Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Carotid artery stenosis is a condition in which cholesterol, or in other words, fat, is deposited deep within the artery wall, leading to the formation of plaque that causes narrowing (stenosis) of the artery.
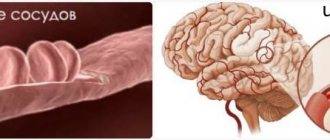
The main reason leading to the development of carotid artery stenosis is atherosclerosis. Blood supply to the brain
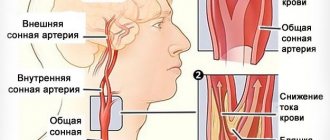
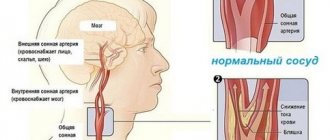
The blood supply to the brain is carried out through 4 arterial vessels: two carotid (right and left) and, accordingly, two vertebral arteries. The main volume of blood (up to 80%) enters the brain through the carotid arteries, so their narrowing (stenosis) significantly increases the risk of stroke.
The carotid arteries depart from the aorta in the chest cavity, go through the muscles of the neck and, passing through the bones of the base of the skull, approach the brain. If you place your fingers on the anterolateral surface of the neck on both sides, you can feel their pulsation. Near the larynx, the common carotid artery divides into the external and internal carotid arteries. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the muscles, soft tissues of the head and face, and the internal carotid artery supplies the brain. Most often, an atherosclerotic plaque forms in the area of division (bifurcation) of the common carotid artery into internal and external.
Most often, carotid artery stenosis develops in patients of the older age group - more than 60 years.
The damaging effects on the internal lining of the artery are caused by:
- hypertension - a persistent and prolonged increase in blood pressure over 140/90 mm. rt. Art.;
- diabetes - the risk of developing carotid artery stenosis in diabetic patients is 4 times higher than in healthy people;
- smoking - in addition to damaging the arterial walls, it leads to blood thickening, increased “bad” cholesterol, provokes thrombosis, and reduces the transport ability of red blood cells to deliver oxygen to tissues;
- An increased level of cholesterol in the blood (mainly its “bad” fraction - low-density lipoproteins) contributes to the formation of cholesterol plaques in the thickness of the arterial wall.
Risk factors contributing to the development of carotid artery stenosis are:
- overweight and obesity;
- cardiac ischemia;
- family history of atherosclerosis;
- age over 70 years;
- insufficient physical activity (sedentary lifestyle);
- metabolic syndrome.
The risk of developing carotid artery stenosis in smokers with high blood cholesterol and high blood pressure is eight times higher than in non-smokers with normal cholesterol and blood pressure.
Metabolic syndrome refers to a collection of risk factors that increase the risk of stroke and other diseases such as diabetes and coronary heart disease. Five components of metabolic syndrome: 1. wide waist (indicates abdominal obesity - fat deposition in the abdominal cavity);
2. increased levels of triglycerides (one of the fractions of cholesterol) in the blood;
3. low level of high-density lipoproteins (“good” cholesterol fraction) in the blood;
4. high blood pressure;
5. increased blood glucose levels.
The diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is made when three or more of the above components are present in a patient.
In addition, fibromuscular dysplasia and aneurysmal disease can cause carotid artery stenosis, but these conditions are uncommon.
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease, so plaques form not only in the carotid arteries, but also in other arteries. Patients with carotid artery stenosis have an increased risk of coronary and leg artery disease, which may present with angina and intermittent claudication.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Narrowed cervical vessels and dizziness: how to treat
The blood vessels of the cervical spine are elastic, smooth muscle, hollow formations that supply blood to the brain. In total, about 15% of the total volume of circulating blood and almost a quarter of the amount of oxygen that a person receives during breathing enters the brain.
Vasoconstriction in this section is a form of vascular obstruction and, in the absence of timely correction, can lead to complete occlusion (blockage) of the arteries supplying blood to brain cells.
The pathology is dangerous not only due to persistent vertebrobasilar and vegetative-vascular disorders, but also severe organic brain damage: stroke, impaired swallowing and speech function, paralysis of the facial muscles.
Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine
Pathogenetic and morphological changes
The most important blood vessels in the neck are the carotid arteries, through which up to 80% of the blood enters the brain. The remaining volume circulates through the vertebral arteries, which (like the carotid arteries) begin in the chest cavity and supply blood to the posterior parts of the brain and the cerebellum.
The vertebral arteries in the central part of the ventral surface of the brain merge to form the main artery, which is called the basilar artery. The outflow of blood to the heart occurs through paired jugular veins, which belong to the superior vena cava system and are located in the cervical spine.
Arteries of the head
The pathophysiological changes during the formation of partial vascular obstruction may be based on two processes.
- Blockage of arteries with blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques .
This is the main cause of vasoconstriction in the cervical region, developing against the background of hematological pathologies and atherosclerosis. Blockage by atherosclerotic plaques - Spasm of blood vessels in the neck and brain . Spasm of blood vessels in most cases is a secondary pathology (a consequence of sclerotic changes in the carotid and vertebral arteries), since prolonged and strong contraction of the muscle walls occurs against the background of acute or chronic tissue hypoxia.
Cerebral vasospasm
When blood vessels narrow, their capacity decreases, which leads to insufficient supply of blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the brain and cerebellum.
At the initial stage, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, but with a chronic course, the patient develops characteristic clinical manifestations and complaints: headache, tinnitus, dizziness, instability of blood pressure and other symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
Note! Symptoms of stenosis are usually more pronounced if the carotid arteries are affected, since they supply the brain with the bulk of the blood necessary for normal functioning (about 70-80%).
Possible reasons
There are quite a few reasons that can provoke stenosis of the carotid or vertebral arteries. The main risk factor is atherosclerosis - a chronic pathology characterized by the deposition on the walls of blood vessels of cholesterol, as well as some complex proteins consisting of fatty acids, phospholipids and neutral fats.
The basis of pathophysiological changes in atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and basilar artery is a violation of lipid and protein metabolism, which can be facilitated by excess body weight, endocrinological pathologies, smoking, chronic intoxication of the body with toxic substances (wine alcohol, heavy metals, harmful emissions, etc.) .
Carotid artery stenosis
Among other possible causes of vasoconstriction in the cervical spine, experts also name the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- arterial hypertension in the subcompensation stage (maintaining pressure at 140/90 mm Hg);
- an eating disorder, expressed in frequent and abundant consumption of foods high in fat (in 60% of patients with this diagnosis, the level of total cholesterol exceeds 5 mmol/l);
- diabetes;
- hypodynamic disorders of blood circulation and respiratory function associated with a sedentary lifestyle and prolonged stay in a static position (sedentary work).
Symptoms of diabetes
Spasm of the neck vessels, which also narrows the lumen and impairs the patency of the artery, can occur against the background of chronic heart diseases (coronary artery disease, tachycardia, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, etc.
), as well as nervous and emotional overload.
Muscle tension is the body’s physiological response to stress, so psycho-emotional factors with prolonged exposure can cause chronic vasoconstriction of the neck and head.
Connection with osteochondrosis
Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical region can also be the result of degenerative changes in this segment of the spine. The cervical vertebrae are connected to each other using elastic formations consisting of fibrocartilaginous ring plates.
Such formations are called intervertebral discs. Inside they are filled with a gelatinous jelly-like substance - the nucleus pulposus, which acts as a shock absorber.
The pulp is nourished by blood vessels located in the central spinal canal.
What are intervertebral discs
Dystrophy of the disc nucleus is manifested by its dehydration and drying out, as a result of which the fibrous membranes surrounding the disc become thinner and cannot tightly hold the jelly-like nucleus in an anatomically correct location.
The pulp is displaced and disc bulges (protrusions) or protrusions (hernias) form.
Intervertebral hernias in the cervical region are more dangerous, since they are large in size, and if left untreated for a long time, there is a high risk of sequestration - complete separation of the nucleus pulposus from the intervertebral disc and its prolapse into the spinal canal.
One of the manifestations of osteochondrosis and its complications is compression (squeezing) of nerve endings. A hernial protrusion can also put pressure on the blood vessels located in the neck, causing them to narrow and spasm. Osteophytes - bone growths in the form of hooks and spines, mainly along the edges of the vertebral body and spinous processes - can also cause pinching of neck vessels.
Vertebral artery
Congenital vasoconstriction
Narrowing of the neck vessels can be a congenital pathology, which is rarely isolated and usually develops against the background of other diseases, for example, vascular hypoplasia, abnormal development of the cervical vertebrae, vertebral arthrosis.
Of great importance in the prevention of congenital defects of the spine is the intake of folic acid (vitamin B9) during the period of preparation for pregnancy and in the first trimester, when the formation of all vital organs of the fetus, including the neural tube, occurs.
Folic acid during pregnancy
Not only deficiencies of various vitamins, but also other factors (from the mother’s side), for example:
- infectious diseases of the mother, leading to infection of the amniotic fluid and amniotic membrane;
- intoxication of the fetus with decay products of ethyl alcohol, nicotine, ammonia and other toxic substances (if the mother has bad habits or the woman lives in environmentally unfavorable areas);
- injuries received during pregnancy.
Trauma during pregnancy
Deformation of the cervical vertebrae and the resulting narrowing of the neck vessels in a newborn may be the result of a protracted or difficult labor, especially if obstetric forceps or a vacuum aspirator were used to remove the baby.
Signs and symptoms
Clinical manifestations of the pathology are determined by sclerotic and hypoxic changes. Almost all symptoms are associated with insufficient oxygen and nutrients that enter the brain along with the blood. The typical clinical picture of pathological narrowing of the vessels of the neck and head depends on the degree of narrowing.
Table. Symptoms of stenosis of the carotid and vertebral arteries.
Degree of narrowingPossible symptoms
| First (no more than 10-15%) | The course of the pathology at this stage can be practically asymptomatic. Some patients at this stage complain of fatigue, frequent mood swings, and asthenic syndrome. Performance during first-degree narrowing is preserved almost completely; the most typical signs of stenosis (headache and hearing and vision impairment) are mild or completely absent. |
| Second (no more than 20-30%) | Despite the fact that the disease is progressing, most symptoms still remain mild or moderate, and the overall picture of the disease is poorly visible due to the erased course. Patients with second-degree vascular lesions in the neck complain of periodic headaches, dizziness, emotional instability, and decreased performance. Such patients do not tolerate hot weather well (shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air appears), and suffer from disorders of the vestibular apparatus. |
| Third (up to 50%) | The following symptoms may be added to the symptoms listed above: tinnitus, impaired visual function, flashing spots and dots before the eyes, severe dizziness. Headache becomes a constant symptom and may worsen after physical activity or waking up. |
| Fourth (more than 50%) | All of the above symptoms are characteristic of grade 4 stenosis. The symptoms are severe, the patient complains of throbbing, pressing and bursting pain in the temporal, parietal, frontal and occipital parts of the head. In some cases, there may be a disorder of swallowing and speech function, paresthesia and paralysis of the facial muscles (manifested by impaired facial expressions), short-term fainting and loss of consciousness. |
Source: https://novosibmemorial.ru/suzheny-sosudy-shejnogo-otdela-i-golovokruzhenie-kak-lechit/
Diet
An effective method of treating and preventing stenosis is dietary nutrition. To strengthen the vascular walls, doctors will add flaxseeds and fish oil to the patient’s diet. The diet includes a large amount of vegetables, fruits, fish and seafood. To recover, the patient must eliminate bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, and also begin to engage in physical exercise to strengthen and maintain the shape of the lower extremities and the whole body.
Blood vessels, which are hollow elastic tubes made of muscle fibers and connective tissue, entangle all parts of the human body in a network, saturating the body with oxygen and nutrients. But with age, under the influence of negative external factors and a number of diseases, they can no longer cope with their functions.
Vascular stenosis is one of the most common pathologies that impede normal blood circulation. The disease can affect arteries and veins of any organs (heart, neck, brain, etc.), while the gaps inside the vessels narrow, making it difficult for blood to flow.
Traditional methods
Various internal remedies are used, as well as vascular exercises.
The simplest option: drink a glass of hot water in the morning on an empty stomach.
One of the best folk remedies for restoring the tone of the blood vessels of the cervical region and head is given below.
So, the recipe: take fresh or dried, but always young pine shoots. Place 25 cones in a pan, pour in about 1.5 liters of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for three hours. If the buds have not become soft, they can be boiled until soft over low heat, but usually young fruits soften on their own after three hours in boiling water. Add four lemons minced in a meat grinder, a kilogram of sugar, bring to a boil and turn off.
It is preferable to use honey, then it should be introduced after the lemons and buds have cooled. The product is taken one tablespoon at a time with each meal. During the period of treatment with this remedy, you must definitely drink tea brewed with hawthorn fruits and field clover flowers.
Another remedy: chop 200 grams of figs, dried apricots, raisins, prunes and twenty walnut kernels, add honey, and store in a jar in the refrigerator. Take a spoonful morning and evening. The product perfectly strengthens vascular walls.
It is useful to use deyasil root infused with vodka. Aging period – 40 days. Take one dose per day, 25 drops per hundred grams of water.
Remember that many diseases of the blood vessels of the brain and neck can be overcome, but for this a person must want to live and fight, because neither taking medications, nor surgery, nor the doctor’s instructions can turn the situation around if you do not change your lifestyle.
Vessels
Arteries of the Head and Neck: Anatomy, Diagram, Atherosclerosis
Feb 06, 2020 Kokh V. A.
15927
Vessels
Transverse Cervical Artery
Feb 06, 2020 Kokh V. A.
7784
Vessels
Pathogenesis of carotid artery stenosis
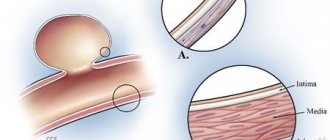
The carotid artery in young and healthy people has an elastic structure. Its inner lining, called intima, is a smooth surface, which prevents the formation of blood clots in the lumen of the artery. Aging and high blood pressure, which cause microtears in the intima, contribute to the deposition of cholesterol in the thickness of the arterial wall and the formation of plaque. An atherosclerotic plaque is a substance of heterogeneous structure, having a consistency ranging from cheesy to cartilage-like. This is due to the gradual deposition of cholesterol, its calcification, and, over time, growth in the thickness of the connective tissue plaque. All this leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the artery. As atherosclerosis progresses, the wall of the internal carotid artery changes from elastic and pliable to dense and rigid.
The mechanism of stroke development with carotid artery stenosis can develop in several ways:
- as the atherosclerotic plaque increases in size, it causes a narrowing of the artery to the point of complete blockage (occlusion), which disrupts the flow of blood to the brain;
- the surface of the plaque, as a rule, has irregularities, often ulcerations, where blood clots form, which partially or completely block the artery and lead to insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- in some cases, usually due to hemorrhage from newly formed pathological vessels, the plaque cracks or ruptures, and fragments of cholesterol or blood clots formed on its surface move with the blood flow into the arteries of the brain, causing their blockage.
Symptoms at different stages of the disease
There are two forms of the disease:
1. Spicy. A sharp narrowing of blood vessels inevitably leads to a stroke.
Without urgent medical attention, death is possible. Most often, this form is caused by a chronic one.
- Chronic. The long-term development of a disease to the symptoms of which the patient’s body adapts without feeling discomfort. Therefore, people often go to the hospital at the last stage, when the symptoms become too obvious and characteristic.
As the disease progresses, symptoms change. At the first stage of the chronic form, headache, constant drowsiness and fatigue are noted. A person’s short-term memory is impaired, and emotional stability fails. In most cases, this condition is attributed to bad weather, the influence of magnetic storms, heavy workload and other factors. For those who neglect to visit a doctor, the first stage gradually turns into the second.
At the next stage, general health deteriorates more significantly. The headache turns into a constant migraine, sudden mood changes are observed, and a depressive state may develop. The patient's gait changes - the disease affects the vestibular apparatus. The urinary system may be bothersome.
The third stage is characterized by an absolute lack of coordination: the patient cannot walk independently, constantly loses his balance and stumbles. In isolated cases, the musculoskeletal system may fail completely. Dysfunction of the pelvic organs and uncontrolled urination occurs. Forgetfulness and speech impairment are noted as the first signs of dementia. Sometimes the last stage is no longer amenable to quality treatment, and some disorders of the brain and other organs remain irreversible. To make an accurate diagnosis, especially with a prolonged illness, symptoms alone may be sufficient. However, for accurate diagnosis, identification of affected areas and analysis of possible complications, a comprehensive examination is carried out.
Symptoms of pathology
The cause of narrowing of blood vessels in the head, neck, and other organs is often high levels of cholesterol in the blood. An excess of this fat-like substance is deposited in the form of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels, which leads to the development of stenosis. The risk of blockage or narrowing of the bloodstream is especially high in people who:
- have elevated blood sugar levels;
- suffer from hypertension;
- are overweight;
- eat a lot of fatty foods;
- smoke;
- lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- suffer from vasculitis;
- undergoing radiation therapy.
Also, vascular pathology can be congenital, provoked by an inflammatory process or the proliferation of malignant or benign neoplasms. Hereditary predisposition also matters. Therefore, those people whose close relatives have been diagnosed with vascular stenosis should be more attentive to their health so that, if necessary, treatment is carried out in a timely manner.
In the early stages, the disease has almost no symptoms. However, the appearance of frequent pressing pain in the forehead or back of the head, periodic noise in the ears, unusual absent-mindedness and inattention, memory impairment, difficulty in neck mobility are the first alarming symptoms of the disease.
Osteochondrosis causes neck pain.
And if there is causeless nausea and severe dizziness, this is a direct indication for immediate examination. Oxygen starvation can cause numbness of the tongue and hands, increased blood pressure and periodic loss of consciousness.
Treatment methods for atherosclerosis
After diagnostic procedures, the patient may be additionally referred for consultation to a cardiologist if heart disease is detected, or to a neurologist if cerebral vascular pathologies are detected. Determining the exact clinical picture is necessary to prescribe a comprehensive treatment method for cervical atherosclerosis.
Drug therapy is usually prescribed. Surgery is resorted to only in cases where the patient's life is in danger. The complex method involves, along with taking medications, changing your lifestyle, following a diet, adjusting your daily routine and, if necessary, changing your job.
Drug therapy
Traditional therapy does not provide immediate results, and depending on the extent of the disease, medications are taken in courses or continuously over many years. Medicines have a number of side effects and compatibility, so they must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Self-medication can result in an exacerbation of the disease, a heart attack, or the development of irreversible complications.
Several groups of drugs are used to treat atherosclerosis of the vessels of the cervical spine. The first and most important are statins. Their role is to block enzymes responsible for the production of cholesterol by liver cells. The use of statins reduces cholesterol deposition on the walls of blood vessels, lowers the lipid content in plaques and prevents the development of thrombosis. Statins are prescribed to patients even after a stroke or myocardial infarction.
The next group of drugs are fibrates. They are needed to reduce the amount of fat and activate lipoprotein lipases. Medicines promote an intensive process of lipid oxidation, improve nutrition of the walls of blood vessels and reduce the severity of inflammatory internal processes.
Medicines of the hypolipid group are aimed at increasing the amount of protein and lowering cholesterol levels in the blood, balancing the proportions of LDL and HDL. Nicotinic acid belongs to a group of drugs, but is vitamin B3. Daily consumption leads to a gradual decrease in cholesterol and LDL, an increase in HDL and an improvement in the blood's ability to dissolve blood clots.
If the patient has intolerance to statins, then drugs from the group of bile acid sequestrants are prescribed. They bind bile acids, which stimulate the absorption of fats in the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, blood cholesterol levels decrease and lipid levels normalize. To thin the blood, medications from the group of antiplatelet agents are prescribed.
Along with medications, patients are prescribed antioxidant and vitamin-mineral complexes, hormonal and vasodilating medications, and biostimulants.
Surgical methods
The need for surgery is determined based on the results of diagnostics and tests by a cardiologist, neurologist, surgeon and neurosurgeon. Surgical methods for the treatment of atherosclerosis are prescribed to patients with a high degree of vascular stenosis. Traditional drug therapy at this stage of the disease will no longer provide positive effects.
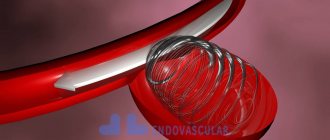
Carotid stenting is designed to widen the diameter of blood vessels. An elastic catheter is inserted into the affected artery, which delivers the main catheter with a special balloon to the site of vascular damage. Air is supplied to the balloon, resulting in expansion of the lumen and reduction of the atherosclerotic plaque.
Endarterectomy involves clearing the walls of blood vessels through incisions. Another type of surgical treatment is bypass surgery. This is the implantation of a shunt into a damaged vessel, through which blood flows bypassing the damaged area. Usually the anastomosis is a part of a vein or an artificial vessel.
Non-traditional treatment methods
The use of traditional medicine must be agreed with a doctor: not all of them are compatible with medications and can cause unpleasant side effects. Typically, folk remedies are prescribed at the initial stage of atherosclerosis of the cervical vessels and in addition to drug therapy.
If prescribed by a doctor, atherosclerosis of the neck vessels can be treated with leeches. Hirudotherapy includes from 7 to 12 sessions, the frequency of which is selected individually. Place leeches behind the ears. The active biological substances contained in their saliva lower cholesterol levels, restore capillary structure, and improve the movement of biological fluids.
Of the simple folk methods, unrefined corn oil is recommended. Daily intake 1 tbsp. improves the condition and elasticity of blood vessels. Before breakfast, you can take a mixture of corn or olive oil with honey and fresh lemon juice. All components are taken in equal proportions, and an adult needs only 1 tbsp.
For atherosclerosis and how to prevent it, fresh potato juice mixed with carrot or celery juice is useful. Another effective recipe: 2 heads of garlic and a lemon, mixed in a blender bowl with a glass of hot water. Infuse the resulting puree for 3-4 days, and take 40 ml before breakfast.
Complications of carotid artery stenosis
A stroke is the death of cells (neurons) in the brain. As a cause of death, stroke ranks second after myocardial infarction. According to the World Health Organization, worldwide, 6.24 million people died from stroke in 2020.[1]
About 85% of strokes develop due to cessation of blood flow through the arteries supplying blood to the brain, they are called ischemic. 15% of strokes are the result of a ruptured vessel, which leads to intracranial hemorrhage, they are called hemorrhagic.[2]
Half of all ischemic strokes develop due to narrowing (stenosis) of the arteries supplying blood to the brain, 20% - due to the formation of blood clots in the cavities of the heart, usually against the background of heart rhythm disturbances and their movement with the blood flow into the arteries of the brain, 25% - so-called lacunar strokes , their main cause is hypertension, 5% are a consequence of arterial dissection (dissection) or congenital atrial septal defect.[3]
Mortality rates from stroke in Russia are extremely high. Of stroke patients, every third patient dies within 30 days, and this figure increases to 50% (every second patient) by the end of 1 year.[4]
The brain is constantly dependent on a stable and adequate blood supply due to the high activity of metabolic processes occurring in it and the lack of other energy sources. The human brain weighs only 2% of the total body weight, but it consumes 20% of the oxygen carried by red blood cells circulating in the blood.[5] Therefore, even with a short-term decrease in blood flow to the brain, oxygen starvation (ischemia) develops, which can lead to the development of a stroke.
Narrowing of blood vessels in the head and neck - symptoms, treatment
Sharp pain, dizziness, tinnitus, and forgetfulness are symptoms of a disease such as head and neck stenosis. In other words, their narrowing, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the brain.
How does the disease appear?
The main function of blood is to saturate tissues and organs with oxygen and nutrients. Its circulation passes through veins and arteries. If they are damaged, deformed, or blocked, then there is a loss of tone and a narrowing of the lumen . In this case, the flow of blood to the brain is limited, which causes memory impairment, mood swings and headaches.
Atherosclerotic plaques that form on the walls of blood vessels impair blood circulation.
The mechanism of their formation is as follows: when the human body enters large quantities of fatty or spicy foods, this leads to an increase in LDL. The walls of blood vessels cease to be elastic and become injured.
The damaged areas are filled with particles of cholesterol and platelets. This creates a plaque that can completely block the vessel.
A disease such as neck stenosis develops after contraction of the carotid arteries.
Stages of development of stenosis
Stenosis can be chronic or acute. In the latter case, the lack of treatment measures can lead to death.
Chronic stenosis takes years to form. The first symptoms may be pain, dizziness, and forgetfulness. Atherosclerotic conditions are the result of many causes, which accumulate over time and form a pathology of a chronic nature. The main stages of the disease are:
- Mild – symptoms may be completely absent. Or expressed in headaches, fatigue, mood changes.
- Medium – vasoconstriction provokes improper functioning of the urinary, reproductive and musculoskeletal systems. Changes when walking become noticeable, there is numbness in the limbs and frequent false urge to urinate. Such people become more irritable and experience unreasonable mood swings. If such symptoms appear, then you should not postpone visiting a doctor.
- Severe – in such a case, the functioning of the brain is impaired. Any movement is difficult, coordination is lost. Vision deteriorates, speech is confused, and dementia appears.
Many people do not appreciate the severity of their condition until the disease becomes severe. Without the help of specialists and adequate treatment, the consequences can be severe, such as a heart attack or stroke.
Causes of the disease
The reasons why the disease occurs are conventionally divided into two types:
- Purchased
- Hereditary
The first include:
- Related chronic diseases
- Frequent stay in suffocating, crowded rooms. What causes an acute lack of oxygen?
- Lack of sleep. An adult should receive 7-8 hours of proper rest every day.
- Tobacco smoking. Nicotine causes blood vessels to contract, and when this happens regularly, they become damaged. In addition, when smoking a cigarette, a person receives a dose of carbon monoxide, which reduces the absorption of oxygen by the body.
- Failure to comply with temperature conditions. Frequent overheating or hypothermia negatively affects blood vessels.
- Stress. Their consequence is pressure drops and the formation of microcracks in the veins and arteries.
- Atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis. Cholesterol plaques that are deposited on the vessels narrow their lumen.
Treatment
Treatment of vasoconstriction of the head and neck should be comprehensive. For this purpose, medications, dietary nutrition, herbal decoctions, and surgical intervention are used.
Drug therapy consists of the use of statins, tranquilizers, antioxidants, fibrates, simvastines, antidepressants and vasodilators. These drugs have a lot of contraindications and side effects, so their use should be under the supervision of a doctor.
Diet. Very often, it is poor nutrition that can cause vascular diseases. Therefore, following a diet will support and strengthen the circulatory system. Strictly prohibited:
- Fatty foods
- Smoking
- Acute
- Marinades
- Fast food
- Animal fats
- Coffee
- Chocolate
- Mayonnaise
Each dish should be prepared with a minimum amount of salt. Enriching your diet with cereals, fresh vegetables, fruits and dairy products will help reduce the level of LDL in the blood and stabilize blood pressure.
Surgery. This is the last and most radical stage of treatment. It is used when all of the above does not produce any results. It can be done using three methods:
- Caratid endarterectomy, its essence is to dissect the damaged vessel and eliminate the plaque.
- Angioplasty is a minimally invasive technique that allows you to expand the lumen of the vessel with a catheter and push through the cholesterol plaque.
- Placement of a stent in narrowed areas prevents subsequent narrowing of the vessel. But this method can cause complications in patients and is therefore rarely used.
Each given stage is specific for different patients . This is due to different reactions to medications, the cause of the disease, and the physiological characteristics of the body. Therefore, treatment is prescribed by a specialist on an individual basis.
: ultrasound of neck vessels
Source: https://sosudask.ru/suzhenie-sosudov-golovy-i-shei-simptomy-lechenie/
Clinical manifestations
At an early stage, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. The first symptoms usually appear when the diameter of the vessel is reduced by more than half. They depend on which part of the body the affected areas are located.
In the cervical region, the carotid arteries are more susceptible to narrowing. Stenosis of the vessels of the neck and head leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which causes:
- impairment of memory, hearing, vision;
- emotional instability;
- dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- the appearance of noise in the ears and “floaters” before the eyes.
All symptoms do not have to be present; the presence of even a few of them is a reason to consult a doctor. By ignoring the manifestations of narrowing of the neck arteries, a person exposes himself to the risk of developing a cerebral infarction.
Stenosis of the vessels supplying blood to the heart causes ischemic changes in the organ and heart failure. Pathology can be suspected by periodic or constant pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, arrhythmia, and swelling of the legs.
A dangerous complication of narrowing of the coronary and coronary arteries of the heart is myocardial infarction. At its first symptoms: pain in the left side of the chest, accompanied by weakness, shortness of breath and cough (sometimes dizziness, nausea and other manifestations are possible), you should seek emergency medical help. Because treatment started late can be fatal.
In approximately half of the cases, stenosis of the lower extremities in the early stages does not cause discomfort in the patient or is manifested only by pain in the legs with increased loads. In the future, you may experience:
- pain in the legs after light exertion and at rest;
- feeling of numbness in the legs;
- loss of hair growing near the affected vessels;
- lameness.
If the patient does not receive treatment, the condition worsens. The consequences of advanced stenosis of the veins and arteries of the legs are trophic ulcers and gangrene.
Neck vascular stenosis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, danger
Stenosis of neck vessels is characteristic of such diseases as diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cervical osteochondrosis. Often the condition is dangerous and requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Its causes and how it manifests itself are described further in the text.
What's happened
Often this disorder occurs as a result of atherosclerosis in the cavity of the coronary veins. Stenosis is a narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck.
This area contains the main arteries that supply blood to the brain. The saturation of cells with oxygen and nutrients depends on their functionality.
Pathology leads to the closure of the lumen in the circulatory system. This is due to the large formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the veins. They interfere with normal blood flow.
The danger of their development is due to the fact that there is a risk of them being torn off from the walls and moving freely. Thus, a blockage can occur in a small capillary, blocking it completely.
Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine is associated with various diseases. The carotid arteries are often affected. This condition can lead to dangerous complications.
Why does it occur
Taking into account statistical data, provoking factors are bad habits and severe pathologies. People often confuse the causes of stenosis of neck vessels with other pathological processes. The risk group includes people who suffer from such diseases.
- Atherosclerosis. The etiology is due to excessive deposition of cholesterol deposits. In this case, such a narrowing of the lumen is observed that the blood flow is significantly impaired. There is a constant lack of oxygen in the brain.
- Diabetes. Leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the body. As a result, the structure of the elements of the circulatory system changes.
- Arterial hypertension. The effect of high blood pressure leads to dilation of the arteries. After cholesterol plaques appear, their walls begin to thin out. Against this background, a critical condition develops over time. This can lead to rupture of the carotid artery.
Provoking factors:
- osteochondrosis;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Such factors are almost always found in people with similar diagnoses. It is important to understand what vascular stenosis is and how to deal with it in order to prevent complications.
Why is it dangerous?
The danger of violations is due to the fact that in the early stages there are no warning symptoms. Usually a person learns about this diagnosis after a full examination. They can be determined only after contacting a medical institution with complaints of deterioration in well-being.
In order to identify the etiology, diagnostic procedures and manipulations are prescribed. After the development of the acute phase of the disease, only surgical treatment will be required.
When symptoms appear, the patient may be in a dangerous condition. There is usually little time left before the transition to the severe stage. In rare cases, peripheral vascular stenosis is diagnosed.
In most cases, the lesion extends to the left and right carotid arteries. Stenosis of neck vessels provokes serious consequences in the form of:
Against this background, a person is more susceptible to panic attacks.
The development of complications depends on the degree of damage and impairment. Therefore, it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner and not wait for dangerous manifestations.
Symptoms
Symptoms of vascular stenosis can manifest in different ways.
Primary signs include:
- frequent dizziness;
- weakness, even after rest;
- loss of consciousness for no apparent reason;
- blurred vision, appearance of strings, spots, spots before the eyes;
- noise in ears;
- pain is usually in the back of the head, which can be persistent.
A person should be alarmed by a decrease in his performance. Few people go to the doctor for this. Over time, pain syndrome joins such manifestations.
In severe cases, the patient requires urgent hospitalization. The disease cannot be cured at home. The injured person should be under the supervision of specialists.
When and which doctor should you contact?
It is important to consider that only timely consultation with a doctor increases the chances of favorable treatment. This is the basic recommendation that every person should remember. A comprehensive examination will help determine appropriate therapy.
Diagnostics
Stenosis of the cervical arteries can be determined only after a full examination. It is not enough to listen to the symptoms that are bothering the patient. Basic diagnostic methods:
- Doppler scanning. This dangerous and accessible examination makes it possible to determine the condition of the walls of the arteries, their lumen, and blood circulation.
- Angiography. In this case, a contrast agent is used to study the disease.
- CT, MRI. Prescribed to study the condition of the cervical spine. It is obtained using a 3D image.
It is worth noting that the pathology has a genetic predisposition. Therefore, it is necessary to study the victim’s medical history and eliminate such risks. The results of these studies allow the specialist to assess the stage of development of the disease and determine the cause of its occurrence.
Based on the data obtained, effective therapy is selected. But in most cases, surgery will be required.
Treatment of cervical spinal stenosis without surgery is possible only in the initial stage of development. But this pathology is characterized by the absence of warning signs. Therefore, complications mainly arise, and the disease can be diagnosed only when it becomes severe.
At the first signs of deterioration in health, you should consult a doctor. This will increase the possibility of treating disorders without surgery.
The material was prepared specifically for the website venaprof.ru, edited by clinical pharmacologist K.V. Nedelko.
Source: https://venaprof.ru/stenoz-sosudov-shei/
Forecast. Prevention
Patients with carotid artery stenosis require supervision by their attending physician. It is necessary to regularly measure blood pressure, cholesterol, and sugar (if you have diabetes) in the blood. The results of the examination will show whether additional drug treatment is required or whether the situation is under control. You will also need an annual ultrasound (duplex scan) to show how well blood is flowing through the narrowed carotid arteries. Duplex scanning over time will show whether the degree of stenosis is increasing, or, if surgery was performed, how effective it was.
It is important to remember that carotid artery stenosis is a progressive disease. Without appropriate treatment, the risk of stroke is 13% per year for patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis and 2.2% for patients with asymptomatic stenosis. One should not be dismissive of newly developed manifestations of insufficiency of blood supply to the brain! You should consult a doctor immediately.
After carotid edarterectomy, carotid artery stenosis can develop again, usually within up to 2 years; as a rule, it is not clinically manifested. With a newly formed plaque, it is possible to perform a repeat operation with intravascular expansion of the artery lumen and installation of a stent. However, the degree of narrowing of the carotid artery may decrease with treatment, so there should be no rush to perform intravascular intervention until the degree of stenosis reaches 80%. Restenosis that developed over 2 years is associated with the progression of the underlying disease - atherosclerosis. Summarizing the above, reoperation or stenting is indicated for symptomatic restenoses or their severity is more than 80%.
Traditional treatment
Before treating cerebral vasoconstriction, it is necessary to accurately establish the diagnosis. After all, as we have already found out, cause-and-effect relationships are very important for proper treatment. Drug therapy can be aimed at eliminating neuropathological, therapeutic, cardiac and other signs. The course and dosage are prescribed individually, but there are general recommendations:
- vasodilators;
- statins, fibrates, lecithin;
- anion exchange resins;
- iodine-containing and antioxidant preparations;
- medicinal complexes to improve blood circulation;
- drugs that stimulate metabolic processes.
Establishing a diagnosis
The disease must be diagnosed by a doctor who specializes in treating the organ from which the symptoms arise. Thus, for problems with the blood supply to the heart, therapy is selected by therapists and cardiologists, neck and head - by neurologists, legs - by vascular surgeons.
In addition to collecting the patient’s medical history and visual examination, an additional examination is prescribed, depending on the location of the affected vessels. Studies that allow us to draw a conclusion about the state of the circulatory system and its performance include:
- CT scan.
- Dopplerography. More often used to diagnose diseases of the veins and arteries of the neck and lower extremities.
- Magnetic resonance angiography.
- Ultrasound examination and electrocardiogram of the heart.
Also part of the mandatory examination is a blood test to determine cholesterol levels. When the pathology is confirmed, the doctor selects treatment based on the reasons that caused the vascular stenosis.
Narrowed blood vessels in the cervical region and how to treat dizziness – Fighting dizziness
Poor blood supply caused by osteochondrosis can cause severe headaches, fatigue and even cause depression. The cervical spine is the most mobile.
At the same time, he has the weakest muscle corset and therefore the narrow spinal canal can easily be injured and pinched.
Narrowing of the vessels of the cervical spine leads to oxygen starvation of the posterior parts of the brain responsible for tactile sensations and processing of auditory and visual information.
Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine
Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine is a fairly common occurrence in our time. What are the causes of this disease? How to identify it, and most importantly, what are the dangers and what to do if such a terrible disease was discovered?
Ultrasound with Doppler
First of all, with CDK, blood flow through the veins and cervical vessels is measured. Also, the color flow test allows you to determine the movement of foreign fluids in the body.
This mapping allows you to see:
- Direction of fluid movement in the analyzed area;
- The nature of the movement (directional, chaotic, etc.);
- The speed of blood flow. This parameter is especially important in cases where it is important for the patient to know about the condition of the cervical vessels. In particular in cases where the subject is elderly;
- Patency (it is affected by smoking, which can significantly affect the final result of the study);
- Resistance;
- Diameter of the cervical vessel. This parameter is no less important than the others for one simple reason. There are standards for the diameters of the cervical vessel, and if in some places or along its entire length it differs from the norm, this means that the cervical vessel has been adversely affected. In particular, cholesterol plaques may be seen, which can cause blockages that can later lead to death.
Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics using color Doppler mapping, it is possible to identify a number of diseases that are impossible using other non-invasive research methods. So, first of all, the CDK allows us to identify such phenomena as:
And this is not the entire list of pathological changes that are visible only when undergoing color Doppler mapping. For example, a common indication for undergoing such ultrasound diagnostics is the presence of coronary heart disease, or tachycardia. Even very harmless symptoms can indicate serious pathological changes in the body.
What are the dangers of stenosis?
Pinching of blood vessels in the cervical region can lead to death. Everything else is unnecessary to describe. As a result of a decrease in the diameter of the vessel, or partial closure, the brain begins to receive less and less oxygen.
Coordination problems and partial paralysis may occur. Why? It's very simple, this disease disrupts brain and muscle communication.
As a result, the brain is unable to issue orders quickly enough.
- We recommend reading: cervical spinal canal stenosis