Treatment of VSD - Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Hello Anatoly.
My name is Alsou, I am 38 years old, of which I have suffered from VSD for 14 years. Please tell me, did you have extrasystoles in large numbers, and if so, how did you fight? Just like you, I went through a bunch of examinations during this time. This is my situation today. I haven’t left the house for 3.5 years now because... there were fainting spells.
Last year there was a rhythm disorder - paroxysmal tachycardia. They fitted me with a pacemaker. Although no pathologies were found. They said that this could be due to taking antidepressants.
Currently I am taking beta blockers, phenazepam, seduxen. Every day I re-read your site, read prayers. Panic attacks almost constantly or anxiety.
My diagnosis is anxiety-phobic syndrome, somatoform disorder of the autonomic nervous system. MRI of the neck - there is a small hernia, protrusion.
Hello Alsou!
Yes, I had heart rhythm disturbances. Starting from single extrasystoles and ending with attacks of atrial fibrillation. How did you fight them? Exactly the same as you are now.
At that time I didn’t really understand the reasons for what was happening. The attending doctor prescribed me medications that were good for people with heart disease, but they had no therapeutic effect on me.
Then, having calmed the nervous system a little with the help of a tranquilizer and medicinal herbs, he began to eliminate the panic fear, which was the cause of everything.
You are an intelligent woman and must understand that in your diagnosis there is not a single word about any terrible and serious organic disease of the heart or its conduction system.
This means that your heart is normal and completely healthy. And attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia / a sharp increase in heart rate to 150-200 beats per minute / is one of the symptoms of a panic attack during VSD.
Your hernia and protrusion in the cervical spine have nothing to do with VSD. The development and course of vegetative-vascular dystonia is in no way connected with spinal osteochondrosis, although osteochondrosis makes its contribution to the quality of life and general sense of health.
Arrhythmia, or heart rhythm disturbance, in its pathogenesis is associated with various diseases, since in rare cases it is a self-occurring pathology.
The heart is primarily affected by the nervous system, and when its parts are disrupted, as happens with vegetative-vascular dystonia, changes in heart rate can be observed, both upward and downward.
Vascular arrhythmia is most often observed in individuals prone to nervous system imbalance, who, in addition to VSD, may experience phobias, neuroses, etc.
Home -{amp}gt;Symptoms of VSD -{amp}gt; Arrhythmia and vegetative-vascular dystonia
The heart is a unique organ that has special cells - pacemakers, capable of independently producing an electrical impulse, due to which the heart muscle contracts.
The sinus node, or pacemaker, is located in the wall of the right atrium and therefore the heart rhythm, normal according to the source of its passage, is usually called sinus rhythm.
If the heart functions normally, then with each beat there is a sequential contraction of its parts: the atria, then the ventricles. In healthy people, these contractions follow each other at regular intervals, but with arrhythmia their sequence is disrupted, and the frequency can be either higher than normal or lower than normal.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, sinus tachycardia is very often observed. at which the heart rate reaches 90-100 beats per minute or more with the correct rhythm. In this case, tachycardia decreases markedly with breath holding.
This arrhythmia is called respiratory arrhythmia. in which the heart rate increases as you inhale and decreases as you exhale. Typically, respiratory arrhythmia is characteristic of people with increased excitability of the autonomic nervous system, that is, it is neurogenic in nature.
The general condition does not suffer with such arrhythmia. But as soon as a VSD student learns about this problem, almost immediately he experiences a whole range of subjective sensations, such as pain in the heart area not only during physical activity, but also at rest.
With such an arrhythmia, an additional beat or several beats are noted at regular intervals. Respiratory arrhythmia is not life-threatening and does not require special treatment.
And yet, if a person suffering from VSD experiences an irregular heart rhythm, then this patient should be consulted by a cardiologist.
Very often, as lifestyle improves, this condition goes away on its own without any drug treatment.
But if a doctor, who still needs to be contacted, suspects that a person has a type of arrhythmia that requires diagnosis, then in this case Holter ECG monitoring is used, or recording a cardiogram for a long time, which makes it possible to detect much faster rhythm disturbance.
Causes of arrhythmia
In healthy people, the cause of sinus tachycardia is physical activity and psycho-emotional arousal. If the arrhythmia is the result of emotional stress or increased body temperature, it usually goes away on its own without special treatment.
Heart failure, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, heart failure, myocarditis can also cause persistent tachycardia. In a healthy person, arrhythmia can be triggered by tight clothing, constipation, heavy food, and insect bites.
Very often, arrhythmia can be caused by a seemingly natural cause - premenstrual syndrome, when the heart rhythm is disturbed, pain appears in the chest, and suffocation occurs.
Predisposition to arrhythmia can be inherited genetically. There are several types of arrhythmias: bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystole and atrial fibrillation.
But with any type of arrhythmia, you cannot self-medicate, and especially if atrial fibrillation is diagnosed. It is imperative to visit a medical institution, where a special study will be carried out and appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
In articles on our website, the concept of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” is often encountered. At the request of site visitors, we expand on this concept in this article. What is vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD)?
This is a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system monitors the preservation and maintenance of the internal environment of the body, and also adapts the body systems to changes in the external environment.
That is, if you have such a disorder, then the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia may be: increased or decreased blood pressure, arrhythmias, sweating, metabolic disorders, lack of air, low stress resistance, high fatigue, weather dependence, inability to quickly adapt to a new climate, headache , dizziness, trembling, cold hands and feet, increase or decrease in body temperature and other unpleasant conditions.
Often more than half of the described symptoms are observed at the same time, which seriously reduces the quality of life.
Unfortunately, 80% of people suffer from vegetative-vascular dystonia to one degree or another. 40% of women and 20% of men noticeably feel its influence. Every hundredth person truly suffers from this disorder.
Let us say right away that this dysfunction is, to a much greater extent, the work of neurologists, rather than cardiologists (despite the disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system).
During what periods does vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) occur?
Most often during puberty or withering (menopause), in difficult physical or mental conditions, during pregnancy.
Causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD)
- hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, menopause, puberty);
- climate change;
- physical and mental overload;
- neurotic disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- physical inactivity;
- endocrine diseases;
- stress.
Complete list of manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD)
- Cardiovascular system: hypotension, hypertension, arrhythmia (most often this is its increase - tachycardia), pain in the left half of the chest (cardialgia);
- Respiratory system: suffocation, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing and hyperventilation syndrome;
- Gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, heartburn, belching, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain;
- Thermoregulation: increased or decreased body temperature, chills, increased sweating, sensations of heat or cold;
- Vestibular system: dizziness, presyncope;
- Urogenital system: frequent urination, itching and pain in the genital area;
- Emotional disorders: anxiety, restlessness, irritability, fatigue, decreased performance, internal tension, low mood, tearfulness, sleep and appetite disorders, fears.
On what basis is the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) made?
- It is necessary to differentiate VSD from somatic, neurological and endocrine diseases;
- Next, diagnose disorders of the system in which there are autonomic dysfunctions (Echo-CG, ECG, Holter monitoring, EEG, ultrasound, TCD, hormonal profile tests).
How to treat vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) and how dangerous it is
Dystonia is successfully treated and is, in the vast majority of cases, a harmless disease.
Vegetotropic, vascular, nootropic and psychotropic drugs, psychotherapy, hardening, massage, spa treatment, and physiotherapy are used as treatment.
Dosed and gradually increasing physical activity, as well as hardening, are an excellent means of self-medication, unlike vegetotropic, vascular, nootropic and psychotropic drugs.
Taking medications on your own, without a doctor’s prescription, is very dangerous. Firstly, there is a high risk of making a mistake in choice (this is very dangerous), and secondly, they are persistently addictive (no less dangerous).
Neurosis or hypertension?
Good afternoon I am 35 years old. Labile nervous system. Blood pressure jumps with excitement and panic. Increases instantly. At rest at home the pressure is 116-135/75-85. Once you get a little scared, your pulse and blood pressure immediately rise. Pulse 120, blood pressure up to 170/100. This is at home. I immediately calm down and my blood pressure and pulse return to normal. Outside the home, that is, at doctors, the pressure is always high 160-180/100-110. I'm terribly worried. Lump in the throat, sweaty palms, tachycardia, dry mouth. The therapist immediately diagnosed hypertension as grade 3, risk 3. I am very afraid to measure my blood pressure outside the house. I stress myself out a lot. These jumps make my ears ring and my head buzz. The tablets prescribed by doctors in different years of visits, Concor, Niperten, do not hold pressure at all in case of panic. Even the emergency medicine Capoten doesn’t help until I calm down myself.. Or rather, it helps when you chew the whole tablet, but Corvalol helps more with panic. After some stress at night I jump up in panic, there is noise in my head, ringing in my ears. High pressure. I’ll breathe, I’ll calm down and it’ll go back to normal. But out of fear, my thoughts can instantly raise it again, I just have to think about exciting things. And so all day long, if at work he is nervous and jumps here and there. From 130-170/85-110. I'm tired of these jumps. If this is hypertension, then why is it normal at home? It doesn’t even occur to me to measure it. And how to go somewhere, go somewhere, I start to worry, fuss, I feel hot inside and I need to measure it, although I know that it’s elevated, but I can’t help but measure it. I will twitch and think about him constantly. I measured it and saw 160/100. Upset. I'm trying on. 130/80. Not satisfied. Some kind of psychosis. Measure again. 150/95. And just like that, I can’t leave the house. Are these jumps dangerous for the body? Why such big jumps? I agree to swallow the pills, but the panic during the measurement has not gone away. During pregnancy I was forced to make smad. So I panicked for days. I still regret that I didn’t rip off the device. After all, I know that I will worry. It increased to 180/100, 160/100 many times. At the same time, I drank Concor and drank a package of motherwort. Apparently, when everything took effect, the brain became foggy and the pressure dropped to sane numbers. And due to this decrease, the daily average is 150/90. Why isn’t there such close monitoring of temperature and sugar, since I have a thermometer and a glucometer. And I'm obsessed with pressure. Sorry for the many words. I tried to describe my condition.
Good afternoon, I’m ready to chat with you. look at the conditions of my demo consultations, do you agree with them?
Why does arrhythmia occur during VSD?
A certain part of the brain controls the heartbeat every second or even more often. From it, information goes to the sinus node, from which impulses are subsequently generated for the heart muscle.
Circumstances contributing to damage to the functioning of the ANS:
- Emotional state - stress, fear, anxiety, intense joy, excitement.
- Bad habits.
- Long-term use of energy drinks and caffeine-containing drinks.
- Uncontrolled eating.
- Systematic lack of sleep.
- Excessive work.
- Infectious diseases.
- Overheating, hypothermia of the body.
- Chronic diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
Main 7 symptoms of VSD
Disturbed regularity and frequency of CV may not be associated with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, but may signal heart disease.
Treatment methods
To cure neurotic heart disorder, the following methods are used:
- Normalization of lifestyle. It is necessary to eliminate mental and emotional stress, as well as give up bad habits.
- Diet. To normalize the functioning of the nervous system, they create a menu consisting of vitamin-containing products. It is forbidden to drink a lot of tonic drinks, as well as eat fatty and spicy foods.
- Physical activity. To tone the body, you need to do therapeutic exercises, play active games and take walks in the fresh air. Severe exhaustion and physical inactivity should also not be allowed.
- Physiotherapy. Manual treatment methods, as well as swimming and other water procedures, can help you get rid of mental stress.
- Psychological methods. They include procedures aimed at making the patient aware of the source of the disease.
- Pharmacological agents. Used in the acute stage of heart disease.
Psychotherapy
For the treatment of cardiac type of neurosis the following is used:
- cognitive technique;
- dialogue;
- hypnosis.
Recovery takes place only if the patient realizes that the source of heart problems is psychosomatics, and not physiological disorders. During the dialogue, the patient is shown the insignificance of his experiences, and he begins to live normally, without constantly waiting for heart attacks.
Cognitive therapy
This is a psychological treatment method that includes procedures that reproduce the situations that caused the disorder. The patient is simulated the events that led him to an obsessive feeling of anxiety and fear of pain in the heart, maintaining a sense of security.
To enhance the effect of therapy, the patient is put into a trance state using hypnotic methods, where the situation of the onset of the disease is simulated.
After this, the psychologist conducts a conversation with the patient, which allows him to convince him of the correctness of the treatment. Also, dialogues with a doctor during hospitalization prevent the occurrence of attacks, since an atmosphere of security is created.
Drug therapy
To improve the effect of psychological treatment, as well as in the absence of effect from its use, medications are prescribed:
- neuroleptics;
- multivitamin complexes;
- beta blockers;
- distractions;
- tranquilizers;
- psychostimulants.
Neuroleptics are drugs against the cardiac type of neurosis with antipsychotic effects. Prescribed for the acute stage of the disorder, which is characterized by frequent attacks. Their use has a calming and hypnotic effect, and also eliminates hallucinations. The negative side of the use is the possibility of apathy or depression, as well as a strong decrease in emotional activity.
Folk remedies are used to supplement treatment.
Classification
An abnormal heartbeat is an arrhythmia. There are such types of it:
- Tachycardia – increased heart rate.
- Bradycardia – low heart rate.
- Extrasystole is a single powerful contraction of the ventricles or atria.
- Atrial fibrillation is numerous chaotic superficial contractions of the atria that spread to the ventricles.
Each of these types occurs in VSD. All of them are characterized by disruption of the heart, poor blood supply to all organs and tissues of the body. This leads to their similar symptoms and treatment methods.
Extrasystole
Characteristic manifestations of extrasystoles are single heart beats of increased power (extrasystoles), which do not fit into the normal rhythm. Before the generation of an extrasystole impulse during VSD, an unpleasant sensation of cardiac arrest may appear.
After a pause, the heartbeat starts again, but there is a more powerful beat than usual. This is how the built-in defibrillator works.
Such fading can also occur with bradycardia.
Symptoms of extrasystole:
- weakness;
- pallor;
- sweating;
- fear;
- feeling of lack of air.
Both forms of rhythm disturbance often do not cause significant discomfort in the patient and therefore do not require special treatment. Only very emotional people may need to take antiarrhythmic drugs.
There are several types of arrhythmia with VSD. The following types are distinguished:
- Tachycardia.
- Bradycardia.
- Extrasystole.
- Atrial fibrillation.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is characterized by an increase in the rate of contractions. This can happen even in a state of complete calm. The number of beats can exceed 100 per minute.
In severe exceptional situations, the heart muscle can contract from 30 to 220 beats per minute. VSD and arrhythmia are frequent companions; heart rate varies up to 90–140 times per minute, and this is accepted as the norm.
With dystonia, the following types of pathological conditions may appear:
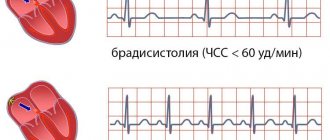
- Tachycardia is an increased heart rate ≥ 90 beats per minute.
- Bradycardia is a disorder of sinus rhythm, determined by a low heart rate, up to 60 beats per minute.
- Extrasystole - the heart or its individual chambers contract untimely.
- Atrial fibrillation is a frantic heart rhythm, accompanied by frequent and unsystematic excitation, erratic contraction of the atria, reaching 600 beats per minute.
Tachycardia with VSD is divided into two types:
- Intracardiac. The nature of the formation is associated with the cardiovascular system and indicates impaired functioning of the ventricles and heart failure.
- Extracardiac. The “extracardiac” nature of the disease, which is determined by the neurological, psychological nature of its appearance. May indicate kidney disease.
According to the manifestation of symptoms, it has three types:
- Regular accelerated heartbeat. Fast but more or less stable heartbeat.
- Episodically severe symptoms. A sudden increase in pulse in some cases up to 240 beats.
- Sinus arrhythmia. An increase in heart rate does not affect the rhythm of the heart itself.
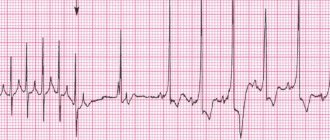
Types of arrhythmias on ECG
Signs and treatment of cardiac neurosis
The main cause of the development of heart neurosis (cardioneurosis) is stress. The process of the onset of the disease is simple: stress provokes a sharp release of adrenaline, which harms the heart and blood vessels. People of all ages are at risk for developing this disease.
Especially if you have heart defects and heart diseases, such as myocarditis, rheumatic carditis and others. Also at risk are people who often suffer from acute respiratory infections and sore throats, are subject to frequent mood swings, depression, smokers and drink alcohol, and have had pneumonia.
Let's look at the signs and treatment of heart neurosis.
Signs of cardiac neurosis.
A strong sound is enough - and the patient is covered in perspiration, his heart is tormented, and he may even faint in severe cases. Patients with cardiac neurosis are very excitable.
How can you identify heart neurosis?
The disease heart neurosis can easily be mistaken for another disease of the cardiovascular system, for example, ischemia or angina pectoris
Therefore, you need to pay attention to the following signs of illness:
To prescribe adequate therapy, a full comprehensive diagnosis of the patient’s body and consultation with a psychotherapist are necessary.
It is very important to find the right approach to each patient in order to try to eliminate exactly the cause of the disease instead of constantly fighting the symptoms
The first important step in treating neurosis is visiting a psychotherapist. A long, calm conversation with a friendly specialist in a cozy environment allows the patient to open up and explain the reasons for his restless condition.
The patient should learn not to take all surrounding problems to heart, especially those that he cannot change, and temporarily distance himself from the everyday bustle.
If these are problems in the family, then you need to gather at a round table and calmly discuss all the misunderstandings, come to a consensus, or, as a last resort, maybe you should not delay the divorce. Sometimes, to recover, you may need to change your field of activity, find a new job with a lower level of responsibility, more pleasant working conditions or a friendly team.
To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of neurosis, the patient sometimes has to completely change his lifestyle. Doctors recommend:
- follow a daily routine, go to bed and get up at the same time, sleep in a ventilated area;
- eat right, add foods rich in vitamins and minerals to your diet, exclude fried, smoked, salted, spicy, pickled foods;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up alcoholic beverages, smoking, strong coffee;
- add rational physical activity, for example, engage in amateur sports (running, gymnastics, fitness, swimming, cycling), if you have a sedentary job, you should take breaks more often and walk around the office, do simple exercises;
- make new friends, find a hobby you like, do something that will bring positive emotions, take evening walks in the fresh air, spend weekends outside the city, plan a vacation trip.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a very positive effect on the state of the nervous and cardiovascular systems:
- electrosleep;
- electrophoresis;
- pine and pearl baths;
- Charcot's shower;
- circular shower;
- "comb";
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy.
Diagnostics
To select the correct therapeutic tactics, the cause of the myocardial dysfunction is determined.
First of all, electrocardiography is prescribed, which can detect most rhythm disturbances. Depending on the type of arrhythmia, characteristic signs will be determined on the ECG.
Sinus tachycardia is interpreted on the ECG as follows:
- Heart rate is more than 100 times per minute;
- the presence of a P wave in all leads indicates sinus rhythm;
- pronounced sinus tachycardia is indicated by an increased amplitude of the P wave in the first two leads, as well as a shortened PQ interval.
Extrasystole is very variable, but on the ECG it is most often expressed as tachycardia, that is, the above ECG signs are observed. With atrial extrasystole, the P wave will be deformed, and with ventricular extrasystole, the QRS complex will be widened.
In some patients, arrhythmias cannot be immediately diagnosed. For such cases, other research methods are provided:
- Electrophysiological study - helps to determine the arrhythmogenic focus.
- Daily ECG monitoring is effective in 80% of cases, as it helps to identify asymptomatic arrhythmia.
For sympathotonia, medications are prescribed - Propranolol or Metoprolol. And for vagotonia - Atropine, Grandaxin or Gidazepam. This is how vegetative dystonia is divided.
Their main difference is that with sympathicotonia the heartbeat accelerates and tachycardia is observed, while with vagotonia, on the contrary, it slows down. The treatment is comprehensive and involves a neurologist, a psychotherapist, and a cardiologist.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
To find out the cause of extrasystoles, an ECG and ultrasound of the heart are performed, and if necessary, 24-hour Holter monitoring is prescribed.
If the arrhythmia is caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia, then an electrocardiogram and questioning of the patient is sufficient. If necessary, procedures are prescribed by a cardiologist and a neurologist.
Extrasystole against the background of VSD is determined using electrocardiography. In addition, the patient is shown an ultrasound examination of the heart to identify possible structural anomalies that could lead to impaired contractility of the organ.
The patient is recommended to undergo a general and biochemical blood test. To exclude possible consequences for the brain, it is necessary to conduct magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as electroencephalography.
Treatment of the problem
The main difficulty lies in the patient’s lack of understanding of the nature of his disease. The main method of therapeutic intervention is psychotherapy, but in combination with drug treatment and strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
The point of therapy is to neutralize the factors that stimulate the occurrence of the disease. The patient is recommended to visit a psychotherapist who will help relieve the subconscious fear of further attacks. First, anxiety is removed.
During the conversation, the psychotherapist lets you talk, listens carefully and teaches how to get rid of stress using auto-training or meditation. In extreme cases, hypnosis is used to determine the root cause of stress. With heart neurosis, the cause of anxiety and dissatisfaction is problems at work, personal life and one’s own shortcomings. Constant stress and contradictions cause depletion of nerve cells and lead to decreased ability to work, fatigue, and depression.
A psychotherapist helps you recognize weaknesses and understand how to avoid repeating the wrong reaction to stressful situations. She also conducts training sessions on managing emotions by delving into painful memories and developing ways to overcome them.
Prognosis and danger of arrhythmia in VSD
With VSD, any changes in the functioning of the heart carry a certain danger. Even short-term disruptions will worsen over time and lead to irreversible changes. In advanced cases, even death is possible.
Long-term arrhythmia without appropriate treatment has the ability to take a malignant form of course, in which a decrease in pressure, fainting and severe pain in the heart area can be observed, and subsequently can cause myocardial infarction.
Arrhythmia with VSD is practically incurable and in the vast majority is not dangerous, but one cannot ignore it. Every change, new incomprehensible symptom in the life of the heart should be referred to the doctor. Timely recognized pathology is the key to a long and fulfilling life.
Even if the diagnostics did not reveal any pathology, do not forget about heart rate fluctuations. The heart is the most important member of our body, and the consequences of “frivolous” abnormalities can be disastrous.
Systematic disorders will cause the heart to eventually fail and fail. To prevent serious pathologies, you should carefully monitor your health.
Palpitation in neuroses
Complaints of palpitations not only during physical effort and the slightest excitement, but also at rest (in accordance with the daily fluctuations in well-being that many patients have and with an influx of thoughts of anxious and depressive content) are one of the almost indispensable components of hypochondriacal disorders in the clinic of neurotic and pseudoneurotic states. Particularly characteristic are attacks of palpitations in the morning (at the moment of awakening), when falling asleep and often at night (due to insomnia or superficial, intermittent and anxious sleep), as well as (“cold sweat”) with any surprise and “fright”. Extremely painful and painful psychogenic sinus (and sometimes even paroxysmal) tachycardia (with fear of death, pronounced hypochondriacal coloring and increased heart rate up to 140-160 per minute) can be caused in these patients by the mere mention of angina or myocardial infarction. Paroxysms of sinus and supraventricular (much less often ventricular) tachycardia are considered as possible somatic manifestations and equivalents of the depressive phase of cyclothymia.
Cardiac neurosis: causes, signs, manifestations, how to treat
It consists of a timely visit to a therapist, cardiologist, arrhythmologist, psychotherapist, neurologist. Treatment of the underlying disease - vegetative-vascular dystonia - helps to cope with vascular arrhythmia as effectively as possible. For this purpose, drugs from the following pharmacological groups are prescribed:
- nootropic;
- vegetotropic;
- psychotropic;
- vascular.
Asymptomatic arrhythmia does not require special treatment. If the patient has extreme discomfort, antiarrhythmic drugs or beta-blockers are prescribed.
- constant stress and nervous breakdowns;
- malfunction of the central nervous system - skull injury, circulatory disorders, brain tumor;
- it can also be caused by a violation of the biochemical composition of the blood;
- poisoning with various substances (toxic or drugs);
- myocardial disease.
As we have already defined above, arrhythmia has a number of types of diseases that are distinguished by dissimilar symptoms.
For example, a malfunction in the body system with sinus tachycardia is accompanied by heart contractions at a frequency of 90 beats per minute. This figure may be higher.
At the same time, a person who has such a cardiac pathology most often suffers from shortness of breath and palpitations. He is constantly weak and broken, and with little physical activity he gets tired quickly.
Causes
The body's normal reaction to life
Tachycardia with neurosis, VSD, panic disorder occurs at the same time as in all other people on the globe. Another thing is that an anxious neurotic, concentrated on the work of his body in general and the heart in particular, interprets these normal physiological reactions as symptoms of an impending serious illness and even death.
The following can provoke an increase in heart rate both in neurosis and in good health:
- insomnia;
- alcohol consumption;
- caffeine;
- increased body temperature (both in the heat and during acute respiratory infections);
- changes in hormonal levels (primarily in women);
- a drop in blood sugar during hunger (the hunger itself may go unnoticed);
- smoking, etc.
And, of course, the heart rate always increases during physical activity. This is the norm. But suspicious, anxious people sometimes become so afraid of this norm that they notice a terrible heartbeat even when getting out of bed and walking across the room.
In fact, when rising from a horizontal to a vertical position, all people's heart rate increases. But not everyone thinks to count it.
Therapeutic measures
It is logical to assume that arrhythmia due to VSD is eliminated after treating the underlying cause, since drugs to normalize the rhythm, at best, will give only a temporary result.
Therefore, not only a cardiologist, but also a neurologist, psychologist or psychotherapist should take part in therapy. The treatment algorithm is based on the following rules:
- take medications prescribed by a cardiologist and psychologist;
- undergo psychotherapy sessions;
- go to therapeutic massage, acupuncture and physiotherapeutic procedures;
- take a complex of vitamins.
Regarding drug treatment, there are several effective groups:
- Antidepressants are prescribed as a last resort, in case of high anxiety.
- Sedative group - sedatives that are harmless to the body and help with panic attacks and their prevention.
- Neuroprotectors are designed to improve blood circulation in the brain and improve its functioning.
Treatment of cardioneurosis
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to find the causes that provoked cardioneurosis. And if it is impossible to completely eliminate them, at least reduce the negative impact.
Often people do not understand that it is not the heart that needs to be treated, but nervous disorders. To do this, the doctor conducts explanatory conversations and gives recommendations.
First aid during an attack of cardioneurosis
Since the long course of this disease can subsequently lead to real cardiac disorders, attacks should in no case be ignored. Help is provided in the following ways:
the patient is provided with fresh air (a window is opened or taken out of a stuffy place); invite the person to lie down in a quiet place; If possible, measure blood pressure and pulse with a tonometer; divert the patient’s attention to other topics so that he is distracted from the problem; offer a sedative (valerian, valocordin or corvalol).
Attacks of cardioneurosis should never be ignored
When providing assistance, there is no need to make noise and fuss. Tachycardia that occurs in such conditions must be constantly monitored. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically check the pulse and if it increases, and weakness appears, then call an ambulance or take it to the hospital using your own means of transportation.
It is recommended to take sedatives throughout the day, at intervals of 3-4 hours. Once all symptoms disappear, you must undergo an examination and consult with a specialist.
Treatment methods
The main methods of treating cardiac neurosis include psychotherapeutic effects. It is carried out in combination with medications. The psychotherapist helps to identify the cause of the patient’s nervous condition. The most common reasons include dissatisfaction with oneself or profession, problems in personal life. All these problems reduce the body's immune resistance and cause fatigue.
Medicines are prescribed based on the patient’s complaints and well-being. It is recommended to start with mild herbal-based soothing remedies.
Debilitating conditions such as panic attacks, migraines and poor sleep lead the patient to the doctor. Typically, the following series of medications are prescribed to eliminate neurotic attacks:
- mild antidepressants (azafen, amitriptyline, nialamide);
- tachycardia and arterial hypertension in a borderline state suggest the use of beta-blockers (Trazicor, anaprilin);
- Light-type sleeping pills to normalize sleep, but to prevent addiction, they should not be taken for more than three weeks.
Another treatment method is physiotherapy:
- electrosleep;
- electrophoresis;
- pearl and pine baths;
- Charcot's shower (for increased excitability);
- circular shower (for hyposthenia).
Coniferous baths are often used to treat tachycardia in neurosis
Plants in the treatment of cardiac neuroses
Folk remedies use various herbal tinctures and decoctions. One widely used herb is valerian. Its decoctions and pharmaceutical tinctures are good at calming the nervous system. A collection of hop cones, calamus rhizomes, valerian and motherwort will help calm your heartbeat.
A collection of cumin, motherwort, medicinal chamomile, cudweed herb and hawthorn flowers will help relieve nervous disorders with dizziness and suffocation. Another plant-based sedative is peony tincture.
In addition to plants, honey has beneficial effects. Using a spoon of honey with warm water at night will relieve tension and allow you to fall asleep easily.