- November 22, 2019
- Cardiology
- Shpakovskaya Ekaterina
Like any complex mechanism, the human heart has peculiar doors that ensure the correct flow of blood, that is, its flow in the only correct direction, blocking the veins and arteries at the right time. This is a very important mechanism of the human heart, which plays a decisive role in the timely regulation of blood flow, ensuring reliable and uninterrupted operation of an important organ, including in extreme situations, for example, with a dangerous increase in pressure. In the modern world, it is incredibly difficult for a person to protect himself from all kinds of stressful situations, so proper functioning of the heart is very important. There are quite a lot of such auxiliary valves in the human heart, for example, you can tell a lot about the aortic heart valve, the pulmonary valve, there is also a valve called the Eustachian valve... However, let's take a closer look at which valves are located between the atrium and ventricles of the heart.
There are four cavities in the human heart
The two cavities are like hallways in a residential building. These cavities “meet” and “receive” blood, which is transported through the vascular bed to the heart. These cavities are called atria.
Why are there two hallways? Because the heart is a house for two owners. Each owner has his own hallway and his own room. These two halves of the house do not communicate with each other in any way. Because they belong to different owners.
So, there are two hallways or two atria: right and left. This is where the blood that rushes to the heart from a long journey through the human body comes.
The right half receives blood, which has passed through the human body, washing all its organs. To the left is the blood that has traveled through the lungs.
Read the articles: “Structure of the human heart”, “How does the heart work?” and “Two circles of blood circulation.”
But blood completely filled two small hallways. Now she should be invited further into the room. Each owner has such a room - this is the left and right ventricle. And so that blood can get from the hallway into the room, there are holes in the walls separating these rooms.
Symptoms of heart disease
The symptoms of heart disease are quite varied. Moreover, many of the signs do not appear in the initial stages, since the organ is able to compensate for functional and pathological changes for a certain time.
One of the main problems of cardiology is late diagnosis of diseases. Often the patient consults a doctor when the disorders are already severe and practically untreatable. Therefore, doctors recommend that people over 40-45 years old undergo routine examinations annually, even if there are no obvious symptoms of heart disease. And if you have any of the ailments listed below, immediately contact a cardiologist.
Heartache
Heart pain is the main symptom of possible diseases. Most often it is a sign of developing coronary heart disease - angina or even myocardial infarction.
During a heart attack, the pain is different from normal:
- Vividly expressed.
- Does not go away from changing body position, going out into fresh air and other external factors.
- It is not relieved by nitroglycerin tablets (take 2-3 pieces with a 5-minute break).
With angina, the pain is characterized as pressing, and initially occurs only during physical exertion and stress (angina pectoris). As CHD develops, it can manifest itself at rest, for example at night.
We invite you to read How to decorate a Christmas tree: 17 ready-made decor ideas
Pain in the heart and sternum can also indicate the following problems:
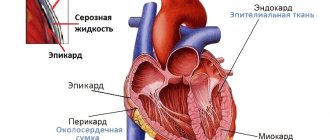
- Inflammatory processes in the outer (pericardium), middle (myocardium) and inner (endocardium) layer of muscle.
- Aneurysm (thinning of the vessel wall) of the aorta.
In addition, pain may occur for reasons unrelated to the heart:
- Radiculitis.
- Diseases of the costal cartilages, fractures and cracks in the ribs.
- Neuralgia.
- Lung diseases, including pneumonia.
One of the symptoms of heart disease is palpable palpitations. Tachycardia (a condition in which the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute in an adult) is often accompanied by an increase in blood pressure. Under certain conditions, such an acceleration of the rhythm is justified by external factors. Physiological tachycardia is a characteristic reaction to stress or active movements.
But if palpitations occur suddenly, you should definitely consult a cardiologist. Heart rhythm disturbances are accompanied by the following sensations:
- Lack of air, shortness of breath.
- Pulsation in temples.
- Dizziness.
- Darkening in the eyes.
In heart failure, coronary artery disease and other diseases, symptoms of circulatory disorders are often observed. They are due to the fact that the heart cannot cope with its functions and cannot pump blood in the required volume.
Characteristic symptoms of heart disease:
- Swelling of the legs, especially in the evening.
- Blueness or pallor of the skin.
- Fatigue with little physical activity, shortness of breath.
- Cold fingers and toes, inability to warm extremities.
- With insufficient blood circulation in the brain, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and loss of consciousness are observed.
In infants, changes in skin color, lethargy and drowsiness should be a reason for additional examination by a cardiologist, since the symptoms of circulatory disorders are signs of congenital heart defects.
Normal blood pressure in an adult should be 120/80 Hg. Art.
- The first number is the blood pressure on the vessel during systole, contraction of the heart muscle and ejection of blood into the artery.
- The second number is blood pressure during diastole, a relaxed heart.
Hypertension (arterial hypertension) is persistent high blood pressure, which is often isolated as a separate disease and has several stages. Moreover, if the readings do not exceed 140/90 Hg. Art., cardiologists diagnose “normal high” blood pressure.
Regardless of how exactly the indicators differ from the norm, hypertension affects the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system and can accelerate the development of diseases or cause dangerous conditions. Hypertension is quite common, affecting 50-60% of the adult population of the entire globe, and the older the person, the higher the risks.
Hypotension (low blood pressure) is a condition in which readings fall below 95/60 mmHg. Art. in women and 100/65 mm Hg. Art. in men. Hypotension does not affect the functioning of the heart as much as hypertension, but it still significantly affects a person’s well-being and can be a symptom of functional disorders of the organ or defects. With low blood pressure, a person suffers from the following ailments:
- Muscle weakness, lethargy.
- Drowsiness.
- Fainting conditions.
- Memory loss and irritability.
Heart disease can also present with other symptoms. Moreover, if a person associates the above with problems of the cardiovascular system, then these are often attributed to other diseases.
You need to pay attention to your heart health if you experience:
- Poor sleep, inability to fall asleep without a high pillow. This often indicates the development of heart failure.
- Attacks of dry cough, especially when lying down. At the same time, no other symptoms of acute respiratory infections (fever, runny nose, sore throat) are observed.
- Irritability, low resistance to stress, tearfulness.
- Increased temperature along with pain in the heart. May indicate the development of an inflammatory process in different layers of the heart muscle. It is especially dangerous in children after a sore throat, since it indicates rheumatic lesions that cause acquired valve defects.
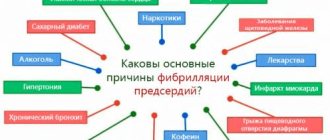
Heart disease is caused by pathological congenital or acquired changes in the structure of the myocardium, valves, and coronary arteries. Diseases can develop independently or be a complication of other problems in the body. For example, hypersecretion of adrenal hormones can cause degeneration of the heart muscle, and diabetes mellitus can increase the risk of developing myocardial infarction.
Coronary heart disease is the most common and one of the most dangerous diagnoses in cardiology. According to the World Health Organization for 2012, ischemic heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide.
The disease develops against the background of atherosclerosis - deposits of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Only in the case of coronary artery disease such changes occur in the coronary arteries - the vessels of the heart. As a result, the blood flow through them gradually slows down, the myocardium does not receive the necessary oxygen, and ischemia develops.
IHD is an incurable disease, but with timely diagnosis, stable remission can be achieved. The problem is that in the early stages, coronary artery disease does not manifest itself with any symptoms - the heart is able to compensate for the lack of blood flow up to a certain point and work as usual. Afterwards, when cholesterol plaques increase, heart pain, shortness of breath, fatigue and other symptoms occur.
Coronary heart disease can develop in any person, it is especially dangerous for people over 40-50 years old, therefore, upon reaching this age, it is recommended to undergo examinations with a cardiologist once a year. However, doctors identify some risk factors that accelerate the development of coronary artery disease:
- Smoking.
- Male gender. In women before menopause, atherosclerosis develops extremely rarely, since sex hormones protect blood vessels.
- Heredity.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Diet with a predominance of fats and simple carbohydrates.
- Overweight.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Diabetes.
Atrioventricular or leaflet valves
The openings between the atria (hallways) and the ventricles (rooms) were called atrioventricular openings. This compound word consists of two Latin words: atrio - atrium and ventriculum - ventricle. Everything is logical, isn't it?
Of course, these openings are equipped with doors. The doors installed in these openings are hinged and consist of more than one leaf. The door on the right half has three leaves. The door on the left half has only two leaves.
These doors are nothing more than two valves of the heart. Two valves that close and open the atrioventricular orifices, the openings between the atria and ventricles. Therefore, without thinking twice, they were called that - atrioventricular valves.
But then, having looked closely at them and studied their structure, we noticed that they consist of valves. Therefore, this pair of valves received a second name - leaf valves.
Mitral valve
They are called valves together. But each of the leaf valves received its own separate name. The left atrioventricular valve was called bicuspid (after all, it consists of two leaflets). Its Latin name is mitral, which simply means valve.
So, mitral valve and bicuspid valve are two names for the same valve. It is located on the left side of the heart and covers the opening between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Tricuspid valve
The owner of the right half of his heart also has a swing door between the hallway and the room, which consists of three leaves. Therefore, this valve was called tricuspid, which in Latin sounds like tricuspid.
Semilunar valves
But the rooms are filled with blood, which is ready to move forward. As soon as this happens, as soon as both ventricles are completely filled with blood, the folding doors immediately slam shut. Reverse traffic is blocked. And no matter how much the blood yearns to return back to the hallway, she fails. Why?
Because leaf valves only open in one direction. In the other direction, they are prevented from opening by strings stretched between the wall of each ventricle and each valve leaf. These dense strings are called chords.
Where does the blood go? She is offered another exit - into the large arteries leaving the heart. From the right half, blood can only enter the pulmonary artery, and from the left - into the aorta. Moving towards the arteries, the blood encounters another door-valves on its way. These are semilunar valves.
Why crescents? Probably because they are also folded. But you can’t call them folded. There will be confusion. Therefore, someone very attentive and to some extent romantic, having examined this pair of valves, discovered their resemblance to the halves of the moon. So a simple and beautiful name arose - semilunar valves.
Pulmonary and aortic valves
So, two openings lead from the ventricles of the heart into the arteries extending from it, which are covered by semilunar valves. But, as in the previous case, each of these valves has its own personal name.
All articles about blood and circulation
All articles about the heart
All articles about heart disease
The right valve that opens into the pulmonary artery is called the pulmonary valve or pulmonary valve.
The left one, opening into the aorta, is called aortic.
Both of these valves have three leaflets and open only towards the arteries. Blood that leaves the ventricles is unable to return, since the closed flaps of the semilunar valves do not allow it to pass through. They are designed in such a way that the blood itself, rushing in the opposite direction, closes them tightly.
Cardiac activity and nervous system
Cardiac activity is influenced by certain substances released by various organs into the blood. Adrenal hormone - adrenaline, like sympathetic nerves, increases the frequency and strength of heart contractions. Consequently, neurohumoral regulation ensures that the activity of the heart, and consequently the intensity of blood circulation, adapts to the needs of the body and environmental conditions.
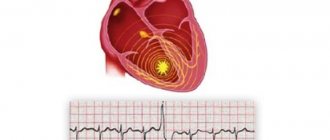
When the heart contracts, blood is ejected into the aorta and the pressure in the latter increases. The wave of increased pressure spreads through the arteries to the capillaries, causing wave-like vibrations of the artery walls. These rhythmic vibrations of the walls of arterial vessels caused by the work of the heart are called pulse.
The pulse can easily be felt in the arteries lying on the bone (radial, temporal, etc.); most often - on the radial artery. The pulse can be used to determine the frequency and strength of heart contractions, which in some cases can serve as a diagnostic sign. A healthy person has a rhythmic pulse. With heart disease, rhythm disturbances—arrhythmia—may occur.
The beating of the heart is ensured by the heart muscle - the myocardium. It contracts and relaxes under the influence of various factors, including the nervous system:
- The parasympathetic nervous system slows the heart rate.
- Sympathetic – increases the number of heart beats per minute.
Therefore, in some cases, disruptions in heart rhythm are associated not with structural disorders of the organ, but with diseases of the nervous system.
Another factor influencing cardiac activity is the production of hormones. The adrenal glands are considered one of the main organs of the endocrine system that affects myocardial contractions. It is here that the hormones norepinephrine and adrenaline are released, the presence of which in the blood can increase the heart rate.
For the proper functioning of the heart, the macroelements calcium, potassium and magnesium are also necessary, which maintain normal cardiac activity.
The brain has two regulatory structures - the vascular and respiratory centers, located at the level of the back of the head. In case of hypoxia, the amount of carbon dioxide in the body quickly increases, which leads to irritation.
Signals from the brain centers are delivered to the lungs, and shortness of breath (rapid breathing) occurs. In response to shortness of breath, the work of the heart increases. When the amount of carbon dioxide equalizes, signals from the respiratory and vascular centers stop.