At-risk groups
Typically, focal changes in the white matter of the brain of a dystrophic nature most often occur in old age. Most lesions appear during life and as a result of hypoxia and ischemia. People who lead a sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle are also susceptible to the disease. Genetic predisposition also plays a role. The risk group includes people suffering from high or low blood pressure, diabetes, rheumatism, obesity and atherosclerosis. In addition, emotional individuals prone to stress are at risk of developing pathology.
The white matter of the brain coordinates all human activity. It is what connects different parts of the nervous system. White matter is necessary for the two hemispheres to work together.
What are foci in the white matter of the human brain?
20.03.2019
Lesions in the white matter of the brain are areas of damage to brain tissue, accompanied by a violation of the mental and neurological functions of higher nervous activity.
Focal areas are caused by infection, atrophy, loss of blood supply and trauma. Most often, affected areas are caused by inflammatory diseases. However, areas of change may also be of a dystrophic nature.
This is observed mainly as a person ages.
Focal changes in the white matter of the brain can be local, single-focal, or diffuse, that is, the entire white matter is moderately affected. The clinical picture is determined by the localization of organic changes and their degree. A single lesion in the white matter may not affect the dysfunction, but massive damage to neurons causes a disruption in the functioning of nerve centers.
Symptoms
The set of symptoms depends on the location of the lesions and the depth of damage to the brain tissue. Symptoms:
- Pain syndrome. Characterized by chronic headaches. Unpleasant sensations intensify as the pathological process deepens.
- Rapid fatigue and exhaustion of mental processes. Concentration deteriorates, the volume of operative and long-term memory decreases. It is difficult to master new material.
- Flattening of emotions. Feelings lose their sharpness. Patients are indifferent to the world and lose interest in it. Previous sources of pleasure no longer bring joy and desire to engage in them.
- Sleep disturbance.
- In the frontal lobes, foci of gliosis disrupt the control of the patient’s own behavior. With deep violations, the concept of social norms may be lost. Behavior becomes provocative, unusual and strange.
- Epileptic manifestations. More often these are small convulsive seizures. Individual muscle groups contract involuntarily without threat to life.
White matter gliosis can manifest itself in children as a congenital pathology. The lesions cause dysfunction of the central nervous system: reflex activity is disrupted, vision and hearing deteriorate. Children develop slowly: they get on their feet late and begin to speak.
Causes
Damaged areas in the white matter are caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- Group of vascular diseases: atherosclerosis, amyloid angiopathy, diabetic microangiopathy, hyperhomocysteinemia.
- Inflammatory diseases: meningitis, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's disease.
- Infections: Lyme disease, AIDS and HIV, multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
- Poisoning by substances and heavy metals: carbon monoxide, lead, mercury.
- Vitamin deficiency, especially B vitamins.
- Traumatic brain injuries: bruise, concussion.
- Acute and chronic radiation sickness.
- Congenital pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident: ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral infarction.
Causes
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature occur in a number of diseases of different origins:
- Changes in vascular origin: atherosclerosis, migraine, hypertension, etc.
- Inflammatory diseases. Multiple sclerosis, Behcet's disease, Sjögren's disease, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease).
- Infectious diseases. HIV, syphilis, borreliosis.
- Intoxication and metabolic disorders, carbon monoxide poisoning, B12 deficiency.
- Traumatic processes associated with radiation therapy.
- Congenital diseases caused by metabolic disorders.
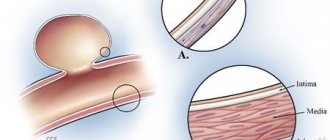
The occurrence of pathology is caused by impaired blood supply in any part of the brain. It is fraught with loss of function of brain tissue. The more blood flow has decreased, the more noticeable the consequences. An example is damage to the spinal or cerebral blood flow. Such violations progress slowly, but entail serious consequences.
Diagnosis and treatment
Gliosis of vascular origin is diagnosed by consultation with a psychiatrist, medical psychologist and with the help of instrumental research methods. During a subjective examination, the patient’s appearance, speech, movements, vocabulary, and reaction speed are studied. Instrumental methods identify lesions. This is done using magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause and symptoms. Thus, etiotropic treatment consists of restoring cerebral circulation. Medicines are prescribed to improve cerebral blood flow and the susceptibility of brain tissue to oxygen. Symptomatic therapy is aimed at improving cognitive abilities and eliminating emotional disturbances. Nootropic drugs, antidepressants, anti-anxiety and sedatives are prescribed.
Each part of the brain performs specific functions - regulates speech, thinking, balance, attention, and controls the functioning of internal organs. The brain stores and processes an incredible amount of information; At the same time, many processes take place in it that provide a person with normal life activity. The functioning of this entire complex system directly depends on the blood supply. Even minor damage to blood vessels leads to serious consequences. One of the manifestations of this pathology is considered to be focal changes in the brain.
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
Signs
The signs of focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature are also different. With focal changes, not the entire brain suffers, but only its individual parts. Tissue degeneration occurs when there is insufficient supply of nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the body’s nervous systems. We are talking about proteins - the building material of the human body. Proteins break down into amino acids, which, in turn, stimulate the nervous system. It also requires fats and carbohydrates - the main sources of energy needed by every living creature.

Of the vitamins, the brain needs B1 (activates its work), B3 (provides energy at the intracellular level), B6 (it is difficult to imagine metabolic processes without it, in addition, it is also a kind of antidepressant), B12 (promotes memory preservation and helps to stay alert) . All these vitamins can be obtained in sufficient quantities by creating the right diet.
Stages of development of dyscirculatory changes
There are three stages of this pathology:
p, blockquote 6,0,1,0,0 —>
- Initially, discirculatory changes are characterized by a slight disturbance in the movement of blood in certain brain areas. Because of this, the patient quickly gets tired and often experiences bouts of dizziness and headaches.
- When the disease develops and moves into the second stage, the damage worsens. Memory deteriorates, intellectual abilities decrease. The person becomes extremely irritable and emotional. Coordination of movements worsens, and tinnitus appears.
- At the third stage, a significant part of the neurons die. In this case, the muscles noticeably suffer, obvious signs of dementia appear, and the organs of touch and senses may fail.
How the functionality of organs sensitive to such disorders changes depends on where focal diffuse changes of a vascular nature are localized in the brain and spinal cord.
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
Pathologies
Focal changes in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature most often take the form of pathologies such as:
- A cyst is a small cavity that is filled with fluid. It often interferes with the normal functioning of neighboring areas of the brain, as it compresses blood vessels. Cysts are divided into intracerebral (cerebral) and arachnoid. The latter appears in the meninges. Its occurrence is promoted by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and inflammatory processes. Cerebral occurs in place of dead brain tissue.
- Necrotic state of tissue - appears when the supply of important nutrients to areas of the brain for any reason deteriorates. Dead cells form so-called dead zones and are not regenerated.
- Hematomas and brain scars occur after severe trauma or concussion. Foci of this type lead to structural damage.
What is a focal change in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature?
The brain is a key part of the human nervous system. This is a complex and vulnerable organ, any pathology of which can lead to irreparable health consequences. This is often caused by a focal change in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature - a dangerous and common phenomenon.
Causes
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature occur in a number of diseases of different origins:
- Changes in vascular origin: atherosclerosis, migraine, hypertension, etc.
- Inflammatory diseases. Multiple sclerosis, Behcet's disease, Sjögren's disease, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease).
- Infectious diseases. HIV, syphilis, borreliosis.
- Intoxication and metabolic disorders, carbon monoxide poisoning, B12 deficiency.
- Traumatic processes associated with radiation therapy.
- Congenital diseases caused by metabolic disorders.
The occurrence of pathology is caused by impaired blood supply in any part of the brain. It is fraught with loss of function of brain tissue. The more blood flow has decreased, the more noticeable the consequences. An example is damage to the spinal or cerebral blood flow. Such violations progress slowly, but entail serious consequences.
Signs
The signs of focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature are also different. With focal changes, not the entire brain suffers, but only its individual parts.
Tissue degeneration occurs when there is insufficient supply of nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the body’s nervous systems. We are talking about proteins - the building material of the human body.
Proteins break down into amino acids, which, in turn, stimulate the nervous system. It also requires fats and carbohydrates - the main sources of energy needed by every living creature.
The act of defecation: mechanism, regularity, causes of violations
Of the vitamins, the brain needs B1 (activates its work), B3 (provides energy at the intracellular level), B6 (it is difficult to imagine metabolic processes without it, in addition, it is also a kind of antidepressant), B12 (promotes memory preservation and helps to stay alert) . All these vitamins can be obtained in sufficient quantities by creating the right diet.
initial stage
At the initial stage of damage to the human brain, signs of the disease practically do not appear. The patient can only complain about lack of strength and apathy. At this stage, sources of problems in blood vessels are just emerging and are difficult to distinguish.
Second stage
A focal change in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature in the second stage is manifested by more serious symptoms: a person’s headache intensifies, the ability to perceive and process information decreases, ringing in the ears appears, coordination of movements is impaired, the character becomes more irritable and aggressive.
Third stage
When the disease reaches the third stage of development, the brain pathology is considered irreversible. Gradually, the patient develops symptoms of dementia, paralysis and paresis rapidly develop, and the senses work with less and less efficiency.
Pathologies
Focal changes in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature most often take the form of pathologies such as:
- A cyst is a small cavity that is filled with fluid. It often interferes with the normal functioning of neighboring areas of the brain, as it compresses blood vessels. Cysts are divided into intracerebral (cerebral) and arachnoid. The latter appears in the meninges. Its occurrence is promoted by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and inflammatory processes. Cerebral occurs in place of dead brain tissue.
- Necrotic state of tissue - appears when the supply of important nutrients to areas of the brain for any reason deteriorates. Dead cells form so-called dead zones and are not regenerated.
- Hematomas and brain scars occur after severe trauma or concussion. Foci of this type lead to structural damage.
Diet
In the early stages of this disease, it is enough to reconsider your lifestyle and diet, choosing a more gentle regimen and diet. In the diet, it is advised to reduce the consumption of animal fats, and it is better to completely replace them with vegetable ones. You should eat fish and seafood instead of fatty meat, and reduce the amount of salt in your diet. Fresh vegetables and fruits will be of great benefit.
Treatment
There are a huge number of focal anomalies, so each has its own cause. Treatment of brain pathologies is based on the destruction of those factors that led to the appearance of lesions in brain tissue. In addition to eliminating the underlying disease, the doctor may also prescribe vitamins and medications to help combat the deterioration of cerebral blood flow.
The treatment process depends directly on what somatic problems in the body led to the occurrence of lesions in the brain. For infections, for example, antibiotics are taken; for injuries, diuretics, decongestants, and anticonvulsants are taken. If the damage to the brain tissue was caused by a circulatory disorder, then nootropics and coagulants are prescribed.
Source
Source: https://1ku.ru/zdorove/31694-chto-takoe-ochagovoe-izmenenie-veshhestva-mozga-distroficheskogo-haraktera/
Diagnostics
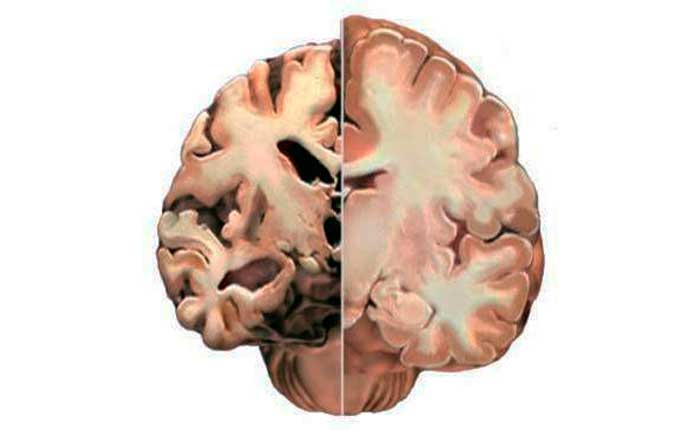
The complete picture of focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature is determined using an MRI study. This procedure allows you to see even small areas of transformation in the white matter. And they, in turn, lead to cancer and stroke.
Focal dystrophic lesions come in different sizes and differ in location. Based on this, the examination may show some types of disorders.
In the cerebral hemisphere, blockage of vital arteries is usually diagnosed due to abnormal development of the embryo or acquired atherosclerotic plaques. A herniated cervical spine is also detected.
Changes in the white matter of the brain indicate hypertension and congenital developmental anomalies. In other cases, numerous areas of brain pathology may indicate a pre-stroke condition, senile dementia, or epilepsy.
Sometimes doctors perform tests on a patient to detect the presence of cognitive impairment. That is, cognitive dysfunction. Such as orientation in space and time, understanding of external processes, the ability to remember information, drawing, writing, reading, etc.
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature can develop in three ways:
- In the first case, the disease is remitting in nature. Symptoms increase gradually, the condition worsens, and brain productivity decreases. But from time to time, remissions occur—temporary improvements in health, after which the patient becomes worse again.
- Progressive focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory dystrophic nature develop very quickly. Each stage of the disease takes no more than two years, which is considered a short period for organic brain lesions.
- Typically, the deterioration of a person suffering from focal changes lasts for many years, eventually leading to dementia.

It should be remembered that single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature often appear in young people, and single damage to the white matter in an elderly person is considered normal. Structural disorders of the cerebral arteries of the atherosclerotic type appear in 50% of patients over 50 years of age. For the most part, hypertensive patients suffer from this. Therefore, you need to show the MRI result to a neurologist so that he can determine the severity of the disorders in the brain by comparing the MRI result and the clinical picture of the disease.
Features of treatment
Having identified focal changes in the brain substance on MRI, you should immediately begin to treat their manifestations so that the disease does not progress quickly. Treatment of such pathologies should always include not only medication, but also correction of lifestyle, because many factors of everyday life complicate the activity of cerebral vessels.
This means that the patient needs:
- Smoking less, or better yet, getting rid of addiction altogether.
- Do not drink alcohol, much less drugs.
- Move more, do the exercises recommended by your doctor for this disease.
- Get enough sleep: when such diseases are detected, doctors recommend slightly increasing the duration of sleep.
- Eat a balanced diet, it is advisable to develop a diet together with a doctor to take into account all the necessary nutritional components - in dystrophic processes, a complete supply of neurons with vitamins and microelements is very important.
- Reconsider your attitude towards some nuances in your life that cause stress. If your job is too stressful, you may need to change your job.
- Determine the best ways to relax for yourself.
- Do not ignore regular examinations - they will help to timely detect certain changes in the pathological process and respond to them in a timely manner.
Drug treatment is necessary for:
- Reduced blood viscosity - its excessive thickness interferes with blood flow in the cavities of the blood vessels of the brain.
- Optimizing gas exchange between neurons and the circulatory system.
- Replenishing the body's reserves with vital elements and vitamins.
- Reducing pain.
- Reducing blood pressure.
- Reducing the patient’s irritability, eliminating his depressive states.
- Stimulates blood circulation.
- Supporting the vital activity of neurons and their resistance to stress.
- Reducing cholesterol levels.
- Controlling sugar levels (diabetes).
- Rehabilitation of patients after head injuries (if necessary).
Thus, treatment should include all necessary measures to eliminate any factors that contribute to the progression of the disease in the future and interfere with normal mental activity and nervous regulation.
Naturally, full-fledged therapy is impossible if the doctor’s prescriptions are ignored.
The patient must be prepared for a long and possibly difficult struggle against further destruction of brain structures.
But timely therapeutic measures can postpone negative irreversible processes that complicate the life of a person and his loved ones.
For their part, those around them should be sympathetic to some unpleasant changes in the patient’s personality, because they are entirely due to the illness.
A favorable environment and a minimum of stress inhibit the destruction of the psyche, and sometimes provide an opportunity to improve the implementation of fading vital functions.
In fact, it is possible to eliminate such a pathology as focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory nature if we approach the problem in a comprehensive manner. First of all, you need to do everything to establish blood supply to the brain. In any case, treatment will be selected individually. After all, each patient had his own special reasons for the development of this disease.
First of all, it is very important to establish blood supply to the brain, as well as provide support to healthy nerve cells so that the disease does not continue to progress. If necessary, the patient can take sedatives and other medications. This must be done to support normal life activities. Very often, oxygen starvation leads to complications, so it is important to eliminate this phenomenon in a timely manner.
You also need to strengthen your nervous system. To do this, experts recommend taking safe and effective herbal preparations. It is also necessary to ensure that the brain cells receive a sufficient amount of nutrients, microelements and vitamins. It is very important to tone the blood vessels and expand them so that oxygen starvation does not occur.
If the patency of the arteries deteriorates significantly, then the doctor may decide to perform surgical intervention. However, this is done only as a last resort.
The doctor explains to patients why brain dystrophy is dangerous, what it is and how to deal with the disease. When deciding on treatment tactics, the neurologist collects a general medical history of the patient. Since it is impossible to find the only and true cause of the pathology, it is necessary to improve cerebral circulation by any means. Therapy, both for single lesions and for multiple ones, is based on several specific postulates:
- Adhering to the correct regimen and following diet No. 10. The patient is advised to devote sufficient time to rest every day. Do not overload yourself with physical work, eat right. The diet should contain organic acids (raw or baked fruits, compotes, juices, fruit drinks, almonds). Patients at risk or those who, after examination, have been diagnosed with focal changes in the brain, should exclude foods fortified with calcium. It impairs blood flow, which leads to oxygen starvation and isolated focal changes in brain structures.
- Drug treatment is carried out with drugs that have a positive effect on the blood supply to the brain. Such medications stimulate blood flow, dilate blood vessels, reduce viscosity, and prevent blood clots.
- The patient is prescribed analgesics to relieve pain, sedatives, and vitamin therapy.
- For hypo- or hypertension, take medications that normalize blood pressure, which is necessary for proper brain function.
If focal brain lesions are not treated and the disease starts, severe disorders develop that modern medicine cannot fight. This:
- Alzheimer's disease is one of the common forms of degeneration of nerve cells and structures.
- Pick syndrome is a rare progressive disease that affects people over 50 years of age.
- Huntington's disease is a genetic disorder that appears between 30 and 50 years of age.
- Cardiocerebral syndrome, in which brain function is impaired due to severe diseases of the cardiac system.
- Arterial hypertension, the exacerbation of which can lead to serious problems with the patient’s health.
The development of an oncological process is possible.
Therapy for focal brain damage is aimed at eliminating the cause of the changes and restoring the functions of the organ.
For example, if the pathology is caused by a disease characterized by increased blood pressure, then the patient is prescribed to take medications that lower blood pressure. These may be diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or beta blockers.
Restoration of brain activity and elimination of pathological phenomena is carried out with the help of drugs that increase metabolism in nerve tissues: nootropics. Also used are agents that improve blood circulation, rheological properties of blood, and reduce the need for oxygen.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at reducing the manifestations of pathology: taking anticonvulsants, antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants, and tranquilizers for anxiety.
Individual changes in the white matter, which are clearly visible on MRI, may mean that the patient has abnormalities in the blood circulation of the brain of vascular origin. Based on these data, the doctor will prescribe an examination that will more clearly show the causes of this situation and allow you to prescribe the correct treatment.
To select treatment for focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory nature, the doctor first prescribes therapy for the disease that led to this situation. Drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation between brain structures, oxygen exchange, reduce blood viscosity, have a sedative and analgesic effect, as well as complexes of vitamins and essential elements.
In addition, to restore the functions of the white matter of the brain, if possible, the patient is prescribed a strict diet, bed rest and rest. This will help avoid further changes in the brain substance. The patient's regimen should be normalized, it is important to exclude any physical activity, and also completely review his diet. You should unquestioningly obey the doctor’s orders.
Diet
In the early stages of this disease, it is enough to reconsider your lifestyle and diet, choosing a more gentle regimen and diet. In the diet, it is advised to reduce the consumption of animal fats, and it is better to completely replace them with vegetable ones. You should eat fish and seafood instead of fatty meat, and reduce the amount of salt in your diet. Fresh vegetables and fruits will be of great benefit.

Symptoms of focal lesions

p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
Focal brain lesions are caused by damage to blood vessels, which lose elasticity with age. For some, this manifests itself minimally, while for others, the disorders develop into a pathological form. Can appear:
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
- High blood pressure caused by a lack of oxygen due to the degenerative state of the cerebral vessels.
- Epileptic seizures, during which a person should not put metal objects in his mouth, pour water on him, hit him on the cheeks, etc.
- Mental disorders, memory impairment, distorted perception of reality, atypical behavior.
- Stroke or pre-stroke condition, which can be detected on CT or MRI.
- Increasing throbbing headache in the back of the head, eye sockets, superciliary areas, radiating across the surface of the entire skull.
- Uncontrolled muscle contractions, tremors of the limbs, chin, eyes, neck.
- Ear noise, ringing, congestion leading to nervousness.
- Regular attacks of dizziness leading to nausea and vomiting.
- Photophobia, decreased hearing acuity, blurred vision, double vision, noticeable blurred vision.
- Constant fatigue, apathy.
- Slurred speech.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Muscle paresis, pathological reflex reaction of the limbs.
Many people ask what diseases are caused by focal brain damage, what it is, and why it occurs. It is known that the causes of this disorder may lie in:
Treatment
There are a huge number of focal anomalies, so each has its own cause. Treatment of brain pathologies is based on the destruction of those factors that led to the appearance of lesions in brain tissue. In addition to eliminating the underlying disease, the doctor may also prescribe vitamins and medications to help combat the deterioration of cerebral blood flow.
The treatment process depends directly on what somatic problems in the body led to the occurrence of lesions in the brain. For infections, for example, antibiotics are taken; for injuries, diuretics, decongestants, and anticonvulsants are taken. If the damage to the brain tissue was caused by a circulatory disorder, then nootropics and coagulants are prescribed.
Gliosis of the brain - what is it?
To understand what gliosis changes in the brain are, you need to understand how the central nervous system (CNS) works.
Neurons are the main cells of the nervous system, a kind of “minicomputers” that receive and process information coming from the environment and issue commands to all internal organs. The functioning of the body as a whole depends on the coordinated work of neurons.
For reference. But besides neurons, the central nervous system contains glial cells. These are auxiliary structures of nervous tissue. They perform supporting, trophic (nourish, regulate metabolic processes of neurons) functions, and participate in the development of nerve cells.
Glial cells are located next to neurocytes and can replace them after death: if neurons die, glial cells grow and fill their place.
Like scars on the skin, glial changes in the brain can be figuratively considered scars on the “body” of nervous tissue.
Such cellular replacement, especially if multiple foci are formed, leads to disruption and changes in the central nervous system.
Single pathological foci of glial growths may be an accidental finding during a diagnostic examination.
If a neurological problem occurs, the manifestations of gliosis may include the following:
- Headache. Painful sensations can be of varying degrees of severity and duration: from moderate constant to unbearable, migraine.
- Dizziness.
- Deterioration of memory and attention.
- Mood lability.
- Unsteadiness of gait, unsteadiness when walking.
- Forgetfulness.
- Noise in the head.
- Instability of blood pressure (typical of gliosis of vascular origin).
- Convulsive attacks.
- Insomnia.
- Paretic disorders, paresthesia (feeling of “crawling goosebumps”).
- Deterioration in the functioning of visual analyzers: hearing or vision.
- Increased fatigue, weakness, manifestations of general asthenia of the body.
- Speech disorders, dysarthria.
Clinical manifestations can be varied and depend on the underlying disease that provoked the formation of gliosis.
Symptoms and complaints may be completely absent if the lesions are few in number and discovered by chance after a long-term TBI without consequences.
For reference. The prognosis for life with cerebral gliosis depends on the disease that caused its appearance.
Single lesions formed as a result of long-term consequences of a TBI, or the onset of senile changes according to the patient’s age, do not pose a danger to life and have a favorable prognosis. The same cannot be said about pathological changes in brain tissue in multiple sclerosis or malignant tumors with glial growths.
To assess the severity of the disease and form ideas about the prognosis of its course, the patient should undergo all the necessary examinations to identify the root cause and stage of the disease that caused gliosis.
For reference. Isolated gliosis of the brain cannot be treated, since it is only a symptom. The disease that caused it should be treated. Therefore, the main methods of treatment and drug therapy will depend on the underlying pathology.
If cellular changes in TBI with developed edema are the basis, the main means of eliminating the consequences of injury and the progression of neuronal replacement with glial cells will be the normalization of blood circulation, respiration, the prescription of diuretics, vascular drugs, and symptomatic therapy (prescription of analgesics, sedatives).
The severity of glial changes in multiple sclerosis can be reduced by taking glucocorticosteroids in an individual dose, cytostatics, beta-interferon, Clonazepam, Amantadine.
Timely treatment of neuroinfections, taking antiviral or antibacterial agents, depending on the nature of the pathogen that caused the inflammation, can reduce the risk of post-infectious transformation of nervous tissue.
When brain tumors are detected, neurosurgeons often recommend surgical treatment aimed at removing all or part of the tumor.
Radical removal reduces tissue compression and prevents the destruction of neurons, slows down the formation of glial scars. If there is inoperability or the presence of multiple metastases, they try to stop the process by treating the tissue with radiation therapy or antitumor agents.
Attention. What a patient should not do is, if there are neurological problems and clinical symptoms, self-medicate on the advice of friends or the Internet, or try therapy with folk remedies. In the presence of gliosis, this may not only be ineffective, but also dangerous!
If the patient has any complaints from the nervous system, you should definitely consult a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
To date, there is no effective treatment to restore neurons. All therapy for gliosis is aimed at slowing down the expansion of these lesions. This is done by treating the underlying disease.
In case of TBI, treatment is carried out in an intensive care unit. Therapy is aimed at preserving the functionality of neurons.
Vascular pathologies are treated with medications aimed at restoring normal blood flow.

Infectious lesions require treatment with antiviral or antibacterial drugs.
Even severe gliosis cannot be treated surgically. Any operation is damage, which is the cause of pathology.
Treatment also requires adherence to a special diet. The most important thing that is required of a person is to completely eliminate foods containing fats. It is believed that the progression of pathological glial proliferation accelerates impaired fat metabolism. Therefore, a person has to switch to a low-fat diet and count the number of calories in food.
Gliosis is an extremely serious disease, during the development of which dead nerve cells are replaced by glial cells, which serve to protect the nervous system and help neurons (transmit impulses and form new connections). When excess glia appear in a specific area, we can talk about a diagnosis such as cerebral gliosis.
The disease itself is incurable; it is the result of functional problems in the central nervous system. Foci in the brain are voids that arise with the presence of pathology in certain areas. Neurons become dead and neuroglia appear, giving rise to the described glial transformation.
Micromovements occur every second in the brain at the neuronal level, affecting the functioning of the entire organism. These are processes invisible to humans, so the violations are invisible for some time. In a smoothly functioning nervous system, some components have main tasks, while others have auxiliary tasks.
The central nervous system consists of the following cell type formations:
- Neurons. Function – generation and distribution of signals;
- Ependymal cells – canal of the spinal cord;
- Neuroglia are responsible for metabolic processes.
If the brain is injured, pathologies are present, neural death begins, and illness occurs. The number of neuroglial cells increases, empty areas are filled, acting as an impetus for neural reorganization. Neuroglia are provocateurs of the formation of a focus of gliosis in the brain. Cells are smaller in size than neural cells, but they significantly exceed them in number, occupying about 40% of the total mass.
Age is not a key factor provoking the formation of lesions. Although, of course, older people are at risk. If no structural changes are visible, no damaged area where neuroglia are located, then there is no obvious effect on brain functions.
It would be wrong to say that the formation of glia in empty zones is a destructive process. Although cells do not have the ability to perform neuroregulatory functions, they:
- Support brain activity;
- Protect healthy tissues;
- Form new nerve fibers;
- Receive and distribute signals.
Brain gliosis cannot be predicted, since the root cause is a mutated type of gene that affects the processes of hexoseamidase A.
The vital activity of brain cells will work as required, provided that the required amount of blood flows to them through the vessels. When arteries stop doing their job and feeding neurons, this leads to diseases of vascular origin.
There are no characteristic symptoms for the disease. All types of disorders are symptoms of many other ailments.
The triggering mechanisms may be different, but the manifestations of all have similarities:
- Regular headaches, with ineffective classical therapy;
- Pressure surges without specifics;
- Weakness, high fatigue;
- Poor coordination;
- Low mnestic functions.
The disease can cause seizures. This is due to the presence of a large lesion. In order for an accurate diagnosis to be made, you need to immediately contact a specialist, because similar problems can also indicate other diseases.
Cerebral gliosis, not being a separate disease, does not have any characteristic symptoms. All disorders associated with disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system are inherent in many other ailments.
Moreover, unless gliosis is associated with a neurological disease such as multiple sclerosis, there are no symptoms at all. Diagnosed randomly, along with the underlying disease.
The causes of the disease may be different, but the manifestation, if any, is approximately the same:
- constant headaches, treatment with standard anti-spasm drugs has no effect;
- changes in blood pressure are not specific;
- constant dizziness, general weakness or excessive fatigue. The causes of the condition may be different, but against the background of memory deterioration they should cause concern;
- deterioration in coordination of movements. The cause of the symptom is associated with the replacement of damaged nerve tissue by glia and, accordingly, poor signal transmission;
- memory deterioration, noticeable decrease in mnestic functions. The reason is the same - lack of functional nerve tissue. Treatment in this case is useless.
Norm of magnetic resonance imaging
What does “normal on an MRI of the brain” mean? These are the results of an MRI of a healthy person. Data is assessed according to several parameters:
- structures are developed correctly and fully, there are no displacements;
- Magnetic resonance signal is normal;
- the gyri and sulci are normal, do not have inclusions, inflammation or changes in structure;
- parts of the brain such as the sella turcica and the pituitary gland are clearly visible and have no pathologies;
- the perivascular, subarachnoid space is developed normally and has no pathologies;
- the ventricular system has normal standard dimensions (neither enlarged nor reduced), there are no pathologies;
- the ear canals, nasal sinuses, and eye sockets are clearly visualized, have normal sizes and regular shapes;
- general assessment is when there are no focal changes, brain tissue is developed normally, brain vessels are of the correct shape, do not have diffuse changes, are evenly filled, there are no bleeding, blood clots and purulent formations of various sizes.
Magnetic resonance imaging does not affect the brain itself and does not change its structure. Unlike X-rays, MRI is not limited in frequency; it can be done as often as needed.
There are no obvious contraindications; moreover, MRI is prescribed only with a doctor’s referral, issued after the examination.
Contraindications include, for example, the inability to lie quietly for about half an hour (30 minutes). This may be due to the person’s mental state or other diseases that do not allow lying still for a long time. An MRI cannot be performed if the patient has any metal implants, an insulin pump, or a pacemaker. This will not affect the MRI machine itself, but the functions of metal elements in the human body may be impaired.