The formed elements of blood perform the basic functions of liquid connective tissue. In general, there are three main types of these structures.
- Leukocytes. They perform the task of protecting the body. These are immune cells, they work as protectors.
- Platelets. Red records. The main function is to create a plug that covers the wound surfaces. To prevent the development of massive, life-threatening bleeding. There are other tasks as well. But they are secondary.
- Red blood cells. Red bodies. Within the framework of the topic under consideration, they play a special role. They act as transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Responsible for normal cellular respiration and removal of processed products.
Hematocrit is an indicator that is calculated as the ratio of the number of red blood cells to the total mass of plasma.
Sometimes other shaped cells are used for calculations, but no large deviation in levels is observed. Since over 90% of the structures are red bodies.
If the hematocrit is elevated, this means that the number of red blood cells has increased relative to the plasma volume. The condition is not normal and usually accompanies various pathological processes. Which ones exactly?
Methods of determination and norm
Red blood cell volume (hematocrit) is the total number of white blood cells and red blood cells in the blood plasma, expressed as a percentage. The indicator takes into account all formed elements, but red blood cells have diagnostic value. In simple terms, the hematocrit determines the viscosity of the blood. In the study protocol it is designated by the following abbreviation – HCT.
The research sample is capillary or venous blood. The biomaterial taken for research is placed in a graduated glass tube and centrifuged in the laboratory. After separating the blood components, the results are calculated using the measuring scale of the test tube.
The normal value for adults is:
- formed elements – 45%;
- blood plasma – 65%.
If hematocrit is examined in children, the norm depends on age and presents the following picture:
- in infants – 56%;
- from the 5th day of life to a month – 53-45%;
- from one to 5 years this figure varies from 35 to 37%;
- at the age of 10 years –39%;
- in adolescents it is 47%.
The deviation of the hematocrit number indicates the degree of blood concentration.
What to do if a child has a low hematocrit?
Many parents are faced with the fact that their child has a low hematocrit, and do not know what it is and what to do about it.
Hematocrit number (hematocrit) is a value characterizing the ratio of the number of red blood cells to the volume of blood plasma (its liquid part).
In adults this value is constant, but in children it changes with age or under the influence of various factors. Hematocrit is determined by centrifuging the blood taken for analysis.
Normal hematocrit values depending on age are shown in the table :
| Age | Index |
| Newborn | 33-63% |
| Infancy | 34-44% |
| Year-5 years | 32-41% |
| 5-12 years | 32-42% |
| 12-17 years old | 34-45% |
If the value is lower than specified, the hematocrit is considered insufficient.
This indicates the influence of various factors: hormonal changes, pathologies, etc.
When is the analysis performed?
A blood test for hematocrit is practiced to clarify the following diseases:
- Anemia (a reduced number of red cells, hemoglobin in the child’s blood is confirmed by a reduced hematocrit);
- Polycythemia (a high number of red blood cells leads to an increase in the rate);
- When monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of anemia and erythremia;
- When giving a blood transfusion during blood loss or when other treatment is recommended;
- Determining the degree of dehydration of the baby.
It is considered the most significant indicator in diagnosing anemia.
Increased hematocrit
The hematocrit is increased when the content of formed blood cells exceeds the normative value or the plasma volume decreases. During the neonatal period during long labor, the child’s body experiences hypoxia. Lack of oxygen activates the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Hypoxia in a newborn baby manifests itself as hyperemia of the skin.
In the first days of life, an increased hematocrit in children is considered normal and does not require treatment.
Dehydration
An increased hematocrit in a child is more common, the main causes of which are dehydration. Dehydration is typical for the following diseases and conditions:
- High body temperature;
- For infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting and diarrhea;
- If you do not comply with the drinking regime;
- During excessive exercise.
A decrease in the volume of water in the body promotes its entry from the blood plasma. This means that the number of red blood cells increases, therefore the hematocrit increases.
Hypoxia
Another reason for increased hematocrit is the activation of the hematopoietic organs during chronic hypoxia. Oxygen deficiency increases the formation of red blood cells by the hematopoietic organs. Activation of erythropoiesis is observed in diseases of the heart, lungs, and while in the mountains.
Diseases
The list of diseases and conditions with an increased volume of formed cells in the blood is:
- Polycythemia (erythremia);
- Body burns;
- Acute blood loss;
- Leukemia;
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- Multiple injuries.
Taking medications (diuretics, glucocorticoids) promotes the formation of new red blood cells.
A child’s hematocrit is increased or decreased: what does a deviation from the norm mean?
A blood test for hematocrit is another important indicator by which doctors determine the child’s health status and the presence of disease processes. The study helps to identify deviations from the norm in the ratio of red blood cells to the amount of plasma, either upward or downward. Minor fluctuations are considered acceptable, but if the balance is significantly disturbed, the doctor, based on the indicators, diagnoses a specific disease.
In addition to standard tests, the level of red blood cells in the child’s blood is checked, which makes it possible to diagnose diseases.
How is a hematocrit test done?
To calculate the hematocrit number, blood taken from a child is sent into a special test tube with divisions marked on its wall, inserted into a centrifuge and processed for an hour and a half. The centrifugation process allows you to separate red blood cells from plasma: heavy elements, including red blood cells, sink to the bottom of the vessel, and the plasma remains at the top.
Visually, the ratio of red blood cells to plasma is determined using a scale on a test tube. Hematology analyzers are used to accurately calculate hematocrit. The resulting Ht indicator expresses the number of red blood cells without assessing their quality, but such information is enough for doctors to accurately make a diagnosis. The Ht value is expressed as a percentage and written as a fraction - liter/liter.
Age norms of hematocrit in children
Dear reader!
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to know how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free!
A general blood test shows the level of hemoglobin, hematocrit and other blood characteristics (we recommend reading: what kind of hemoglobin should a newborn child have?). When assessing the numerical value of red blood cells to determine whether the hematocrit is low or high, doctors rely on their standard value, characteristic of a healthy newborn. In addition, doctors have derived the norm for each age period of childhood, from birth to adulthood.
READ ALSO: why are red blood cells in a child’s blood low? The results of a blood test for hematocrit differ depending on the age of the child READ ALSO: general blood test in children: interpretation and norm
For clarity, we have combined all the numerical indicators of the norm into a separate table, which looks like this:
| Child's age | Standard indicators in % |
| Newborns (1–28 days) | 44–62 |
| From 1 month of age to 3 months | 32-44 |
| from 6 months to 1 year | 36-44 |
| 2–6 years | 36–40 |
| 6–12 years | 37–44 |
| 12–18 years old, boys | 37–48 |
| 12–18 years old, girls | 36–44 |
What does deviation from the norm look like?
Experts consider deviations from the norm in the form of a decrease or increase as a sign of a painful pathology or physiological characteristics of the child. High Ht indicates an increased number of formed elements, which make the blood viscous and thick. Having blood in this state provokes the formation of blood clots. However, exceeding the norm by 10-12% in infants and children under one year old is considered a physiological factor that does not cause concern. The picture looks alarming if the hematocrit is increased in a baby after one year.
In babies under one year of age, deviations from the normal Ht are most common, and this is not a sign of disease
The hematocrit is reduced - this means that the volume of blood cells has decreased, and they are responsible for supplying nutrients and oxygen to the organs. There is a violation of the acid-base balance, leading to oxygen starvation of the cells, which negatively affects the general condition of the baby. Weakness appears, the heartbeat quickens, the skin becomes pale, and there is shortness of breath.
Why does hematocrit increase?
A marked increase in Ht is directly related to hyperproduction in the bone marrow (an increase in the number or size of red blood cells). The reason for the increased concentration of cells lies in the area of pathological changes occurring in the body of a small patient. However, the process does not always occur due to pathological disorders in the body.
Main factors of increase
We will necessarily increase Ht in case of disease processes that affect the growth of the number and size of red blood cells. The main factors for high hematocrit in children can be:
- True and redistributive erythrocytosis.
- Excessive reproduction of red blood cells or erythremia (Vaquez disease, polycythemia). It manifests itself as uncomfortable tingling in the fingers and toes, heaviness in the head, sudden redness of the skin, and cardialgia. Similar symptoms accompany diseases that cause an increase in the size of red blood cells.
- Compensatory reaction of the cardiovascular system to certain factors: pulmonary insufficiency, being at high altitude, kidney pathology, “blue” heart defects.
An increase in hematocrit may be associated with serious diseases, including heart disease
Relative reasons
Incoming processes can provoke an increase in the Ht level. Doctors include these:
- frequent bouts of vomiting;
- profuse diarrhea, causing blood thickening;
- intestinal obstruction, in which fluid moves into it;
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- peritonitis;
- hereditary and acquired kidney diseases;
- pathology formed in the respiratory organs;
- leukemia (more details in the article: causes of leukemia in children);
- burns and injuries;
- erythremia;
- asymptomatic oxygen starvation;
- long-term use of certain medications (for example, glucocorticosteroids).
What affects the decrease in Ht?
A decrease in hematocrit is recorded when its level is clearly low, that is, it drops to 25%. Having discovered that the hematocrit is reduced, the doctor prescribes an additional examination for the small patient to determine the cause.
Anemia is the most common cause of low hematocrit in a child
As a rule, a decrease in Ht is a consequence of the accumulation of excess fluid, due to which the blood thins and the percentage level of red blood cells and plasma changes (overhydration), and hemoglobin decreases (see also: how to treat high hemoglobin in a child?). The cause may be hyperproteinemia (excessive concentration of proteins). Such changes are caused by:
READ ALSO: how to effectively increase hemoglobin in a 2-year-old child?
- Severe blood loss.
- Violation of the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow towards a decrease in their number or size.
- Hereditary or acquired hemolytic anemia, typhoid fever, malaria, hemolytic poisons, in which rapid destruction of red blood cells occurs.
- Intravenous administration of large amounts of fluid for impaired renal function, leading to an increase in blood volume.
- Various types of anemia.
- Overhydration - blood thinning due to disturbances in the excretory system, insufficient blood circulation, water intoxication.
- Increased protein levels in the blood (hyperproteinemia). Occurs with frequent vomiting, acute infections, diarrhea, paraproteinemic hemoblastoses, Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma.
Anemia is a common cause of decreased hematocrit. The child needs medical supervision and the establishment of a proper diet. The doctor may suggest taking medications that increase Ht.
Why is a false test result possible?
If the doctor suspects that the test result is incorrect, the child will have to donate blood again to obtain reliable information.
Some factors that arise at the time of blood sampling can distort the test result, showing an increase or decrease in hematocrit. For example, if blood sampling is done after severe blood loss, or before it, an intravenous infusion of a drug that thins the blood was given. A false indicator will also be obtained when taking an analysis from a child who has been in a supine position for a long time. The Ht level will also be lower when the vein has been compressed with a tourniquet for a long time. If the doctor has doubts, a repeat test is prescribed.
It should also be taken into account that the hematocrit indicator does not serve as the basis for establishing a diagnosis; it only warns that there is a pathology in the child’s body or there is a risk of developing any disease. The final verdict of the doctor is announced only after studying all the tests, and in the case of hematocrit, its relationship with hemoglobin level is taken into account. If a decrease or increase in hematocrit level is detected, parents should conduct a thorough examination of the baby in order to begin treatment on time.
READ IN DETAIL: hemoglobin norm in children by age with table
vseprorebenka.ru
Low hematocrit
A low hematocrit (less than 20%) indicates:
- a decrease in the number of red blood cells, due to their insufficient formation or reduction in cell shape;
- hemolysis of red blood cells;
- plasma dilution.
Blood diseases
The cause of low hematocrit is impaired erythropoiesis (formation of red cells). It is observed in the following diseases:
- Anemia (iron deficiency, Addison-Beermer, B12 (folate) deficiency, aplastic);
- Leukemia;
- After taking cytostatics and antitumor therapy;
- Significant blood loss (during the postoperative period, injuries).
Hematocrit is reduced during intense hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells):
- For hemolytic anemia (hereditary and acquired);
- For infectious diseases.
Kidney diseases
There is a decrease in hematocrit in the following conditions:
- Hematocrit is reduced during large volume intravenous fluid administration to children with kidney disease. The increased plasma volume disrupts the normal blood ratio and reduces the indicator;
- With overhydration, when the number of red cells remains the same, and the volume of fluid increases. This condition is observed in cases of circulatory failure and disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system.
Hyperproteinemia
The accumulation of proteins in the blood is observed during infection, vomiting, diarrhea, malignant formation of blood cells, cancer of the lymph nodes (Hodgkin's disease). Most often, the accumulation of proteins in babies is observed when artificially feeding goat or cow milk. The protein content in these products is higher than in breast milk. To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to adjust the baby’s diet.
What does this mean for children's health?
The importance of red blood cells (erythrocytes) for health is very great. The shape of the red blood cell resembles a biconcave disk, which has the ability to move through the smallest capillaries. One third of the red cell is filled with hemoglobin, consisting of protein and ferrous iron. It is a transporter for the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Hemoglobin from the lungs carries oxygen to the body's tissues. On the way back, it returns carbon dioxide to the respiratory organs.
When the hematocrit deviates from normal by more than 10%:
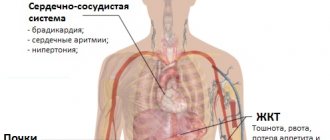
- Low hematocrit leads to oxygen deficiency in the body. Red blood cells carry amino acids and lipids to cells, providing them with nutrition. Lack of oxygen in a child leads to functional disorders of internal organs, and the brain suffers.
- An increased hematocrit in the blood of children disrupts the blood supply to internal organs. A decrease in plasma volume makes the blood viscous, movement through the vessels is difficult and is fraught with the formation of clots that disrupt blood flow through small capillaries.
Blood test indicators in children
Modern laboratories are equipped with special innovative equipment that facilitates the work of a specialist. The material to be tested is inserted into the device, and within a minute the device produces a result. After this, the blood test in children is rechecked by a laboratory assistant. Before issuing a decryption, the specialist must make sure that the device has not made an error.
The following indicators are analyzed:
- hemoglobin;
- reticulocytes;
- red blood cells;
- leukocytes;
- ESR;
- monocytes;
- lymphocytes;
- basophils;
- platelets;
- segmented;
- eosinophils;
- stabs and so on.
Hemoglobin in the blood
This is a complex protein found in red blood cells. The main task of this substance is the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. During the study, hemoglobin is detected in a general blood test. To be more precise, the amount of g of this protein in 1 liter of heme liquid is calculated. The rules are:
- newborns – 138-220;
- 1-12 months – 99-138;
- 1-6 years – 109-144;
- 6-12 years – 114-148;
- over 12 years old – 114-150.
When the hemoglobin level is higher than normal, this indicates that the baby is dehydrated, caused by severe vomiting, diarrhea, or pathology in the cardiovascular or excretory system. Medical attention is needed immediately. A low value is also dangerous. It is accompanied by anemia, poor nutrition, leukemia or other hematological diseases.
Blood test in a child - ESR
This indicator indicates the rate of red cell sedimentation. In a healthy child (this also applies to adults), red blood cells have a negative charge, so they repel each other. A protein present in the blood plasma, such as fibrinogen, promotes the clumping of red cells. Such red blood cells settle faster than healthy ones. The presence of protein indicates inflammation or other pathology. ESR in a general blood test helps to “see” such a deviation. The standards are as follows (mm/hour):
- newborns – 0.1-2.0;
- 1-12 months – 2.0-12.0;
- from 1 year and older – 2.0-10.0.
If the indicator is below normal, this indicates the following pathological conditions:
- viral hepatitis;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- prolonged vomiting;
- circulatory failure.
With an increased ESR value, the following pathologies may occur in the child’s body:
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- infectious diseases;
- allergy;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of a malignant formation.
Red blood cells in a general blood test
The study determines not only the volume of red cells, but also their width of distribution (the difference between the largest and smallest cells is revealed). When conducting a blood test for children under one year old, the season is also taken into account. So, during hot periods, babies drink a lot of liquids, which is why anisocytosis is possible. However, this phenomenon is not considered a pathological condition. When a blood test is performed - interpretation in children, the norm is as follows (x10 to the 12th power of cells per liter of heme fluid):
- newborns – 4.41-6.61;
- 1-12 months – 3.61-4.91;
- 1-6 years – 3.51-4.51;
- 6-12 years – 3.51-4.71;
- over 12 years old – 3.61-5.12.
The following factors that reduce the volume of red blood cells are considered dangerous:
- failure of bone marrow development;
- anemia;
- parasitic diseases;
- monotonous, meager food.
If a general blood test in children shows a high level of red blood cells, this may be caused by the following reasons:
- pulmonary dysfunction;
- heart problems;
- poisoning;
- renal artery stenosis.
Platelets in a general blood test
The task of these cells is to create a platelet aggregate in case of vascular damage and accelerate plasma coagulation. A clinical blood test of a child helps determine the quantitative value of this indicator. The norms are as follows (x10 to the 9th power of cells per liter of heme fluid):
- from birth to 6 years – 180.5-400.0;
- 6-12 years – 157.0-380.0;
- over 12 years old – 157.0-390.0.
If the comparison reveals the growth of these cells, this often indicates the following problems:
- severe blood loss;
- leukemia;
- tuberculosis;
- cancer;
- spleen dysfunction.
Thrombocytopenia can be caused by the following reasons:
- the baby was born premature;
- the child has hemophilia;
- the baby has aplastic anemia;
- with DIC syndrome.
Hematocrit in general blood test
This is an indicator that indicates the percentage of red cells in the total volume of heme. Blood test norms in children vary depending on age:
- in newborns – from 43% to 63%;
- baby up to one year – from 36% to 44%;
- 2-10 years – from 37% to 44%.
A high rate is most often caused by the following reasons:
- dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- intestinal obstruction;
- burns;
- blood leukemia;
- injuries.
A low value indicates the following problems:
- heavy bleeding;
- large volume of blood;
- increased protein content in heme fluid.
Leukocytes in a general blood test
These cells take part in the creation of cellular and humoral immunity. When analyzing a child’s blood – lymphocytes, they take into account the fact that the norm varies depending on age (x10 to the 9th power of cells per liter of heme fluid):
- newborns – 7.21-18.51;
- 1-12 months – 6.15-12.0;
- 1-6 years – 5.1-12.0;
- 6-12 years – 4.4-10.0;
- over 12 years old – 4.3-9.5.
An increase in the indicator indicates the following problems:
- failure in the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases;
- internal bleeding;
- parasitic diseases;
- allergy.
A reduced value is provoked by the following factors:
- bacterial infections;
- bone marrow dysfunction;
- lack of zinc, selenium, iodine in the body.
What is a color index in a blood test?
“Calculated” only when the research is done manually. The blood color index is a value indicating the hemoglobin content in red blood cells:
- hypochromia – there is practically no hemoglobin;
- normochromia – the value of the indicator is ideal;
- hyperchromia - excessive saturation with hemoglobin.
What to do?
Hematocrit in the blood does not give a complete picture of the disease in the absence of other indicators. To make an accurate diagnosis, the pediatrician considers the hematocrit number in conjunction with other analysis points (erythrocytes, leukocytes, hemoglobin, ESR, leukocyte formula). A deviation of the hematocrit from the norm should be a signal for additional examination of the child.
What does increased and decreased hematocrit mean in children?
The materials are published for informational purposes only and are not a prescription for treatment! We recommend that you consult a hematologist at your medical institution!
Co-authors: Natalya Viktorovna Markovets, hematologist
There is no doubt that the safety and health of the child is a priority for all parents. But not everyone has heard about hematocrit and knows what this blood indicator means. Meanwhile, back at the beginning of the 20th century, the great healer Metropolitan Seraphim Chichagov said that all diseases come from poor circulation and poor blood quality.
Normal hematocrit indicators
The percentage of hematocrit in laboratories equipped with modern technology is determined automatically. And some 20 years ago, to carry out this analysis, centrifuges and glass tubes with a graduated scale were required (the GM level was calculated using it).
Hypoxia is one of the reasons for deviations in hematocrit in newborns
Back in 1997, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Alexander Moiseevich Vein defined standards for GM indicators in healthy children. This norm directly depends on the age of the child:
- Newborns - 51±9%;
- 1 month - 43±12%;
- 6 months - 35±6%;
- 1 year - 36±3%;
- From 2 to 6 years - 37±3%;
- From 6 to 12 years - 40±5%;
- From 12 to 18 years - 42±6%.
Hematocrit is the percentage of space occupied by cells to the total volume of blood. Pregnancy increases the body's need for blood. By the end of the first month, the volume of moving blood increases noticeably due to plasma, but the number of cells remains unchanged. Their percentage falls, so the hematocrit during pregnancy is lowered.
At-risk groups
A child's hematocrit is almost always at the same level and changes slightly only with age, during the growth of the child's body. But there are groups of children in whom the hemotocrit number may change pathologically. Pediatricians classify such children as a risk group, and they are registered at the dispensary.
The risk group includes:
- Newborns born with a large body weight and infants who pathologically quickly gain weight.
- Children who eat poorly or suffer from metabolic disorders.
- Children with a tendency to develop iron deficiency anemia.
- Newborns with congenital abnormalities of the liver and kidneys.
These children need careful monitoring and exclusion of all provoking factors. If the underlying disease can be cured, the erythrocyte composition will soon stabilize without specific treatment.
Is a low hematocrit level dangerous? Regardless of the cause that caused it, this condition is dangerous because it disrupts the supply of oxygen to the cells of the child’s body. If this condition persists for a long time, it will negatively affect the growth and development of children.
What is hematocrit?
Hematocrit is a blood indicator that reflects the ratio of blood plasma and blood cells. Given the fact that most of our blood contains red blood cells, it is sometimes believed that hematocrit is the ratio between plasma and red blood cells.
In blood tests, hematocrit is referred to as HCT.
How is the indicator calculated?
The indicator is calculated in several ways.
The first is using a centrifuge.
Blood is poured into a test tube in which the blood will not clot due to the introduction of special substances.
There are ways to collect blood directly into a centrifuge tube.
The tube with blood is centrifuged for an hour. It is worth noting that the test tube has a graduated scale, which indicates the volume of formed elements and blood plasma.
The second way to determine hematocrit is using a hematology analyzer.
The calculation is performed according to a certain formula, for which it is necessary to know the concentration of red blood cells in the blood, their average volume.
HCT = red blood cell count * average red blood cell volume / 10.
The result is expressed as a percentage.
An indicator such as the average erythrocyte volume or MCV is also calculated in the hematology analyzer.
Elevated pediatric hematocrit
There are two main mechanisms, as a result of which increased GM is observed. The first is due to the fact that the number of formed elements increases relative to the plasma. And the second is when the number of plasma decreases relative to the formed elements. Moreover, the signs of these mechanisms will be different.
Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) - this diagnosis is made as a result of the first mechanism. The prerequisites for its diagnosis are: respiratory tract diseases, stress conditions, lack of water or oxygen during the birth period. Under such unfavorable conditions, the body increases the production of red blood cells to increase hemoglobin.
Redness of the skin is a symptom of hypoxia. This is usually observed in newborns. This condition in infants goes away with adaptation after the intrauterine period. If a child’s hematocrit is increased due to hypoxia, then this cannot be considered a pathology and such children do not need treatment.
Blood diseases (coagulation abnormality) - this diagnosis is associated with increased blood thickness and clotting. In this case, as with hypoxia, the first mechanism of increasing GM operates.
The diagnosis of dehydration (dehydration of the body) is made due to the action of the second mechanism. The main causes of dehydration are all kinds of infectious diseases (mainly associated with the gastrointestinal tract) and burns of varying degrees of severity.
Dehydration of the body should not be allowed, as this leads to increased hematocrit
Manifestation of symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease:
- pale skin;
- dry skin;
- constant feeling of thirst.
Important! If a decrease in body weight is recorded (more than 3%), then it is necessary to immediately go to the doctor, since this is already a cause that threatens the child’s life.
For mild dehydration, measures to stabilize hematocrit can be taken at home. Their essence lies in taking, according to certain rules, electrolyte solutions. The patient should be given drinks frequently, but in small volumes: 2–3 sips every 15–20 minutes throughout the day. In addition, you need to carefully monitor your child's urination. Fluid losses should not exceed 80% of consumed. In a clinical setting, infusion therapy is performed (drips are placed) to restore fluid balance.
Electrolyte solution for children
Today, many people suffer from the problem of low hemoglobin from time to time. Long-term imbalance can lead to serious complications, so it is important to detect the cause of the imbalance as early as possible and take appropriate measures.
Decreased hematocrit level
The mechanisms for the implementation of a decreased hematocrit are polar to the mechanisms of an increased one. In the first case, the number of formed elements decreases against the background of a normal amount of plasma. And the second is to increase the volume of plasma with a normal number of formed elements.
Overhydration (triggered by the first mechanism) is a disease inverse to dehydration associated with excess fluid in the body, usually due to malfunction of the kidneys. When a child’s hematocrit is reduced due to hyperhydration, symptoms manifest themselves in the form of edema. They can be visualized on the baby's face and limbs.
Important. In cases where swelling is not clearly expressed, treatment can be carried out at home: give the child various diuretics for 7–14 days. As with dehydration, control the volume of urination.
Pale skin with anemia may indicate reduced GM
Anemia is a disease also associated with the work of the first mechanism. There are different types of anemia. The most common are:
- Deficient - associated with a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body. To restore balance, it is recommended to take a course of multivitamins, and, as prescribed by a doctor, vitamins B12, iron, and folic acid preparations.
- Posthemorrhagic - not typical for children, occurs due to bleeding against the background of emerging complications in the postoperative period. It is treated exclusively in inpatient settings.
- Aplastic - especially characteristic of childhood. The causes of development are associated with improper functioning of the bone marrow. It is diagnosed during examinations by a pediatrician based on the results of a general blood test.
- Hyperproteinemia is a disease triggered by the second mechanism, in which low GM is provoked by feeding children goat or cow milk. The amount of protein in this milk is significantly greater than in breast milk. The main recommendation for stabilizing GM in such cases is to transfer the baby to breastfeeding or milk formulas with a reduced protein content.
If your child exhibits the above symptoms, you should contact your pediatrician. After taking a general blood test and making a diagnosis, he will prescribe treatment.
Why is a low hematocrit dangerous?
Red blood cells supply nutrients and oxygen to organs. If their level drops, the organs begin to experience oxygen starvation, in addition, this leads to an imbalance in the acid-base balance.
External signs of low hematocrit:
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- a person gets tired quickly;
- the skin becomes pale.
Important: a decreased hematocrit, like an increased one, is not a reason to immediately start treatment. These indicators tell the specialist in which direction to look for a possible problem, and only if additional tests reveal it, only then treatment is prescribed.
If a child’s blood test shows a low or high hematocrit level, there is no need to panic right away. This is not necessarily evidence of a dangerous disease. As we have already noted, a deviation from the norm can be caused by temporary factors, and in children under one year of age, a deviation of hematocrit from the norm within 10 percent is generally a common occurrence and is caused by normal physiological processes. When the child reaches the age of 12 months, the indicator should return to normal, but if even then the hematocrit number continues to remain above or below normal, additional examination should be carried out.
Timely identification of a possible problem contributes to effective treatment and will help the specialist choose the right course of preventive measures. Regular medical examination will help monitor your health, because it is always better to find out about a possible problem at the time of its inception than to deal with the consequences.
Let's figure out what this means if the hematocrit in a child's blood is low, and when this indicator should be measured.
The composition of the blood and the number of formed elements respond to the influence of external and internal factors. Even minor pathological disorders lead to changes in laboratory blood parameters.
Measuring the hematocrit value will allow diagnosing anemia at an early stage, when the disease does not manifest itself in the form of clinical symptoms. A decrease in the indicator will also indicate an increase in total protein levels or overhydration.
The hematocrit value in medicine is defined by two concepts:
- total volume of red blood cells in blood plasma;
- the ratio of the total volume of all blood cells to the total volume of blood.
It should be noted that the equivalent use of these two concepts is permissible, since 99% of the total number of blood cells are directly erythrocytes. It is known that up to 48% of the blood is cells (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets), and 65% is plasma.
The method for determining the indicator is simple: the collected venous blood is placed in a special measuring tube with graduation. The tube with the biomaterial is centrifuged. As a result, the formed elements end up in the sediment, the plasma on top. The total volume of deposited elements is an indicator of hematocrit.
Currently, the process is automated and does not have a large error due to the subjective assessment of the laboratory assistant. However, the risk of obtaining inaccurate results cannot be excluded. This is possible at the stage of taking biomaterial. If the baby’s vein was tied with a tourniquet for a long time or hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) occurred in the test tube, then the obtained indicators are unreliable. The biomaterial should be taken again.
A repeat study is also necessary if results are obtained that deviate slightly from the norm or are at the lower limit of the norm. It is necessary to understand precisely whether such a deviation was the result of the influence of temporary external factors or a sign of a disease.
When should you check your hematocrit?
The hematocrit value is not determined separately from other indicators of the general blood test. Since this data is not enough even for a screening examination. The value of hematocrit is important to consider when suspecting anemia, assessing the degree of dehydration, assessing the severity of hypoxia, kidney disease (polycystic disease, hydronephrosis, neoplasms), suspecting an increased amount of proteins in the blood, as well as excess water content in the child’s body.
What does it mean to have a low (below normal) hematocrit in a child’s blood?
A general blood test is performed to determine the child's health status. This test is performed to monitor blood flow and eliminate the possibility of changes in blood parameters. A child’s hematocrit can be reduced for a variety of reasons; its design depends on age, gender and some other physiological characteristics of the body. If a deviation has been identified in children, then it is necessary to respond to the changes in a timely manner.
Causes
Parents are wondering: if a child’s hematocrit is low, what does this mean? To answer, you need to consider the reasons for the decrease in this indicator:
- Bleeding. The death of red blood cells can be caused by both internal and external bleeding due to injury or disease (for example, cancer, urolithiasis, hemophilia, etc.).
- Fanatical adherence to a diet without a doctor’s recommendation. This is especially true for teenage girls and children from vegetarian families.
- Prolonged physical inactivity (being without movement), for example, due to bed rest.
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
- Genetic mutations (sickle anemia).
- Increased protein in the blood caused by cancer.
- Fluid retention in the body due to kidney disease, infections, infusion therapy, etc.
Children often have to have blood tests done. This is very important, since the cellular composition of the blood at this age is constant and its disturbances during the development of diseases play an important diagnostic role. The concentration of red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets in the blood is: the norm in children is established by specialists.
The norm and what is a deviation
Immediately after the birth of the child, his analyzes are studied in detail. This is done in order to exclude the possibility of congenital pathologies. Do not forget that a child’s blood composition at 3 months cannot be the same as that of an adult.
Over time, the child’s body begins to adapt to the world around it, and the composition of cells begins to change. For a newborn, the hematocrit should be 44-62%, which is a higher value compared to an adult.
During the first 8-10 years, the indicator can be low or high, 37-44% is considered the norm. Changes begin as the child enters puberty. During this period, it is recommended to undergo periodic tests to constantly monitor the composition of the blood, since it should not be too thick.
Children under one year old undergo periodic checks. This is due to the fact that changes can occur almost every week. Afterwards, blood donation is performed every few years. When breastfeeding, the baby's body is also influenced by the condition of the mother.
A decrease in level to 25% indicates that the blood is too thin or blood loss is occurring in the body. To determine the reasons, repeated tests are carried out.
Organization of normalization of hematocrit in a child’s body
In a situation where a child’s hematocrit is low as a result of anemia, it is important to normalize the diet - consume more apples, nuts, liver, eggs, and meat. Food should contain a lot of iron. It is good for a child's body to consume hematogen. Special medications, vitamins containing iron, which are prescribed by a doctor, can completely overcome anemia. Sometimes they are administered intravenously, taken in solutions or in tablets.
Don't panic. It is best to independently study all the results of clinical blood tests, because the information will not be a final diagnosis. If the hematocrit does not correspond to the norm, then this does not indicate the development of a deadly disease in the body. The volume of red blood cells and their ratio to plasma is only a general clinical picture that does not directly indicate the disease. Establishing hematocrit indicators and their correct interpretation can only be carried out by specialists who take into account all the nuances of conducting a hematological examination.
In general, the treatment process involves eliminating problems that have caused a low hematocrit in an infant or an older child, or where its indicators have increased. In accordance with the specification of the pathology, the doctor prescribes medications to restore blood.
It is important!
Low hematocrit is diagnosed somewhat less frequently than high levels of this value. People who smoke are often at risk, since their body lacks oxygen, and therefore red blood cells are produced in large quantities. Climbers can also be included here, because at altitude their bodies also develop a lack of oxygen.
Among the indicators determined during a child’s blood test, there are some that are not entirely clear to parents. One of them can be called hematocrit, which in the analysis is denoted by the abbreviation Htc.
Why is the level lowered?
A decrease in hematocrit in a child can occur for a variety of reasons. The most common are the following:
- Disorders occurring in the human bone marrow.
- Increased amount of proteins in the blood.
- Blood density is too thin.
- Anemia of varying complexity and origin.
- Various diseases that cause the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Various infectious diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Various liver problems.
Prolonged bed rest can also cause a drop in this indicator. An insufficient level of physical activity is compensated by a proper diet. When conducting a blood test, attention is often paid to how the hematocrit level correlates with hemoglobin. A false result may be obtained if blood is collected incorrectly.
Anemia
Infants and children of other ages may develop anemia. The features of this problem are the following:
- Anemia means that hemoglobin is lower than normal. This moment causes a significant decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- Hemoglobin is an important iron-containing protein, which means it is responsible for transporting oxygen to the body's tissues.
There are many reasons for this problem. Symptoms may include dry and pale skin, and a lack of sufficient protein causes the digestive system to malfunction.
Overhydration
The hematocrit in the blood is also reduced in the case of an excess amount of water, which may be contained in the entire body or individual parts. Overhydration is associated with the following symptoms:
- Clinical symptoms include swelling of the extremities and excess fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
- Some conditions in this condition can be life-threatening for the child. The disease in question causes heart rhythm disturbances and disruption of the digestive system.
In some cases, with overhydration, redness of the skin appears, body temperature rises, and sleep is disturbed. To determine the cause of such symptoms, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination.
Hyperproteinemia
A condition in which the concentration of protein in the blood increases significantly is called hyperproteinemia. Such a symptom may indicate a variety of diseases developing in the child.
The indicator in question is checked by donating blood and performing a general analysis. A change in the amount of hematocrit in the blood indicates that there is less or more protein in the blood.
Reasons for the decline in indicators
In accordance with the definition, it must be shown that the child develops when the concentration of red blood cells in the blood decreases. This number will be considered reduced at 20 - 25%, but to clarify the diagnosis you will still need to conduct a thorough examination and identify the provocateurs of the decrease in hematocrit.
The following problems contribute to the change in indicators:
- Slow formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
- High rate of breakdown of red blood cells in the blood.
- A large volume of blood in a child.
- High concentration of proteins in the blood.
- The blood is too thin.
- Acute bleeding.
- Anemia.
It is important!
It should be noted that a separately considered indicator of a decrease in hematocrit cannot accurately indicate the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the body. To obtain an accurate picture, these indicators are combined with the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. Still, making a diagnosis requires a thorough study and identification of the factors that provoked the problem.
If the indicators exceed the norm, then there is reason to talk about the development of a threat of increasing the concentration of red blood cells in the blood. This condition requires a separate diagnosis. In addition, an increased hematocrit can occur with erythremia, which is considered a very serious pathology. During its development, red blood cells quickly spread to the most important site of blood formation - in the bone marrow. Also, an increase in the hematocrit norm is observed with hidden or asymptomatic oxygen starvation in the body, with polycystic kidney disease or the presence of other neoplasms in them. Peritonitis, leukemia, thrombosis, burns, diabetes and even the usual heavy sweating can be triggered by high hematocrit values.
Hematocrit is elevated when the concentration of red blood cells increases, which correlates with the following pathologies:
- The presence of neoplasms in the kidneys.
- Development of polycystic disease or hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys.
- Oxygen starvation of varying degrees of severity.
- Blood leukemia.
- Receiving severe burn wounds.
- Erythremia.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
- Peritonitis.
Is it dangerous to reduce the indicator?
Conducted studies indicate that a slight decrease in hematocrit concentration is not dangerous to the child’s health. This is due to the change in the indicator depending on the regime, since insufficient water causes a decrease in the amount of hematocrit in the blood.
Any change in the indicator is a reason for parents to contact a specialist for help. There is no need to panic, but you should not delay the examination. This is due to the fact that some diseases can cause changes in blood composition and lead to the development of other pathologies. A reduced hematocrit indicates a decrease in hemoglobin and problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
What to do
If the composition changes, you should immediately contact a specialist. Only qualified help will solve basic health problems. The most widely used treatment methods are:
- If signs of anemia appear and an appropriate diagnosis is made, the specialist prescribes a change in diet. It is recommended to include a large amount of nuts, lean meat and apples in your diet. A normal diet will allow the body to develop, maintain immunity, the task of which is related to protecting the child from various infections. Only a professional doctor can develop a diet correctly.
- A drug called Hematogen. Its purpose is to improve the bleeding process; it contains useful microelements that the body requires. It is forbidden to give a child a large amount of this drug, as this may cause an increase in the concentration of iron in the blood.
- In some cases, liquid medications with a high concentration of iron are prescribed. It is not recommended to give them to a child without a doctor's prescription.
Too high an NST rate also becomes the reason why fortified foods and various medications are prescribed. In most cases, an increase in the amount of fluid consumed per day is prescribed.
If parents pay timely attention to the composition of the blood, the child will develop in accordance with his age. Minor changes in composition should be verified by performing a general analysis.
Materials used in the article:
https://moyakrov.ru/normy-i-patologii/gematokrit/norma-gematokrita-u-detey/
https://medicalok.ru/analiz-krovi/gematokrit-ponizhen-u-rebenka.html
https://gipertonia03.ru/davlenie-120-na-90-chto-eto-znachit.html
Post Views: 55
How to bring the indicators back to normal?
If the hematocrit is low or high, then you should definitely pay attention to this. First of all, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of this or that deviation and make a diagnosis of the disease.
Treatment consists of eliminating exactly the problem that caused the deviation from the norm. The following treatment methods are currently used:
- If the cause is anemia, you need to reconsider your diet. It is recommended to eat more apples, nuts, lean meat, and food should contain a large amount of iron.
- The drug Hematogen. This is an excellent tool for improving the process of hematopoiesis, containing trace elements, nutrients and other useful substances.
- Another important rule is that you should take liquid dosage forms of iron supplements for children, but you should not give them double doses of such medications, even if a previous dose of the medication was missed.
High levels of HCT in the blood of a child are also considered abnormal, and therefore are treated with fortified foods and medications that normalize the level of red blood cells. Increased fluid intake is also prescribed.
Parents need to make sure that all indicators are normal, and that the baby develops in accordance with his age, without experiencing any health problems.
The above figures are given as percentages, but they can also be written in the ratio of liters to liters, and then it will not look like, for example, 43%, but like 0.43/1, that is, there are 0.43 liters of red blood cells in 1 liter of blood. They can only write it in numbers - 43, or 0.43.
In particular, you should not donate blood for testing if:
- the day before there was strong physical activity;
- the day before there were emotional upheavals and stress;
- after blood loss (in this case, the analysis will show a reduced hematocrit, but it will not be clear whether this indicator is caused by blood loss or signals other health problems).
Remember that the blood test is done for specialists, not for you, so there is no need to make independent decisions and self-medicate, especially when we are talking about children. Follow your doctor's instructions strictly.
With a low hematocrit, doctors recommend not only hematogen, but also a special diet with a large amount of iron-rich foods, in particular:
- nuts;
- apples;
- liver;
- meat.
The decision about the diet should be made taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient, because a person may have other problems, not just a low hematocrit, and then some useful product will immediately cease to be useful. This is another reason why it is dangerous to self-medicate: you may not take into account all the factors and do nothing to help, and this at best, at worst, will cause harm.