Main symptoms:
- Restlessness
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Heartache
- Impaired consciousness
- Fainting
- General swelling
- Dyspnea
- Low blood pressure
- Heart failure
- Blueness of the skin
- Weak pulse
- Liver enlargement
- Cardiopalmus
- Cold sweat
- Feeling of fear
Heart rupture is a violation of the integrity of its tissues, which occurs due to myocardial infarction. There is an opinion among people that it is possible for a heart to break due to fear or severe fright, but this is not so. The heart is a strong muscle that can become damaged if its original form is compromised.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention
It is believed that the heart is the most important organ in the circulatory system, on which the delivery of blood to the internal organs depends. If something happens to it, then the organs suffer, and in the most critical situations, especially when it ruptures, the person dies.
Rupture of the left ventricle of the heart is more often observed in older people, mainly women. In addition, people with diabetes, high blood pressure, and chronic ischemia suffer. The use of certain medications and untimely initiation of therapy during a heart attack provoke the formation of a scar, and this is the first “bell” that a heart rupture may occur during a myocardial infarction. Rupture of the vessels of the initial part of the aorta occurs due to vasculitis and deep atherosclerosis.
Etiology
The main causes of rupture of the aorta of the heart include:
- heart attack;
- traumatic chest injuries;
- inflammatory processes of the inner lining of the heart muscle;
- tumors;
- metabolic disorders;
- congenital heart defects.
The main factor in the rupture of the heart muscle is a change in its tissues, because a healthy organ is strong and elastic.
Most often, rupture occurs due to a heart attack. It is this that causes it in three percent of cases, and in half of the patients, heart rupture can occur on the first day of a heart attack.
During a heart attack, not only the right but also the left ventricle of the heart ruptures, because this section is subjected to the greatest load. In some cases, the septum between the ventricles ruptures. Usually, before a rupture, a person experiences a large infarction that covers most of the heart. The risk of rupture in the first fourteen days is very high.
Traumatic injury can occur during a motor vehicle accident, after being stabbed, or due to forceful impact in some sports.
Inflammatory processes, metabolic disorders and the occurrence of neoplasms have a strong impact on changes in the structure of the heart. The muscle becomes weaker and may rupture.
In addition to the obvious reasons, there are also predisposing factors, for example:
- Advanced age of a person. It should be noted that after fifty years all regeneration processes in the body become slower, in addition, many people already have signs of ischemic disease.
- Hypertension, which puts extra pressure on the heart.
- Inappropriate treatment for acute infarction.
- Wakefulness after a major heart attack. Usually the doctor prescribes bed rest, and the patient is forbidden to even get out of bed, because this requires additional stress on the heart.
- The patient is very thin. This condition slows down the formation of a heart attack scar, which can lead to rupture.
- The use of medications that contain hormones. Also, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should not be used: they slow down the formation of connective tissue too much.
The hereditary factor has not been established.
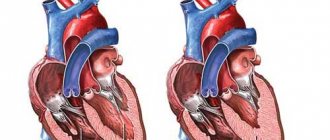
Rupture of the heart wall
What is a heart rupture and what causes it?
Cardiac rupture is a violation of the integrity of the walls of the heart. Most often it occurs as a serious complication of myocardial infarction (death of a section of the heart muscle due to the closure of a supply vessel), accompanied by high mortality. Heart rupture is recorded in 2-8% of patients with a heart attack. In most patients, there is a rupture of the wall of the left ventricle, less often of the right ventricle, and even less often of the interventricular septum (the partition between the left and right ventricles of the heart) and the papillary muscles (the internal muscles of the heart that ensure the movement of the valves).
Classification
Depending on the area of localization where the rupture occurred, as well as on the time of occurrence, two types of pathology are divided:
- external - a through defect occurs in the wall of the heart muscle, through which blood begins to enter the heart sac;
- internal - the structure of the internal organs of the heart is disrupted, such as the papillary muscles or the formation of a defect in the septum.
With an external rupture, the blood pressure in the heart muscle is too high, so if there is even the slightest violation of its integrity, it immediately rushes there. Due to the fact that the heart sac quickly fills, heart contractions are disrupted, even to a complete stop. The internal organs of the body do not receive the required amount of blood, the person goes into shock, which leads to death.
But internal breaks are a little easier. For example, a rupture of the papillary region must be urgently treated with surgery. In this case, a person can live with him for about fourteen days. Uncharacteristic movement of the valve leaflets after damage to the papillary muscles can provoke acute heart failure, which can be fatal. A rupture of the interventricular septum is accompanied by blood transfusion from one half of the organ to the other. This violation is also dangerous to human life.
Extensive heart attacks are dangerous because a rupture can occur in one moment - the person dies suddenly. If the pathology has not spread to the entire organ, then death is not instantaneous. Blood circulation deteriorates gradually, which is why this condition is called slow-flowing.
What other reasons can lead to heart rupture?
The causes of cardiac rupture may be the following:
- Heart injury. An accident can provoke a heart rupture if the driver hits his chest on the steering wheel, or a strong blow from an opponent during a single combat
- Anomalies of cardiac development. If there is a congenital thin section in the heart, it can rupture under minor loads
- Tumor lesion of the heart
- Endocarditis - inflammation of the inner lining of the heart - endocardium
- A dissecting aortic aneurysm is a rupture of the largest artery, the aorta, which leads to blood flowing between the layers of the aortic walls and dissecting them further.
- Infiltrative heart diseases. These include sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis, amyloidosis - diseases in which substances accumulate in the heart that should not normally be present.
Symptoms
The signs of cardiac muscle rupture depend on the area of myocardial damage, the development of hemopericardium, and the level of hemodynamic decrease. If the integrity of the pericardial wall is slightly compromised and blood enters the heart sac slowly, then the symptoms will increase gradually over several hours.
The patient experiences the following sensations:
- severe sharp pain in the heart and sternum;
- fear and anxiety;
- dyspnea;
- the skin begins to turn blue;
- swelling appears.
With the rapid appearance of signs of acute heart failure, the following appears:
- Thready pulse.
- Blood pressure drops sharply.
- Consciousness may change a little.
- Fainting.
- Pain in the right side, which indicates an increase in the size of the liver. This occurs due to stagnation of venous blood. Subsequently, swelling appears.
If the pathology develops slowly, then the person is worried, tries to take his usual medications, however, does not get any effect from it. The pain subsides a little, but later intensifies again.
In this condition, the symptoms are as follows:
- cold sweat;
- cardiopalmus;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure.
This condition is worsened by the fact that the heart arteries do not receive blood in the required quantity - cardiac oxygen starvation occurs. In this regard, the development of deficiency cannot be avoided.
An acute cardiac rupture disrupts the blood flow in the system, so the patient dies. Unfortunately, this happens in 90% of cases, so the ambulance team that arrives at the call can only ascertain the death of the patient from a broken heart.
What is a heart rupture and what causes it?
Cardiac rupture is a violation of the integrity of the walls of the heart. Most often it occurs as a serious complication of myocardial infarction (death of a section of the heart muscle due to the closure of a supply vessel), accompanied by high mortality. Heart rupture is recorded in 2-8% of patients with a heart attack. In most patients, there is a rupture of the wall of the left ventricle, less often of the right ventricle, and even less often of the interventricular septum (the partition between the left and right ventricles of the heart) and the papillary muscles (the internal muscles of the heart that ensure the movement of the valves).
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods for this pathology are as follows:
- Studying the medical history - when the pain occurred, general malaise, what caused the appearance of symptoms, the presence of traumatic injuries to the chest, and much more.
- The patient's lifestyle is studied - what diseases the person suffered in the past, what his relatives suffer from (we are talking about heart diseases). Presence of genetic diseases in the family. Use of any medications by the patient.
- Visual inspection. The doctor examines the shade of the skin, the occurrence of edema, and measures pulse and blood pressure. Listens to the heartbeat.
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood are prescribed.
- The patient's blood coagulability is determined.
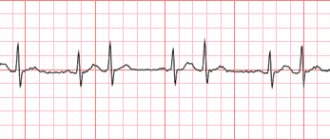
- Electrocardiography. With this pathology, the results of the ECG remain normal, but after some time the indicators worsen. It should be noted that this diagnostic method is ineffective.
- Echocardiography, so-called ultrasound of the heart muscle. During this study, it is possible to determine the area of the lesion, its size, and the volume of blood in the heart sac. In addition, this diagnostic method determines the strength of heart contraction, and if it is too reduced, then the prognosis of the disease is unfavorable.
- A catheter is inserted into the right side of the heart muscle to determine the amount of oxygen. Its amount should be the same in the atrium and ventricle. If there is a break in the heart line, then the oxygen level in the ventricle is much increased compared to the right atrium.
Transesophageal echocardiography
Based on the diagnostic results, therapeutic measures will be determined.
Treatment
In case of heart rupture, therapy consists of emergency cardiac intervention, as well as intensive treatment.
The following operations are performed for ruptures:
- suturing the rupture or applying “patches”;
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- valve replacement;
- heart transplant.
During surgical treatment, the rupture of the heart muscle is sutured. In addition, the resulting defect can be covered with a special plate. If there is fluid in the heart sac, it is removed using a puncture.
If the coronary vessels are damaged, then coronary artery bypass grafting is used. It will help stabilize blood flow and accelerate tissue scarring in the area of the defect.
In cases where the disease has damaged some elements of the heart muscle, prosthetics is performed during the operation - an artificial valve is installed.
In case of large ruptures that occur due to an extensive heart attack, there is no point in performing an operation to restore the organ, because most of it is damaged. In this case, the patient can only be saved by a donor organ transplant. However, there are certain difficulties, for example, there is little time for a transplant, and there is no suitable donor.
Treatment with medications will help stabilize blood pressure and also support the functioning of internal organs.
For this, the patient is prescribed:
- diuretics;
- analgesics;
- cardiac glycosides.
Blood and saline transfusions are used as infusion therapy.
Every person should know that this cardiac pathology requires only emergency medical care. In addition, people suffering from heart disease must strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. If the chest pain that occurs lasts more than five minutes, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Possible complications
The main complications are as follows:
- If a person has a rupture of the heart muscle, then without proper medical care he dies. To prevent this from happening, he needs urgent surgery. If the gap is small, then a person can live only two months without surgery.
- The forecasts, unfortunately, are disappointing, because almost half of the patients may die, even if the operation was performed on time and with proper quality. The thing is that the sutures placed during suturing often come apart.
If you start treatment in a timely manner, it is possible to eliminate complications.
What other reasons can lead to heart rupture?
The causes of cardiac rupture may be the following:
- Heart injury. An accident can provoke a heart rupture if the driver hits his chest on the steering wheel, or a strong blow from an opponent during a single combat
- Anomalies of cardiac development. If there is a congenital thin section in the heart, it can rupture under minor loads
- Tumor lesion of the heart
- Endocarditis - inflammation of the inner lining of the heart - endocardium
- A dissecting aortic aneurysm is a rupture of the largest artery, the aorta, which leads to blood flowing between the layers of the aortic walls and dissecting them further.
- Infiltrative heart diseases. These include sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis, amyloidosis - diseases in which substances accumulate in the heart that should not normally be present.