Can osteochondrosis provoke tachycardia?
Tachycardia can occur against the background of a completely healthy heart. One of the reasons for this phenomenon is osteochondrosis.
Increased heart rate is usually caused by pathology of the cervical or thoracic region. In the neck area, the muscle frame is underdeveloped, which provokes displacement of the vertebrae. At the same time, the nerves and blood vessels in this area are compressed.
When nerve endings are pinched, the functionality of the cardiovascular system is disrupted, which can provoke tachycardia. The heart is forced to increase the number of contractions to pump blood through the compressed vessels.
This mechanism for the development of tachycardia is inherent in osteochondrosis not only of the cervical, but also of other parts of the spine. Heart rate may increase in various conditions:
- after physical activity;
- at rest;
- in an awkward position;
- with increasing load on the spine.
If osteochondrosis affects the lumbar region, this affects the functioning of the abdominal organs. Due to some changes, your heart rate may increase.
Various variations in the manifestation of tachycardia against the background of osteochondrosis mean the need for a comprehensive diagnosis. For correct treatment, it is necessary to find out the features of both pathologies.
Increased heart rate with osteochondrosis can be a reflex. In this case, the pathology is caused by a violation of the blood supply to the brain structures. This development mechanism often accompanies vertebrogenic vertebral artery syndrome. Usually this disorder is associated with pathology of the cervical spine.
The opposite situation is also possible, when osteochondrosis of the thoracic region occurs against the background of a pathological increase in the size of the heart. Tachycardia in this case is of cardiac origin.
With prolonged tachycardia against the background of osteochondrosis, changes in the heart muscle are possible. This means there is a risk of extrasystole when the heart rhythm changes. Such disorders usually occur only at the late stage of osteochondrosis and appear after heavy physical exertion.
A person who is not familiar with the specifics of osteochondrosis does not know whether the disease can cause tachycardia, therefore, when turning to a doctor, he will most likely name signs of cardiac dysfunction, but forget to mention pain in the neck, back, and numbness of the limbs.
Meanwhile, it is the disease that destroys the spine that contributes to the development of complications such as rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and dizziness. Often such attacks are accompanied by a feeling of anxiety, or even panic attacks.
In any case, you should seek medical help, even if the main symptoms of cardiac dysfunction are absent, but the person feels neck pain and numbness in the limbs. A doctor who knows whether tachycardia can occur with osteochondrosis will begin treatment in a timely manner and prevent the development of complications.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of cardiac dysfunction are palpitations, which are accompanied by:
- sudden hot flashes;
- dizziness;
- attacks of suffocation;
- feeling of tightness in the chest area;
- increased fatigue;
- pain in the cervical spine.
There are a number of features that distinguish heart pathology from complications arising from vascular spasm during degenerative processes occurring in the spinal column. Long-term heart pain:
- appear suddenly and disappear after a few weeks;
- from the beginning of the attack they gradually intensify, but after at least three days they weaken;
- are not fraught with a heart attack.
If the cause of tachycardia is osteochondrosis, the doctor will not notice changes in cardiac activity on the cardiogram.
In most cases, heart pain is preceded by physical exertion, sudden careless movements, such as turning or bending, and even coughing. If cervical osteochondrosis is complicated by pathology of the thoracic spine, the pain may become permanent.
Why does it occur
The connection between cardiac symptoms and osteochondrosis is based on two reasons.
- Heart pain occurs when damaged vertebrae compress nerve roots and spinal cord vessels. Painful sensations in the case of compression syndrome occur because impulses from compressed nerve endings spread to the sympathetic center for regulating heart rate.
- Damaged nerves do not send impulses to the receptors in the cervical spine. Because of this, the heart contracts more often and the pulse accelerates. The phenomenon is called reflex syndrome.
If the vertebral artery is pinched, the situation becomes dangerous because the main blood vessel supplies the spinal cord and part of the brain. If arterial blood flow is disrupted, the heart, respiratory organs, and brain centers that are responsible for hearing, vision, and coordination suffer.
Consequences
As mentioned above, osteochondrosis, which caused tachycardia, can lead to:
- partial hearing loss;
- blurred vision;
- loss of coordination, severe dizziness;
- nausea, even vomiting;
- headache.
In an advanced state, the disease provokes attacks of arrhythmia. To compensate for the lack of nutrients and oxygen, the brain sends a signal to the body and blood flow in the clamped vessels increases. A person develops high blood pressure, which becomes normal.
A doctor who knows how the degenerative process occurring in the spinal column affects the condition of the heart will advise the person to immediately begin treatment for osteochondrosis.
Tachycardia in osteochondrosis is a fairly common occurrence that occurs due to the structural features of the spinal column. An accelerated heart rate can be observed during destructive processes in any part of the back, but most often tachycardia is a consequence of damage to the cervical or thoracic spine.
Causes and mechanism of occurrence
As you know, with osteochondrosis, the discs between the vertebrae are destroyed and muscle spasms occur. Protrusions, hernias, etc. are possible as complications. In such cases, there is a possibility of damage and compression of the nerve roots.
All these violations do not go away without leaving a trace and cause, in turn, other disorders. Thus, with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) sometimes occurs. Bone damage leads to impaired blood circulation.
The brain is no longer supplied normally, so the heart begins to pump faster to compensate for the lack of oxygen and nutrients.
A similar picture occurs in the chest area. Osteochondrosis can also cause palpitations here. Although the opposite situation also happens: heart pathology leads to its increase in size and osteochondrosis.
With osteochondrosis, tachycardia has the following origin:
- Nerve signals are transmitted through fibers running in damaged areas of the spine. Further, the impulses, with the help of the autonomic system, ultimately reach the stellate ganglion. This plexus is responsible for the nerve connection with the heart and, accordingly, causes an increased rhythm.
- The mechanism of occurrence can also be caused by reflexes. When nerve endings are compressed as a result of spinal deformation, some areas no longer receive the normal amount of signals. Protective reflexes arise, and receptors begin to transmit special impulses. With the help of the autonomic system, they reach the heart and cause the same consequences: pain, palpitations.
Symptoms of tachycardia in osteochondrosis
Tachycardia and heart pain with cervical osteochondrosis are often confused with a pathological phenomenon arising from heart disease. It is possible to distinguish false painful spasms from true ones by several criteria.
| Criterion | Tachycardia caused by osteochondrosis | Pathological tachycardia, characteristic of angina pectoris and other heart pathologies |
| Duration | Several weeks or months | Not for long |
| Intensity | Gradually intensifies, subsides after 3 days | Each attack is accompanied by severe pain |
| Nature of pain when loading the spine | Getting stronger | Does not change |
| Mental and emotional state of the patient | Stable | Panic attacks, anxiety, fear of death |
| Danger to life | There is no serious harm to the heart | High risk of death |
| Cardiogram data | ECG abnormalities are not detected | Noticeable change in sinus rhythm |
| How you feel after taking Nitroglycerin | Does not change | The pain subsides |
Tachycardia with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine has a number of features:
- occurs during activity and at rest;
- the attack intensifies with increased load on the spine or uncomfortable position;
- worsens after smoking, drinking alcohol, caffeine;
- sinus heart rate is maintained;
- disappears after the start of drug therapy for osteochondrosis.
With cervical osteochondrosis, there may be tachycardia, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- cold extremities;
- throbbing headaches in the morning;
- flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- noise in ears;
- sleep disturbance;
- pain in the affected area of the back;
- lack of air;
- stiffness, chest pain;
- lack of coordination;
- frequent urination.
Depending on which part of the spine is affected, other symptoms characteristic of osteochondrosis may be added.
Tachycardia against the background of osteochondrosis is manifested by typical signs for such a pathology:
- weakness;
- frequent headaches;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased sweating;
- prone to neuroses.
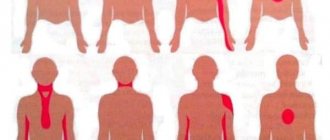
Some specific signs may also indicate a connection between tachycardia and osteochondrosis. Parts of the neck or chest may become numb. There is a tingling sensation in these places. The location of these symptoms depends on which part of the spine is affected.
The connection between tachycardia and osteochondrosis is also indicated by the following symptoms:
- paraspinal muscles are tense;
- mobility of the spinal column is limited;
- sensitivity is impaired;
- in the lower extremities the blood supply is disrupted (manifested by cold feet, brittle nails, peeling of the skin).
Often the symptoms of tachycardia and osteochondrosis appear simultaneously. An attack can be triggered by sudden movements, heavy lifting, or coughing.
Tachycardia due to osteochondrosis can occur for no apparent reason. The heart rate increases suddenly, while the heart rhythm remains unchanged.
An attack of tachycardia with osteochondrosis rarely lasts more than 20 minutes. In exceptional cases, violations are observed for 24 hours or longer. During an attack, there may be a feeling of tightness in the chest, and shallow breathing may occur.
The combination of tachycardia and osteochondrosis may be accompanied by hypertension. Treatment in this case is complicated, since standard drugs do not bring the desired effect, but are addictive. In the future, this may cause ineffectiveness of drug treatment for hypertension.
How does this pathology manifest?
Tachycardia with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine causes pain in the heart, which is often confused with pathologies of the organ.
But the symptoms of osteochondrosis can be distinguished by the following features:
- Unpleasant sensations persist for several weeks or longer.
- The pain gradually increases, but after two or three days it becomes less pronounced.
- The symptoms are not life-threatening and do not harm the heart.
- Even several electrocardiography procedures do not reveal abnormalities.
- The patient is in a stable psycho-emotional state.
- Symptoms increase if the spine is subjected to heavy loads.
- The use of painkillers does not bring relief.
The heart begins to hurt if a person turns sharply, bends over, coughs, or is subjected to physical exertion.
The duration of the attack is approximately twenty minutes. Severe cases are characterized by tachycardia lasting several days. Other manifestations of pathology are accompanied by symptoms of osteochondrosis, including:
- discomfort while moving, changing position, walking;
- no abnormalities in the condition of the heart;
- reduction of manifestations after taking drugs for osteochondrosis;
- constant painful sensations if the vertebral artery is pinched;
- increased symptoms with increased pressure on the vessels.
An increase in heart rate with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine may be accompanied by manifestations associated with pressure on nerve endings and arteries. Wherein:
- body temperature rises;
- there is a feeling of stiffness in the chest;
- Coordination is impaired, dizziness worries, and fainting occurs;
- troubled by breathing problems;
- sleep is disturbed, the patient gets tired quickly;
- temperature changes in the limbs;
- urination becomes more frequent;
- neck hurts.
Treatment is necessary to alleviate the condition.
Diagnostics

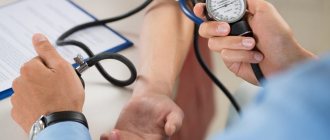
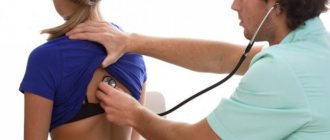
During the initial examination, the specialist performs auscultation of the heart and feels the pulse. It is also important to collect a medical history.
The problem of detecting tachycardia in osteochondrosis is that spinal pathology can cause severe pain, and the pain can radiate to other parts of the body. Tachycardia against the background of such symptoms may go unnoticed, so it is important to conduct instrumental studies.
With tachycardia against the background of osteochondrosis, differential diagnosis is necessary. It allows not only to identify the presence of both pathologies, but also to establish a connection between them.
The primary diagnostic measure is electrocardiography. It allows you to identify signs of tachycardia, but no pathological changes are observed. Depending on the results of the cardiogram, further studies are prescribed.
The most accurate information is obtained using computer or magnetic resonance imaging. CT is more effective for bone structures, MRI for soft tissues.
They also resort to the following studies:
- x-ray of the spine and heart;
- echocardiography;
- tests with physical activity.
X-rays can reveal pathological mobility of the vertebrae when the displacement exceeds 2 mm. Osteochondrosis is also indicated by the reduced height of the intervertebral space and the presence of osteophytes.
In some cases, x-rays are performed with contrast. This approach makes it possible to detect damage to the structure of the spinal canal. Magnetic resonance or computed tomography is also performed with contrast.
To confirm tachycardia against the background of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to exclude other pathologies with similar symptoms.
Tachycardia is primarily associated with cardiac pathologies, so diagnosing the cause of an increased heart rate begins with an electrocardiogram and echo-EG. If no deviations are found, then additional examination methods are prescribed to identify disorders of the spine:
- X-ray – allows you to assess the condition of bone and cartilage tissue.
- Electromyography is necessary to exclude peripheral neuropathy.
- CT, MRI - allow you to more accurately examine the spinal column.
To make a final diagnosis, an ultrasound of the heart and kidneys and blood tests for hormones are prescribed.
Tachycardia - an increase in heart rate from 90 beats per minute. This form of arrhythmia causes frequent visits to cardiologists. Often, after conducting a series of diagnostic studies, the doctor refers the patient to a neurologist or vertebrologist for further treatment. In such patients, thoracic or cervical osteochondrosis is detected, in which tachycardia and accompanying symptoms often occur. This is a rapid heartbeat, discomfort, a feeling of heaviness or pain in the heart area.
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and rapid heartbeat are interconnected either through pinching of the spinal nerves (spinal roots), or through their mechanical damage. In all cases, the cause of tachycardia is destructive and degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs.
As a result of instability of the cervical vertebrae due to their displacement relative to each other, the vagus nerve is affected. The following signs of damage are observed:
- irritation of nerve tissue;
- development of a secondary inflammatory process;
- degenerative changes at the cellular level.
All this provokes a disorder of myocardial innervation, leading to a disruption of the rhythm of contractile activity. But most often, tachycardia occurs with thoracic osteochondrosis, when the patency of the radicular nerve changes. In addition to rapid heartbeat, patients complain to the doctor of severe pain in the cardiac region, radiating to the left arm.
To confirm the diagnosis, preference is usually given to instrumental methods. An x-ray of the spine is prescribed.
If the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the heart and electrocardiography, the procedures will only show the presence of tachycardia and no other pathological changes. With their help, osteochondrosis is distinguished from diseases of the heart structures.
Based on the results of radiography, the location of the pathological focus and the severity of the disease are assessed. The procedure is carried out in maximum flexion/extension. This gives information about how the vertebrae move in relation to each other.
If they are displaced by more than two millimeters, then this indicates an unstable condition.
As an alternative, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are used. The first study examines the condition of the soft tissues, while the second provides information about the bones. These methods provide more detailed information, but are much more expensive.
Features of treatment
How to get rid of rapid heartbeat with osteochondrosis? Effective targeted treatment of spinal pathology is necessary. Then both diseases are eliminated. Therapy includes conventional methods, but also has features:
- When the vessels are compressed, swelling and inflammation are formed. Disruption of the normal movement of arterial blood is sometimes accompanied by a weakening of the flow of venous blood. To correct the situation, anti-inflammatory drugs and diuretics are used.
- When the inflammation is relieved, a course of restorative therapy begins. Blood circulation improves, including at the micro level, and the condition of the nervous tissue is brought back to normal. Nootropic drugs, angioprotectors, etc. are suitable for these purposes.
- If conservative methods do not give the desired result, surgery is performed. In its process, everything that interferes with normal circulation in the vessels and causes palpitations is removed: osteophytes, growths.
A reasonable attitude towards your own health is the key to good health. Often timely treatment allows for a thorough examination and finding the real cause of palpitations.
In some cases, it becomes osteochondrosis. You should not delay treatment, as prolonged exposure to the heart leads to heart disease. It is important to remember that all drugs are prescribed only by specialists.
If you want to get more information like this from Alexandra Bonina, check out the materials on the links below.
Additional useful information:
- My free books, videos and master classes
- My exercise programs and video courses
- My printed books (available in major online stores)
- Free online marathon “How to save your face from old age”
See more useful materials on my social networks:
YouTube | VKontakte | Yandex.Zen | Instagram | Telegram | Facebook
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends 

Diagnostic measures
When a patient has tachycardia, the first thing to do is examine the heart. To do this, the doctor does an examination and prescribes an ECG. If the symptoms of tachycardia are not associated with heart pathologies, additional studies of other organs and systems are prescribed. For this, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- radiography,
- Ultrasound,
- CT or MRI,
- blood and urine tests.
Establishing a connection between tachycardia and osteochondrosis occurs by excluding other pathologies. With chondrosis, pain is observed in the cervical, lumbar or thoracic region. X-rays show disc displacement. If a more detailed study of the condition of the spine is necessary, a CT or MRI is prescribed.
Prevention
A healthy, active lifestyle and correct posture will help avoid problems with the spine and possible complications in the form of tachycardia. If a person’s work activity involves heavy loads on the musculoskeletal system, one should listen more carefully to back pain. At the first symptoms of chondrosis, you should consult a doctor and carry out the necessary treatment.
The development of tachycardia in cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis can be prevented if you follow the following recommendations:
- correctly distribute work and rest time;
- eat properly, balanced;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- get rid of bad habits;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- purchase orthopedic bedding;
- avoid physical overexertion;
- avoid putting too much stress on your back;
- do morning exercises;
- strengthen the immune system.
By following these recommendations, you can prevent the occurrence of tachycardia in osteochondrosis, as well as many other pathological conditions.
What not to do?
For tachycardia caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you must not:
- do thermal procedures (hot compresses, heating pads), visit baths and saunas;
- try to straighten intervertebral discs on your own;
- self-medicate, choose your own medications;
- drink alcoholic beverages, smoke.
You should not follow the recommendations of friends and relatives who also suffer from tachycardia or osteochondrosis. Treatment is selected individually by an experienced specialist.
How to treat tachycardia caused by osteochondrosis
Treatment is carried out comprehensively and has the following areas:
- Drug treatment is aimed at slowing down the inflammatory process and relieving pain in the affected area. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and vasodilators are used. Medicines that can lower the heart rate will help relieve the symptoms of tachycardia.
- Therapeutic exercise is aimed at relieving tension on the spine and strengthening the muscle mass of all its parts.
- Physiotherapy helps improve the patient's general condition. The use of Bernard current and ultrasound helps restore the functions of the paravertebral muscles and improves blood circulation in the affected areas.
- Surgical intervention is used after conservative treatment if it does not bring a positive result. The operation is aimed at removing growths that compress blood vessels and nerve roots.
The doctor decides how and with what to treat tachycardia. To do this, he conducts an examination and refers the patient to hardware diagnostics:
- electrocardiography and electromyography;
- X-ray of the spine and heart;
- computed tomography;
- MRI.
If the diagnosis is confirmed and the cause of tachycardia is osteochondrosis, the person will be prescribed physical therapy, the purpose of which is to slow down the degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs of the spine. Help fight the manifestations of tachycardia:
- acupressure;
- manual therapy.
Painful sensations are relieved by medicinal ointments that contain bee or snake venom. The doctor may prescribe diuretics, anti-inflammatory and vasodilator drugs. People with osteochondrosis are recommended to do special health-improving exercises.
Self-medication at home is unacceptable. Under no circumstances should you:
- Use heating pads, visit steam rooms and saunas to relieve pain symptoms. Heat increases blood flow and increases swelling of inflamed tissue.
- Adjust the vertebrae yourself, because the neck and thoracic region are one of the most vulnerable places of the spinal column. Unsuccessful manipulations will lead to disability or death.
Before taking any action to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of tachycardia, you should consult your doctor.
Diagnosis and identification of the connection between heart rhythm disturbances and osteochondrosis
The occurrence of the phenomenon is accompanied by a general deterioration in health, dizziness, anxiety, weakness and irritability. If these signs appear, it is recommended to independently perform a procedure to identify tachycardia.
To do this you will need:
- Take a comfortable position. Prepare a stopwatch;
- Feel the pulse by pressing the artery on the wrist of the left hand;
- Count the number of heartbeats for exactly one minute.
A normal heart rate is between sixty and eighty beats per minute (for an adult). An increase in the number of contractions to eighty or more indicates the occurrence of tachycardia and requires action. Lack of timely treatment can lead to serious consequences for both the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems. In addition, arrhythmia often develops together with hypertension, which also poses a danger to the health and life of the patient.
We suggest you read: Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy
If an abnormal heart rhythm is detected, the patient is immediately referred to an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram. This is necessary to confirm or refute the presence of heart disease. If they are not detected, the doctor additionally prescribes the following procedures:
- Ultrasound examination of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Electromyography (with its help, neuropathy is excluded, which can also cause cardiac dysfunction);
- X-ray (examination is carried out on the heart and spine, helps determine the current state of bone, muscle and cartilage tissue, detect osteophytes and abnormal mobility of the vertebrae);
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging (allows for better visualization of affected and painful areas.