Hypertension
High blood pressure is another cause of cramping headaches.
Pronounced discomfort appears when the tonometer produces critical values of 200/100. In other situations, the cause of headache is different. Arterial hypertension is dangerous because it has a negative effect on the condition of blood vessels. In a short time, they narrow and their integrity is violated. If the flow of liquid connective tissue is very powerful, the vessels may burst. The natural consequence is hemorrhage. Contrary to popular belief, even a single episode of increased blood pressure is a reason for examination.
The main causes of hypertension:
- Natural age-related changes.
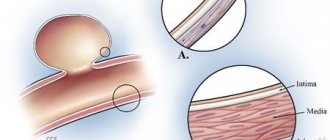
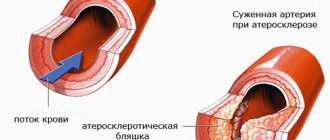
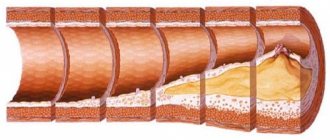
- Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques.
- The body's tendency to form blood clots.
- A lifestyle that does not involve physical activity.
- Excess body weight.
- Frequent consumption of salty foods.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Lack of sleep.
- Frequently being under stress.
- Kidney pathologies.
- Genetic predisposition.
Hypertension goes through several stages of development. In the first, pressure readings periodically return to normal; in the second and third, this happens extremely rarely.
Clinical manifestations of hypertension of the first and second degrees:
- Headache. This is a symptom that is characteristic of any stage of development of the disease. In addition, there is pain in the eyes. The headache is sharp, it can be localized either in one area or around the entire skull.
- "Floaters" before the eyes.
- Frequent episodes of dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Dyspnea.
- Drowsiness or, on the contrary, insomnia.
- An inexplicable feeling of anxiety.
- Excessive sweating.
- Feeling of chilliness.
- Redness of the skin on the face.
- Memory impairment.
- Swelling of facial tissues in the morning.
- Numbness of fingers.
At the third degree, a person is bothered by a severe headache with spasms. His vision deteriorates, his gait changes, coordination of movements is impaired, and his consciousness becomes clouded. In addition, the patient has hemoptysis, arrhythmia, and cannot cope without outside help.
In some cases, the pathology is practically asymptomatic. The danger of this situation is that a person attributes weakness, spots before the eyes and headaches with spasms to meteorological factors or fatigue. Meanwhile, high blood pressure without treatment can lead to heart attack, heart failure, stroke, aortic aneurysm, and hypertensive crisis.
If you experience severe headache, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, convulsions, or fainting, you must call an ambulance. These symptoms indicate the presence of a life-threatening condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the location of the spasm and the size of the affected artery.
Reference. Headache provoked by spasms is the main manifestation of the pathology.
This symptom is characterized by different locations and intensities, and it may gradually spread over a wide area.
Additional symptoms of vascular spasms include:
- dizziness;
- darkening, flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- pale face;
- soreness in the eyes, neck;
- sensation of tinnitus;
- high/low blood pressure;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased feeling of fatigue;
- numbness, tingling of lips and temples.
If spasms occur as a precursor to a stroke or rupture of an aneurysm, then the patient may experience the following manifestations:
- Speech impairment.
- Loss of orientation.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Memory losses.
Spasms can develop quickly, then the symptoms appear suddenly and are pronounced.
With chronic insufficiency of cerebral blood supply, the symptoms are less pronounced, but this condition can be more dangerous due to its complications.
Reference. The main symptom of the acute form is severe headache, the chronic one is increased fatigue.
Diagnosis of the disease
Angiospasm can be considered as an incomplete contraction of vascular muscle tissue. Under normal conditions, the vessels constantly contract and immediately relax. During spasm, the process of relaxation of blood vessels takes much longer, or does not occur at all.
So, there are three mechanisms for the occurrence of spasms:
- disturbances in ion exchange in smooth muscle cells (for example, with an increase in the amount of calcium ions, constant contraction of blood vessels occurs);
- reflex mechanism (for damage to the vascular wall, inflammation and other conditions);
- neurogenic mechanism (has no clinical evidence).
The brain is saturated with an extensive network of blood vessels that provide its nutrition. A spasm is a sharp and unexpected narrowing of the diameter of blood vessels. As soon as this phenomenon occurs, the person immediately becomes ill.
Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted. As a result, serious disruptions in the functioning of the entire body may occur.
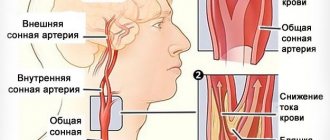
Spasm occurs not only due to problems with blood vessels inside the skull, but also in the neck. It is through this area that large arteries pass that supply blood to the vessels of the brain. If a person is busy with work for a long time, the quality of the blood supply to the head decreases, and this leads to a deterioration in the condition.
The movement of contraction and relaxation of the walls of blood vessels allows blood to pass faster and in greater volume. A spasm occurs when the walls of the blood vessels contract but do not relax. As a result, headaches occur and blood flow is impaired.
The development of spasm occurs due to difficult living conditions or as a complication against the background of the development of other diseases. As for difficult living conditions, this includes physical exhaustion, bad habits and other factors. More details about them:
- Lack of sleep. The whole body, and especially the brain, needs sleep to rest. If a person sleeps for a short amount of time or sleep is constantly interrupted, then there is a high risk of vascular spasm.
- Overwork. If a person’s brain is loaded with a lot of work, it wears out faster. Consequently, he requires more frequent rest. First of all, people with intellectually complex work suffer from vascular spasm due to overwork. People who engage in physical labor are much less likely to suffer from this disease.
- Oxygen starvation. The brain needs to be properly nourished. Oxygen is the main component of nutrition. With a lack of oxygen, not only a spasm is formed, but other pathologies also arise. A person needs to be in a well-ventilated area, spend more time in nature, and have a humidifier in the room.
- Smoking and alcoholic drinks. These are bad habits that affect brain activity. With them, the risk of spasm increases significantly, especially with smoking, which replaces the oxygen needed by the brain.
There are diseases that provoke the development of spasms. Among these diseases:
- malignant brain tumors;
- thyroid pathology;
- heart rhythm disturbance (arrhythmia);
- problems with blood vessels (venous thrombosis, thrombophlebitis);
- kidney disease;
- pathology of the cervical vertebrae.
There are situations that can provoke a spasm. It occurs due to hypothermia, excessive drinking, or stress.
If the above symptoms occur, it is necessary to undergo an examination. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- magnetic resonance imaging of intracranial and cervical vessels;
- Ultrasound examination of the cervical spine.
Certain medications or traditional medicine methods will help temporarily eliminate the spasm. However, they should not be abused: it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination by specialists, establish the cause and follow their recommendations, and use herbal medicine exclusively as an auxiliary method.
You can relieve spasms using the following recipes:
- Infusions of small periwinkle or common agrimony.
- Collections of motherwort, valerian, anise or yarrow. Also tinctures of these herbs.
- Direct a stream of cold water onto your feet for several minutes, as well as onto reflex zones. Then rub well.
- As a preventive measure, decoctions of rose hips, hawthorn, nettle, and St. John's wort are used.
What happens during vasospasm of the head
Vasospasm is a sudden narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels in the brain. When it occurs, the patient’s well-being rarely worsens. Due to oxygen starvation of brain cells, various disorders of the central nervous system develop. Vascular spasms in the head are a dangerous condition that can cause the development of serious diseases.
The occurrence of spasm is associated not only with problems of the brain, but also of the cervical spine. After all, it is through it that the arteries supplying the brain with blood pass. Prolonged hard work affects the quality of blood supply to the brain, which can cause a deterioration in the general condition of blood vessels.
The brain is an organ that regulates the functioning of all processes and systems in the body. To perform its functions efficiently, it needs adequate nutrition, which is provided through blood vessels.
The movement of blood through the vessels occurs when their walls contract and relax. Vessel spasm consists of contraction of its walls, which is not followed by relaxation. As a result, blood circulation becomes difficult and a characteristic pain syndrome also occurs.
Increased intracranial pressure
Under the influence of various provoking factors, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in some parts of the skull is disrupted. The result is a lack or, on the contrary, an excess of cerebrospinal fluid.
Normally, a person secretes 1 liter of cerebrospinal fluid per day. This fluid is continuously absorbed into the blood vessels of the brain. This does not happen against the background of various pathologies. As a result, the cerebrospinal fluid puts pressure on the ventricles of the brain. In this case, it is customary to talk about increased intracranial pressure.
The reasons for the development of this pathological condition are extremely serious:
- Large tumors located in the brain. They can be either benign or malignant.
- Encephalitis.
- Meningitis.
- Thrombosis of the venous sinuses.
- Hematomas formed as a result of various types of head injuries.
- Eclampsia.
- Ischemic stroke.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hypoxia.
- Severe intoxication process.
The main symptom of increased intracranial pressure is a severe headache of a spastic nature. As a rule, it bothers you in the morning.
Other clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Nausea, often turning into vomiting.
- Excessive sweating.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Painful sensations in the eyes. All objects are doubled. The pain is pulsating.
- Presence of small bruises under the eyes.
- Irritability.
- Increased degree of fatigue.
- Impaired joint mobility.
- In severe cases, the patient loses consciousness.
Increased intracranial pressure is a good reason to visit a medical facility. Constant exposure to the brain negatively affects its functioning. In severe cases, death can occur.
First signs
The main symptoms of vascular spasm and circulatory disorders in the brain area:
- headache , which can be localized in a certain area, or can cover the entire head;
- dizziness , spots before the eyes;
- tinnitus , which becomes louder with sudden movements or physical activity;
- lack of coordination;
- nausea and vomiting.
Headaches can be felt almost anywhere on the head. It can be caused by variable weather, stress or fatigue. As a rule, the pressure in this case is increased or decreased.
Article on the topic: Acute inflammatory lesion of the spinal cord meningomyelitis
Symptoms
Vasospasm is a transient condition that is characterized by a pathological narrowing of the vascular lumen, which is often associated with excessive, intense, prolonged contraction of the muscles of the artery wall. Vasospasm is a pathology that is a variant of angiodystonia, when tonic (endothelial) dysfunction of the vascular wall is detected, which entails impaired blood flow.
Unlike other cerebral angiodystonias, vasospasm of blood vessels in the brain is accompanied by focal neurological symptoms. Vascular dystonia, occurring in an acute form, is called vascular crisis.
The symptoms are identical to ischemic brain damage caused by vasospasm. Prolonged vasospasm of the vessels of the head can lead to serious disruptions - circulatory disorders, the development of a heart attack, stroke.
The clinical picture depends on the localization of the pathological process. The symptoms that manifest vasospasm of the vessels supplying the brain are more often associated with dysfunction of the area of the brain damaged due to ischemic processes. The main symptom of vasospasm is headache, which occurs due to deterioration of blood supply to brain tissue. Other signs:
- Dizziness, transient short-term confusion.
- Visual dysfunction (blurred image, appearance of foreign objects in the field of view).
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Decreased performance.
In the chronic form of the pathology, the symptoms manifest themselves mildly. If vasospasm develops rapidly, acutely, the symptoms are pronounced, complemented by signs of focal brain damage (depending on the location of the spasmodic artery) - impaired motor coordination, disorder of gross and fine motor skills, convulsive syndrome, speech dysfunction, paresis, paralysis.
Experts divide the manifestation of the disease according to the degree of its manifestation:
- Light form. The symptomatic picture is weak, treatment is often not required and the body recovers on its own. This form is also called vasospasm.
- Angioedema. Vascular spasm in the head leads to weakness in the body and headaches. The walls of blood vessels practically do not work - they become degenerated. Treatment is required immediately.
- Cerebro-necrotic. The patient's movements are impaired, speech becomes slurred, he vomits, experiences severe headaches, and loses consciousness. Hospitalization in this case is required immediately.
Experts also divide spasms into types depending on the degree of damage:
- Local character. Only a certain area of the brain is affected.
- Are common. Blood circulation in the brain is disrupted because the blood is viscous, there is damage throughout the cortex.
The cerebral vessels have few symptoms and the main one is headache. In this case, pain can occur in different places. This is due to the difficulty of blood passage - blood does not pass through the narrowed vessels in the required quantity and stagnates.
Some areas of the brain remain without nutrition and cannot work with high productivity. Dizziness is also an integral part of the spasm. Other symptoms may also occur. In a typical case, the following symptoms appear:
- high susceptibility to fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- background noise in the ears and head, which becomes more noticeable with physical activity;
- gagging and vomiting itself;
- floaters before eyes.
Symptoms of severe manifestations:
- speech defects;
- partial amnesia;
- lack of coordinated movements;
- inability to navigate in space;
- fainting.
Usually the spasm makes itself felt quickly and sharply. In this case, the manifestation of symptoms occurs suddenly and the person does not feel anything before their onset. There is a chronic form of vasospasm. It is characterized by a mild manifestation of the described symptoms. However, with the chronic form of the disease, complications may develop.
The main complication is ischemic stroke. It occurs when the vessel is completely blocked. The consequences of a stroke are extremely unpleasant - a blocked vessel leads to the death of parts of the brain.
Vasospasm in the brain can also occur in a child. This also leads to the death of certain areas of the brain. The consequence is delayed development, as well as other pathologies:
- decreased vision or loss of vision;
- lack of hearing;
- neuropathy.
The affected child will develop migraines over time.
Clinical manifestations
The first and main symptom of cerebral vasoconstriction is severe pain. It can have varying intensity and localization depending on the area in which the problem arose and how much the lumen of the artery is blocked.
The headache may be throbbing, pressing on the back of the head, temples or eyes, and feel like heaviness or buzzing. Unpleasant sensations intensify in bright light, noise, or if you suddenly stand up from a lying position (or, conversely, bend over while standing or sitting).
In addition, patients complain of:
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- flickering of flies before the eyes;
- weakness, etc.
Symptoms of cerebral vasoconstriction can be expressed to varying degrees. In a chronic process, health problems do not bother patients much and do not always require drug treatment. But with acute spasm, urgent hospitalization is often necessary, since the manifestations are so pronounced that the patient not only loses his ability to work, but may also die.
In addition to the listed symptoms, there may be:
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- impaired facial expressions and ability to speak;
- loss of orientation and more.
Such manifestations indicate complete blockage of the vessel and the development of ischemia in this area. In this case, the patient must be immediately examined by a doctor, provide first aid and prescribe examination and treatment based on its results.
How to recognize acute and chronic spasms
Instructions on how to distinguish acute from chronic spasms are presented in the table below:
| Spicy | Chronic |
| Abrupt development against a background of complete health, symptoms progress rapidly | Violations develop gradually and slowly increase |
| Intolerable headache that does not go away with rest or medication | Headache tolerable, relieved with pills |
| A person loses orientation in space, may lose consciousness, facial expressions and speech are impaired, paresis and paralysis may develop | Concomitant symptoms lead to a gradual decrease in performance, but not to its loss |
| Without medical attention, symptoms worsen and death may occur. | Symptoms go away on their own after resting or taking pills |
Headache due to stomach cramps
Discomfort does not always occur due to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. In some cases, the cause of headaches is muscle spasm. The cervical spine contains a large number of tissues that are extremely mobile and, accordingly, very vulnerable.
At present, the causes of spasms in muscle fibers have not been established. But it has been proven that the following factors are provoking:
- Various types of neck injuries.
- Constant static effect on tissue. A striking example is regular and long-term work at the computer.
- Frequently being under stress.
- Pinched nerve fibers.
- Lack of calcium and magnesium in the body.
- Osteochondrosis.
With muscle spasm, the headache is acute. In the suboccipital region it is stitching.
As mentioned above, sometimes discomfort can radiate into the skull. In this case, the headache is not directly related to damage to blood vessels or muscles located nearby.
A spasm in the stomach is a signal of a dysfunction of the organ. Causes of the pathological condition:
- Regular consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Tobacco smoking. Against this background, an insufficient amount of oxygen enters the stomach cells.
- Food poisoning. The spasm occurs due to constant vomiting or lack of food, which, despite poisoning, should still enter the stomach, but in most cases this does not happen.
- Overeating, especially before bed and at night.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Frequent consumption of dishes with a lot of herbs and spices.
- Prolonged stay in a state of stress.
- It is a bad habit to drink carbonated drinks during meals.
- Following the principles of a low-calorie diet. Many people adjust their diet incorrectly and simply starve.
- Pregnancy.
- General hypothermia of the body.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Erosion of the gastric mucosa.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Inflammation of the appendix.
- Worm infestation.
- Food allergies.
- Diabetes.
- Splenomegaly.
- Kidney pathologies.
- Gastritis.
- Hepatitis.
- Cholecystitis.
In addition to headaches and stomach cramps, a person may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- Nausea, often progressing to work. However, the latter does not bring relief.
- Heartburn.
- Belching accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth. Patients associate it with rotten eggs.
- Constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea.
- Flatulence.
- Bloating.
- Aversion to food.
- Painful sensations in the epigastric zone.
If the first alarming symptoms occur, you should contact a gastroenterologist. As the underlying disease is treated, the headaches will subside on their own. If discomfort is severe, the doctor will prescribe medications to relieve it.
Treatment regimens
The choice of the most effective treatment plan is made only on the basis of diagnostic results.
Treatment of spasms and headaches due to narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels in the brain:
- Taking nootropics. The most effective remedies: Trental, Piracetam, Nootropil.
- Intravenous administration of antispasmodics. Designed to quickly relieve discomfort. Effective remedies for headaches: “No-Shpa”, “Papazol”, “Eufillin”, “Revalgin”.
- Taking medications whose active components normalize the functioning of cerebral vessels. Cerebrolysin is considered effective.
- Taking antiplatelet agents (Aspirin) to reduce blood viscosity.
- Treatment with vitamin complexes and adaptogens (for example, extracts of lemongrass, ginseng, eleutherococcus).
- Physiotherapy. Darsonval and electrophoresis are recognized as the most effective methods.
- Massage of the collar area.
- Stay in health resort areas.
How to relieve spasms and severe headaches with hypertension:
- Diuretics (diuretics). These products help remove excess fluid from the body, thereby unloading the circulatory system. Examples of drugs: Indapamide, Hypothiazide. Potassium, which is essential for the heart, is removed from the body along with the fluid. In this regard, it is additionally necessary to take Panangin or Asparkam.
- Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers. These are drugs that affect the strength of cardiac output and muscle contractions of the organ. As a rule, doctors prescribe Amplodipine, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol or Carvedilol.
- Drugs that affect the tone of blood vessels. Examples of drugs: Lisinopril, Losartan, Monopril, Valsartan.
Treatment of spasms and headaches may also involve one-time use of fast-acting medications. But this is only if blood pressure has risen for the first time and sharply, and there are no symptoms of damage to other internal organs. In such situations, doctors prescribe Anaprilin, Nifepidin, Captopril or Clonidim.
If the doctor has diagnosed “increased intracranial pressure”, treatment directly depends on the cause that caused it. In serious cases, surgery is indicated.
Drug therapy for increased intracranial pressure includes the following:
- Taking diuretics. As a rule, doctors prescribe Furosemide.
- Taking hormonal drugs. The most effective is Dexamethasone.
- Taking neuroprotectors. For example, "Glycine".
- Taking osmodiuretics. Example: "Glycerol".
Treatment of muscle spasms in the neck directly depends on the root cause of the pathological processes. In case of tissue overstrain, it is enough to carry out a course of therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy. If the cause is a neurological disease, the doctor prescribes drug therapy.
If a headache is a consequence of damage to the stomach, doctors prescribe medications related to enzymes, antacids, anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, antibiotics, and probiotics. In addition, vitamin therapy is indicated.
Diagnosis and treatment
Delivery of diagnosis
In order for a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis in the presence of certain symptoms, you will need to conduct research:
- radiography of the vertebrae of the neck;
- MRI of head vessels.
A duplex scan will be required to determine the speed of blood flow and detect blood clots or plaques. An MRI or CT scan, which will be performed using a contrast agent, will provide a large amount of information about the patient’s condition. These studies will be sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
The final decision on taking medications rests with the doctor. You cannot self-medicate, because it is dangerous!
If it’s really bad, you can urgently relieve some of the symptoms at home, but this does not cancel a visit to the doctor for further treatment.
The following factors influence treatment:
- age;
- stage of the disease;
- individual characteristics of a person.
In pharmacies, tablets that can relieve spasms in the brain and also strengthen blood vessels are sold in large quantities. A neurologist will prescribe the drug that you need.
Often, to prevent and treat cerebral vasospasm, the following drugs are used:
- Ginkgo biloba. Its task is to improve blood circulation in the brain. Several drugs are produced based on this active substance.
- Valerian and its extracts. Allows you to relieve spasms and calm the nervous system.
- Papaverine. Take in emergency cases and only with a doctor's prescription. The purpose of the drug is to instantly dilate blood vessels.
- Atomax. The drug allows the blood vessels to maintain a normal state for a long time. This helps prevent new spasms.
- Atromid and similar drugs. Required for preventive measures.
Physiotherapy
The patient will need a neck massage, since due to problems in this part of the body with blood vessels, blood may not reach the head. It is important to pay attention to this area when observing osteochondrosis. The following procedures are also suitable:
- hydro procedures;
- oxygen treatment;
- gymnastics;
- electrophoresis using special means.
All measures are aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels and improving neck mobility.
Seizure prevention
If cerebral vascular spasms are repeated frequently, then this is a signal that changes need to be made to your lifestyle. To prevent recurrent attacks, you must follow these recommendations:
- exclude the influence of provoking factors;
- don't overexert yourself. Get more rest. Get enough sleep so that the body has time to recover;
- play sports or at least do gymnastics every morning;
- often walk in the park;
- avoid bad habits;
- Avoid drinking drinks containing caffeine, rough and irritating foods, and fast food. It is better to eat more vegetables, fruits, and poultry.
In 80% of cases, patients are able to reduce the frequency of spasms and prevent the development of severe circulatory disorders in the brain. Dangerous pathological processes with such problems develop only in 5% of cases. Although at the initial stages of development the danger of this problem is small, it should not be ignored. At the first signs, you need to be examined and treated.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are ideal as preventive measures and as accompanying procedures during the main treatment. The following measures are used to eliminate cerebral vascular spasms:
- Cold compress. It uses ice based on herbal decoction. The broth is poured into ice molds and frozen. They can also give massage.
- Decoctions. Instead of drinking coffee or regular tea, it is advisable to drink a decoction. Rose hips, motherwort or yarrow are used for it. Such drinks bring blood pressure back to normal and the body’s overall well-being improves.
- Using a product based on garlic, honey and lemon. These ingredients are taken in equal parts and crushed in a mixer. The resulting remedy is eaten a teaspoon per day for a whole month.
These measures alone will not quickly stop spasms of cerebral vessels, especially in severe cases. But as an addition to drug treatment, they are effective. Prevention with folk remedies, especially in old age, is a matter of course.
Treatment of headaches and vascular spasms should be carried out by a competent doctor. However, before taking it, in order to relieve painful sensations, it is allowed to resort to methods of alternative medicine.
The most effective recipes:
- Take 3 tbsp. l. pre-dried and crushed lemon balm. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the raw material. Cover the container with a lid or towel and let it brew for half an hour. Strain the resulting liquid. Take the prepared infusion, 2 tbsp. l. every 2 hours. It is advisable to add fresh leaves to regular tea. After a few hours, you can forget about pills for headaches and cramps. In addition, after drinking the infusion, sleep is normalized and tinnitus, which accompanies the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain, disappears.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. crushed valerian root. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the raw material. Place the container on the fire. Boil for 15 minutes. Remove the container from the stove and let the broth brew for 10 minutes. Strain the resulting liquid. This remedy must be taken three times a day, 1 tbsp. l. According to numerous reviews, headaches due to vasospasm subsides within 1-2 hours.
- Take peppermint, oregano and fireweed in equal proportions. Grind and mix the ingredients thoroughly. Take 1 tsp. the resulting collection and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. Cover the container with a lid and let it brew for half an hour. Strain the resulting liquid and drink at once. According to reviews, this multi-component infusion works better than tablets for headaches and spasms. This is due to the fact that the components included in its composition are powerful natural analgesics.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. dill seeds Pour 300 ml of boiling water over them. Let it brew for 30 minutes. Strain the resulting liquid and drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Wash the onion skins well. Fill it with hot water. Place the container on the fire and boil for 2 minutes. Remove the dishes from the stove and let the liquid sit for 1 hour. Take 100 ml once a day. If headaches with spasms bother you regularly, you need to use the product twice a day, 100 ml for 4 days.
- Take a small piece of cotton cloth and soak it in a weak vinegar solution. In this case, liquid made from apple raw materials helps better. For 1 liter of water there should be 1 tsp. vinegar. Wring out the fabric and place it on the forehead so that it covers the temples. After 10 minutes, the compress can be removed.
- Take a raw cabbage leaf. Crush it. Apply the sheet to the frontal part. Keep for half an hour.
- Take 20 g of hawthorn fruit. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over them. Place the container on the fire. Simmer the liquid for 10 minutes. Cool the resulting product to the most comfortable temperature. Drink three times a day on an empty stomach.
- Pour hot water into a basin and cool it to a temperature of 37-40 degrees. Add 2 tbsp to it. l. mustard powder. Stir thoroughly. Lower your legs into the basin for 10 minutes. After this, the limbs need to be quickly rinsed, dried and put on warm socks. This recipe is most useful for those who are interested in how to relieve headache spasms due to hypertension.
It is important to remember that with the help of folk remedies it is possible to relieve discomfort, but they do not eliminate the need to seek qualified medical help. Only a doctor can identify the root cause and tell you how to relieve headache spasms in the future.
How to cure a brain spasm
Depending on the root cause of the pathology, appropriate medications and treatment methods are used.
Treatment of vasospasm consists of eliminating the attack itself, taking measures to prevent it, restoring the performance and functions of the brain, correcting nutrition and lifestyle. How to treat the pathology is determined by the relevant specialists - therapists, angioneurologists, cardiologists.
Typically, various medications and physiotherapeutic procedures are used to treat cerebral vascular spasm. With the permission of the doctor, you can resort to unconventional methods of treatment and traditional medicine. In some cases, to cure the pathology, it will be enough to adjust your lifestyle and carry out a number of preventive measures.
Relieving spasm
If at the moment it is not possible to go to the hospital, then you can temporarily relieve the symptoms using either a simple massage of the relevant areas or cold baths.
At the first signs of a spasm in the initial stages of the disease, you can independently relieve the attack.
How to quickly relieve vasospasm:
- Wash with cold water;
- Soak your feet in a cool bath;
- Drink some warm water with a few drops of honey;
- Take a horizontal position and try to relax as much as possible;
- Provide access to fresh air;
- Perform a light massage of the collar area, neck, temples;
- Aromatherapy - a few drops of lavender or valerian in oil will help you relax and have a calming effect.
If the attack does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. You can get advice from your doctor on how to relieve cerebral vascular spasm with the help of medications.
Drug treatment
To combat such pathologies, there are a lot of medications, but depending on the severity of the pathology, not only medications can be prescribed, but also various massages, electrophoresis, etc.
Treatment of cerebral vascular spasms is prescribed depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, the nature of the pathology, the frequency of attacks and the severity of manifestations and symptoms of pathology.
Preparations:
- To quickly relieve symptoms of spasm:
- Painkillers (analgin, tempalgin, ketanov);
- Aspirin or its analogues (Lospirin, Cardiomagnyl);
- Antispasmodic drugs (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papazol, Andipal, Spazmalgon);
- Calming drugs (Barboval, Corvalol, Valerian).
- To restore cerebral circulation (tablets or injections):
- Calcium antagonists;
- Eufillin, Dibazol;
- Cerebrolysin;
- Cavinton;
- Ceraxon;
- Actovegin.
- Medicines to improve metabolic processes in the brain (Sermion, Piracetam).
Important! You cannot independently select a medicine for vascular spasms, because Each drug is selected taking into account the cause of the pathology. Therefore, only a neurologist should select medications.
Non-drug treatment
Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease – i.e. for the treatment of concomitant pathologies (heart disease, kidney disease, metabolism, etc.).
Physiotherapeutic measures to relieve vasospasm:
- Massages (occipital and collar areas);
- Hydrotherapy (contrast showers, baths);
- Electrophoresis;
- Balneotherapy;
- Darsonvalization;
- Physiotherapy.
A change in diet is of great importance - smoked meats, chocolate, fatty meats, chocolate, strong tea, salty and spicy foods, and caffeinated drinks are excluded from the diet. Preference should be given to natural foods of plant origin, rich in microelements and vitamins.
Alternative medicine
Reviews from patients point to unconventional methods of eliminating vascular spasms, which quickly allow one to cope with the manifestations of the disease. These include: yoga, aromatherapy and manual therapy.
The forum of patients suffering from cerebral vascular spasms notes the strong therapeutic effect provided by the sentiments of the Russian scientist G.N. Sytin. With their help, you can get rid of the disease forever, and Sytin’s attitude is approved by the Russian Ministry of Health, confirming its effect.
Folk remedies
In some cases, traditional medicine may be a completely acceptable option for treating this pathology, especially since some herbs have natural properties that help dilate blood vessels, as well as relax them.
Treatment with folk remedies includes the following measures:
- Contrast baths for extremities - alternately immerse your legs in cold and hot water to improve vascular blood flow.
- Decoctions of rosehip and hawthorn. Drink herbal infusions twice a day for two weeks.
- Cold compress on the forehead during spasms - apply a towel soaked in a solution of vinegar and cold water or soaked in an infusion of herbs (St. John's wort, plantain, dandelion root).
- Garlic, honey, lemon. Prepare a mixture of the listed ingredients in equal proportions. For a month, take a teaspoon of the mixture daily in the morning.
Note! Folk remedies are not a panacea for vascular spasms. Treatment should be carried out in combination with medications.
Preventing new attacks
The more often attacks of vascular spasms appear, the greater the need for a lifestyle review that can be used to prevent the occurrence of new attacks.
What to do to prevent vascular spasm:
- Ensure healthy sleep (at least 8 hours);
- Spend more time outdoors;
- Change your diet;
- Perform daily physical exercise;
- Do not overstrain your brain;
- Avoid stress and overwork;
- Minimize nicotine and alcohol consumption;
- Carry out hardening procedures.
You should carefully monitor your own health and undergo regular medical examinations.
Emergency help at home
If the symptoms of the cerebral vessels are unbearable, and you have to wait a significant amount of time before the ambulance arrives, then it is advisable to alleviate the patient’s condition. To do this you will need:
- take a cold shower;
- place your feet in cool water;
- drink a glass of warm water with a little honey;
- massage the head, especially in the temple area;
- massage your knees;
- Aromatherapy with soothing oils is suitable.
These measures will help not only in emergency cases, but also in case of severe fatigue after hard work.
Classification of spasms
Brain spasms do not develop just like that; a large number of factors always contribute to this.
According to the severity of spasms, they can be classified into several types:
- Angiospasm is the initial form of pathology and is considered the mildest. Despite the fact that there are symptoms, they are not very pronounced, many do not notice them. The patient's condition quickly returns to normal; medications are rarely taken. There is no need for systematic treatment, but this is the first call from the body that cannot be ignored.
- Angioedema spasm is a dystrophic vascular lesion, its severity is bright. In this case, you must seek help from a medical facility as soon as possible.
- Cerebral vasospasm is the most severe type of pathology, the occurrence of which may lead to the development of a stroke. The symptoms are severe, the patient loses consciousness, and there are memory lapses. Immediate hospitalization and examination are required.
In order to get rid of spasms, you need to know not only their classification, but also the cause of their occurrence, and, as you can see, there are many of them. The video in this article goes into more detail about the classification of spasms.
First aid for relieving spasms
If spasms bother a person, but there is no way to immediately visit a doctor, a completely natural question arises - what to take for spasms of cerebral vessels and how to relieve them yourself?
You can relieve discomfort without the use of medications; there are many simple methods for this:
- Find a comfortable position, lie on a sofa or sit in a chair. You need to relax, ventilate the room, massage your forehead and temples.
- You can use essential oil to relieve headaches. It is especially effective to use jasmine or lavender oil. You can simply breathe or refill the aroma lamp.
- Take tea made from herbs: chamomile, mint.
- If your body is hypothermic, you can lie down in a warm bath.
Many people know that blood vessels can be dilated with the help of medications. However, if cramps occur, drinking alcohol is not recommended. Initially, they will indeed be removed, but after a while they will return again, but with a vengeance.
Recommended measures for spasms
The only possible drink that you can drink occasionally is cognac, but its dosage should not be more than 50 grams.
Recommendations from experts
If you follow a number of rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of painful sensations.
Doctors' advice:
- It is advisable to make adjustments to the diet. Products that contribute to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels should be excluded from the menu. These are fatty and fried foods, as well as fast food.
- Take walks in the fresh air as often as possible.
- Avoid getting into stressful situations.
- Properly organize work and rest schedules. It is important to remember that one of the causes of headaches with spasms is lack of sleep.
- Maintain drinking regime. The average norm for an adult is 2 liters of clean still water daily.
- Regularly expose the body to moderate physical activity. Physical inactivity and high-intensity exercise are harmful. In this case, it is important to explore your options.
- If your daily activities involve constant sitting, you should do a few simple exercises periodically (at least every 2 hours).
- Control body weight.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Treat all identified diseases in a timely manner. Even dental pathologies can cause regular headaches with spasms.
- Take a contrast shower.
- Dress according to temperature conditions to prevent hypothermia. In cold weather, a hat is required.
- Organize your night's rest properly. It is recommended to sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow. This prevents muscle spasms from occurring.
Following these recommendations significantly reduces the likelihood of discomfort.
Treatment
Medicines for vascular spasms are aimed at eliminating the root causes of the disorders that lead to the onset of the disease. Antihypertensive drugs for vascular spasms help reduce cholesterol, which prevents the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques, leading to hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Drugs for relieving vascular spasms have a reaction to improve the patient’s adaptation to his environment, if there are reasons for taking them. It is recommended to use sedatives (tincture of valerian or motherwort).
Vasospasm, the treatment of which is mandatory, can be relieved by drugs such as Kaviton, Actovegin. It is recommended to take multivitamins, vitamins E and B on an ongoing basis. Experts advise resorting to the prevention of disease development. Physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, stay at a sanatorium resort, mud baths and mineral waters help restore the body. Medicines for vascular spasms should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. .