Position of neutrophils in blood tests
The number of segmented neutrophils is determined during a general blood test, and their percentage is determined during the calculation of the leukocyte formula. The main stages of analysis are:
- collection of material (capillary or venous blood);
- preparation of equipment and inventory;
- preparing smears for subsequent research;
- their fixation and coloring;
- leukocyte count.
Blood is taken from the fourth (ring) finger of the left (for right-handed) or right (for left-handed) hands. Often the material is taken from a vein. In the first case, treat the finger with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol. Wear sterile, disposable gloves. Take a new scarifier and pierce your finger. The puncture depth is 2-3 mm. The scarifier is held firmly with the index finger and thumb.
Blood consists of plasma and formed elements, which are counted and studied during a general clinical analysis (CCA) - the most common, informative blood test. Based on the results of the analysis, disturbances in microbiological processes in the body are determined, indicating the development of a particular disease.
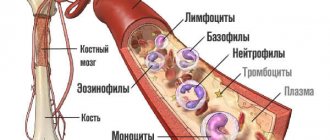
Blood cells are divided into three main groups according to their external characteristics and functional purpose:
- Erythrocytes or red blood cells. They have the shape of a sphere, are responsible for transporting iron-containing protein - hemoglobin, and ensure gas exchange in the body (delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide molecules in the opposite direction).
- Platelets. Blood cells in the form of platelets. The main purpose is to ensure the preservation of the integrity of blood vessels and proper coagulation (blood clotting).
- Leukocytes or white (colorless) cells. A special group of blood cells includes two subgroups: granulocytes (granular) and agranulocytes (non-granular), which, in turn, are divided into several varieties. Agranulocytes are monocytes and lymphocytes, granulocytes are eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils (band and segmented). The totality of leukocyte cells in the OKA is represented by a leukogram, otherwise the leukocyte formula.
Colorless blood cells protect the body from the invasion of foreign agents (antigens) - viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites. When antigens penetrate, leukocytes are mobilized and strive to eliminate them.
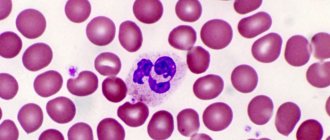
The biochemical process of capture and digestion of “strangers” by leukocytes is called phagocytosis. This protective reaction explains blood leukocytosis (increase in the number of white cells) during inflammatory and infectious processes. Neutrophils are pronounced phagocytes with the function of capturing and destroying pathogenic microorganisms.
Designation of the main blood elements in OKA
| WBC | leukocytes | R.B.C. | red blood cells | |
| Leukogram | ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) | ||
| NEU or NEUT | neutrophils | PLT | platelets | |
| LYM | lymphocytes | RET | reticulocytes (immature red blood cells) | |
| MON | monocytes | |||
| BAS | basophils | |||
| EOS | eosinophils | |||
The norm of segmented neutrophils in the blood
Laboratory calculation of NEU in a clinical analysis is the number of cells per 1 ml of blood or 1,000,000,000 cells per liter (in the analysis form it is indicated as 10^9/l) and is called the absolute number (abs.) of neutrophil granulocytes. The norm for the absolute number of segmented (mature) cells in adolescents over 16 years of age and in adults is 1.8-6.5 * 10^9/l.
Norm abs. stab (immature) cells – 0.04–0.30 * 10^9/l. A simpler calculation is to measure the relative number of formed neutrophilic elements as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes. Starting from the age of 16, reference values for mature neutrophils are 45-70%, immature neutrophils are 1-6%.
In the blood of children, the number of mature and immature neutrophil granulocytes depends on age.
Normal relative indicators by age (in%)
| Child's age | After birth | Baby up to one year old | 2-4 years | 4-8 years | 8-12 years | 12-14 years old | 14-16 years old |
| Mature cells | 48-72 | 15-46 | 33-56 | 33-59 | 43-59 | 44-60 | 44-65 |
| Immature cells | 4-11 | 1-6 | 1-5 | 1-5 | 0-5 | 0-4 | 1-5 |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Recipe for noodle maker with cottage cheese, just like in kindergarten.
Minor neutrophilia is allowed in women carrying a child. During pregnancy, hematopoiesis is activated, immunity decreases, and biochemical processes are completely rearranged.
In the case when segmented neutrophils are significantly increased (1.5-2 times), this means that an infection is actively progressing in the body, threatening premature birth or miscarriage.
General meanings for pregnant women
Deviations from normal values indicate violations. High rates most often indicate acute infectious and inflammatory processes associated with bacterial or fungal activity.
A low level of mature neutrophil leukocytes requires dynamic monitoring. The deciphering of the blood OCA results obtained from the laboratory is carried out by the doctor who referred for the study.
Mature segmental cells are able to penetrate body tissues. However, in the results of a general clinical study, the percentage of band and mature leukocyte granulocytes is calculated. There are always more segmented cells due to the fact that the rate of maturation of rod cells is very high.
Different age groups have different normal levels of neutrophil granulocytes in the blood. Newborns may have a very small number of segmented neutrophils (no more than 45%) and many band neutrophils. With age, the indicator shifts towards mature neutrophils. In children under 6 years of age, the number of segmented neutrophilic granulocytes does not exceed 60%. In adults, the rate can reach 70% and is considered normal.
Approximate content of neutrophils in the blood for different age categories:
- In children under 1 year: 20-45%.
- In children from 2 to 6 years: 30-60%.
- In children from 7 to 13 years old: 20-64%.
- In adults, the norm is 50-70%.
An increase in the number of neutrophils in response to infection is an indicator of “good” functioning of the immune system. The greater the number of neutrophil granulocytes involved in the elimination of the pathogenic microorganism, the faster and more efficiently this process will be carried out. A stable increase in neutrophils in the blood is called neutrophilia. This often leads to thrombus formation or complications of various etiologies.
The norm of segmented neutrophils depends on the age of the person. In newborns, the normal content of these cells is 47-70%. In children 1-2 years old this figure is 28-48%. At 2-5 years, the content of segmented neutrophils should be 32-55%, and at 6-7 years - 38-58%. In children 8-15 years old, the neutrophil content is 41-60%. In adolescents over 16 years of age and adults, the normal content of these cells in the blood is 50-70%.
If neutrophils are increased or decreased in an adult, then additional studies will be needed (ultrasound, CT, MRI, biopsy examination, biochemical analysis, bacteriological and virological studies, serodiagnosis, radiography). Therapeutic tactics depend on the causes of changes in neutrophil levels.
For mild asymptomatic neutropenia (decrease in segmented neutrophils), therapy is not required. If the cause is a viral infection, then antiviral drugs (Ribavirin, Ingavirin, Tamiflu, Acyclovir, Zovirax, Valtrex) and immunostimulants are indicated. If segmented neutrophils are reduced, then lymphopoiesis stimulators can be prescribed. These include Tevagrastim, Leucite, Neupomax and Neupogen.
These medications are contraindicated in severe congenital neutropenia, intolerance, and concomitant radiation and chemotherapy. These medications are used in the form of an injection solution. With low segmented neutrophils against the background of acute leukemia, chemotherapy, control of bleeding, normalization of blood coagulation and increase in hemoglobin are required.
With elevated segmented neutrophils against the background of bacterial pathology, the basis of therapy is the use of systemic antibiotics (penicillins, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, cephalosporins). For foci of purulent infection (abscesses) and tumors, surgical intervention is required.
Auxiliary aspects of therapy are normalization of the daily routine, elimination of stress, refusal to take toxic medications, normalization of blood sugar levels and maintaining the functioning of vital organs.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Causes of Gas in Infants
Normal indicators
Leukocytes provide an immune barrier against infection, inflammation, and the growth of a malignant tumor. Immune functions are carried out by the most numerous populations of white blood cells:
- neutrophils (NEU);
- lymphocytes (LYM).
The concentration of leukocytes is measured as a percentage. The indicators reflect the amount of total leukocytes that accounts for each cell group.
Important information: Lifespan of red blood cells in human blood
The leukocyte norm in children differs from the norm in adults. The newborn has elevated white blood cells due to a high concentration of neutrophils. Their LYM levels, compared to the norm in adults, are reduced.
After 7 days, the parameters of the LYM and NEU cells in the newborn are equalized. This balance is called leukocyte crossover. From 7 days to 5 years, the LYM value should normally be greater than neutrophils.
This distinguishes the leukocyte proportions in children and adults. Parents, not knowing this feature, often get scared and begin to worry.
At 5-6 years, the LYM analysis and the number of NEUs again become approximately the same, as was observed at 7 days in newborns. This phenomenon is called second leukocyte crossover and reflects normal immune development.
Neutrophils
Neutrophilic white blood cells increase during inflammation caused by bacterial infections. There are 2 groups of neutrophils present in the blood:
- immature rod forms (NEUp);
- mature segmented forms (NEUc).
An informative indicator is the number of segmented NEUc cells.
Normal NEUc in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 28-48;
- 2-3 — 32-55;
- 3-6 — 32-55;
- 6-9 — 38-58;
- 9-12 — 43-60.
Lymphocytes
The group is responsible for the production of antibodies to foreign proteins. A significant increase in these blood elements is observed in viral diseases.
Normal lymphocyte counts in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 37-60;
- 2-3 — 33-55;
- 3-6 — 33-55;
- 6-9 — 30-50;
- 9-12 — 30-46.
Why are segmented neutrophils elevated in a child?
A slight increase in segmented neutrophils does not indicate serious pathology. This condition is typical for most viral, bacterial or fungal infections. But if segmented neutrophils in the blood are doubled or tripled, this is a reason to consult your doctor. Exceeding the number of neutrophil granulocytes by tens of times may indicate sepsis.
Severe neutrophilia
Increased segmented neutrophils are observed in diseases:
- Severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock).
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Extensive tissue necrosis.
- Trophic ulcer or gangrene of various parts of the body.
- 3rd or 4th degree burn.
- Diseases of the epidermis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Blood cancer.
- Poisoning with heavy metals or various poisons.
- Anemia.
Neutrophilia develops while taking glucocorticoid drugs. But one blood test cannot tell you anything about a patient’s illness. Neutrophilia is a sign indicating pathological processes, and not an independent disease. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo additional examinations to find out the exact cause that caused neutrophilia.
There are three types of neutrophilia:
- Localized (increase in the number of neutrophils in a specific location)
- Extensive.
- Septic.
Localized neutrophilia occurs due to injury and goes away on its own. Extensive neutrophilia appears due to an infectious disease of a viral or bacterial nature. Sepsis is a serious condition of the body, accompanied by intoxication by pathogenic microorganisms that enter the blood. Sepsis is fatal in most cases and requires emergency medical care. Often, even with appropriate assistance, the patient dies.
When analyzing blood in children, special attention is paid to the percentage of segmented and band neutrophils. If the percentage of segmented neutrophils increases, this indicates severe pathology or physical/emotional stress. Hypothermia often causes mild neutrophilia.
Reasons that can cause neutrophilia in children:
- Influenza virus.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Infectious diseases.
- Blood loss.
- Malignant or benign neoplasms.
- Colitis.
- Severe drug poisoning.
- Diabetes.
Often, neutrophilia occurs in a child in the postoperative period after removal of the appendix or polyps of various etiologies. Medicines can also have a profound effect on the level of neutrophils in the blood.
Causes of low lymphocytes and increased neutrophils
A general blood test makes it possible to confirm a superficial diagnosis of adverse changes in the human body.
If, during such a diagnosis, the ratio of several different types of leukocytes is established, which is called leukogram or leukocyte formula, the specialist can determine the state of the immune system and give a very likely assumption about the progression of the infection (bacterial or viral in nature). So, this article will consider an example of a case in which decreased lymphocytes and increased neutrophils were found.
First you need to find out what their concepts are. Both types of cellular structures are types of white blood cells (as well as monocytes, eosinophils and basophils), but their functions and purposes in the human body differ significantly.
What are neutrophils?
Neutrophil granulocytes are blood cells produced in the human red bone marrow. their purpose is to protect against infection. They can live for several hours or days, depending on whether there is a focus of inflammation in any system of the human body.
As a rule, the content of these bodies in an adult should fluctuate between 47% and 72% of the total number of leukocytes. As the child grows older, their concentration gradually increases, given that their number will still be at approximately the same level.
The percentage of this type of leukocyte in a child who is about a year old will be from 30% to 50%. At seven years old, this ratio increases slightly and is 35%-55%, and in adolescence it will vary from 40% to 60%.
If the analysis showed an increased concentration of these cells in a person, this indicates neutrophilia. The increase factor is usually considered to be the development of the inflammatory process. Depending on the percentage of increase in these cells during inflammation, you can determine its approximate extent and how actively the body itself counteracts it.
Indicators of two forms of neutrophils
When a neutrophil develops in the red bone marrow, it forms into a band. It enters the plasma in certain quantities and after a certain period of time is divided into segments.
So it becomes segmented, that is, fully formed, and after a few hours it penetrates the membranes of the capillaries of various organs.
It is in those areas that it resists foreign agents.
The concentration of segmented cells is written as a percentage in the leukocyte formula. With its help, it is possible to assess the condition of the blood, and therefore the body. However, before this, the norm of these cells in the blood should be determined. As already mentioned, in an adult healthy person the norm of segmented bodies ranges from 47% to 72%, and in band bodies it corresponds to 1–5%.
The analysis can also show changes in the leukocyte formula. Typically, two shifts are specified, either left or right.
A shift of the formula to the left indicates the presence of bodies that are not yet fully formed, which, in accordance with the norm, should be exclusively in the bone marrow, but not in the blood.
And a shift of the formula to the right means that the content of segmented cells is increased, and the number of nuclear segments becomes more than five.
Therefore, when deciphering a clinical analysis, it is necessary to pay close attention to the indicators of both forms, since deviations can warn of serious changes in the body.
If you promptly see the discrepancy between these bodies and the required number, there is a chance of avoiding many of the ensuing consequences that are associated with the development of the inflammatory process.
Reduced lymphocyte count
Lymphocytes are blood cells that are also produced in the red bone marrow.
They are the main cells of the immune system and serve as protective forces against foreign microorganisms that enter the body.
They support both humoral (synthesize antibodies) and cellular immunity (direct interaction with damaged cells), and also regulate the functioning of other types of cells.
Their normal level in an adult is 25%-40% of the total number of leukocytes. In children, the content changes as the body matures and grows.
In newborns, in the very first days of life, their number is no greater than that of neutrophils. The percentage concentration will be approximately 25%. And after a week it becomes equal and reaches about 42%.
At six years, the cell concentration already reaches 45%-65%. This means that in the general leukocyte formula their number becomes predominant. In the blood of a six-year-old child, it is again equal to neutrophils, but as they grow older, it will gradually decrease.
Typically, low lymphocytes and high neutrophils are caused by various pathologies and viruses. It is understood that in both the first and second cases the factors of deviation from the norm will be different.
So, an increase in neutrophils usually occurs due to the following factors:
- acute infections caused by bacteria, which are accompanied by a purulent-inflammatory process:
- localized _ Observed with moderate neutrophilia with certain manifestations (abscesses, infections of the ENT organs, appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, acute tonsillitis, diseases of the genitourinary organs and others);
- generalized. For severe neutrophilia (sepsis, peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), infectious diseases such as cholera or scarlet fever).
- necrosis and necrotic lesions (myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene, severe burns);
- recent vaccination;
- effects on the bone marrow of toxic substances (alcohol, lead);
- bacterial toxicosis without infection directly by bacteria (for example, when there were unbroken botulinum toxins in the food, and the bacteria themselves had already become inactive);
- the disintegration of a malignant neoplasm is a process in which damaged cells stop growing and begin to be excreted naturally.
In turn, a decrease in lymphocytes most often indicates the following problems.
- Miliary tuberculosis (hematogenous, usually generalized form of tuberculosis, accompanied by a dense rash of small tuberculous tubercles in the lungs).
- Tuberculosis of the bronchial glands.
- Hematological diseases of lymphatic tissue (lymphoma, lymphosarcoma).
- Exposure of the body to different types of ionizing radiation. Severe health effects, such as skin burns or radiation sickness, can occur when the radiation dose crosses certain limits.
- Multiple myeloma is a malignant neoplasm of plasma cells, which is mainly localized in the bone marrow.
- Aplastic anemia is a disease of the hematopoietic system. With this disease, the bone marrow basically stops producing different types of blood cells, including red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells in the required quantities.
- The use of glucocorticoids are steroid hormones from the subclass of corticosteroids produced by the adrenal glands.
- AIDS, a condition that progresses due to HIV infection and is characterized by a decrease in T-lymphocytes and multiple opportunistic diseases.
- Renal failure is a dysfunction of the kidneys. The decrease can occur in both acute and chronic forms of renal failure.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is a serious illness during which the human immune system mistakes its own cells for foreign agents and begins to fight them.
- Lymphogranulomatosis is a malignant disease of lymphatic tissue, accompanied by the presence of huge Reed-Berezovsky-Sternberg cellular structures, which are identified during a microscopic examination of the affected lymph nodes.
Based on the reasons described above, if the levels of segmented neutrophils are increased and lymphocytes are decreased, this most likely indicates the presence of a viral infection or the development of inflammation. In this case, you need to immediately consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
Source: https://diagnos-med.ru/prichiny-ponizhennyh-limfotsitov-i-povyshennyh-nejtrofilov/
Increased level of segmented neutrophils in the blood
Segmented neutrophilia (indicator more than 75%) can have physiological and pathological causes of development. Elevated levels of neutrophil leukocytes cause:
- prolonged neuropsychological tension (distress), psycho-emotional shock;
- PMS in women;
- excessive physical activity (intense sports training, other stress).
The number of mature leukocyte neutrophils is increased in chronic alcoholics and with single alcohol intoxication. A pathological shift of the leukogram to the right is a clinical sign of acute infectious and necrotic processes.
Generalized and local infections caused by the activity of pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci, anaerobes, Koch's bacillus). The most common ones include:
- inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis) and purulent inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis);
- acute pneumonia and pulmonary tuberculosis;
- development of acute or relapse of chronic pyelonephritis;
- sepsis (blood poisoning);
- suppuration (abscesses) of different locations (in muscles, subcutaneous tissue, bones);
- intestinal infectious diseases (dysentery, cholera, salmonellosis, etc.);
- parasitic infestations (in the acute period);
- streptococcal and streptococcal lesions of the oropharynx.
Neutrophils higher than normal in a blood test are recorded when infected with sexually transmitted diseases (in the acute period of symptoms). Necrosis:
- gangrenous lesions of the limbs;
- infarction (myocardium, spleen, kidney, etc.);
- pancreatic necrosis (death of pancreatic cells).
Chronic segmented leukocytosis accompanies non-healing trophic ulcers, ketoacidosis crisis in diabetes mellitus, and oncohematological pathologies (cancer of the circulatory and lymphatic systems). The total level of neutrophil cells may be increased:
- in the first days after surgery;
- with cyanocobalamin vitamin deficiency (chronic deficiency of vitamin B12);
- after a course of treatment with hormone-containing medications.
Neutrophilia is sometimes observed after routine vaccination.
According to the degree of shift of the leukogram to the right, three stages of neutrophilia are distinguished. The first stage is moderate (7-10 absolute units * 10^9/l) and the second severe stage (10-20 absolute units * 10^9/l) are characteristic of local (local) inflammation. The third severe stage (20-60 ab. units * 10^9/l) is a sign of a generalized infectious-inflammatory process. An increase in NEU values can indicate the extent of the infectious lesion.
We suggest you read: The child has pain in the left lower abdomen
Treatment in children
Elimination of the cause leads to normalization of neutrophil levels
To treat neutropenia, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. If the disorder appeared after a viral infection, then to restore the normal state, only a gentle regime is required for several weeks after the illness. When an internal pathology is noted that has caused changes in the blood, it is treated. After the child recovers, the blood picture will return to normal.
A lack of neutrophils in a child’s blood should alert parents and doctors. It is imperative to determine what caused this phenomenon. A complete examination will allow you to exclude or diagnose dangerous pathologies and promptly correct the child’s condition.
Decreased cell concentration
A decrease in the levels of segmented neutrophils (less than 45%) is characteristic of chronic low-grade inflammatory processes, viral diseases, blood diseases, and depletion of bone marrow reserves.
Neutropenia accompanies:
- chronic toxoplasmosis;
- zoonotic infections (brucellosis and tularemia);
- ARVI and influenza,
- viral hepatitis A, B, C;
- hemolytic and hypoplastic types of anemia;
- dysfunction of the bone marrow to produce blood cells caused by radiation or chemotherapy.
“Childhood” viral diseases in which NEU values are reduced in a child: measles, rubella, chickenpox. Neutropenia can occur due to incorrect therapy with medications: cytostatics (antitumor drugs), sulfonamides, analgesics.
The physiological reasons for the lack of segmented blood cells are due to the characteristics of dietary habits (when the diet does not contain enough foods containing B vitamins). Nutritional neutropenia is associated with a psychopathological eating disorder (anorexia) and wasting of the body (cachexia).
Decrease in neutrophil values by stages:
- light (1-1.5 absolute units * 10^9/l);
- moderate (0.5-1.0 absolute units * 10^9/l);
- heavy (0-0.5 absolute units * 10^9/l).
A low level of neutrophil leukocytes in a blood test without significant disturbances in the functioning of the body may be associated with genetic Kostmann syndrome - the inability of stab cells to mature.
Important! When assessing a general blood test, the doctor never considers the indicators of certain parameters separately. Conclusions about disorders and diseases are made based on a comparison of all values and the presence of somatic symptoms.
Neutrophils are low, lymphocytes are high - a sign of immunity problems
Before assessing the overall picture and how to lower or increase the white blood cell count, the doctor will need to study many factors. These include:
- methods of therapy;
- symptoms;
- anamnesis;
- gender, age and poor heredity of the patient.
The white blood cell count may be elevated or vice versa if the patient is taking medications. Therefore, in order to avoid a falsely high cell count, you should warn your doctor about taking medications. Medications that can “saturate” the body with low levels of corpuscles include:
- antibiotic group drugs;
- antihistamines;
- diuretics;
- steroid hormones for the adrenal glands;
- clozepine and heparin.
The analysis data is affected by relaxants, chemical or radiation therapy. These drugs cause an increased proportion of white cells.
Other leukocyte cells and their significance
Neutrophils and lymphocytes are among the white cells. Among ordinary people they are known as leukocytes. A certain type of cell in this broad group has a specific function aimed at protecting against disease. When performing a blood test, the doctor takes into account the relative content of each type of white blood cell, not just the level of white cells.
What are leukocytes? These include colorless blood cells that form a “dam”, a shield that will not allow infection to pass through. These cells contain substances with which the body gets rid of pathogenic organisms. They are able to neutralize the decay products of harmful microorganisms.
What functions do lymphocytes perform?
Lymphocytes are specific cells that are formed in the bone marrow. They are a defense mechanism against infections and are therefore considered the main components of the immune system.
Neutrophils are the most numerous class of immune cells (their part ranges from 45 to 72%). The function of neutrophil cells is to destroy bacteria. If foreign bodies enter the body, this type of white blood cell immediately rushes to the part of the body from where they came. Ultimately, infections are absorbed by neutrophil cells and digested.
In order for the picture to be complete, it will be necessary to consider blood components that are less significant for the body (but not for the immune system). These groups of leukocytes include the following:
- Monocytes. Large elements related to phagocytes. Diseases develop depending on the number of monocytic type cells. An increase in the percentage of monocytes indicates relative monocytosis. If monocytes are increased in number, then doctors diagnose absolute monocytosis. Sometimes other blood cells can change their numbers along with monocytes. Lymphocytes and monocytes are rarely elevated at the same time in a child. The main cause of the phenomenon is infections.
- Basophils. They are classified as scouts. Basophils contain histamine, serotonin and other highly active components. Upon contact with allergens, they burst and their contents affect the allergen.
- Eosinophil cells. Eosinophils are a population of leukocytes that perform a marker function. Disease cells are identified. The norm of eosinophils for humans is from 1 to 5%. When lymphocytes and eosinophils are elevated, this indicates the body is allergic. If eosinophils are elevated in a child, an analysis is performed for helminthic infestations, rhinitis, scarlet fever and chickenpox.
Conversation at the clinic
Recently, sitting in the clinic, with the door slightly open, I overheard a conversation between a mother and a pediatrician about the fact that the child’s tests showed elevated lymphocytes. While waiting for my turn, I wondered if all mothers know what lymphocytes are and what they are responsible for. So let's figure it out.
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are the cells your body uses to fight infections. There are different types of white blood cells, each responsible for fighting different germs.
So let's take a closer look at them.
Data decryption
What does the high content of certain cells or their reduced number indicate? If some cells increase, accompanied by a decrease in others, then this indicates one thing - there is inflammation, which the body is fighting.
If lymphocytes are elevated, the following diseases should be diagnosed:
- tuberculosis;
- thyroid disorders;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- illnesses of viral etiology (this is evidenced by decreased cells).
Medicines can cause a reduced number of lymphocytes. Radiation therapy for cancer can affect the indicators. And if the test results exceed the norm or the number of cells is reduced, then you should think about the reasons. Only the attending physician will tell you why lymphocytes are increased in an adult and neutrophils are decreased.
A high proportion of leukocytes will indicate problems with immunity
It is worth considering other decryption options that are encountered. If segmented neutrophils are reduced in an adult, and lymphocytes are increased, this indicates that the disease has passed. There will soon be no trace of the increase or decrease - the leukocytes will return to normal.
Important! Segmented cells are called mature cells, i.e. those that interacted with infections.
Application of ionizing radiation also results in low or high white blood cells. Therefore, this should not be ruled out. There may be many or few leukocytes in the case of immune agranulocytosis. This disease represents the death of neutrophils even before formation.
The role and indicators of the number of neutrophils in the blood
Neutrophil balance is an important indicator for the body. The number of these cells is normal if their percentage ranges from 45 to 72%. A lower value is typical for children under one year old, and the older the child, the more leukocytes of this type are in the body.
What happens when neutrophil activity increases or decreases?
If neutrophils are elevated, then this is neutrophilia. Most often, the disease is caused by the development of inflammation. By examining the number of neutrophil granulocytes, conclusions are drawn about the scale of inflammatory processes and the resistance of the immune system. If children are 1 year old, then there is no need to worry about neutrophilia when their percentage of corpuscles is about 30%.
If a child’s neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are high, then it makes sense to consider not only viral infections.
The reasons why neutrophils are reduced and lymphocytes are increased in adults or children are malignant tumors, radiation and medications.
If, when neutrophils decrease, other cells increase, then the immune system fights the disease.
A decrease in neutrophils is associated with the following factors:
- infection of the body with viral infections;
- advanced inflammation;
- use of radiation therapy;
- exposure to radiation;
- development of agranulocytosis (signals that there are no granulocytes and lymphocytes in the blood).
Low neutrophils in the blood can be caused by medications, or rather, side effects from them.
Therefore, in the deciphering process, it is worth considering the number of neutrophils, since their increase or decrease indicates violations. If you pay attention to these changes in time, you can avoid some of the negative consequences caused by inflammatory processes.
Lymphocytes and neutrophils can tell a lot about a patient's condition. Therefore, it is recommended to take a general blood test once a year. Deciphering will allow you to detect hidden pathological processes caused by low levels of leukocytes or their high proportion in the blood.
Low corpuscle count is determined by blood test
An increased or decreased proportion of corpuscles indicates disease.
- Acute viral infection. It is indicated by an increase in the number of leukocytes, low neutrophils and an increased content of lymphocytes.
- Chronic viral infection. Here the analysis is ambiguous. Therefore, the following picture is observed:
- the quantitative content of leukocytes is optimal or reduced;
- increased lymphocytes or their presence at the upper limit of the normal value;
- the low content of neutrophils is insignificant or they are close to the lower limit of normal.
- Acute bacterial infection. There is a reduced level of lymphocytes. The total number of leukocytes increases, the level of neutrophils is high.
- Chronic or local bacterial infection. The same symptoms are noted as in the previous case. But they are closer to normal levels.
Counting the number of white cells will identify many infections. By analyzing the high or low percentage of white blood cells, the doctor will order tests and make a diagnosis. The analysis will help detect rare autoimmune diseases, blood diseases and immune deficiencies. When white blood cells decrease or some of them increase, the quality of chemotherapy is judged.
The process involves taking fluid from a vein and finger. Most often, material collection for diagnostics is carried out without complications. But sometimes it happens that the doctor cannot find the vein or the needle gets stuck in the muscle.
Functions and norm of lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are responsible for the adaptive function of the immune system. This means that the ability to resist infection adapts to the environment as we age.
These particles belong to one of the following categories:
- T-lymphocytes – contribute to the formation of thymus and thymus cells; play an auxiliary role in the process of synthesis of signal substances;
- B-lymphocytes - take part in the production of bone marrow cells, which allows us to call them the “parents” of the body’s immune function; with their help, antibodies are produced.
- natural “killers” – secrete cytotoxins that help cope with pathological cells.
High lymphocytes make it clear that the body has the following ailments:
- viruses;
- tuberculosis;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- hyperthyroidism – increased production of thyroid hormones;
- lymphosarcoma.
Depending on the increased or decreased portion of the corpuscles, the state of the body and the presence of diseases of viral etiology are judged. Elevated lymphocytes will indicate inflammation. Therefore, it is imperative to visit a doctor after a disappointing analysis.
It is worth noting the possibility of human vaccination, which opens up thanks to lymphocytes. This is possible due to the fact that the bodies contain memory cells. They store antigens in a coded state.
Source: https://znk-mos.ru/nizkie-neytrofily-vysokie-limfotsity-rebenka/
What to do if there is a high level of neutrophils in the blood?
First, consult your doctor for additional examinations. An increase in this indicator above the norm indicates a huge number of diseases.
Since the cause of an increased number of neutrophil granulocytes is inflammation, viral or bacterial infection, the attending physician prescribes antibacterial drugs. For allergies, antihistamines of the latest generation are prescribed (they do not affect brain activity and selectively block peripheral receptors).
Infection with parasites (helminthiasis)
Neutrophilia occurs when infected with parasites. In such cases, it is necessary to prescribe special medications - antiparasitic and hepatoprotective. Diagnosis should only be carried out by a qualified specialist; you should not engage in self-diagnosis or treatment.
General recommendations that will help reduce the level of neutrophils in the blood:
- Get enough sleep and sleep up to 8 hours a day.
- Do not abuse psychotropic substances and medications.
- Do not overeat and dilute your diet with foods rich in vitamins.
- Eat more foods containing unsaturated fatty acids: fish oil, cod, salmon, olive oil.
- Do not overexert yourself physically or mentally. Stress affects the level of neutrophils in the blood and can aggravate the underlying disorder.
- Develop a dynamic stereotype: sleep, eat, exercise at a clearly designated time of day. This will teach the body to prepare for various tasks and reduce the level of psychological stress.
- Visit your doctor regularly to have your condition diagnosed or treated.
How to detect low neutrophil levels
If symptoms appear, the child should be examined by a doctor
To identify a disorder, a blood test is required, for which venous blood or blood taken from a finger can be used. Which one will be chosen depends in each individual case on what other indicators need to be determined, as well as the analysis method used in a particular medical institution. If this is not an emergency, you should donate the material on an empty stomach.
The speed of determining the level of these leukocytes in the blood is also determined by whether the study is carried out routinely or urgently. Typically, the data will be ready in a day, and if it is necessary to obtain it urgently, then within a few minutes specialists will conduct a study on the main indicators of interest.
If, for health reasons, the child must regularly take medications that may disturb the blood picture, this is taken into account during the study. In such a situation, with a strong decrease in neutrophils, a simple adjustment to the drug dosage regimen may be required.
Results
Segmented neutrophils are mature neutrophils (a type of leukocyte) responsible for eliminating infections, primarily the activity of pathogenic bacteria. With bacterial infection, the number of segmented cells increases.
In clinical practice, this is an indicator of an acute infectious process. Sluggish chronic diseases of bacterial etiology and viral diseases are not accompanied by an increase in the values of segmented cells. Chronic neutrophilia may indicate the development of oncological processes.