Why do the vessels of the limbs hurt?
For normal brain function, it needs nutrition, which is provided through constant blood circulation.
For this purpose, numerous capillaries pass through the brain tissue. As a result of exposure to negative factors on the body, blood flow may be disrupted due to prolonged tissue contraction or spasms of the vascular walls. Capillaries or small arteries are primarily susceptible to vasospasm. As a result, blood flow through them is limited or completely stopped.
Oxygen starvation of brain cells leads to various disorders in the functioning of the human nervous system.
There are many reasons that cause pain and redness in the blood vessels of the eye. But the persistence and duration of this phenomenon confirms the seriousness of the problem requiring medical intervention.
We list some causes of pain in the blood vessels of the eye:
- the eyes are in constant tension;
- personal insensitivity or incorrect use of contact lenses;
- allergy;
- infectious infection;
- high blood pressure;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
To relieve tension in the eye vessel, it is enough to carry out a gentle massage, stroking the eyelids with your fingertips. It is recommended to simply cover your eyes with your palms and relax them for two to three minutes.
Your daily routine has a big impact on your eye health. Sleep should last at least 8 hours, this time is enough to restore the mucous membrane of the eye. Your eyes should also rest throughout the day. Work at the computer should be interrupted for a 10-minute rest.
Causes
Encephalopathy of complex origin may have several causes. The most common cause is impaired cerebral circulation and, as a result, a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients in brain cells. If the disruption of blood flow is prolonged, some of them die.
On this topic
- Encephalopathy
5 types of cerebral encephalopathy
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
Impaired blood flow can occur from an unhealthy lifestyle, low mobility, consumption of large amounts of fatty and sweet foods, abuse of cigarettes and alcoholic beverages.
There are also hereditary causes. Signs of encephalopathy may appear after severe injuries, poisoning, or prolonged oxygen deprivation. Stress and high physical and mental stress make the signs of the disease more pronounced and provoke its development.
What is reactive pancreatitis
The reactive state of the liver occurs in the form of hepatitis. However, in this case, the pathology is not caused by a virus, but by diseases of other organs. This is a response from the liver to harmful influences. Reactive hepatitis is milder and has a more favorable prognosis than infectious lesions. The disease does not progress.
The symptoms are mild, and sometimes the disorder occurs without painful manifestations and is detected only during a medical examination. Deviations in liver enzyme activity and bilirubin levels are minor. If the cause of the reactive state of the liver is treated, then all disorders are completely stopped.
The pancreas is closely related to the digestive system. Therefore, many gastrointestinal pathologies negatively affect the functioning of this organ. The gland produces pancreatic juice, which then mixes with bile and enters the intestines through the ducts. However, various diseases disrupt this process, and then a reactive state of the pancreas occurs (reactive pancreatitis).
Pancreatic juice enzymes begin to work after entering the intestines. In the pancreas they are in an inactive form. Special intestinal fluids activate these enzymes. This is how the digestive process functions in a healthy person. But with gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal fluid may reflux into the bile ducts.
If a person often has a headache, dizziness, noticeable memory deterioration, slow reactions and fatigue, then perhaps he has a constant deficiency of brain nutrition. Many people take such signs lightly. They attribute them to work pressure or lack of vitamins.
In order for the brain to function normally, it needs energy. The blood provides it with nutrients and oxygen. The body's functioning system is designed in such a way that the nutritional process of the brain is carried out through 4 arteries. Failure of its blood supply leads to various diseases. As a result, vascular genesis occurs.
Therefore, the primary symptoms associated with headache and fatigue should not be ignored. It is necessary to visit a doctor. He should be asked to conduct the necessary examination; perhaps the person has a vascular origin. Identifying disorders of the body at an early stage makes the treatment process more fruitful.
Complex of therapeutic measures
In the process of treating psychogenics, it is important to establish the cause of the disorder and take measures to eliminate circumstances that are traumatic to the psyche.
Patients are most often hospitalized because they exhibit unpredictable behavior and can be dangerous to others. In addition, people with mental disorders are often suicidal. For this reason, medical supervision is necessary.
In some cases, just a change of environment has a beneficial effect on a person, but this is not enough for recovery. During the treatment, medications are used, such as:
Vascular genesis of the brain: what it is, symptoms, treatment
Therapy for focal brain damage is aimed at eliminating the cause of the changes and restoring the functions of the organ.
For example, if the pathology is caused by a disease characterized by increased blood pressure, then the patient is prescribed to take medications that lower blood pressure. These may be diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or beta blockers.
Restoration of brain activity and elimination of pathological phenomena is carried out with the help of drugs that increase metabolism in nerve tissues: nootropics. Also used are agents that improve blood circulation, rheological properties of blood, and reduce the need for oxygen.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at reducing the manifestations of pathology: taking anticonvulsants, antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants, and tranquilizers for anxiety.
Therapy for transient changes, started on time, makes it possible to prevent more serious disorders and completely restore lost functions.
The patient will need:
- support of the correct daily routine, dosed nervous stress, proper rest;
- The duration of bed rest depends on the type of lesions, most often due to the speed of disappearance of clinical symptoms;
- nutrition is carried out according to dietary table No. 10 (hypertension, atherosclerosis);
- medications are prescribed taking into account the tendency to high or low blood pressure;
- to normalize vascular tone in case of venous insufficiency, venotonics are indicated;
- with obvious signs of ischemia, drugs that dilate blood vessels are used.
If there is evidence of phlebitis, vasculitis, or an autoimmune disease, the doctor considers the advisability of using antibiotics and desensitizing agents.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uGV-JrKF-aU
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are prescribed very carefully. To do this, you need to be sure that there are no hemorrhagic signs.
The vascular genesis of the disease is not of the same type; it requires clarification of the cause and localization. Complete blood supply to the brain can be achieved with the help of medications and stabilization of blood pressure. It is rarely necessary to resort to surgical treatment methods. The preservation of cerebral vessels ensures a person’s personal qualities, and therefore requires particularly careful attention.
If hypertension or atherosclerosis occurs, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of doctors. The sooner treatment begins, the faster the symptoms will go away:
- For spasms of veins and arteries, antispasmodics are recommended to improve the condition: No-Shpa, Papaverine.
- It is necessary to treat blood pressure with a course of Captopress, Captopril. Veroshpiron and diuretics help relieve swelling.
- When venous blood flow decreases, Eufillin and Pentoxifylline are used in long courses.
- Anticoagulants help improve blood composition in atherosclerosis.
- For focal changes, nootropic drugs are selected individually.
Moderate exercise, swimming and walking become a kind of training for the circulatory system, increasing tone and endurance. Any visual impairment due to vascular origin requires additional treatment under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
Neurologists do not advise enduring pain; they suggest potent drugs. Nimesil is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that inhibits the synthesis of hormones that provoke spasms. The main substance nimesulide is recommended for vasculitis, migraines, VSD, it reduces discomfort and increased muscle tone.
But the medicine requires strict adherence to the dosage: side effects negatively affect the liver, digestive system, and can cause heart rhythm disturbances. If necessary and on the recommendation of a doctor, Nimesil can be replaced with the following medications - Nurofen, Ibuklin, Ibuprofen.
Symptoms of reactive inflammation of the pancreas are usually pronounced. At the initial stage, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Severe pain appears in the abdomen and under the ribs, the discomfort intensifies after eating.
- Vomiting often occurs, which does not bring relief.
- The patient suffers from heartburn and belching.
- An increased amount of gases is formed in the intestines, causing bloating.
- Diarrhea occurs up to several times a day.
Then severe intoxication of the body occurs. The patient's skin turns pale, extremities become cold, heart palpitations appear, and blood pressure drops. The general condition is rapidly deteriorating. In severe forms of reactive pancreatitis, immediate hospitalization is required.
The clinical picture also depends on the cause of the pathology. If the reactive state arose due to diseases of the liver and gallbladder, then patients complain of pain in the solar plexus area. If pancreatitis was provoked by lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, then the unpleasant sensations are localized in the upper abdomen.
The symptoms of a reactive state of the pancreas in a child have their own characteristics. In addition to the above manifestations, children experience high fever, coating on the tongue, dry mouth, diarrhea is replaced by constipation. The blood sugar level increases in the blood test. In infancy, the disease often occurs without pronounced symptoms, but lethargy and decreased appetite can be noticed in infants.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using ultrasound. In this case, not only the pancreas is examined, but also all digestive organs. This is necessary to establish the cause of reactive inflammation. In addition, a urine test for pancreatic enzymes, a blood test for leukocytes and ESR, and an endoscopy of the duodenum are prescribed.
The underlying disease that caused reactive pancreatitis is treated. Anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antispasmodics are also prescribed. This helps relieve pain. A diet with limited spicy and fatty foods is required.
Reactive pancreatitis has a favorable prognosis. Timely therapy leads to complete recovery. If left untreated, the inflammatory process can become chronic; in addition, patients' blood sugar levels often increase.
A good blood supply to the brain is the main component of its full functioning. If violations occur in this process, first minor and then sometimes irreversible disruptions in the work of this body inevitably occur.
One of the manifestations of such disorders is the medical diagnosis – vascular genesis.
Vascular genesis
Vascular genesis is not an independent disease, but only a consequence of the development of vascular diseases. The brain is supplied with nutrients and oxygen through blood, which flows through several arteries.
In addition to the arteries, the venous system also plays an important role in transporting the required amount of blood to the brain. Vascular pathology, which entails negative changes in the blood supply system to the brain, is called “vascular genesis.”
Depending on the nature of the patient’s brain damage, they can diagnose:
- Organic or general pathological changes. They are quite often accompanied by severe headaches, including dizziness and nausea.
- Focal pathologies. If only certain areas of the brain are affected, patients will experience completely different signs of the disease. For example, with small focal leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin, the patient experiences damage to the white matter, which, in turn, leads to senile dementia.
Depending on the type of cerebral circulatory disorders, it is customary to distinguish:
- Transitory. In this case, it is customary to talk about general cerebral disorders or small-focal vascular disorders. The former cause severe headaches with nausea and even vomiting. The latter cause disruptions in the motor functions of organs, and sensitivity may be lost in certain parts of the body. This type of disorder is reversible and can be easily treated with complete recovery.
- Narrowing of the artery lumen. This pathology greatly affects the functioning of the area of the brain associated with this artery. Ischemic pathologies are often observed here. Treatment can be lengthy and complex, including surgical interventions.
- Aneurysm rupture. This process leads to hemorrhage into the brain cavity, the consequence of which will be a stroke, which can be hemorrhagic or ischemic in origin.
Considering that this pathology consists of insufficient blood supply to the brain, the doctor, in order to conduct effective treatment, is faced with the question of what led to the development of this disease. Most often, this situation is caused by hypertensive phenomena and the development of atherosclerosis of the vessels through which blood is delivered to the brain.
In the presence of hypertensive pathology, the patient develops thickening of the walls of blood vessels, which means that their lumen narrows significantly. In especially severe cases, sometimes complete stenosis of one or another vessel occurs, and the circulatory process can completely stop.
When the body is damaged by atherosclerosis, which, in turn, develops due to disruptions in the patient’s fat metabolism and the appearance of cholesterol deposits on the walls of blood vessels, normal blood flow becomes impossible.
This leads to insufficient blood supply to the brain. In the most severe situations, due to the breakdown of cholesterol plaques, a blood clot can form in any of the blood vessels.
It also usually causes blockage of the blood flow - complete or partial, thus creating foci of vascular origin.
In addition, other diseases lead to the development of vascular origin:
- aneurysm of the arteries supplying the brain;
- systemic diseases;
- pathological disruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- diabetes;
- anemia of any type;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- osteochondrosis, leading to pinching of the paravertebral arteries.
The most common causes of these disturbances in the functioning of the body are:
- Constantly or frequently rising blood pressure;
- high blood glucose levels;
- head injury;
- psycho-emotional overload of the patient;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages in excess, overeating;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Types of pain with VSD
According to the degree of severity, vasospasms are:
- Light shape. In this case, the symptoms of brain spasm will be mild, and the patient’s condition will quickly return to normal, even without special treatment.
- Angiodystrophic. This disorder is characterized by pain and general weakness of the patient. In this case, degeneration of the vascular walls occurs. This condition must be treated urgently.
- Cerebro-necrotic spasm. The victim has impaired coordination of movements, vision and speech, fainting, headache and vomiting are possible. The patient requires hospitalization.
According to the nature of the spread of damage, spasms are divided into:
- Local - occurs in one area.
- General – extensive damage. Possible with increased blood density, hypertension and various circulatory disorders.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, headache can take one of three common forms. Tension (TTH) Develops against the background of mental overstrain due to stress or the specifics of professional activity associated with long-term monotonous work, constant presence at a computer monitor, etc.
Nature of pain
It is difficult to answer the question of how to treat the disease right away. The first priority will be to determine the type of vascular pain. The treatment process must be comprehensive and include medications, medical and other methods.
If the cause is high blood pressure, then medications are prescribed that will relieve mental stress (for example, tranquilizers) and those that will lower the blood pressure. And for low blood pressure, the medications should contain caffeine (Pentalgin, Citramon).
In both cases, care must be taken to improve the supply of oxygen to the brain. This can be achieved, for example, using Piracetam or other nootropics. It must be taken for a long time. The course lasts a couple of months.
The types of brain nutritional disorders are classified as follows:
- Binswanger's disease. This disease is associated with damage to the white matter. Foci of vascular origin appear in the brain. These lesions consist of dead neurons. The main symptom of the disease is pressure surges. For example, at night it can rise or fall sharply. As a result, a person experiences poor sleep. Symptoms of this disease also include deterioration of thought processes and memory impairment. The patient has problems with gait and urination. This disease can occur in a person at a young age. People over the age of 50 are diagnosed with a disease such as leukoencephalopathy of vascular origin. This disease is also associated with damage to the white matter. Its cause is high blood pressure.
- Insufficient brain nutrition can lead to micro-strokes. Clogged vessels contribute to the death of the nervous tissue of the gray and white matter. A mini-stroke usually occurs due to blockage of small arteries in the brain. The disease can also be caused by atrial fibrillation. Because of this, blood vessels become clogged, since, firstly, blood clotting increases (it affects the formation of blood clots), and secondly, blood clots can form in the cavities of the heart.
- Another cause of poor brain nutrition is damage to major arteries that are not in the brain. The causes of this phenomenon may be thrombosis, as well as various bends and kinks.
The mechanism of occurrence of VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (IBC code 10) refers to pathological changes in the central nervous system code G with a clarifying diagnosis - 44. 1 headaches of a vascular nature, not classified in other ranges without additional clarification.
In this case, both arterial and venous channels are affected.
Enlarged vessels put pressure on the meninges, causing depression of sensitive nerve endings, which leads to pain and a throbbing headache.
Upon visual inspection, it is noted:
- Temporary or permanent pain;
- Meteor dependence;
- Redness of the capillary network of the eyeball;
- Feeling of nasal congestion;
- Swelling, heaviness, swelling of the eyelids;
- Sore throat;
- Emotional disorder, constant tension;
- Pale skin;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- Decreased hearing and vision.
In this case, the signs of headache depend on the type of vascular disorder:
- Cardiac - a symptom of arrhythmia, tachycardia, extrasystole;
- Hypotensive - muscle weakness, chilliness, fainting, pallor;
- Hypertension—rapid heartbeat, fatigue.
How long do people live with metastases and is it possible to cure the disease?
Diagnosing metastases in the spine already gives an unfavorable prognosis. Metastatic lesions of the spine are usually observed at the terminal stage of the primary cancer. In this case, secondary metastasis of bones is much easier compared to secondary metastasis of visceral organs. Life expectancy ranges from one to two years. The unfavorable factors in this case are:
- Rapid and aggressive growth of primary tumor formation;
- Multiple tumors in other organs;
- Large size of metastatic formations;
- Short period of time between treatment of primary cancer and spinal lesions;
- Poor general condition of the patient.
Favorable factors include:
- Slow growth of the primary tumor;
- Single metastasis in the spine and its small size;
- Satisfactory health of the patient.
Reactive mental disorders in childhood
A reactive state in children occurs after suffering fright and other traumatic factors. It is most often observed in infancy and preschool age. There are two types of reactions of the child's psyche to trauma. The child either becomes restless (tossing around, crying, screaming) or freezes in place and stops talking. This is accompanied by vegetative disorders: sweating, redness of the skin, tremors, involuntary urination and defecation.
Then the child becomes lethargic, whiny, and is worried about fears. Behavioral traits that are characteristic of younger children may appear. For example, a 5-6 year old child begins to behave like a 1.5 year old child. Reactive mental states in children require immediate treatment. All changes are reversible.
Vasoconstriction in babies
Complaints about cephalalgia are more common in adults, but headaches also appear in childhood.
You can suspect a headache in a small child if he shows lethargy, stiffness, restlessness, often spits up, spontaneously shudders and throws his head back. In this case, it is worth consulting a pediatric neurologist.
In older children, cephalgia can be caused by the following reasons:
- Infectious diseases (otitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc.). In this case, if a child complains of severe pain in the head, a thorough examination is required in order to promptly recognize possible serious complications, such as meningitis.
- Head injuries. Due to their mobility, children often fall, and the consequences of the injuries they receive sometimes do not have pronounced symptoms. If, some time after a fall or hit to the head, a child complains of cephalalgia, he should be seen by a doctor.
- Stressful situations associated with adaptation to kindergarten, school, etc.
- Migraine. Doctors believe that there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease, so if the mother is familiar with it, it can also appear in the child.
- Visual impairment and incorrectly selected glasses.
- Poor circulation in the brain, provoked by changing weather conditions, eating foods with a high content of artificial additives that cause vasoconstriction (for example, processed meat products, cheese), prolonged exposure to a stuffy room, and dehydration.
Pathology of the arteries and veins of the head is also observed in children, but much less frequently. The causes of narrowing of blood vessels are lack of physical activity, mental stress, and poor diet. In infants, the disease is caused by congenital underdevelopment of the circulatory system, pathology of the kidneys and heart.
With age, blood flow in the vessels worsens due to a decrease in their elasticity. In children, the causes of vasospasms are somewhat different.
Vascular pathologies in children’s bodies are caused by the same reasons as in adults. That is, the walls of the blood vessels that are responsible for feeding the brain are also affected.
Diagnosis of pathology
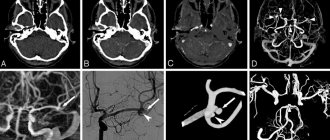
To make a diagnosis, a thorough examination of attention, memory and intelligence is necessary. At the same time, other studies are carried out - magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels, angiography with a contrast agent, electroencephalogram, blood test. If necessary, an additional examination by an ophthalmologist may be prescribed. Since the symptoms of the disease are similar to other diseases, differential diagnosis is carried out with Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Types
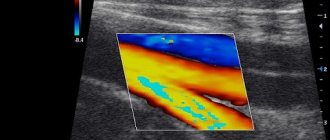
MRI images allow us to identify all pathologies that affect brain tissue. I determine affected areas by changes in color, echogenicity of individual areas of the cortex or other organ structures. Using the data obtained, specialists measure the area of the destroyed area and also predict the development of pathology.
Focal brain damage may result from:
- Demyelination;
- Presence of neoplasms;
- Tissue swelling;
- Circulatory disorders;
- Gliosis (replacement of functional cells with glial tissue).
Manifestations of pathology depend on the location of the lesion. Therefore, MRI diagnostics is considered the most informative method for detecting diseases of the central nervous system.
Based on the location of brain lesions, there are:
- Juxtacortical;
- Periventricular;
- Lacunar.
Juxtacortical lesions of nervous tissue are characteristic of multiple sclerosis. In this case, they are located as close as possible to the cerebral cortex. When describing an MRI picture, experts recommend using this particular definition, since the term “subcortical” cannot fully convey the nature of the spread of the pathology - it describes any changes in the white matter up to the ventricles.
The periventricular location of the foci of destruction is diagnosed with hypoxic-ischemic damage to the brain substance. In this case, they are located near the ventricles.
Lacunar lesions are a consequence of damage to the deep arteries. They are located in the thickness of the white matter along the blood vessels. Typically their diameter varies between 1–20 mm.
Demyelination
Characterized by the presence of areas of destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. Because of this, the transmission of nerve impulses between neurons in the area of the brain is disrupted, which negatively affects the performance of the central nervous system.
Tissue destruction of this type is observed in multiple sclerosis, multifocal leukoencephalopathy, Marburg disease, acute dissimulating encephalomyelitis, Devic's disease.
In these diseases, the MRI picture is identical: the images clearly visualize single or multiple white spots, which are located in one or several parts of the brain. The size of the areas depends on the extent of the disease, as evidenced by the presence and strength of neurological abnormalities.
At the moment, there is no common understanding of perivascular spaces. Some scientists believe that they surround only the arteries, while others believe that they surround all the large blood vessels that penetrate the brain. Some describe them as a space that is located between the wall of the vessel and the nervous tissue, others - as a natural continuation of the subarachnoid and pia mater.
Pericular spaces perform several functions at once:
- Participate in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- In them, the exchange of substances between the cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue occurs;
- They are part of the blood-brain barrier;
- They contain immunocompetent cells, that is, with the help of them, immunoregulation occurs in the tissues of the organ.
Perivascular spaces occupy a small volume, so in a healthy person they are not visible on an MRI image.
In dangerous conditions, for example, before a stroke, the patient’s ICP increases due to an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid. This leads to expansion of the cavity between the brain vessels and nervous tissue. Along with this process, the echogenicity of the area increases, which appears on an MRI image as a white spot.
The disease is characterized by the loss of neurons and a decrease in the number of synaptic connections between them. This leads to a decrease in the thickness of the gray matter and pronounced atrophy of the affected areas.
Dark spots appear on MRI images, which indicate necrosis of brain cells. An accurate diagnosis is made based on the results of several examinations, that is, over time.
It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the cells of the head and intercellular space. Due to this, the volume of the organ increases and intracranial pressure increases.
In the affected area on the MRI image there is a light spot, which, as the process worsens, increases and gradually covers the entire organ.