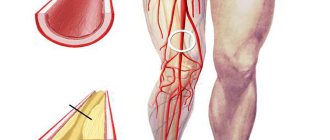
Principles of therapy
It should be noted that only complex treatment can normalize the condition of the arteries.
And it needs to start as early as possible. Treatment with folk remedies, as a rule, does not bring the expected results. In this case, precious time is lost, and instead of relief, a pronounced exacerbation of the pathology occurs.
First of all, you need to adjust your diet. The diet prohibits the consumption of foods such as:
- smoked dishes;
- salo;
- fatty foods;
- soda;
- alcohol;
- coffee and strong tea;
- bread made from premium flour;
- sweets.
The menu should include more fresh vegetables, fruits, and steamed dishes.
Drug therapy is also mandatory:
Medicines are used that relieve the symptoms of atherosclerosis. The patient is usually prescribed medications that lower blood pressure.
The need for their appointment must be weighed. It is very important to take medications to lower blood cholesterol levels. They help reduce the intensity of deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. In parallel, drugs are also used to normalize metabolism and generally strengthen blood vessels. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe a patient to take a small amount of acetylsalicylic acid to prevent blood clots from forming
Such treatment must be carried out for a long time. Constant use of aspirin helps to normalize blood circulation and reduces the risk of dangerous complications.
Self-medication of atherosclerosis is strictly contraindicated! It can lead to extremely dangerous consequences.
Therapeutic measures
If the disease of the vertebral arteries is at the initial stage of its development, then it is usually easier and faster to eliminate, since symptoms and treatment are inextricably linked. Drug therapy is mainly used as treatment. It involves taking individual medications from different groups by the patient.
If the disease is at a later stage of its development, then the patient needs surgical treatment of the stenosis of the disease so that the lumen begins to narrow. In addition, as the lumen decreases, the signs of the disease begin to gradually disappear. In this case, there are several methods of surgical intervention. The first is called carotid endarterectomy. The method is a procedure for scraping plaques located on the walls of the patient’s blood vessels. This makes it possible to restore the lumen of blood vessels. Angioplasty is a procedure for expanding the lumen through the use of special catheters that are installed in the affected area. This method can be carried out by using a wire frame. All these methods have not only certain advantages, but also disadvantages.
In addition to the above methods of treating the disease, special attention must be paid to the patient’s lifestyle and nutrition. As for the latter, in this situation it means following a diet
It is recommended to exclude foods that are high in fat, smoked or overly spicy. The patient's diet should include fresh vegetables and fruits.
Another effective way to eliminate the disease is hirudotherapy, that is, treatment must be done through the use of leeches. Also, patients often resort to acupuncture procedures, massages and special gymnastics to narrow the lumen. Many patients also note the effectiveness of traditional medicine methods. They are not entirely suitable as an independent treatment, but as a supplement they have a place to be, and they are also capable of increasing the effectiveness of basic therapeutic measures.
The most popular recipes include:
- A combination of honey and lemon. The ingredients are used in equal quantities and are crushed using a meat grinder. The resulting mass is placed in a container and filled with the required amount of water. After this, the medicine is infused for a little more than a week, after which it is filtered. It is necessary to use the product one tablespoon before each meal.
- Hawthorn decoction. In this case, not only berries, but also flowers can be used for cooking. The components are poured with boiling water and infused for about half an hour. The procedure is similar to the previous recipe.
- Honey and dandelion root. For cooking, the root is used in dry form, as it will need to be grated. The resulting powder is placed in a container and filled with honey. All contents are thoroughly mixed and can then be used. The dosage corresponds to the volume of a teaspoon, and is taken immediately after meals.
Thus, vascular pathology associated with stenosis of the neck arteries is a fairly serious disease that requires immediate diagnosis and effective treatment. That is why, if initial signs of the disease occur, the patient should immediately consult a doctor.
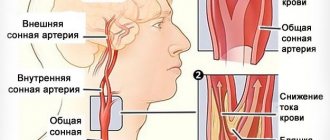
Manifestations and diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis
There are no specific symptoms that indicate carotid artery stenosis. Since the narrowed artery cannot deliver the required volume of blood to the brain, the symptoms will consist of signs of ischemia in the brain. The narrowing of half the lumen of the vessel does not cause hemodynamically significant disorders, and therefore proceeds unnoticed by the patient. As the degree of stenosis increases, clinical signs will appear.
The first “bells” indicating trouble may be transient ischemic attacks (TIA), which are accompanied by:
- Headache;
- Dizziness and imbalance;
- Feeling of numbness in the face and limbs;
- Slurred words, impaired understanding of spoken speech, which makes contact with the patient difficult;
- Vision disorders;
- Fainting.
The listed symptoms are short-lived, usually lasting about half an hour, and then gradually regress, and by the end of the first day not a trace remains of them. However, even if the condition has completely returned to normal, you need to consult a doctor to clarify the cause of ischemia in the brain. If you have had a TIA in the past, the risk of stroke increases tenfold, so these attacks can be regarded as harbingers of cerebral infarction and should not be ignored.
Chronic cerebral ischemia due to stenosis of the neck arteries is manifested by decreased performance, weakened memory, difficulty concentrating, and behavioral changes. Signs of such discirculatory encephalopathy may become noticeable, first of all, to others, who will begin to note that their loved one or colleague’s character is changing, it is more difficult for him to cope with his usual responsibilities, it is more difficult to achieve mutual understanding when communicating, while the patient himself will try to maintain his usual image life, “attributing” symptoms to fatigue or age.
Critical stenosis of the right or left carotid artery can lead to much more serious consequences than TIA. A large atherosclerotic plaque can rupture with the release of its contents onto the surface of the vascular wall, in which case thrombosis will necessarily develop, and the resulting clot will completely block the artery, leaving it without the opportunity to deliver blood to the brain.
The result of a complete cessation of blood flow through the carotid artery is an ischemic stroke - a cerebral infarction, in which nerve cells die in the area of the blood supply to the affected artery. A thrombus or its fragments can break off and move into smaller vessels - basilar, cerebral arteries, and then the symptoms of a stroke will be caused by damage to a specific vascular area.
Symptoms of a stroke include paralysis, paresis, loss of consciousness, speech disorders, swallowing, and sensitivity. In severe cases, cerebral coma occurs and the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is disrupted. These symptoms often occur suddenly, against the background of a severe headache, and can take a person by surprise in the workplace, on the street or at home
It is important that those around you quickly get their bearings and call an ambulance, because both life and the prognosis of the disease depend on the speed of providing qualified assistance.
Based on the predominant symptoms, several options for the course of the pathology can be distinguished:
- Asymptomatic form, when there are no signs of ischemia in the brain, but stenosis has already been identified through additional examination;
- Discirculatory encephalopathy – chronic ischemia without focal symptoms of brain damage;
- Transient ischemic attacks - can occur with focal neurological disorders that disappear within a day;
- Consequences of a mini-stroke - symptoms disappear within a month;
- Stroke (cerebral infarction) is an acute disturbance of blood flow with cerebral and focal symptoms.
One of the first signs of stenosis, which can be detected already during the initial visit to the doctor, is considered to be a kind of noise above the artery when listening to it. To confirm the diagnosis, a variety of instrumental examinations are used - CT, MRI, ultrasound, angiography.
The most accessible, safe and cheap way to diagnose stenosis of the neck arteries is the ultrasound method, supplemented by Doppler ultrasound. The specialist evaluates the structure of the vessel wall and the nature of blood flow through it.
CT and MRI make it possible to exclude other causes of circulatory pathology, and radiocontrast angiography helps to accurately localize the site of narrowing. Contrast is also used at the stage of surgical correction of stenosis.
Symptoms and signs of pinched blood vessels in the neck
Even if a person has experienced headaches before, they are incomparable to the pain that occurs when pinched.
If this happened at night, for example, due to an unsuccessful posture, then in most cases the person gets up in the morning with a terrible, throbbing pain in the back of the head. Moreover, as soon as he takes a vertical position, the pain becomes more aggressive, there is a feeling that blood is pulsating in the temples and under the back of the head. This happens because the vessel was compressed for some time and the blood flow stopped. And when the person stood up and straightened up, the vessel was freed due to the fact that the vertebrae returned to their place. In this case, the person will feel relief only while lying down or if he applies light pressure with his hand for some time in the area of the first vertebra.
Often the patient experiences other, no less striking signs of a pinched neck vessel:
- severe nausea;
- repeated vomiting;
- increased pain after vomiting;
- deterioration of vision: film on the eyes, “flies”;
- severe tinnitus, hearing loss.
The more often pinching occurs, the more constant the symptoms become. The central nervous system is involved in the process and pinching of blood vessels in the cervical spine results in the following symptoms:
- irritability;
- poor sleep;
- fatigue;
- exacerbation of psychosomatic disorders, especially against the background of insomnia.
If you ignore such signs and do not allow osteochondrosis to develop, this can cause ischemic brain disease. Cervical osteochondrosis (cervical migraine) often provokes pinching of various kinds, so you need to keep such an insidious enemy as osteochondrosis under control.
Pathological tortuosity of the ICA on both sides: what does it mean?
Tortuosity of the ICA on both sides is a common vascular pathology. It is found in approximately every fourth adult. Even if a diagnosis has not been established, but there are clinical manifestations, such a deviation should be suspected.
Pathological tortuosity of the ICA on both sides can occur both in early childhood and in adulthood. There are cases where pathology began to form in old age. In such patients, the disease is discovered randomly during clinical diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis.
Of course, it is unlikely that it will be possible to restore the completely normal position of the carotid arteries. But with the help of manual therapy methods, gymnastics, and reflexology, it is possible to restore the conductivity of blood vessels and compensate for their partial incorrect position.
We do not recommend using pharmacological drugs to expand the vascular bed. This does not give a long-term positive result and often leads to the development of unwanted side effects.
If you need treatment for tortuosity of the ICA, you can make a free appointment with a chiropractor in our clinic in Moscow. He will conduct a full examination, make an accurate diagnosis and talk about the prospects for using methods to treat pathology in your individual case.
Among the potential causes of the development of pathological tortuosity of the internal carotid arteries, doctors name the following negative factors:
- congenital deformations of connective tissue, which is designed to fix blood vessels;
- genetic hereditary predisposition;
- predominantly the predominance of the quantitative content of elastic tissue fibers over collagen;
- wear and tear of the walls of blood vessels and their deformation under the influence of nicotine and alcohol breakdown products (smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages is a primary risk factor in the development of ICA tortuosity);
- in adults, the cause may be arterial hypertension of the renal, essential or atherosclerotic type;
- in adolescents, tortuosity is provoked by sharp jumps in blood pressure and vascular fullness against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- weakness of the neck and collar muscles;
- atherosclerotic changes in cerebral blood vessels;
- cervical osteochondrosis and poor posture in the form of straightening physiological lordosis;
- disruption of the innervation process in radicular syndrome;
- posterior vertebral artery syndrome;
- deformation of the uncovertebral joints of the spine;
- various injuries;
- increased body weight and sedentary lifestyle;
- sedentary work with neck muscle tension;
- improper organization of sleeping and working spaces.
Identifying and eliminating all potential causes of pathological tortuosity of the internal carotid artery is a primary task for the doctor, who will develop an individual treatment plan for the patient
Therefore, it is extremely important to provide the doctor with reliable information when collecting anamnesis. The more accurately the cause of tortuosity is determined, the higher the chances of a full recovery.
Symptoms of various vascular diseases of the head and neck
There are many known diseases of blood vessels in medical practice. Each of them has its own clinical picture. But the final diagnosis is made only by a specialist based on the results of the examination. Signs common to all diseases:
- sudden attacks of dizziness, which are accompanied by loss of coordination and fainting;
- pain that is localized in the back of the head is the main symptom of stenosis;
- state of lethargy, fatigue or, on the contrary, increased irritability;
- limited physical activity;
- problems with memory, concentration, signs of dementia;
- feeling of heaviness in the head.
Important!
Cause for concern - these signs are observed regularly.
Atherosclerosis
The most common cause of violations. The disease develops against the background of the formation of atheromatous plaques on the inner surface of the arteries. If left untreated, the connective tissue gradually grows, making it difficult to fully supply the brain with blood. Signs of atherosclerosis are most often observed in people over 50-60 years of age.
The condition occurs against the background of regular intake of fatty foods, physical inactivity, and metabolic disorders. Bad habits are also important - smoking, drinking alcohol.
Spasms
The condition is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen between the walls of capillaries and blood vessels. This can be observed against the background of vasospasm - intense reflex muscle contraction. The reason for this may be the following conditions:
Latest information: Trophic ulcers on the legs
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- kidney and thyroid dysfunction.
Provoking factors also include regular hypothermia, overwork, and lack of sleep. Among the congenital pathologies that can cause stenosis are:
- underdevelopment of neck vessels;
- bone formations on the vertebrae.
Hypertension
The main characteristic is high blood pressure. The stenosis that occurs against this background leads to the fact that the vessels lose their elastic qualities. Pathology can cause spasms, paralysis, decreased or even loss of sensation in the limbs.
Advice!
The clinical picture is observed extremely rarely. Therefore, hypertensive patients should regularly measure their blood pressure. If three times the results may exceed 140 mmHg. Art., you should consult a doctor.
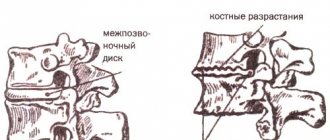
Cervical hernia
The condition is accompanied by rupture of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc and release of the nucleus. The clinical picture is formed by the following phenomena:
- pain in the upper spine, which intensifies due to changes in head position;
- numbness, tingling in the hands;
- muscle weakness;
- headaches, coordination problems.
The symptoms of a hernia are the most striking. Therefore, detection of pathology occurs in the early stages. Especially when compared with other vascular diseases.
Osteochondrosis
Dystrophic changes in intervertebral discs in the cervical region. The damage also extends to the vertebrae, soft and cartilaginous tissues. It can lead to the development of a hernia, which in medicine is called intervertebral protrusion.
Osteochondrosis is caused by a number of factors. For example, cervical injuries, lack of physical activity. Also, holding the neck in an uncomfortable position for a long time, hereditary predisposition, prolonged mental stress.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis are absent in the initial stages, when the narrowing is just beginning. As it progresses, due to chronic oxygen deficiency, neurological general and focal signs of circulatory disorders in the brain appear. The first group of symptoms include:
- Deterioration in sleep quality. Complaints appear at the very beginning of the disease, progressing slowly but steadily. Disturbing sleep that is shallow or with frequent awakenings. Sleeping pills help in the short term.
- Headache. Has a paroxysmal character. The intensity is medium, lasting up to a couple of hours. Pain is noted in the back of the head or temples, sometimes covering the entire skull, often spreading to the face, neck and eyes.
- Dizziness. Resulting in the inability to stand on one's feet and loss of orientation in space. It appears in the form of attacks and does not last long. Sometimes the dizziness becomes constant, but not severe.
- Lability of the emotional background. Euphoria can instantly give way to irritability and a fit of anger. In some cases, apathy, tearfulness, reluctance to perform any actions, and a depressive state appear.
- Inhibition in the sphere of intellectual activity. It becomes impossible to quickly answer a question or solve a problem. At the same time, cognitive and mnestic functions remain at the same level.
- Inadequate perception and poor memory of information.
Important!
If such complaints occur, it is recommended to conduct an examination. This will help to identify signs of narrowing of the carotid arteries and take timely measures to eliminate the pathology.
The appearance of focal symptoms indicates the development of a transient ischemic attack. Pathology can be suspected if the following symptoms are present:
- Visual impairment in one or both eyes. Narrowing or loss of the field of view, altered perception of colors, darkening of the eyes, blurred contours, flickering spots or dots.
- Unsteadiness when walking. Appears when coordination is impaired, dizziness, or severe muscle weakness.
- Fainting state. Regular but quickly passing attacks of loss of consciousness indicate negative dynamics in the development of stenosis and a high risk of developing a cerebral stroke.
- Slurred speech. In addition to the fact that the patient cannot clearly pronounce words, he poorly understands speech addressed to him.
- Asthenia. They are worried about weakness, apathy, drowsiness, total fatigue, and the inability to take care of themselves in everyday life.
- Vomiting or nausea. The symptom appears and disappears suddenly, without any intervention. Classical treatment methods do not bring relief.
- Difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia indicates damage to the brain stem, which may result in cardiac and respiratory arrest and a critical increase in body temperature. This often leads to death.
The duration of the attacks does not exceed an hour; the patient’s condition returns to normal within 24 hours. Even a single transient ischemic attack is a good reason to visit a doctor, since such a condition is considered a harbinger of a cerebral stroke.
If measures to eliminate carotid artery stenosis have not been taken, the patient will experience the following signs of chronic cerebral ischemia:
- weakening of memory;
- decreased concentration;
- violation of tolerance to mental stress;
- change in character;
- inability to perform normal activities.
Important!
When the blood flow is completely blocked, an ischemic stroke develops, the first signs of which include loss of consciousness, paralysis or paresis, impaired sensitivity, speech, and swallowing.
Treatment of carotid artery stenosis
To treat stenosis of neck vessels and the resulting blood flow disorders in the head, medication and surgery are used.
Conservative therapy is aimed at improving brain activity, protecting it from the harmful effects of hypoxia, for which nootropic and metabolic drugs are prescribed - piracetam, mildronate, B vitamins.
Blood pressure correction becomes an obligatory component of drug therapy. Hypertensive patients should take antihypertensive drugs constantly, according to the regimen suggested by the doctor. Hypotonic patients should be careful and also control their blood pressure, as reducing it will worsen oxygen starvation of the brain.
For atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid arteries, and this is the most common cause of pathology, drugs that normalize fat metabolism (statins) are indicated, diet and rational physical activity are necessary.
Drug treatment can somewhat improve brain activity in non-critical stenosis and plays a supporting role after surgery, but in case of decompensated narrowing of the artery, repeated ischemic attacks or a stroke, surgery is not necessary.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- Arterial stenosis of more than 70%, even not accompanied by obvious clinical symptoms;
- Conditions after a stroke associated with damage to the carotid arteries;
- Recurrent TIAs with stenosis of 50% or more.
Surgery for carotid artery stenosis is aimed at restoring normal blood flow and can be radical or minimally invasive. Radical interventions are carried out openly, minimally invasive - without a large skin incision.
Radical treatment - carotid endarterectomy - an open operation in which an incision is made in the neck in the area where the vessel passes, the artery is isolated, the surgeon finds the site of narrowing and removes plaques together in a section of the vascular wall, then the integrity of the vessel is restored by plastic surgery, and the wound is sutured. With concomitant bending, looping, and tortuosity, the entire affected fragment of the artery can be removed. The operation requires general anesthesia.
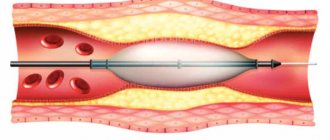
Stenting is a more gentle method of treatment, which consists of introducing a special tube into the lumen of the vessel, which expands it and maintains it in a straightened form, ensuring blood flow. The purpose of such an operation is to prevent possible vascular accidents and minimize the manifestations of chronic hypoxia, therefore it is indicated for subcritical narrowings.
Stenting is performed under local anesthesia with constant monitoring of the patient's blood pressure and pulse. The femoral artery through which the guidewire is inserted is punctured, a catheter and contrast agent are placed into it to accurately determine the location of the stent. The operation is performed under fluoroscopic control, but the dose of radiation received is minimal and does not pose any danger.
A stent is installed at the site of stenosis of the left or right carotid artery, it expands, and it is possible to use special balloons that inflate the vessel at the site of narrowing. To prevent thromboembolic complications with damage to smaller arterial vessels of the brain, during surgery, special filters are installed in the artery that do not interfere with blood flow, but retain the smallest particles of blood clots.
Once the stent is in place, the filters and catheter are removed and the stent remains in place at the site of the stenosis. The intervention lasts no more than an hour, after which the patient can be sent to intensive care for some time or immediately transferred to the ward. Strict bed rest is recommended for the first day; there are no restrictions on food and fluid intake in the postoperative period.
The duration of hospitalization for surgical treatment is determined individually. After stenting, the patient spends 2-3 days in the hospital, after which he can go home. Open surgery requires longer observation - about a week, at the end of which the skin sutures are removed.
Prevention of carotid artery stenosis against the background of atherosclerotic lesions includes a special diet, rational physical activity, weight loss, smoking cessation and drug treatment of existing cardiovascular and metabolic pathologies. In addition, you should regularly visit doctors for routine medical examinations.
Treatment: drugs, surgery and recommendations
Drug treatment of carotid artery stenosis can be quite effective, but only if the course is uncomplicated and there are no other diseases.
Drugs
Depending on the degree of narrowing, the following drugs may be included in the treatment regimen:
- microcirculation correctors (“Actovegin”, “Trental”);
- neuroprotective drugs (“Pantogam”);
- vasodilators with antihistamine action (“Cinnarizine”);
- statins for correcting cholesterol levels and cholesterol load (“Atorvastatin”).
Treatment also includes correction of the underlying disease, which causes narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck and head. For example, for osteochondrosis, drugs from the group of NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, and centrally acting muscle relaxants are additionally prescribed. If there are intervertebral hernias that compress the blood vessels of the cervical spine, they are reduced (surgically).
Clinical guidelines
To achieve and maintain positive dynamics, it is also important for the patient to follow the clinical recommendations of specialists on lifestyle and diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods containing large amounts of fats and carcinogens (smoked meats, lard, sausages, etc.), as well as alcoholic beverages and hot spices. About 30% of the daily food intake should be vegetables and fruits. This group also includes berries and greens: their consumption improves the viscosity and fluidity of the blood and enriches the diet with essential vitamins and minerals.
If the patient suffers from tobacco addiction, you should contact a specialist who will prescribe complex therapy and help cope with the addiction. At the same time, it is important to understand that the craving for smoking is very difficult to correct, so observation by a narcologist is not enough: in most cases, patients also need the help of a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Obese people should control their body weight, as excess weight is one of the main factors in the development of atherosclerosis and other vascular pathologies.
Clinical recommendations for the treatment of vascular insufficiency caused by pathological narrowing of the neck vessels also include the following points:
- control of psycho-emotional state;
- providing adequate physical activity appropriate to age and level of fitness;
- selection of anatomical sleeping accessories;
- regular walks (necessary to prevent hypoxia).
Experts also call therapeutic exercises as one of the main measures for complex treatment of stenosis. Sets of special exercises for the cervical spine help eliminate muscle spasms, increase the flow of blood and lymph in the vessels, improve metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs of the neck, reducing the risk of dystrophic changes and degeneration of neighboring vertebrae.
Surgery
One of the most effective and safe methods of treatment for narrowing of the vessels of the cervical spine is stenting. The essence of the operation is to install a special metal stent in the form of an elongated tubular plate, which expands the internal lumen of the affected artery and restores its capacity. The speed of recovery depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and is about 3-10 days. In some cases, the patient is discharged home the very next day with recommendations to follow a gentle regimen and to attend a follow-up appointment with a surgeon and neurologist after 10 days.
Video - Carotid artery stenosis
The blood vessels of the neck are one of the most important arteries in the human body, as they carry blood directly to the brain. Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine is a dangerous pathology, which doctors recognize as one of the main factors determining the risk of ischemic stroke. It is necessary to treat the disease at the initial stage, when the effectiveness of drug correction reaches 70-90%. In the absence of positive dynamics within 6 months, the use of surgical methods is indicated.
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
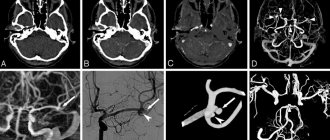
The main method for diagnosing narrowing of the carotid and basilar arteries is CT angiography. This method allows you to study a three-dimensional image of the blood vessels under study and evaluate the strength and characteristics of blood flow. Unlike conventional angiography, computed tomography eliminates the risk of complications from surgical interventions associated with the introduction of contrast (with CT angiography, the solution is injected into the femoral vein). Significant contraindications for this study are allergies to iodine and iodine-containing drugs, high obesity, pregnancy, severe forms of tachycardia or other heart diseases. The use of CT angiography is contraindicated in cases of decompensated diabetes mellitus, as well as acute renal or heart failure.
CT angiography
If there are such contraindications, CT angiography can be replaced by the following types of diagnostics (usually in combination):
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head (using Doppler ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance scanning;
- determination of blood cholesterol levels and study of blood lipid balance;
- instrumental examination of the arterial pulse (used quite rarely).
Ultrasound of neck vessels
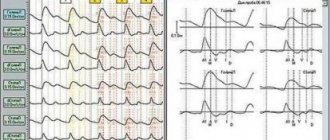
An ECG is also used to identify provoking factors and assess the functioning of the heart muscle.
Treatment methods for carotid artery stenosis
Treatment tactics are determined based on the results of the study - the degree of narrowing, the extent of damage to the vessel.
Conservative therapy
In case of a stroke associated with complete occlusion of an artery by a thrombus, therapy is aimed at its resorption. Conservative treatment is allowed to be used within 4 hours from the moment of the stroke, until irreversible reactions occur in the brain. The prognosis of the disease depends on the speed of medical care. For a moderate degree of narrowing with compensation of blood supply by additional vessels, the following is used:
- Anticoagulants - resolve blood clots and blood clots (Heparin, Warfarin).
- Antiplatelet agents - thin the blood, speed up its flow (Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl).
- Nootropics – improve blood circulation in the brain (Piracetam, Glycine).
- Metabolites - to improve metabolic processes in the body (Cerebrolysin, Pentoxifylline).
- Statins - reduce the amount of cholesterol, slow down the formation of atherosclerotic plaques (Mertenil, Lovastatin).
During TIA, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator is prescribed. When blood pressure decreases or increases, use the appropriate groups of drugs. With stenosis, against the background of reduced pressure, oxygen deficiency in the brain increases; against the background of high pressure, the risk of stroke increases, therefore, when taking drugs that affect blood pressure, it is controlled (monitored). For diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemic agents and insulin injections are prescribed.
Surgery
Indicated for people after TIA, stroke, or a degree of narrowing greater than 50%. The goal is to expand the lumen of the vessel and restore full blood flow. In the surgical treatment of stenosis, there are 3 methods: removing the cholesterol plaque from the vessel, expanding the area of stenosis with the installation of a stent, and forming an anastomosis between the vessels. The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of narrowing, concomitant diseases, and previous operations in the carotid artery area.
Carotid endarterectomy
Used to remove cholesterol plaques. After a 7-11 cm incision in the neck, the carotid artery is exposed from tissue, 2 clamps are applied (above, below the plaque) to stop the blood flow. The blood supply to the brain at this time is provided by the opposite carotid artery and vertebral vessels. The isolated artery is dissected over the area of stenosis, and the plaque is removed. Stitches are placed, the clamps are removed, and blood flow is resumed.
Stenting
A gentle surgical intervention aimed at crushing the plaque and expanding the diameter of the vessel using angiographic equipment. A tube is inserted through a puncture in the artery of the thigh and forearm and advanced to the area of narrowing, recording the actions on the monitor. A catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted through the tube and stopped at the level of cholesterol deposits. The balloon is inflated, its walls crush the atherosclerotic plaque, thus expanding the lumen of the vessel.
After restoring the diameter of the artery, the balloon is deflated and removed through the tube. To prevent re-narrowing, a stent (a mesh-shaped tube) is inserted into the affected area of the vessel through a catheter, which is fixed over the crushed plaque. The catheter and tube are removed. The purpose of the stent is to maintain the diameter of the artery and prevent re-growth of plaque.
Bypass surgery
Used for complete blockage of the carotid artery. The essence of the operation is to create additional blood flow bypassing the affected vessel due to a shunt (the person’s own vessel, which is taken from a person’s arm or leg). The shunt is sutured with one edge to the carotid artery, the other to the brain vessel, through a burr hole in the skull.
Important!
Bypass surgery is performed only according to strict indications, if it is impossible to restore blood flow by other surgical methods, which is associated with the need to perform a craniotomy - craniotomy.
Causes of narrowing of the carotid artery
Narrowing of the carotid artery owes its rather high prevalence to risk factors that affect a large number of people, especially the elderly. Vascular pathologies contribute to:
- Heredity;
- Bad habits, in particular smoking;
- High blood pressure;
- Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism (diabetes mellitus);
- Old age and male gender;
- Excess weight, lack of physical activity.
If the family already has patients suffering from atherosclerosis and narrowing of the carotid arteries, then it is likely that other blood relatives may have a hereditary predisposition to the pathology.
Apparently, genetic mechanisms of susceptibility to lipid metabolism disorders are the basis. Such common conditions as hypertension, diabetes, obesity also provoke atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. Excessive pressure changes the structure of the vascular walls, making them dense and vulnerable, promoting the accumulation of lipids there, and the combination of atherosclerosis with high blood pressure significantly increases the risk of acute disorders of blood flow in the brain.
With age, the likelihood of structural damage to the walls of the carotid arteries increases, so the pathology is usually diagnosed in the 6th-7th decade of life. In men, this process occurs earlier, and in women, the protective function is performed by the sex hormones estrogens, so they get sick later, after menopause.
Stenosis of the carotid artery against the background of atherosclerosis can be aggravated by congenital anomalies of vascular development, among which kinks, loops, and tortuosity are quite common. In these zones, there is an increased likelihood of damage to the endothelium by turbulent blood flows, atherosclerosis progresses and hemodynamically significant stenosis can manifest earlier, compared to the direct course of the vessel.
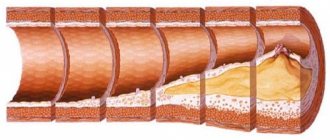
The morphological basis of stenosis of neck vessels is cholesterol plaque. The pathology of the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates provokes the deposition of fat not only in the aorta, coronary and cerebral arteries, but also in the vessels of the neck, which makes it difficult to deliver blood to the brain.
A plaque in the carotid artery does not manifest itself for the time being, especially if it is localized on one side. With its gradual increase, the lumen of the vessel narrows more and more, and signs of a lack of blood flow in the head appear - chronic ischemia, clinically expressed in dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
With relatively preserved blood flow through the main arteries of the neck, the phenomena of chronic ischemia will gradually progress, but when the plaque is destroyed, thrombosis will inevitably develop with complete blockage of the vessel. This is one of the most dangerous manifestations of carotid artery stenosis, which is accompanied by necrosis of brain tissue (stroke).
Depending on the extent of damage to the vascular walls, focal atherosclerosis is distinguished (over one to one and a half centimeters) and prolonged, when plaques occupy more than 1.5 cm of the length of the artery.
To assess the degree of risk of vascular accidents and determine indications for surgical treatment, it is customary to distinguish several degrees of narrowing of the carotid arteries, determined by the percentage of stenosis of the lumen of the vessels:
- Up to 50% is a hemodynamically insignificant narrowing, which is compensated by collateral blood flow;
- 50-69% - pronounced narrowing, manifested clinically;
- Stenosis up to 79% is subcritical, the risk of acute circulatory disorders is very high;
- Critical stenosis, when the lumen of the artery is narrowed by 80% or more.
The most susceptible to the atherosclerotic process are the initial sections of the common carotid artery, the place of its division into external and internal branches and their mouths.
Main reasons, who is at risk
In modern cardiovascular surgery, it is generally accepted that the manifestations of carotid artery stenosis make it possible to determine the degree of atherosclerotic pathology of all vessels of the human body.
One of the main reasons for the development of carotid artery obstruction is atherosclerosis. This disease causes the formation of cholesterol plaques on the vascular walls, the growth of which ultimately leads to a decrease in the lumen of the vessel. Often the cause of arterial stenosis is thrombus formation, as a result of which the lumen of the vessel is simply blocked. In both cases, the lack of proper treatment leads to unpleasant consequences, even death is possible.
In addition, the following causes of the disease are distinguished:
- significant proliferation of connective tissue (collagenosis);
- diseases that cause problems with blood clotting;
- pathologies in which the wall of the carotid artery is capable of dissection;
- fibromuscular dysplasia, when formations of fibrous and muscle tissue contribute to blocking the vascular lumen;
- diseases in which the vascular wall becomes inflamed (arteritis).
As a result of various damage to the vessel wall, changes occur in the direction of blood flow. Encountering an atherosclerotic plaque on its way, the blood tries to bypass the obstacle, and due to the resulting pressure, damage to the vessel is possible, which is why a blood clot is formed. Over time, this clot can block the lumen, leading to carotid artery thrombosis.
People at risk of developing this disease include:
- old age;
- with diabetes mellitus;
- who have had cases of this disease in their family;
- eating fatty foods;
- hypertensive patients;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Diagnostics
The most common and accessible research method that allows you to determine the narrowing of the lumen of a vessel (regardless of its degree), changes in the volume of blood flow in it, the presence and location of atherosclerotic plaques. Ultrasound scanning also allows you to evaluate the condition of the brachial trunk, vertebral and subclavian arteries.
More expensive and modern computer research. It is prescribed for suspected pathological changes in the structures of the brain and the vascular bed in the cranium.
Angiography
The most accurate method showing changes inside the vessel. It is prescribed after strokes, when the degree of narrowing of the lumen is 50% or more. Diagnosis is carried out in a special operating room equipped with an angiography unit.
- Computed tomography angiography involves inserting a special catheter into the patient's femoral vein and then injecting a contrast agent. This allows you to get a clear picture of the x-ray.
- Magnetic resonance angiography has the same principle, only during the procedure a device is connected that creates a strong magnetic field.
To determine whether you have stenotic lesions of the carotid arteries or not, your doctor will examine you.
Even if you have no symptoms, your doctor may hear a murmur over your carotid arteries caused by blood flowing through the stenotic area.
If necessary, you will be prescribed Doppler ultrasound of the main arteries of the head (USDG MAG), electroencephalography of the brain (EEG) or computed tomography (CT).
For a more detailed assessment of the condition of the carotid arteries, your doctor may recommend an angiography (x-ray examination of blood vessels).
This study is performed by catheterization, usually of the femoral artery, under local anesthesia in a special operating room equipped with an angiography unit.
The doctor may suspect carotid artery stenosis even at the stage of listening to the heart. In this case, a characteristic noise is noticeable above the vessel, upon hearing which, the specialist refers the patient for a detailed examination:
- Ultrasound. Today this is the most accessible and safe method for detecting stenosis of the cervical arteries. It allows you to see deviations in the structure of the vascular wall, as well as identify problems in the nature of blood flow. Doppler ultrasound is performed as an additional procedure.
- MRI and CT. They represent the most accurate methods, the purpose of which is to exclude other causes of circulatory disorders. In addition, they allow you to accurately determine the source of pathology.
- Blood test for cholesterol levels.
- Angiography. Since the procedure is a minor surgical intervention, it is performed using local anesthesia. During it, a catheter is inserted into one of the vessels, through which it penetrates the carotid artery. After this, the problem area is filled with a contrast agent and an x-ray is performed. With a professional approach, the procedure is completely safe.