
Venous stasis entails multiple disorders, regardless of the location of the stagnation, let's look at the general disorders:
- Slowing blood circulation.
- The pressure relationship between the venous and arterial veins is disrupted.
- In places where stagnation is localized, a strong decrease in local temperature is observed.
- Veins and capillaries enlarge significantly, literally swelling before your eyes.
- Stagnation of lymph is noted.
In such a situation, a large amount of plasma threatens with big problems. It begins to compress the nearest organs and flow into various cavities. Then the deformation of the walls of blood vessels and an increase in pressure begin; accordingly, red blood cells begin to move beyond the boundaries of the vessels, filling the free space.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid the development of congestive pulmonary processes, patients who have been on bed rest for a long time need to make the maximum available movements and resort to physical activity (physical activity).
The main preventive rules are:
- Change your body position at least every 4 hours - roll over or go into a sitting position.
- You should not sleep on a flat surface or low pillows, as this weakens respiratory function.
- Self-breathing training using a balloon or straw with a glass of water.
- Breathing exercises from the exercise therapy course, which will increase the activity of the diaphragm.
- Massage procedures for the chest, especially vibration massage to cleanse the cavities of the lungs.
- Drink hot drinks if the disease allows this possibility, for example, tea with lemon and honey.
- It is necessary to follow the principles of a high carbohydrate and protein diet.
If the patient is unable to exercise or move around in any way, the help of nursing staff should be sought. The initial stage of stagnant processes can only go away with the use of physiotherapeutic methods of exercise therapy, that is, physical activity.

Prevention for people with the possibility of an active lifestyle is:
- Quitting alcohol, smoking and other harmful habits.
- Following a healthy diet, which means avoiding fatty foods and eating plenty of vegetables.
- Timely treatment of diseases, especially of the respiratory and circulatory systems.
- Regular medical examinations to identify disorders of the internal organs and their prerequisites.
- Physical activity, primarily of a general strengthening nature.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air, which will provide your lungs with regular exercise.
Regardless of the reasons for the development of congestive pathological processes in the pulmonary system, the main symptomatic indicators are similar. In the absence of qualified assistance, conditions such as emphysema or bullae in the cavity of the lungs may gradually develop, which in turn leads to complications and long-term treatment.
Preventive procedures for patients in a supine state are the optimal method for preserving and restoring respiratory functions than treating pulmonary congestion.
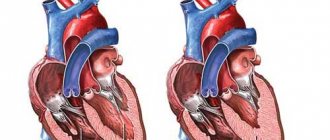
Hypostasis, or congestion in the lungs, is a consequence of impaired circulation in the pulmonary circulation . In left ventricular heart failure, the ability of the right ventricle to pump blood to the lungs remains unchanged, while the left ventricle cannot cope with the volume of blood coming from the lungs. As a result, a significant part of the blood moves from the systemic circulation to the pulmonary circulation. An increase in blood volume leads to an increase in pressure in the vessels. If this pressure exceeds the level of plasma oncotic pressure (28 mm Hg), blood begins to exit into the lung tissue through pores in the walls of the capillaries.
Stagnation of blood leads to chronic respiratory failure. In severe cases, cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema develop, which can result in death within a few hours.
Venous congestion, what is it, types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Venous stagnation of blood is a disease in which blood flow in them is complicated, while arterial blood flows without problems. It happens due to poor elasticity of blood vessels and high blood density. There are several options for naming this disease: venous stasis, passive hyperemia, venous hyperemia.
The main factors for the occurrence of pathology:
- Injuries. Due to severe blows or bruises, hematomas often appear at the sites of hemorrhages. Vessels that have fused incorrectly often contribute to impaired blood flow, which leads to hyperemia.
- Sedentary lifestyle. When a person sits in one place for too long, intracellular pressure begins to increase in his pelvic organs, and if there is thickening of the blood, stagnation may develop, leading to health problems.
- Neoplasms. Large tumors affect nearby vessels and tissues, compress them, thereby disrupting blood circulation, or rather its outflow in a specific area.
- Lack of any physical activity. If you don't exercise, your body muscles will atrophy. Because of this, there is a lack of oxygen, which results in stagnation in the blood vessels of the lungs.
- Vein thrombosis. Under certain conditions, a blood clot attaches to the walls of blood vessels, thereby preventing the normal outflow of blood.
- Wearing narrow shoes and tight-fitting clothing. It is necessary to wear clothes and shoes of the appropriate size, because tightening and squeezing are also the culprits of circulatory disorders.
Types of blood stagnation: classification
Pathology can occur in the pelvis, brain, lungs, kidneys or lower extremities.
Specification of the disease by place of development:
- Pelvic plethora. Happens quite often. Manifestations can appear in both sexes. Involves problems with the genital organs, infertility, painful sensations in the lower abdomen. In pregnant women, it provokes premature birth, which can become a factor in the underdevelopment of the child or his death.
- Congestion of the brain. Develops due to disorders outside the skull or inside it. The chronic form of stasis provokes edema and increased intracranial pressure due to oxygen starvation.
- Lung stasis. The lung tissues become denser and take on a brown tint, and swelling appears. Complications such as tissue sclerosis are possible.
- Kidney hyperemia. The disease causes hardening of the kidneys and changes in their size (enlargement). Kidney spasm is likely due to poor blood flow.
- Stasis of the lower extremities. It progresses slowly, causing deformation of blood vessels, the consequences of which are problems in the circulatory system.
Degrees of the disease:
- Chronic degree. At the beginning of development, the pathology cannot be detected; it is a rather sluggish process. The patient’s well-being worsens over time: severe fatigue, swelling, and soreness occur.
- Acute degree. Promotes blockage of blood vessels, serious condition of the patient. The affected area begins to hurt and swell, the temperature of the skin there quickly drops, and the skin turns blue. Also, due to hemorrhage, spots and blisters are possible. If you do not provide help, negative changes become irreversible.
General signs
A dull, long-lasting headache that may get worse in the morning or while drinking alcohol.
The skin and mucous membranes may turn blue, which also becomes more noticeable in the morning.
Congestion in the ears, fainting, short-term blindness, and mental problems are possible.
In the acute stages of the manifestation of pathology, a sick person is able to take a vertical position with great difficulty.
Consequences
Due to excessive filling of the veins, they begin to bleed into nearby tissues; in the legs and pelvic veins, these changes can provoke vein occlusion.
Due to insufficient saturation of blood vessels with oxygen, tissue necrosis begins.
If left untreated, there will be a failure in the saturation of the organs, their ability to function normally will decrease, and a tendency to a long inflammatory process will develop.
When veins dilate over a long period of time, their walls stretch, and as a consequence of this, hypertrophy of the muscular layer occurs. If the cells and tissues of the body experience oxygen starvation for a long time, irreversible atrophic and sclerotic changes occur.
You can see congestive processes in organs and tissues, which is a deviation in the functioning of the heart, and patients can die from heart failure.
Pelvic plethora
This pathology does not have typical symptoms. Usually this disease can be identified only by a complex of manifestations:
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- prolonged, aching pain in the pelvic area (can radiate to the thigh, lower back);
- numbness in the arms or legs;
- Over time, the pain becomes sharp and unexpected.
Congestion of the brain
An insignificant course of the disease provokes:
- depressed, drowsy, lethargic state, apathy, can suddenly change to euphoria, mental excitement;
- fatigue, headache, dizziness;
- blueness of the skin on the face, swelling of the jugular veins, superficial vessels on the head;
- vomiting;
- sleep disturbance, emotional instability, irritability.
And due to severe stagnation, the brain swells, convulsions and a coma begin.
Lung stasis
- weak cough, sometimes with bloody patches;
- breathing quickens, dull pain appears in the chest;
- slow, intermittent speech;
- increased weakness;
- shortness of breath when lying down;
- cold sweat is released at any time of the day;
- pale skin, swelling in the legs.
Kidney hyperemia
It is provoked by existing chronic heart failure, which makes it difficult to determine.
Stasis of the lower extremities
- heaviness in the legs;
- noticeable swelling of veins, nodes;
- the skin on the affected areas turns blue;
- interruptions in the sensitivity of the limbs;
- dry skin;
- excessive fatigue, especially at the end of the working day.
How to treat
If any symptoms appear, you need to go to the hospital. Which doctor should I see? Phlebologists, urologists and surgeons are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of such ailments.
After the examination, tests are prescribed, as well as instrumental examination - ultrasound, CT, MRI, phlebography with a contrast agent.
Often, it may be necessary to undergo several studies to obtain a more reliable picture of the disease.
Sometimes it happens that the cause of the pathology is not related to neoplasms or other diseases, in which case preventive measures and treatment with medications that help improve blood supply are sufficient.
Options for other reasons:
- Hormone therapy, surgery - if the cause is tumors.
- Physical activity, antibacterial or antiviral therapy - if the cause is a sedentary lifestyle.
- Exercise therapy – due to physical inactivity or wearing clothes that cause discomfort.
- Treatment methods for venous stagnation in different organs depend on the location of the anomaly. Therapy includes several methods.
- Pelvic plethora. Mostly medications (drugs, suppositories) are used, but sometimes surgical intervention is still necessary.
- Congestion of the brain is eliminated by lowering pressure and reducing swelling. They use pills, injections, neck massage, and electrical stimulation.
- Pulmonary stasis is mostly treated with medication; in case of serious complications, surgery is performed. Disability may be assigned.
- Kidney hyperemia requires the prevention of infectious complications and pain relief. In this regard, it is imperative to take antibacterial drugs that have the ability to relieve pain. Blood flow is restored by surgery.
- Stasis of the lower extremities is treated with diuretics, venotonics, and ointments. When treating leg stasis, it is important to use compression stockings, or tights. A contrast shower and daily walking come to the rescue. To alleviate the condition, you can raise your legs.
The best prevention of venous blood stagnation is a healthy lifestyle. Namely: moderate, regular exercise, healthy eating, giving up bad habits.
: what is venous stagnation and why is it dangerous?
Source: //venaprof.ru/venoznyy-zastoy/
Causes of lung congestion
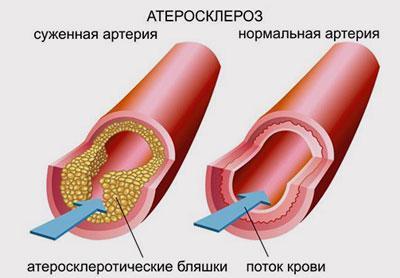
Lung congestion most often occurs with congenital and acquired pathologies of the cardiovascular system, such as:
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocardial infarction;
- atherosclerosis;
- pericarditis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- stenosis of the mitral or aortic valves;
- arterial hypertension.
Symptoms

There are two stages of pathology. During the first, or interstitial, stage, blood plasma moves into the lung tissue. In the second, or alveolar, stage, which is life-threatening, swelling spreads to the alveoli.
The first sign of the disease is shortness of breath, which occurs after physical exertion, stress, or large meals . The respiratory center of the medulla oblongata responds to a decrease in oxygen content in the blood by a reflex increase in the frequency and intensity of respiratory movements.
With concomitant heart failure, patients are concerned about:
- feeling of chest tightness,
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle,
- difficulty in inhaling,
- characteristic crunching sound at the end of inhalation.
In the absence of timely treatment, shortness of breath increases. Filling of the lung tissue with fluid leads to a decrease in the volume of inhaled air. The patient does not have enough breath to utter a long sentence. Attacks of suffocation occur with minor physical effort and are accompanied by panic and fear of death. Possible loss of consciousness.
The interstitial phase of stagnation in the lungs is replaced by the alveolar phase with physical or emotional stress or increased blood pressure.
The feeling of lack of air increases in the lying position . A person begins to sleep sitting, using 2-3 pillows. A cough appears. At the alveolar stage of the disease, exudate, foam with blood, or blood is released during coughing.
In heart failure, compensatory reflex mechanisms are activated. The baroreceptors of the heart respond to increased atrial pressure by stimulating the sympathetic nerve centers. Under the influence of the sympathetic nervous system, the heart rate increases. At the same time, the pulse in the peripheral vessels remains weak.
Symptoms of hypostasis may vary depending on the causes that caused them.
Why does stagnation occur?
Doctors say the main factor in the development of the disorder is an incorrect, sedentary lifestyle. Modern man moves little and is nervous a lot, exposing his body to constant emotional stress. Perhaps this is why the diagnosis: venous congestion of cerebral vessels has ceased to be a rarity and is being diagnosed more and more often. Like varicose veins.
Causes:
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- hormonal imbalances;
- atherosclerosis;
- aneurysm;
- osteochondrosis, when compression of blood vessels occurs;
- infections and viruses for which treatment was insufficient;
- circulatory disorders in the neck;
- tumors;
- strokes;
- cardiac ailments: heart attacks, myocarditis, ischemia;
- dropsy;
- head injuries (they cause swelling and hematomas);
- hypertension;
- uncontrolled or long-term use of hormonal drugs (for example, contraceptives);
- frequent childbirth;
- excess body weight;
- physical inactivity;
- pulmonary diseases: asthma, bronchitis, tuberculosis, emphysema;
- the child suffers due to congenital pathologies;
- genetic predisposition;
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a doctor based on the patient’s complaints, examination, auscultation and additional examination data.
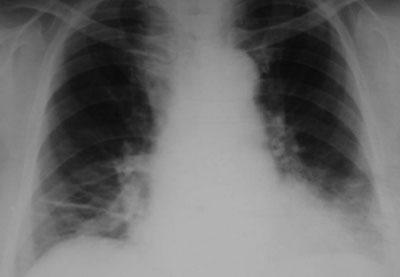
To identify congestion in the lungs, an x-ray is taken. The expansion of the main trunk of the pulmonary artery is clearly visible in the image. At the same time, peripheral vessels remain narrow. When the capillary pressure rises above 20 mm Hg. Art. pulmonary-diaphragmatic Kerley lines appear. Their presence is considered a prognostically unfavorable sign. The spirogram shows restrictive disturbances in pulmonary ventilation.
To assess the functioning of the heart, electrocardiographic and phonocardiographic studies, catheterization of the heart chambers with measurement of intracavitary pressure are performed. Indirect signs of cardiovascular pathologies are:
- swelling of the limbs,
- increase in liver size,
- liver pain on palpation,
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Laboratory examination of sputum reveals alveolar macrophages containing phagocytosed hemosiderin. Hyaline casts, protein, and red blood cells appear in the urine. The oxygen content in the blood is reduced, the carbon dioxide content is normal or slightly reduced .
Treatment

Diuretics are used to reduce the volume of circulating blood. This helps prevent blood vessels from stretching. To avoid infectious diseases of the lungs, regardless of the causes of stagnation, antibiotics are prescribed, and mucolytics are prescribed to thin the sputum.
In case of acute pulmonary edema, the patient is immediately hospitalized. To prevent hypoxia, he is given pure oxygen to breathe. In a hospital setting, fluid is artificially removed from the lungs.
It is recommended to treat pulmonary congestion in elderly people and patients forced to remain in a horizontal position for a long time using physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment methods
Treatment of congestion in the lungs comes down to two options:
- Surgical intervention.
- Drug therapy.
It is necessary to resort to surgery in cases where the disease is caused by an aneurysm or heart defects. The main goal of any treatment is to eliminate the root cause of the disease, which makes it possible to eliminate its consequences, especially if you consult a doctor in a timely manner.
When selecting medications, you cannot act independently; the correct combination of drugs must be selected by a doctor. Drug therapy includes a whole range of drugs, the ratio of which is determined by a specialist based on diagnostic results.
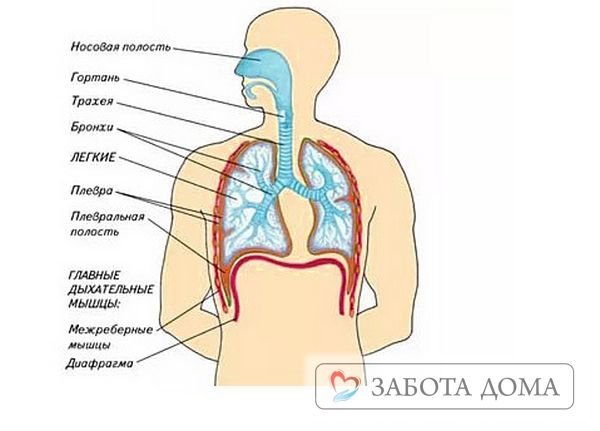
If pulmonary edema has acquired life-threatening proportions, the patient is immediately hospitalized. In a hospital setting, fluid is pumped out of the lungs and the patient is allowed to breathe pure oxygen.
Elderly people or bedridden patients, who are especially susceptible to the development of congestion in the lungs, are recommended to undergo physiotherapy procedures. This will artificially maintain blood circulation in the lung area.