Everyone is well aware of the sad statistics of heart disease, vascular pathologies and the fact that the largest number of deaths occur for these reasons. Lifestyle, bad habits and complete indifference to diet lead to sad consequences and affect how long and how a person lives after a stroke.
Recently, the incidence rate has been steadily getting younger. Every fourth thirty-year-old person is prone to high blood pressure, and by the age of sixty, the number of hypertensive patients doubles.
Features and first signs of the disease
A stroke is the result of a person’s pre-existing medical conditions. Patients who have suffered a stroke are in a different state for the rest of their lives. Over the past 10 years, there has been an epidemic of strokes. After the first incident, a person has a huge risk of developing a second stroke, myocardial infarction or other vascular disease. Depending on the severity of the stroke, the likelihood of death increases. It is impossible to predict how long a person can live after a stroke.
Every year, about 450 thousand cases occur in the country, but the number of patients who survive a stroke is just over a million.
Stroke is an insidious and unforgiving disease. To increase the likelihood of a positive outcome, it is necessary to be able to recognize the first symptoms of an impending vascular disaster. Patients often ignore the first signs: slight changes in coordination, speech disorders, dizziness. Many perceive them as a temporary deterioration in well-being and expect a quick disappearance. Under normal conditions, an ambulance is called when a disaster has occurred and it is difficult to help the patient.
The definition of stroke is characterized by the occurrence of acute neurological symptoms associated with impaired blood flow in the brain or spinal cord.
Main manifestations:
- a feeling of numbness on the left or right side of the body depending on the affected hemisphere,
- sudden deterioration in health,
- weakness in arms, legs,
- dizziness,
- headache,
- nausea, vomiting.

A rapid increase in symptoms should alert a person. If you suspect a stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance.
How long do people live after a stroke, statistics, how many strokes can a person suffer?
Some people, faced with a stroke, may wonder: how many strokes can a person suffer and how dangerous is it for him? It may seem that these diseases only affect older people. However, in reality everything is much more serious. Therefore, in order to avoid a stroke, you need to know what it is, the reasons for its occurrence and what to do during an attack.
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. It can occur in both young (from 22 years old) and older people. Characterized by sudden or gradual onset of noticeable symptoms. Its occurrence may be the result of factors such as blockage of blood vessels in the brain and bleeding into its membranes or the brain itself.
Risk group, reasons
Circulatory disorders are classified as cerebrovascular diseases. When it occurs, there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain. Stroke can be of two types: hemorrhagic and ischemic.
In the first case, a vessel ruptures, causing blood to enter the brain and exert strong pressure on all tissues, disrupting the functioning of the organ. In the second case, the cause of a stroke is a blockage of blood vessels, which deprives the brain of oxygen and important substances and gradually leads to tissue death.
In this case, the disorder can occur in the left or right parts of the brain, which often affects symptoms, and sometimes the hemorrhage can become extensive.
Risk group
There are several risk factors that can make some people more likely to experience circulatory problems. These can be either ordinary diseases or simply changes in the body associated with lifestyle. If possible, it is important to make every effort to avoid becoming at risk.
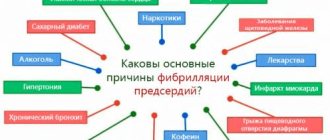
Things that can increase your chance of having a stroke:
- Heart diseases, aneurysms;
- Periodic increase in pressure;
- Problems with blood clotting;
- Diabetes;
- Poor nutrition, obesity;
- High cholesterol;
- Smoking and alcoholism.
Older men who have at least one risk factor in their lives are most at risk of having a stroke. Women, on the other hand, experience circulatory problems much less frequently. Even a child can suffer from it, but this happens quite rarely.
Causes
Circulatory problems of any type can occur for various reasons. In most cases, it can be detected at the diagnostic stage. It is important to do this because... After emergency medical intervention and basic therapy, it will be necessary to treat the underlying cause to avoid another stroke.
Main reasons:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Weakened arterial walls;
- Serious injury, blow to the head;
- Vascular thrombosis;
- Embolism.
In women, a stroke can occur during pregnancy, which occurs with pathologies, disruptions in the hormonal system, and also after taking contraceptives that cause increased blood clotting with an increased likelihood of blood clots.
Stroke in young children can be caused by pathologies of vascular development, brain tumors, intoxication or vitamin deficiency.
Features of the rehabilitation period
The recovery of patients after a stroke can be compared to the development of a newborn child in the first months and years of life.
Acute hypoxia and death of brain cells leads to partial or complete loss of many body functions. The victim has to relearn everything that he could do previously.
To restore lost abilities, surviving brain cells require time and regular training to learn new functions.
First, the patient learns to coordinate movements, then sit and walk. At the last stage, the patient learns to move and care for himself independently. Control over the body's excretory system appears and improves.
Physical development is accompanied by the formation of social skills. Speech develops and pronunciation improves. A person masters the telephone, learns to use a spoon, household appliances, and settles into his apartment space.
For successful rehabilitation, the patient needs the support of loved ones and their confidence in a successful outcome. This attitude gives strength to the victim and strengthens the desire for recovery.
To increase the restoration effect, you can attract specialists. Correct and regular performance of a set of exercises under the supervision of a trained person will speed up the return of motor functions and body control. At each stage of training, new exercises are added for the harmonious development of lost abilities.
Drug support is undergoing changes. Treatment is adjusted by a neurologist and depends on the progress and speed of recovery. Taking into account the specifics, each case requires an individual approach and prescription of medications.
about rehabilitation methods:
Paying attention to your health and the health of loved ones can reduce or completely eliminate the risk of developing such a serious complication as a stroke.
Symptoms, complications
Recognizing a stroke in a timely manner is the most important task for the victim’s relatives and medical workers. The speed and correctness of care are the determining factor in the future prognosis and the likelihood of complications. Therefore, it is important to know exactly what signs may indicate a circulatory disorder, as well as how dangerous the possible consequences are.
Symptoms
It is not so difficult to distinguish a stroke from the manifestations of various pathologies. However, it is worth considering that the symptoms completely depend on which side the circulatory failure occurred.
Among the main symptoms:
- Dizziness, headache;
- Problems with coordination, changes in gait;
- Confusion or loss of consciousness;
- Failure of visual, speech and hearing function;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Weakness throughout the body;
- Numbness of the limbs or some areas of the skin;
- Increased sensitivity to light or noise.
In children, a stroke is manifested by constant anxiety, tearfulness, sleep disturbance, muscle tension in the back of the head, failure of swallowing reflexes, convulsions, the inability to raise two arms at once and a distorted smile. Often, parents of children confuse a stroke with other problems, which is why they do not immediately call an ambulance.
Complications
If treatment is incorrect or delayed, there is a high probability of complications. But even with quick and correct therapy, there is a risk of serious consequences. It is for this reason that the patient needs to approach the rehabilitation process very responsibly.
Possible consequences:
- Coma – it can last several days or months. Most often it occurs with a hemorrhagic type of stroke.
- Paralysis – when parts of the patient’s body lose physical functionality. If the stroke affected the left side of the brain, then paralysis will be reflected in the right. Also, when hemorrhage occurs on the right, paralysis appears on the left.
- Brain swelling – it increases the risk of developing coma, as well as disruption of the functioning of certain parts of the brain.
- Motor disorders - the patient experiences a change in gait, constant loss of coordination, weakening of muscles, as well as prolonged muscle spasm.
- Aphasia – the victim loses the ability to fully speak, understand speech or write text. Appears after a stroke in most patients.
There is also a high risk of another stroke. It can only be avoided with complex treatment combined with full rehabilitation.
Prevention of contractures, bedsores and pulmonary congestion
Contracture is a pathological condition in which a person’s joints do not work, an arm or leg cannot bend due to muscle disease, tightening of the skin and tendons. Cerebral contractures occur due to damage to the brain. The patient feels pain in the back, shoulders, muscles, joints. We must not forget about the prevention of bedsores and pneumonia due to the patient’s immobility.
In the absence of contraindications, after mandatory consultation with a doctor and with his permission, the victim must do passive exercises from 1-2 days after the stroke.
This means that the patient, independently or with the help of others, takes a certain position. For those who have suffered a stroke, physical activity is necessary. After feeling better, passive gymnastics is changed to more complex exercises, and physiotherapy is included in the course of treatment.
Local application of magnetic therapy is possible for the rehabilitation of muscle tissue and tendons. If indicated, muscle spasms are treated with dry heat, this promotes blood flow and vasodilation.
It is possible to use electrical stimulation - one of the types of physiotherapy, during which an effect is exerted on nerve and muscle fibers.
First aid, diagnostics
Minimal treatment for a cerebral stroke should begin immediately after its signs appear.
First aid
If a person has a stroke, he will need to quickly provide first aid. Without it, the risk of death will be significantly higher. First you need to urgently call an ambulance, and then perform a series of actions:
- Place the victim on his back with his head slightly elevated using a pillow or other soft object.
- In the absence of consciousness, the patient's head should be turned to the side, and his tongue should also be extended.
- Unfasten the belt and buttons on clothing to provide the person with a sufficient amount of air.
- Warm the victim's legs with a heating pad or a basin of hot water so that the blood moves away from the brain.
- If necessary, give the person medications to lower blood pressure or others appropriate to his illness.
It is important to remember that the patient should not be lifted, fed or given water. It is also forbidden to give him vasodilators, because the need to take them can only be determined by doctors.
Source: https://NarkoPro.ru/preparaty/insult-posledstviya-skolko-zhivut.html
Types of strokes
- Hemorrhagic. The most severe form of stroke. It is caused by a rupture of a vessel and is accompanied by hemorrhage in the brain tissue. The most common cause is high blood pressure. When it occurs, the victim loses consciousness and cannot talk about other symptoms because he is in a coma. In this case, you need to urgently seek medical help, describing the symptoms in detail. Teams specializing in transporting stroke patients are dispatched to such calls. In this case, before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to measure the victim’s blood pressure and try to give medications to lower it. Patients with signs of stroke must be taken to intensive care units for acute treatment in a hospital.
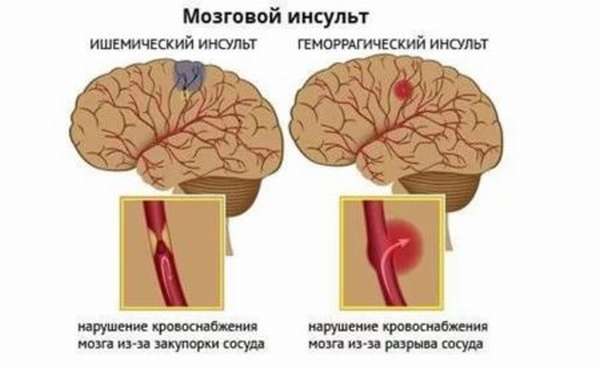
- Ischemic. A less severe form, less often leading to death. But it is accompanied by a high risk of complete paralysis. The main cause of ischemia is atherosclerosis, in which there is a gradual deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels in the brain. Over time, the size of the deposits increases, which can lead to complete closure of the lumen of the vessel and blockage of blood flow. A common cause is blockage of a vessel by a blood clot or cholesterol plaque that breaks off in other arteries and travels through the bloodstream into the vessels of the brain. The development of ischemia is accompanied by severe circulatory disorders and lack of oxygen. Hypoxia causes the death of nerve cells and the death of brain tissue. Depending on the size of the blocked vessel, the lesion can be of different sizes. The extent of injury determines the severity of symptoms and consequences for the victim.
Video with the first signs of a stroke:
Types and classifications of strokes
Stroke can be divided into several main types encountered in medical practice. Each of them has different properties. The disease is divided into:
- ischemic;
- extensive;
- spinal;
- hemorrhagic;
- lacunar;
- spicy;
- repeated;
- microstroke.
The most common form is ischemic stroke. According to statistics, 80% of attacks are ischemic. Its second name is cerebral infarction. This happens due to a disruption in the blood supply to brain cells. The causes are considered to be all sorts of blockages and narrowing of blood vessels. A modification of a cerebral stroke is a lacunar stroke. It occurs due to limited damage to the small arteries that connect the large arteries.
The initial period of formation of the disease is characterized by an acute stroke. It generally lasts for about 21 days, during which time brain cells are slowly destroyed. It is most intense during the first six hours. After a few days, brain cells undergo necrosis, and initial focal symptoms of the disease appear.
The most dangerous of all types of strokes are extensive, hemorrhagic and recurrent. When one of them appears, there is a high probability of death for the patient. This happens because the reasons for their occurrence are quite serious.
In a hemorrhagic stroke, the basis is the formation of severe hematomas in the brain, which subsequently forms an area of necrosis.
A major stroke is characterized by mass and frequency. Its result is either death or long-term loss of ability to work and speech.
Risk factors for stroke
For most, a stroke means the end of a full life and guaranteed paralysis, and many people would rather die than survive it. The opinion of modern medicine is different.
Doctors have a clear conviction that it is quite possible to avoid a brain catastrophe, and with the right and comprehensive approach, reduce the severity of the consequences of a stroke. And sometimes it can completely restore the functionality of the body and return the patient to a full life.

The main thing a person should strive for is the elimination and reduction of risk factors for the disease. A common cause of strokes is hypertension. Its danger is that in recent years the age of the disease has been rapidly decreasing. Quite often, very young people experience a persistent increase in blood pressure. This leads to a shift in the risk of stroke closer to the age of forty.
Hypertension can be asymptomatic for a long time. A person in such a situation lives in a state of constant risk. Lack of proper attention to health and adequate treatment increases the problem, which increases the risk of complications every year. Reducing blood pressure in a hypertensive patient by even 10 mm reduces the danger by 30%.
Those at increased risk of getting sick include heavy smokers, alcohol drinkers and people exposed to frequent stress. Various stressful situations lead to the development of hypertension, and bad habits increase blood pressure, which increases the risk of stroke during a hypertensive crisis. Changes in weather conditions or physical fatigue can trigger risk factors.
Obesity, high blood cholesterol and diabetes mellitus increase the risk. Such factors can and should be eliminated to reduce the risk of complications. A balanced diet and monitoring blood glucose and cholesterol levels will prevent circulatory disorders in the brain tissue.
Unavoidable risk factors include a person’s age. Every year the risk of stroke increases.
How many strokes can a person suffer?
The number of strokes suffered depends on their severity. Statistics show that few patients managed to recover from a second attack, not to mention subsequent ones. If there was a mini-stroke, then the consequences after a second blow will not be fatal. But over time, a major stroke is possible.
Can a patient have several strokes?
A person can suffer no more than 2-3 strokes, and only if the first one refers to episodes with the prefix “micro”. If you ignore the doctor’s recommendations, even the 2nd attack can be fatal.
A stroke is an acute circulatory disorder in the brain. The main reason is blockage of blood vessels and bleeding in the brain. Most often, attacks occur in men who are over 60; in women, the age limit is higher - over 75 years.
Causes of attacks:
- circulatory disorders in blood vessels;
- blockage of them with embolus - clots of fat-like substances;
- vasoconstriction;
- thrombosis – formation of blood clots;
- cerebral hemorrhage.
Thrombosis often occurs after operations in patients suffering from pressure changes or leading a sedentary lifestyle. Women who use oral contraceptives are also at risk.
The most dangerous types of strokes:
- Extensive. Often leads to loss of mobility and speech impairment.
- Hemorrhagic. It occurs due to severe hematomas in the brain when the area is affected by necrosis.
- Repeated. It is often provoked by hard work, extreme heat, and chronic lack of oxygen. A typical example is working at a dacha in the summer.
When can you expect another stroke?
If sudden changes in pressure during the first stroke pose a health threat, but are not fatal, then subsequent surges can become fatal. The first attack can only provoke a strong increase in pressure, but to give impetus to subsequent ones, even a slight fluctuation in the numbers on the tonometer is often enough.
It is important to know that:
- According to statistics, every 3rd case of stroke is a recurrent one.
- Patients over 45 years of age are 15 times more likely to have a recurrent stroke.
- The second and, especially, the third blow in 75% of cases ends in death.
- Life expectancy after repeated attacks is from 2 to 3 years.
A high risk of relapse persists for the first six months; in such cases, a second attack will be fatal or lead to complete paralysis. How long such a patient will live largely depends on the treatment, rehabilitation conditions and the care of relatives. Therefore, it is important to constantly monitor the patient’s condition.
Of particular danger are:
- Atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the lumens in the blood vessels.
- Blood clots that form in the heart valves. Getting into small vessels, it causes immediate blockage.
- Lack of oxygen can also cause a repeat attack, which, in turn, is provoked by:
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- violation of proper nutrition.
- overwork, stress.
Can there be different types of strokes?
From the moment of the attack and in the subsequent minutes after, about 2 million brain cells die, which results in speech impairment and immobility of the patient.
Stroke is also divided into 2 types:
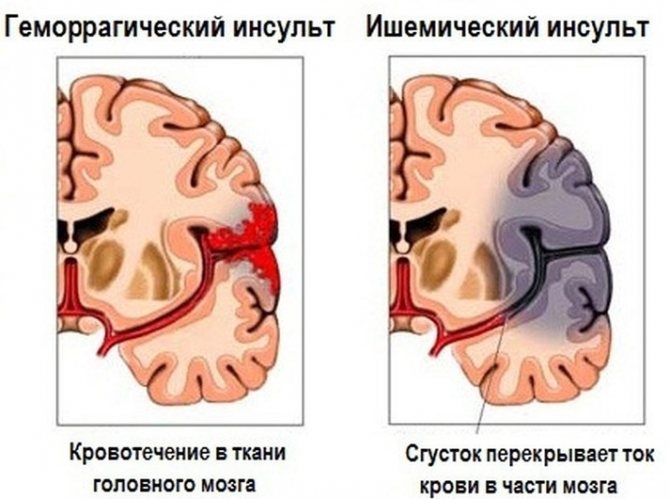
- Hemorrhagic. The cause is a rupture of a cerebral vessel and hemorrhage into the tissue. Brain cells begin to die.
- Ischemic. It is called an analogue of myocardial infarction, only the processes occur not in the heart, but in the brain. A blood clot or plaque breaks off and clogs a vessel, the blood flow is blocked, and brain tissue dies.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke:
- red face;
- a sharp increase in pressure;
- muscle cramps;
- disturbance of consciousness and breathing;
- wandering gaze;
- urinary incontinence;
- blurred vision;
- poor coordination.
The more symptoms there are, the worse the prognosis promises to be. If the patient manages to survive, then the neurological disorders will be very strong; hearing, vision, mobility, and clarity of consciousness may not return. After the third attack, these changes will be irreversible.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KKuHs6jF4ZY
Symptoms of ischemic stroke:
- numbness, tingling of the skin in the face, arms and legs;
- severe morning headaches;
- general weakness;
- spots before the eyes;
- difficulty speaking;
- dizziness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- fainting;
- attacks of heart pain.
Only 1-2 symptoms from the list may appear, but they will become more pronounced. Manifestations depend on the size of the burst vessel.
Patients who have had a stroke remain susceptible to developing blood clots.
Very often, a recurrent stroke occurs in people suffering from hypertension, arrhythmia, and diabetes. The risk increases significantly if a person does not consider himself sick and ignores the doctor’s recommendations. Competent stroke prevention can eliminate risk factors.
To avoid recurrent strokes, you need to:
- undergo periodic examinations;
- control blood pressure;
- follow a daily routine and diet;
- adhere to moderate loads;
- do therapeutic exercises;
- take vitamins, antiatherosclerotic and antihypertensive drugs, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents prescribed by your doctor;
- do physiotherapeutic procedures;
- eat more potassium, fresh fruits and vegetables, they help reduce the risk of stroke;
- put less salt in food;
- include fats from the Omega-3 fatty acid group in the menu: fish oil, flaxseed oil, flax seeds, soybean, olive, rapeseed oil.
What are the consequences of subsequent attacks?
One of the most common and characteristic problems faced by stroke patients is impaired ability to move. Many people lose muscle sensation on one side of the body.
Other unpleasant consequences:
- Confusion, poor thinking.
- Memory failures.
- Bad speech.
- Fecal and urinary incontinence in bedridden patients.
- Weakening of facial muscles, problems with swallowing.
- Coma is a disease of the nervous system due to periodic circulatory disorders.
- Swelling of the arms, legs and brain can occur at different times and simultaneously. The reason is weak functioning of the heart and blood vessels. A surge in intracranial pressure may indicate cerebral edema.
- Paralysis. Complete or partial loss of ability to move.
In 65% of cases, after the third and subsequent blows, patients fall into a coma, from which they rarely emerge.
Risk factors and prognosis
If the stroke passes without particularly unpleasant consequences for the patient, this does not mean that the body is not at risk of receiving another blow. The mechanism of a stroke is the blockage of cerebral vessels by blood clots, and the impetus for it can be not only a surge in pressure or a spasm of blood vessels.
Risk factors:
- nervous tension;
- binge eating;
- strong physical activity;
- mental overstrain, which is perceived as stress and requires a strong flow of oxygen to the brain.
People who have concomitant diseases such as:
- Heart disease.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
The impetus for a recurrent stroke can be a passion for tobacco or alcohol, or changes in weather conditions.
In 9 out of 10 cases, an ischemic stroke is recorded, but a higher mortality rate is observed in hemorrhagic strokes.
If we talk about the statistics of strokes, then they cannot be called particularly comforting. About 40% of patients who managed to recover from an attack live no more than a year, and another half of the survivors are dependent disabled people. Only 25% of patients manage to recover more or less fully.
Facts verified by practice:
- If you do not adhere to prevention, a secondary attack has a very dismal prognosis.
- The risk of a second attack during the first year is 15%, and during the first 5 years – 40%.
- Only 35% of hypertensive patients manage to recover from a hemorrhagic stroke; recovery is much more difficult.
The only way to protect yourself from another stroke is to lead a healthy lifestyle. The scheme is simple: give up bad habits, follow a sleep and rest schedule, and react less violently in stressful situations. And be sure to adhere to the treatment prescribed by the doctor, and the correct selection of medications will help keep your blood pressure normal and stop the attack in time.
Source: https://serdce.biz/zabolevaniya/ibs/insulty/skolko-insultov-mozhet-perenesti-chelovek.html
Treatment and rehabilitation
According to accepted standards, after a patient is admitted to the neurological department, in addition to complex drug therapy, the necessary care and rehabilitation, which begins in the acute period, is of great importance. Starting therapy within the first 90 minutes increases the chances of success. A longer period reduces the effectiveness of therapy. The severity and extent of damage to brain cells determines how long victims are able to live.

Rehabilitation is a set of measures aimed at eliminating existing defects in a patient or adapting the patient to existing disorders. Neurorehabilitation is a powerful factor in the prevention of recurrent stroke.
Regular training, movement, and performing the necessary tasks are highly likely to prevent recurrent acute circulatory disorders and increase life expectancy after a stroke.
Rehabilitation in the acute period and in the first six months of treatment is accompanied by the greatest effectiveness. Social rehabilitation is also important for the patient’s recovery, including the ability to do without the help of loved ones and return to work capacity. In some cases, the consequences of a stroke are quickly eliminated, and after some time the victim is able to return to normal life.
In case of extensive lesions and severe stroke, rehabilitation is slow. Long-term and regular exercise therapy and exercises to normalize speech will increase the chances of success. Particular perseverance should be shown in the first months with a gradual increase in the intensity of classes.
The necessary treatment and a set of rehabilitation procedures are prescribed by a neurologist. After discharge, you should regularly follow the instructions at home. Rehabilitation in specialized centers can bring considerable benefits, where the patient will receive a set of measures for intensive recovery. Future life after a stroke depends on the quality of care provided. How many years people live after a stroke is determined by the completeness of restoration of lost abilities.
The complex of rehabilitation measures includes:
- physiotherapy,
- massage,
- classes with a speech therapist,
- walking training.

Place special emphasis on restoring those movements that the patient cannot achieve. An important role is played by the patient’s psychological attitude and the desire for a speedy recovery. Depression and lack of faith in the future delay improvements indefinitely. Relatives should strive to support the patient and encourage him to be active.
Elderly patients are the most difficult to rehabilitate.
It is difficult to say how long older people live after a stroke. Most often, after 80 years, it is impossible to restore the ability to move; the victim is often only able to lie down. This situation is characterized by the most unfavorable prognosis. Old age and immobility accelerate the decline of other vital functions.
How to avoid repeated attacks - a list of recommendations
Prevention of strokes can be carried out with medications and lifestyle changes. The first recommendation the doctor gives is to quit smoking. This significantly reduces the risk of ischemic stroke. There is evidence that people who abstain from smoking for five years have the same risk of developing a stroke as those who have never smoked.
Regarding alcohol consumption, it is known that small doses of alcohol (comparable to a bottle of beer) reduce blood viscosity and blood cholesterol levels. Thus, moderate doses of alcohol may reduce the likelihood of a first stroke. As for repeated ones, there is no such data, so it is better to abstain completely from drinking alcoholic beverages.
Patients after a stroke are required to undergo moderate physical activity to maintain optimal body weight and reduce blood cholesterol levels. After a stroke, for most patients there is no talk of intense physical exercise. But walks in the fresh air are shown, as is a complex of physical therapy for patients with limited movement.
It is also important to monitor your diet to prevent obesity, atherosclerosis, and decreased glucose tolerance.
The doctor certainly recommends taking a number of medications, including those that prevent the formation of blood clots and regulate blood pressure. An increase in systolic blood pressure of only 12 mmHg. Art., and diastolic blood pressure by 5 mm Hg. Art. increases the risk of stroke by more than 30%.
Repeated stroke
For the first six months after the first episode, the risk of a second stroke remains high. Most often, a repeated case becomes the last or leads to paralysis. Only a small percentage of women and men are able to survive it and recover from a second stroke. How long a person who has suffered a relapse of the disease will live depends on the level of drug therapy and rehabilitation measures. This situation requires close attention to the condition of the victim to prevent a third episode and increase life expectancy.
How many strokes a person can suffer depends on their severity. Few people manage to survive after another, not to mention subsequent ones. Micro-strokes occur quite often. In such cases, cell damage is minimal, and the person is able to recover quickly. Accordingly, such injuries, after repetition, do not lead to death as their number increases. However, changes in the brain persist and accumulate, and over time the risk of major stroke and death increases.

How to live after a brain stroke: can you drink coffee and non-alcoholic beer?
Stroke is a disaster that can strike at any age. Increasingly, it is faced not only by the elderly, but also by people under forty who have many years of life ahead of them. Life after a stroke is a completely new and difficult experience for a person. In this article we will tell you what to do after a stroke, we will analyze the possibilities and limitations.
How to live a full life after a stroke?
Life doesn't end after a stroke. It can be almost full-fledged, filled with work, travel and entertainment. But this depends on many factors: the severity of the blow, the patient’s condition after the stroke, his mood, concomitant diseases, and proper rehabilitation.
The faster medical assistance is provided, the easier the consequences. It is most effective in the first 3–5 hours. If you notice signs of a stroke in yourself or your loved ones, call an ambulance immediately.
Complete extraction is not always possible. But the patient can adapt and become independent.
A prerequisite for recovery is long-term rehabilitation. Doctors recommend starting it on the first day - the patient needs to move, try to sit down. Recovery continues both in the hospital and at home.
For people with minor injuries, it is enough to endure some restrictions during this period: do not smoke, eat right, and follow all the doctor’s prescriptions. Patients with more severe injuries may permanently lose some function, but rehabilitation will help them adapt to these changes.
Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes: which one is more dangerous?
Hemorrhagic stroke is accompanied by rupture of blood vessels in the brain. Because of this, hemorrhage and swelling of the organ occurs. This type is the most dangerous and difficult to restore. The person's condition is very serious. Hemorrhagic accounts for twenty percent of the total number of strokes. Most of the survivors become disabled.
The ischemic type is more common. When it occurs, blood vessels become clogged and blood circulation in any part of the brain is disrupted. Because of this, cells are destroyed and the patient's body functions are impaired.
Help and support from relatives is an important factor for recovery
Doctors emphasize that the support of relatives and friends is extremely important during the rehabilitation period. Households contribute to a quick recovery: they help with household chores and gymnastics. The patient benefits from communication to restore speech.
During this period, loved ones need to show sensitivity and attention, but at the same time, patience and perseverance. To fully recover, the patient must train skills and develop damaged parts of the body.
But often he only wants to lie down and does not understand why he needs to move. And those around him indulge him in this. Relatives should soberly assess his condition and not overdo it with care.
A person after a stroke, if he is able, is recommended to eat, walk to the toilet, and take care of himself. Then he will sooner return to a full life.
It is useful for the patient to discuss his condition with loved ones. This helps avoid depression after illness. To restore speech and memory, they talk to a person about the past, recall incidents from life, and look at photographs.
Depression after an illness
A sudden stroke is a blow not only to the body, but also to the psyche. Often patients and their relatives become depressed.
A person experiences despondency and anger because he has lost his usual skills, cannot work, support his family, or do what he loves. He becomes irritable and whiny, transmitting his mood to everyone around him.
This affects his relationship with his family. It is difficult for them to get used to the new situation and be patient.
Depression after a stroke is common, affecting up to half of all patients. It appears both due to the psychological consequences of the disease and due to brain damage.
During this time, it is important to remember that most problems are real, but temporary. The quality and speed of rehabilitation depends on the patient’s mood. The patient and his relatives are recommended to consult with a psychologist. In severe cases, the doctor refers the patient to a psychiatrist for treatment with antidepressants. Remember that there is nothing wrong with this. Mental health is just as important as physical health.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
The quality and length of life depend on several factors:
- Danger of recurrent hemorrhage. A second blow reduces life expectancy to 2–3 years.
- Type of impact. With the hemorrhagic type, the likelihood of death is higher
- Extent of damage: with large damage, the lifespan is reduced.
- Developing complications lead to the formation of other symptoms that worsen the quality of life.
- General health.
- Presence of paralysis: they contribute to the formation of blood clots, increasing the risk of another stroke.
- Patient safety. Due to lack of coordination and weakness, he may get injured.
Lifestyle after a stroke
In order to recover as much as possible, the patient needs to change his lifestyle. The first is the mandatory and regular use of all medications prescribed by the doctor.
Regular physical activity is very important.
In addition to special gymnastics, it is useful for the patient to engage in walking and moderate activity every day - playing with children or grandchildren, pets, cleaning, gardening, riding public transport.
Sometimes light sports are recommended: patients go to the pool or do yoga. If there are no problems with coordination, cycling is possible. Even if a person moves in a wheelchair, he can exercise with dumbbells and do special exercises.
To protect yourself from a second blow, you need to eliminate risk factors. This:
- excess weight;
- passive lifestyle;
- smoking and alcohol;
- stress;
- high pressure.
Is it possible to smoke after a stroke? It is forbidden. Old habits will have to be abandoned. Smoking after a stroke is strictly contraindicated, as it increases the risk of blood clots.
Recovery period
The recovery period lasts on average up to two years after the impact. It is divided into early and late - up to 6 months and up to several years. It begins in the first days after a stroke, when the patient is in the hospital. Then he is transferred to the rehabilitation department. In the early period, body functions are restored in the following ways:
- medicines;
- kinesiotherapy;
- massage;
- psychotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- gymnastics: yoga, swimming.
First, the patient re-learns to control the body and make simple movements - get up and sit down. Then occupational therapy is involved: simple everyday skills are restored. To work on speech, they work with a speech therapist.
To correctly determine the rehabilitation program, you need to talk with your doctor about the goal. With hard work, after 6 months the patient can return to work and hobbies.
Life expectancy after stroke
Life expectancy for 31% of those who suffer an ischemic stroke is more than five years. For hemorrhoids, this figure is 24%.
Survival rates decrease with age. Young patients are more likely to live longer if the problem does not recur. Up to 45 years of age, the number of deaths after an impact does not exceed 25% of all patients.
Healthy approach to nutrition
In the period after the illness, it is important to prevent the formation of blood clots. Therefore, doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle and paying attention to nutrition: it is necessary to reduce the content of fat and cholesterol in the diet. Include more of these foods in your diet:
- fruits and vegetables;
- cereals;
- lean fish and meat;
- dairy products.
Excluded from the diet:
- fried foods;
- red meat;
- confectionery;
- food with palm and coconut oil;
- pickles;
- energy.
During the early recovery period, the patient has difficulty chewing and swallowing food. Let the food be cut into small pieces. DO NOT cook anything hard or sticky.
Returning to work
Patients ask the question: “When can I return to work?” If a person has undergone rehabilitation and feels well, then he is sent to a medical labor commission. Doctors check on it:
- restoration of mental abilities;
- mental condition;
- degree of impairment of speech and vision functions;
- muscle tone;
- cardiovascular system;
- coordination of movements.
If the commission sees that the consequences are minimal, it will issue a permit. The employer will be obliged to provide a position that does not conflict with the employee’s health condition. When working after a stroke you should avoid:
- intense physical and mental stress;
- noisy rooms;
- interactions with toxic substances;
- prolonged sitting in one position.
Even if returning to your old job is impossible, there are several options for returning to work:
- freelancing;
- distant work;
- half-holiday;
- work according to an individual schedule.
Doctors' experience shows that some patients return to work even after several strokes.
Driving after a stroke
Is it possible to drive a car after a stroke? This issue is resolved by the attending physician.
You can return to driving a car no earlier than three months later, if the damage was minimal. Patients experience difficulty driving due to poor coordination and vision.
Therefore, driving until fully recovered is dangerous for the driver and passengers. To be sure that a person is ready to return to the wheel, a special test is carried out in the presence of an instructor.
People whose profession involves driving are worried about whether they can work as a driver after a stroke. This should be determined by a special commission. Unfortunately, most often she recommends changing your profession.
Travel and tanning
Illness does not mean a complete refusal to travel. Often relatives seek to take their loved ones to a sanatorium for rehabilitation. Is it possible to go to the sea and sunbathe after a stroke? Yes, if you are careful. You can travel south and sunbathe after going through the early recovery period. Here are the main rules:
- control the pressure level;
- wear a hat;
- do not go outside between 12:00 and 16:00;
- watch how much liquid you consume;
- do not go out into the open sun.
Flights
It is not always clear whether a stroke will prevent you from going on vacation. For minor injuries, you can fly on an airplane two months after consulting a doctor.
To make your flight easier, take all the necessary medications and a pillow into the cabin to find a comfortable position. Wear compression garments and get up periodically to stretch.
Relationships and sex
Sex and love relationships are part of the fulfilling life that patients strive for. Doctors recommend resuming intimacy after three months if you feel well. If your blood pressure has not yet returned to normal, consult your doctor. At first, choose poses with the least physical stress.
Bath and sauna
Bath lovers are wondering whether it is possible to take a steam bath after a stroke. This is decided by a neurologist.
During the recovery period, he strictly limits the period of stay in the steam room. When used correctly, a bathhouse can even be beneficial. It helps in rehabilitation: it relaxes muscles and improves blood circulation.
Alcohol during recovery
Drinking alcohol is not recommended. Sometimes it is allowed to use it no more than three times a month in small doses:
- no more than 50 grams of strong;
- 150 grams of wine;
- 300 ml beer.
Is it possible to drink non-alcoholic beer after a stroke? Yes, but not much, since carbonated drinks are also not recommended. This applies to kvass and lemonades.
Coffee during rehabilitation
During the recovery period, coffee is excluded from the diet. It does not combine well with medications and procedures, raises blood pressure and excites the nervous system.
The drink is returned to use gradually under the supervision of a doctor.
Refusal of medications
Sometimes, when health improves, a person stops taking medications. Doctors advise not to do this. The consequences of hemorrhage are serious. Life after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is not immediately possible without medications.
The tablets are needed to prevent the damage from spreading and to prevent another attack. So, under no circumstances stop taking the pills without your doctor's instructions.
Life statistics after a stroke
Secondary stroke occurs in 10-15% of people during the year. In the first 5 years it occurs in 25% of women and 45% of men. This is why rehabilitation is so important.
About 12 million strokes are recorded worldwide every year. Half of them end in death. In Russia, 450 thousand people encounter it.
75% of patients under forty and 60% of people over 50 survive and are rehabilitated.
So, a person after a stroke can live a full life or restore many functions. This requires careful and long rehabilitation. If you follow all the doctors' recommendations and take medications, the patient has a chance of returning to work and social activities. But he will have to reconsider his lifestyle and make it healthier.
Causes and symptoms of stroke
According to statistics, an attack is most often observed in men over 60 years of age, and in women over 75. The main causes of an attack include:
- vascular circulatory disorders;
- blockage of blood vessels with embolus (clumps of fat-like substances);
- degenerative modification of vessel walls (narrowing in areas);
- thrombosis (formation of blood clots);
- cerebral hemorrhage.
Thrombosis most often begins after surgery. It is usually observed in people who are overweight, those who smoke and drink alcohol, and those who take drugs. An attack due to a hemorrhage in the head can occur in any person, regardless of age. In general, it appears in people suffering from sudden changes in blood pressure, leading a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, as well as in women who use oral contraceptives.
Symptoms of a stroke can be determined by a doctor or emergency medical technician. The main signs of the disease can be divided into two types: general cerebral and focal.
General cerebral symptoms include most abnormalities associated with traumatic brain injury. These may include incoordination, dizziness, temporary deafness or severe agitation. Focal symptoms include all the initial signs: unbalanced speech, poor coordination of movements, temporary loss of vision, muscle tension and distortion of the left side of the face due to the inability to contract muscles.
At the first general symptoms, a sick person should be immediately taken to the intensive care unit or call an ambulance. To determine whether a stroke is present, a number of tests are performed, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), blood tests, and an electroencephalogram (EEG). Only after this the doctor can accurately diagnose the patient.
Statistics on strokes: how long do people live with damage to the right side and other consequences?
A stroke for a person is a powerful blow to the entire body. It is impossible to say exactly how long the patient will live, since everything depends on rehabilitation and how damaged the brain is.
Each patient should be attentive to the recovery process for improved life expectancy.
The article examines the statistics of life expectancy after a stroke depending on the nature of the lesion, how you can increase the chances of recovery and other issues.
Statistics
The first month is the most dangerous, since during this period there is a high probability of death of the patient (read about periods of stroke here). You can recover from an ischemic stroke much faster than from a hemorrhagic stroke. Positive dynamics are possible only if you follow the doctor’s recommendations.
After a hemorrhagic stroke, one third of patients die within a year.
Important! According to statistics, the average life expectancy after a stroke is from five to ten years, depending on complications.
Lifespan
It is impossible to say exactly how long a person will live after a stroke.
However, when the disease recurs, rehabilitation is more difficult (read about how many strokes a person can suffer in this material).
According to statistics, life expectancy reaches more than ten years. The percentage of pathology and mortality is quite high. In the first month, 30 percent of patients die, and within a year, about half die.
A new attack occurs in 10 percent of patients. In case of relapse, death occurs within six months in 70 percent.
For illness on the left side
There is no exact answer to how long you can live, but survival will depend on:
- Pathologists.
- Localizations.
- Patient's age.
Up to 80 percent of patients survive a year after a stroke.
Right side
After a stroke on the right side, 70-80 percent of patients survive. A second stroke is statistically often the cause of death. About 50 percent of people can live 5-7 years.
Dependence on complications and consequences
The ability to regain skills depends on brain damage. The forecast will depend on:
- Severity of damage.
- Volume of damage.
- Social factors.
- The patient's motivation to work on himself.
After a stroke, about 8 percent return to work. Half of the patients have limited ability to work and require constant assistance and care.
Attention! With extensive hemorrhage and cerebral edema, the prognosis will be disappointing. In most cases, everything ends in death.
If the body is paralyzed
In case of acute disturbance of left-sided cerebral circulation, speech suffers. More attention is paid to this problem than with other manifestations of the disease. Patients with disorders of the left side often end up in the hospital and live no more than five to seven years.
The right side is responsible for movement, so there is paralysis of the left limbs. The death of neurons leads to the fact that the patient does not remember past information and is lost in time and space. In this case, life expectancy depends on care.
For dementia
In severe strokes, consciousness may be absent. The disturbances will progress, and cerebral edema is fixed.
Most often, recovery in this case is almost impossible. Life expectancy depends on care, but on average it ranges from one to three years.
In a coma
If the patient is in a coma, the likelihood of further recovery is very low and he is unlikely to survive. Typically, such patients survive two weeks after the attack.
Find out more about the consequences of a stroke in this material.
How many attacks can you survive?
Important! According to statistics, a person can survive 4-5 strokes.
The recovery process with each will be more difficult than with the previous one.
More than 80 percent of the result can be achieved with proper care in the first six months. If the brain does not get rid of complications, then it will be almost impossible to recover.
For more information about how many strokes a person can suffer, read this material.
Statistics for seniors over 80
The prognosis for the older generation is disappointing. High risk of death. But still, how long do they live after a recurrence of the attack? The answer is below. If a recurrent stroke occurs, the average life expectancy is no more than seven days. The older the person, the less chance of recovery.
The chances of surviving a stroke in older people over 80 are minimal. It all depends on the overall picture of the disease. Some survive only six months after their first stroke.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.
What does the deadline depend on?
- Patient's age. A young body is more resilient and the younger the age, the faster the recovery process (read about why stroke affects children and people under 30 years of age in this material).
- Consequences of a stroke. Keeping a sick person in a supine position provokes bedsores, and an acute respiratory infection can turn into pneumonia.
- Proper organization of life. It is necessary to create a safe environment for the patient and prevent falls and injuries.
Older people's bones do not heal well and take longer to heal. - Healthy lifestyle. The patient should give up alcohol and fatty foods in order to speed up recovery (read about whether you can drink alcohol after an attack and whether a stroke occurs due to alcohol consumption). You need to eat more vegetables and fruits.
Video on the topic
A stroke is a sudden disruption in the circulatory system of the brain, which leads to damage to various parts of the brain that lose functionality.
Along with the blood, the supply of oxygen to the brain stops. This leads to disruption of cell nutrition.
The short answer to the question of how long people live after a stroke depends on the type of brain stroke, as well as how serious the consequences are - with ischemic, mortality in the first 72 hours is no more than 15%; for hemorrhagic – no more than 35%; the most dangerous is subarachnoid hemorrhage - survival rate in the first 72 hours is about 50%. Details are below.
Ischemic stroke and what are its consequences
The development of ischemic stroke is associated with thrombosis and blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, as a result of which cellular structures begin to become oxygen starved and slowly die. A patient with such pathological changes gradually loses a number of physical and intellectual skills.
Clinical signs of pathology may disappear within a few hours, and therefore the patient does not even visit a medical facility, and this is the main mistake, since the neurons are already dying, and the process will not stop on its own.
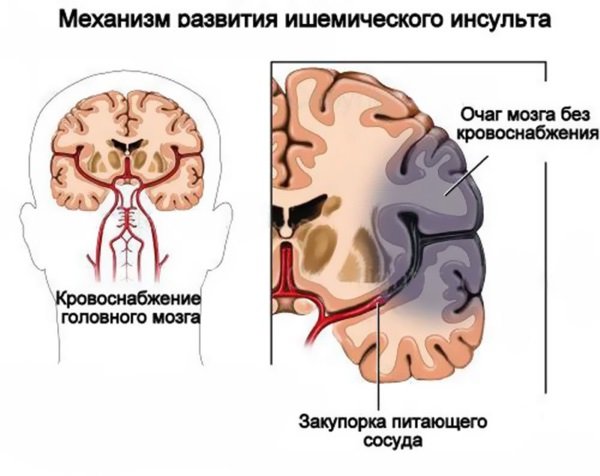
The result of lack of therapy can be:
- Partial loss of the ability to speak or see.
- Feeling of numbness in the upper extremities, loss of sensitivity in them.
- Paralysis.
- Partial memory loss.
- Impaired coordination of movements and fine motor skills.
- Urological pathologies.
- Mental disorders.

It is noteworthy that if a person has a left-sided ischemic stroke, in addition to death, there is a risk of developing such severe consequences as:
Interesting! The chances of survival in patients with ischemic stroke are quite high compared to those who are faced with a hemorrhagic form of the pathology. However, they must follow all the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation course.
Stroke and patient age
The high prevalence of the disease leads to many questions, in particular, many are interested in how long they live after a stroke. This largely depends on the age of the stroke patients. Previously, it was believed that the risk of cerebrovascular accidents was high only among people of mature age (approximately 50 years or more). But nowadays, stroke is registered in people of an earlier period. Of course, the speed of metabolic processes and recovery is higher at a younger age, but diagnosing the disease during this period is difficult, which affects the speed of care and further prognosis.
According to statistics, at the age of 25-45 years, in most cases, a hemorrhagic stroke develops, which develops as a result of a rupture of a cerebral vessel. In patients over 45 years of age, the most often diagnosed ischemic stroke, which occurs due to blockage or compression of blood vessels in the brain. This is largely due to the presence of concomitant pathology.
The risk of developing circulatory disorders increases significantly after 55 years of age, doubling every 10 years, so in 75% of cases, stroke develops in people over 65 years of age. It is worth noting that at this age there is also a high risk of relapse of the disease, which worsens prognosis and quality of life.
In older people, the pathology occurs in a severe form, causing many different complications, this may be due to:
- age-related changes in brain tissue;
- decrease in the speed of metabolic processes;
- the predominance of aging over reparative processes;
- persistent hypertension, difficult to treat;
- the presence of cardiovascular diseases;
- increased levels of cholesterol and other harmful substances, as well as other somatic pathologies.
Even an ischemic stroke, which does not develop as rapidly as a hemorrhagic one, occurs in an aggressive form in elderly people, which negatively affects the recovery process and increases the degree of disability.
Consequences of a stroke
The consequences of strokes are varied (ranging from paralysis of one muscle to death). But if we exclude fatal consequences, then some patients return to normal life or have partial restrictions on normal life activities. In this case, everything will depend on the body itself and its recovery. After returning to work, a person undergoes additional tests and is sent to a medical commission. Only after an examination can doctors determine a disability or prescribe medications.
Frequent consequences of the disease can be swelling of the legs and brain. They pass together or appear one at a time. Swelling of the legs can be attributed to the long-term results of a stroke. This is due to the weak activity of the human cardiovascular system. Swelling can last for several hours and spread evenly down the legs. Cerebral edema is characterized by an increase in intracranial pressure. It occurs due to impaired blood supply to the brain.
More serious consequences include paralysis. Characterized by incomplete or complete loss of motor activity. Everything will depend on the type of stroke and the degree of deterioration of the human body. When the conduction of nerve fibers is damaged, only partial paralysis of the affected part of the body occurs. Central paralysis, that is, excitation of the nerve fibers of the brain, is characterized by the non-independent action of the paralyzed part of the body. If the healthy hand performs an action, the paralyzed hand can repeat it.
The consequences can also include coma. Coma is a disease of the central nervous system due to repeated circulatory disorders. It can develop after an attack and periodic increases in temperature. Coma has 4 stages:
- stun;
- deep dream;
- loss of ocular reflex;
- loss of deep reflexes.
Coma can last from several hours to weeks or even months. Its duration depends on the stage, the condition of the body, and patient care.
Hemorrhagic stroke
The occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke is associated with more severe consequences and a crisis nature of the course, turning into an acute phase. All this is associated with rupture of vessel walls, aneurysms, lacunae or brain tumors.
In such a situation, the slightest delay in providing professional medical care will cause further disability, coma or death due to deep damage to brain tissue.

Consequences at 60 years of age, as well as at other ages, associated with hemorrhagic stroke may include:
- Paralysis.
- Blindness.
- Loss of ability to speak.
- Motor skills disorders.
- Pathologies of intellectual activity.
- Deviations in the psycho-emotional state.
- Necrotic tissue changes, infarction or cerebral edema.
Important! In most cases, even after rehabilitation measures, patients only partially regain physical skills, and older people most often do not survive.
Adverse factors affecting the prognosis
Through incidence analysis, doctors were able to identify factors that are associated with shorter survival. General unfavorable prognostic factors for cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage include:

Hypertension is one of the key risk factors for stroke.
- Floor. Life expectancy after a stroke is much higher in men than in women. For example, the 28-day survival rate for men is 22% and for women 28% (1). According to some data, young, middle-aged men live shorter lives: 5-year survival rates are 60%, 64.5%, respectively (2).
- Age. The younger the person is at the time the stroke develops, the better the prognosis. This is one of the reasons why men have better survival rates: they experience strokes at a younger age.
- Late medical care. From the moment the first symptoms appear until the start of hospital treatment, no more than 3-4.5 hours should pass.
- Complete loss of speech, pain sensitivity, eye reaction to external stimuli.
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Low hemoglobin level.
- The presence of unhealthy habits: overeating, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, tobacco, drug, and alcohol addiction.
- Relapse.
There are also specific unfavorable factors characteristic of certain forms of cerebrovascular accidents that worsen the prognosis.
| Ischemic stroke | Hemorrhagic stroke |
|
|
Statistics about life after a stroke
Statistics provide the following basic data:
- For strokes under 45 years of age, the mortality rate does not exceed 25%.
- When an attack occurs after 50 years, the death rate reaches 40%
At the same time, it also follows from the data that the most severe consequences are observed in the fairer sex, but the very fact of stroke development is more common in men.
As for the elderly category of citizens whose age exceeds 70 years, death is the result of a stroke in almost 80%. And it makes no sense to talk about the complete recovery of the survivors.
In Russia, mortality from ischemic stroke occurs in 67.8% of cases, and from hemorrhagic stroke - 11.5%. In turn, undifferentiated stroke accounts for 17.4%, and subarachnoid hemorrhage – 3.3%.
Things are different with what the statistics are after a mini-stroke. In this situation, death is so unlikely that it is not even included in the average data.

The survival of patients who are at risk due to any aggravating condition, for example:
- Hypertonic disease.
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular bed.
- Pathological damage to cerebral vessels.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, smoking and abuse of caffeine-containing drinks.
- High physical and emotional stress.
- The period of bearing a child.
- History of traumatic brain injury of any kind.
- Senile period of life.

To increase their life expectancy, these people need to visit health care facilities more often for diagnostic testing and treatment when needed.
As for how many strokes a person can experience, even statistics do not give a clear answer. There were cases when the patient had 3-4 or more attacks. And each time the consequences of this condition become more severe.
Stroke death statistics
Stroke ranks second in the sad list of diseases from which the most people die, with coronary heart disease leading here.
Every year, about 6 million people worldwide suffer from cerebrovascular accidents. In Russia, 450 thousand strokes are diagnosed annually, and four times more patients die from this cause than in North America.
- mortality from vascular accidents is higher in women - about 39%;
- in men, the mortality rate is from 25 to 29%;
- ischemic attacks of the brain are recorded much more often - in more than 80% of cases, the mortality rate from them is about 37%;
- With hemorrhagic strokes, mortality rates are higher - up to 82% of patients die.
How long a patient will live after a stroke largely depends on him and his environment. The patient must adhere to all the recommendations of the attending physician, and the task of loved ones is to surround the loved one with care and help him in rehabilitation after a serious illness.
Stroke is a serious illness. The causes of stroke and how it occurs is the topic of our article.
We will talk about the effectiveness of therapeutic exercises in stroke recovery in this material.
Prognosis for people over 80 years of age
Relatively speaking, 80 years for a person becomes the threshold during which survival rate after a stroke sharply decreases. In people aged 90 years, the death rate after a stroke reaches 70%, and half of this number of people first end up in a coma or develop cerebral edema.
In this age period, pathology often develops again, due to insufficiently high-quality preliminary therapy. But even if the patient is saved, he completely loses physical and intellectual skills, and his subsequent life is no more than a few years. This is due to the fact that such patients especially often suffer from infectious and inflammatory diseases and have a weakened immune system.
In many ways, how long people live after a particular stroke attack is directly influenced by the person himself, his motivation and the people around him. If you follow all the recommendations given by a specialist and with the support of loved ones, rehabilitation after an attack is quite possible, and life can be significantly extended.
A stroke is a difficult experience both for the person who survived the stroke and for his family. And even when the worst seems to be over, a person involuntarily thinks about the duration of his own life and looks for the answer to the question: how many years do they live after a stroke? After all, there is an opinion that even minor brain damage, such as a microstroke, shortens the patient’s life expectancy by years and nothing can be done about it. However, awareness of the reasons that provoked a stroke and adherence to the rules of a healthy lifestyle appropriate to the current situation are key points in increasing life expectancy.
Life after a stroke: mental state and recommendations
16.06.2018
A stroke takes you by surprise and makes adjustments to a person’s life. Often the patient has to learn to walk, talk again and adapt to changes in the body. Most people, when faced with the consequences of a stroke, feel helpless and wonder what their life will be like after a stroke.
How to live a full life with a stroke
Cerebrovascular diseases are changes in cerebral blood vessels and disruption of blood flow in the brain. The consequence of these diseases is stroke.
Stroke affects people differently. In 100% of cases, rehabilitation of the patient is required, regardless of the level of brain damage. It is important not to give up and begin rehabilitation as soon as possible. A complete cure is not always possible, but patience, help and support from loved ones can help you adapt and gain some independence.
With minor brain damage, the patient will have to give up bad habits and hard work, change the diet, but this will not significantly affect his life.
In case of severe injuries, patients face long and complex rehabilitation. In such cases, a person sometimes loses some skills and body functions. Even if a person cannot return to the previous level, then with the help of proper rehabilitation it is possible to adapt to changes in life.
Exercises for a stroke survivor
A person who has had a stroke should try to do the exercises on their own, because... his future life depends on it. Muscles and joints need movement to stay in shape. And mental exercises will help the brain recover faster.
Exercises for a person who has had a stroke:
- Train your facial muscles in front of the mirror: puff out your cheeks, push air from one cheek to the other, stretch out your tongue, show your teeth, smile, laugh, wrinkle your forehead.
- Flexion-extension, rotation of the limbs, clenching the hand into a fist, swinging the arms and legs. Be careful not to overtire the person.
- If a person used to love to sing, then try to sing with him. Some people can sing after a stroke even if they cannot speak because singing and speaking are controlled by different parts of the brain.
- Breathing exercises. Exhale air through closed lips or through a straw into the water. As your strength increases, you can try inflating balloons.
- Talk and discuss the news, ask for his opinion.
Rehabilitation
You need to start rehabilitation as soon as possible. The severity of stroke complications and each person's ability to recover varies greatly. People who participate in a targeted rehabilitation program do much better than people who don't. The recovery program is drawn up taking into account the specifics of the case, so it is impossible to talk about exact timing.
the goal of rehabilitation is to improve the patient's condition and prevent another stroke.
Rehabilitation includes:
- speech therapy: speech restoration program;
- physiotherapy: exercises to strengthen muscles and coordinate movement;
- occupational therapy: helps a person improve their ability to perform routine daily activities such as bathing, cooking, dressing, eating and reading;
- support from friends and family;
- proper nutrition.