Glionic changes - what are they?
Until pathological processes of change occur in the structure of cells, the number of glia in the brain does not affect the performance of all brain functions.
Neuroglia in the brain perform certain functions that protect brain cells from the influence of infections, and also serve as protective ballast in case of brain injury.
The greater the number of glia in a healthy brain, the better the brain organs perform their functional duties.
Gliosis of brain cells is the body’s defense against damage to the fibers of the nervous system. When destruction and death of neurons occurs, glial cells take their place and completely try to replace neurons in all their functions.
Glia do not fully carry out metabolic processes in brain tissue, so the pathology of gliosis develops with its clinical manifestations.
The essence of the process
Gliosis affects nerve tissue as a result of triggering a special mechanism - when the brain is damaged. Glial cells and fibers replace lost neurons. Secondary cystic-gliotic changes occur. When glia proliferate, lesions are isolated and protection is created for undamaged tissue. Cystic-glial changes in the brain resemble scarring of a wound.
The size of the lesion may vary. When calculating this indicator, the ratio of the proportion of expanded glia to CNS cells per unit volume is taken into account. If cerebral gliosis develops, the prognosis depends on the degree of proliferation of the affected areas. This pathological process can cause serious impairment of brain function. It is impossible to cure it. If you establish the genesis, you can slow down or stop the development of the disease.
Structural units of the central nervous system
If neurons die, then their place is taken by other elements that fill the voids.
The structure of the central nervous system consists of several types of elements and cells:
- The main elements in the structure of nerve cells are neurons. Neurons perform the functions of generators of nerve signals and their transmitters;
- The elements that make up the lining of the cerebral ventricles of the brain and spinal cord are ependyma;
- Cells that perform a protective function during metabolic processes in the brain organ and also form replacement tissue after the destruction of neurons - neuroglia.
After large-scale destruction of neurons, the process of gliotic transformation occurs.
Neuroglial cells take the place of dead neurons and have several of their derivatives:
- Ependymocyte cells;
- Schwann cells;
- Astrocyte elements.
Glia are constantly present with neurons and constantly participate in all processes for which neurons are responsible:
- Birth of nerve impulses;
- Transmission of nerve impulse signals to the destination;
- Helps in the process of metabolism in the brain;
- Provide protective functions of brain cells.
In estrous situations, glia take over the responsibilities of all brain nerve cells.
Pathology gliosis of brain cells
Gliosis is similar in its properties to the process of healing wounds on the skin, although in the brain the process itself occurs differently.
After the death of neurons, they are replaced by glia, which are living brain cells and know the functional responsibilities of neurons, but they cannot fully perform these functions.
At first, glia try to establish functionality and support brain cells:
- Maintain and control metabolism in the brain;
- They try to transmit nerve impulses;
- Protect healthy tissue cells;
- They take part in the synthesis of new fiber cells of the nervous system.
Neuroglia cannot completely replace full-fledged brain cells - neurons, and as they multiply, glia take up more and more space in the brain space, developing the pathology of gliosis.
Pathology gliosis - this process in the brain organ is irreversible and creates a kind of scar from glia that protects healthy tissue cells from necrosis.
Conclusion
Gliosis is extremely dangerous not only for health, but also for life. If too many glial cells are formed, the consequences will be incompatible with life. At best, such people lose the ability to care for themselves and become disabled.
In order for treatment to bring the desired effect, it is important to eliminate the cause that led to such serious changes. If the catalyst is not eliminated, neither the methods of official nor traditional medicine will be effective. Take care of your health!
Types of occurrence and development of gliosis
Foci of neuronal destruction impair the functionality of the entire central nervous system. It makes no sense to treat this pathology, because dead neurons cannot be restored, and it is impossible to remove the amount of glia, since they serve as a replacement for destroyed neuron cells and replace them as much as possible.
The focus of neuronal damage does not always have a specific location.
Based on the location of glia and the form of concentration, gliosis in the brain organ has the following classification:
- Anisomorphic type of pathology gliosis is a chaotic proliferation of glia along the periphery, which begin to dominate the fibrous structure;
- Fibrous type pathology - in this form of gliosis, the fibrous structure predominates over the glia;
- Diffuse form of the disease - there are no foci of neuronal destruction, lesions occur not only in brain cells, but also in the spinal cord. This symptom is noted to be of a post-ischemic nature of brain pathology and treatment should consist of treatment of the root cause of the disease;
- Periventricular gliosis - glia grow in the cerebral ventricles. The cause of this focus is a cystic type of neoplasm;
- The focal type of pathology is gliosis - a clearly defined localization of the focus. This form of the disease manifests itself during an inflammatory process in the area of the white matter of the brain, and treatment will not bring positive effects;
- The marginal form is marked by foci that are located under the meninges of the frontal and parietal lobes;
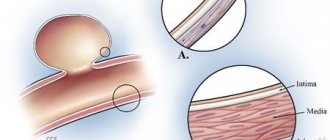
- Perivascular type of gliosis - glia are surrounded by sclerotic cerebral vessels. This form of gliosis most often occurs with systemic vasculitis. In order to prevent the development of even greater proliferation of glia, it is necessary to treat sclerosis of the cerebral arteries;
- Subependymal form - the focus of destruction of neurons and their replacement by glia occurs in the subependymoma of the brain - the cerebral ventricles;
- Marginal form of gliosis - has clear forms of localization in the intrathecal region;
- Isomorphic type - fibers are evenly distributed;
- Supratentorial gliosis of single foci of vascular origin is the cause of trauma in the birth process and age-related changes;
- Subcortical foci of gliosis - in the white matter of the frontal lobes there is a subcortical and periventricular single focus. Lesions can form in the right frontal lobe, as well as in the left part;
- Supratentorial multiple foci of gliosis are vascular causes that affect the blood flow system in the presence of neurological pathologies.
Islands of gliosis at the site of neuronal destruction form:
- Single focal substances;
- A few areas of up to 3 lesions;
- Multiple brain damage.
The dimensions of the pathology of gliosis can be calculated. This value is equal to the increase in glia in relation to healthy neurons.
If the neuronal lesion is large, it means that there is no clear localization, and therefore the functionality of the central nervous system becomes lower.
What is the danger?
The consequences of gliosis are directly related to its location and the catalyst that provoked the pathology. It can be caused by encephalitis, pressure surges, trauma, multiple sclerosis, and hypertension.
The prognosis and life expectancy are affected by the degree of brain damage. If the departments that regulate the functions of internal organs and systems are affected, the prognosis is unfavorable. A favorable outcome can be ensured by early diagnosis and timely comprehensive treatment. It is important to fight not with gliosis itself, but with its cause. Therapy should be prescribed by an experienced neurologist.
The consequences of cystic glial changes can be fatal if symptomatic epilepsy or malignant hydrocephalus occurs.
In the first case, constantly occurring irritation of the area adjacent to the cystic-gliotic transformation leads to its depletion and neuronal atrophy. Epilepsy is fraught with everyday discomfort, limitation of social activity, mental and mental disorders.
Acutely developed dropsy of the brain can cause death. When the liquor pathways are completely blocked, the latter begins to “put pressure” on the substance of the brain. Intracranial pressure increases. The brain tends to the area with less pressure and ends up being pinched into the hole in the occipital bone. Death occurs instantly.
Cystic-glial changes are a serious consequence of brain injuries in the absence of proper control and treatment.
Symptoms of gliosis
Gliosis of brain cells is not an independent disease, and therefore does not have characteristic symptoms of its own pathology.
All symptoms of gliosis disease are associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system and with those diseases that lead to the destruction of neurons.
If the pathology of gliosis is not a secondary disease of neurological diseases, then the symptoms of gliosis may not appear at all.
General signs of illness in neurological diseases of the brain:
- The pain in the head is quite severe, which cannot be relieved with antispasmodics;
- Changes in the blood pressure index - its sharp jumps;
- Constant dizziness;
- Performance decreases or completely disappears;
- There is a disturbance in the visual organ;
- Hearing is impaired;
- Deviations in intellectual abilities occur and memory deteriorates;
- The functioning of the musculoskeletal system is disrupted.
Symptoms directly depend on which part of the brain the damage and death of neurons occurs:
- The supratentorial type of gliosis affects the nerve fibers of the visual organ - a person sees a distorted view of objects, fogginess and blurriness in vision, and can also experience hallucinations;
- Vascular gliosis, or with traumatic etiology, pain appears in the temporal part of the head and blood pressure surges occur;
- Seizures of the epileptic type occur when the white matter is damaged in small foci. Dizziness, as well as convulsions, can occur due to the disease microangiopathy with the presence of foci, as well as due to brain trauma, or the consequences of surgical intervention in the brain;
- Also, glial replacement of tissue cells in the frontal lobes is often observed in older people. In this case, gliosis can act as a primary pathology if it was not preceded by any pathologies. The reason for the death of neurons is that they have already served their term, and in their place, multiple glial cells multiply. This action in the brain leads to the fact that the elderly person forgets more and more often, his vision and hearing deteriorate, and his gait becomes slow and unsteady.
At the first signs of a disorder in the structure of brain cells, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and begin treatment.
The damage to neurons does not stop there, this pathology progresses, and the neurons are replaced by glia, which multiply quite quickly and provoke the following pathologies and abnormalities in the brain:
- Improper blood flow causes wear and tear on the brain organs;
- Impairment of the speech apparatus and loss of speech;
- Paralysis develops;
- Deviations in memory occur;
- Intelligence is significantly reduced;
- Dementia develops;
- Gliosis can also lead to death (this phenomenon is quite rare, but the pathology has prerequisites for such an outcome).
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations in children
They differ from the development and symptoms of an adult. Neuronal death in children has a congenital etiology.
At the initial stage of pathology development, neuronal cells are destroyed, and then this place is filled with glia cells.
Tay-Sachs pathology, which begins to manifest itself in infants before six months of age, causes the development of gliosis in the children's brain.
Symptoms show disturbances in the functionality of all centers of the nervous system:
- There is a delay in the physical development of the baby;
- Regression in intelligence;
- Hearing is lost;
- The child’s vision disappears;
- Problems with swallowing food begin;
- Seizures.
At this stage of the pathology of gliosis and Tay-Sachs, treatment does not bring a positive effect.
These congenital pathologies have their own etiology, this is a disorder in fat metabolism. Predisposition and development of pathology can be identified during the period of intrauterine formation of the baby, no earlier than at the 18th week of pregnancy.
This pathology has irreversible consequences, cannot be cured, and most often an artificial termination of pregnancy (abortion) occurs.
Traditional Treatments
This pathology is easily confused with other diseases and traumatic changes. It is very important to accurately establish the reasons that provoked the degeneration of brain tissue. For this purpose, instrumental methods are now widely used:
- EEG. It will help identify disturbances in the functioning of neurons. This study is prescribed if brain activity is impaired. The diagnostic procedure detects abnormal seizure activity, which helps prevent new seizures.
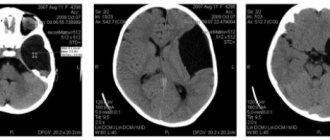
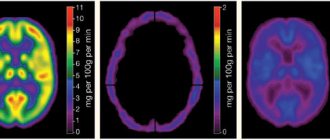
- Tomography (CT, MRI). It will visually show the state of the brain and help determine the extent and location of damage. Tomography can easily identify diseases of vascular origin. MRI records impaired metabolism, scars, tumors, etc. MRI can diagnose white matter gliosis in the frontal lobes. This process cannot be detected by other methods. It is MRI that makes it possible to detect periventricular gliosis, which affects areas near the ventricles of the brain. This method also helps to diagnose peripheral and perifocal lesions.
These methods also make it possible to identify the source that provoked the pathological changes.
Drug therapy is selected by a neurologist. It will be for life. In some cases, the pathological process can be stopped. This is not a separate disease. None of the existing drugs can cope with degenerative changes in the brain.
Traditional medicine uses three areas:
- Prevention. In the early stages of the development of such changes, the body is still able to cope with them. The doctor may recommend a balanced diet, giving up alcohol, smoking, and leading an active lifestyle.
- Treatment with medications. Conservative therapy will help alleviate the condition and restore some lost functions. Drugs that stimulate brain activity are prescribed. Also used are agents that increase the conductivity of neurons, strengthen the arteries, and restore the elasticity of blood vessels. If there is atherosclerosis, drugs are prescribed to treat it.
- Surgical intervention. The help of a neurosurgeon is required in rare cases. The operation is performed for those patients who suffer from epilepsy, seizures, and disorders of the internal organs. If there are many lesions, they are not subject to surgical treatment. Such patients are prescribed conservative treatment for life. During surgery, the surgeon can remove the tumor, drain the cerebrospinal fluid, and bypass the vessel.
Causes of gliosis
The etiology of the destruction of neuronal cells and their replacement by glia in the pathology of gliosis can be the following diseases of the body:
- Congenital and hereditary genetic pathologies - these are Tay-Sachs disease, an autoimmune pathology in which mass death of neurons occurs after 6 months of age and not all children survive to 5 years of age;
- Sclerosis of the tuberculosis type is a rather rare genetic hereditary pathology, which is characterized by multiple foci of benign neoplasms;
- A neurological disease - multiple sclerosis - destruction of myelin cells and the formation of demyelinating foci occur in different parts of the brain and in the spinal cord;
- The pathology of CNMK, as well as stroke, is a disturbance in cerebral circulation in the chronic form of the disease, as well as at the acute stage of cerebral infarction, as well as ischemic stroke. Post-ischemic syndrome is the main cause of the formation of glia in the place of neurons destroyed by ischemia;
- Dystrophic genesis of brain tissue cells;
- Trauma to the skull and consequences of brain trauma;
- Swelling of the brain;
- Epileptic seizures - pathology epilepsy;
- Newborn children suffer injuries when passing through the birth canal, or birth errors by obstetricians when providing assistance during childbirth;
- Hypertension with high blood pressure index;
- Pathology encephalopathy with high blood pressure;
- The disease is hypoxemia (low concentration of oxygen molecules in the blood), as well as hypercapnia (increased content of carbon dioxide in the blood). These pathologies lead to hypoxia of brain cells;
- low concentration of glucose in the blood, leading to the death of neuron cells;
- Pathology of an infectious nature - encephalitis;
- Surgical intervention in brain spinal cells;
- Eating animal fat leads to an accelerated process of destruction and death of brain cells - neurons;
- Also, the cause of the development of gliosis is chronic alcohol consumption; in moderate amounts, drinking high-quality red wine and cognac has a beneficial effect on blood vessels; excessive alcohol consumption kills neurons;
- Nicotine addiction leads to impaired cerebral circulation, as well as cerebral ischemia, which leads to the destruction of neurons and the development of the pathology gliosis;
- Drugs develop an inflammatory process in brain cells, which in a short period of time leads to massive death of neurons and the rapid development of gliosis.
Diagnostics
There are several methods that can diagnose the death of neurons and their replacement by glia:
- MRI of the brain (magnetic resonance imaging) - this technique allows you to determine the localization of the lesion, its volume and scale of the lesion, and MRI also shows a picture of single supratentorial lesions;
- CT (computed tomography) - this technique allows you to determine abnormalities in the functioning of blood vessels, as well as internal organs, which can provoke the death of neurons;
- EEG (electroencephalography) - changes and disturbances in the functionality of brain cells are determined. An EEG is necessary to check the state of the nervous system in cases of seizures and epilepsy.
Various forms of gliosis on MRI images
Diagnosis, treatment
Diagnosing education is not difficult. It is enough to perform a CT or MRI examination. The latter is more preferable, since in addition to better visualization there is no radiation exposure.
Additional diagnostic methods are angiography and electroencephalography (EEG).
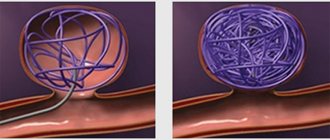
The only effective treatment for cystic gliosis transformations is surgery. It should be understood that dead neurons cannot be restored and the operation is aimed at eliminating epilepsy or hydrocephalus that has developed against the background of atrophy.
Many neurosurgical centers have learned to perform this operation in a low-traumatic manner using endoscopic techniques. The essence of the operation is to puncture the resulting cavity and remove the internal fluid. This eliminates excessive compression of the brain.
Treatment of cerebral gliosis
Treatment of gliosis begins with diagnosing and establishing the root cause of the disease, which provokes the destruction of brain elements - neurons.
During pregnancy, when a congenital pathology is established, then the pregnancy period must be interrupted.
Treatment for gliosis is:
- Diet for gliosis, which completely excludes fatty foods;
- Treatment of pathology with folk remedies;
- Complex treatment with medicinal groups of drugs;
- Surgical surgical treatment.
Drugs prescribed to treat brain cells:
| pharmacological group | therapeutic effect | name of drugs |
| group of vasoactive drugs | blood flow in the cerebral vessels increases, and gas exchange is normalized | · Cavinton product; |
| · drug Cinnarizine; | ||
| · medication Vinpocetine. | ||
| group of antiplatelet agents | prevent thrombosis of cerebral vessels, thin the blood composition and make it more mobile | · drug Aspirin; |
| · drug Thrombo ass. | ||
| phosphodiesterase inhibitors | blood-thinning properties of drugs | · drug Clopidogrel. |
| nootropic drugs | for cerebral blood microcirculation | · drug Actovegin; |
| · Piracetam remedy; | ||
| · medicinal product Glycine; | ||
| · herbal medicine Ginseng extract; | ||
| · medicine Cortexin; | ||
| · medication Phenibut | ||
| group of lipid-lowering drugs (statins) | for the treatment of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels | · drug Atorvastatin; |
| · drug Lovastatin; | ||
| · statins - Rosuvastatin; | ||
| · medication Fluvastatin |
The diet for gliosis consists of eating a diet that completely excludes fat from the menu. Also, for better cerebral microcirculation, folk remedies are taken.
Medicinal plants can be consumed in the form of decoctions, as well as alcoholic tinctures and teas.
Surgical treatment is used in the treatment of gliosis only when a single large lesion has formed in the brain.
Surgical treatment for gliosis is used extremely rarely and only if conservative therapy does not have positive dynamics.
Traditional methods of treatment
No matter how many medications are prescribed to the patient, additional support for the body with the help of folk remedies will help improve the condition.
- Thus, at the initial stage, with a few lesions, herbs support the body well, helping to stabilize the blood supply and increase metabolism.
- For obesity, a raw food diet, fasting days, and fasting are recommended. It also helps cleanse the body of harmful substances that interfere with its normal functioning.
- The use of tinctures and decoctions, the action of which is aimed at combating the symptoms of the disease. You can buy ready-made balanced preparations for treatment at the pharmacy.
I would like to note that treatment with traditional methods can be effective only as a supplement to the main therapy prescribed by specialists. There will be no lasting effect from the use of medications and treatment with folk remedies if the cause of glial formation is not eliminated.
Prevention
In the pathology of gliosis, prevention is more important than treatment.
It is more important to prevent pathologies that lead to the death of neurons:
- Timely identify and treat viral pathologies, as well as infectious diseases;
- Completely stop drinking alcohol;
- Avoid taking narcotic and psychotropic drugs;
- Quit nicotine addiction;
- To strengthen the immune system, consume omega 3;
- Constant walks in the fresh air;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- Do not overload the body physically and intellectually;
- Play sports: cycling, swimming;
- Get full (at least 8 hours) sleep.
Complications, consequences
Most often, this pathology does not cause obvious symptoms. This is her cunning. With large lesions affecting neurons, it may:
- The intellect suffers.
- Problems with speech and memory will appear.
- Increase pressure.
- Asthenia develops.
- Paresis and paralysis appear.
- Coordination is impaired.
- Visual and auditory pathologies appear.
- The psyche becomes deformed.
- Develop dementia (dementia).
More often, such a misfortune happens to adults. In this case, it becomes difficult for a person to perform even the simplest work activities. He cannot drive a car, he is exempt from military service. Complications can be very serious. It all depends on the size of the scar and how active the pathology that caused its appearance is.
Life forecast
Gliosis of brain cells is provoked by vascular diseases, or has a neurological etiology.
Adults and children are on equal terms for the development of pathology.
Children most often suffer from gliosis of a genetic hereditary autoimmune nature, as well as from a congenital pathology of death of neurons in the brain. The prognosis of gliosis in childhood is unfavorable, since few children survive to 5 years of age.
For patients diagnosed with gliosis with multiple foci, the prognosis for life is unfavorable (no more than 3 years of life).
Only timely identified pathology and prescribed comprehensive treatment can prolong the patient’s life for several years and improve his condition and quality of life itself.
Possibilities of traditional medicine
In this matter, traditional medicine can do little to help. Traditional methods are sometimes used in the early stages. Their task is to remove small lesions that have appeared, stabilize the condition, improve metabolism, and stabilize blood circulation.
It has been noted that gliosis can provoke excess weight. This condition is detrimental to blood vessels, including the blood vessels of the brain. Traditional methods help organize therapeutic fasting. A raw food diet and fasting days are also practiced.
Herbs, decoctions, tinctures will help improve metabolism and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Red clover, discoreem, hemlock, and medicinal herbs are often used.