Norm and mechanism of development
Tachycardia is a condition characterized by a deviation in the rhythm of the heartbeat, in which the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle increases. The myocardium is stimulated by special chemicals, catecholamines, the release of which is regulated by the nervous system. Under certain circumstances, a disruption occurs in this process, and the stimulation of cardiomyocytes increases, that is, tachycardia occurs. The rate of heart beats varies depending on age and is presented in the table:
| Age | Norm of blows per minute |
| In the first days of a baby's birth | 140—160 |
| Up to 6 months | 130—140 |
| 6-12 months | 120—130 |
| 1-2 years | 110—120 |
| 2—3 | 105—110 |
| 3—5 | 100—105 |
| 5—8 | 90—100 |
| 8—12 | 80—90 |
| From 12 years old | 60—80 |
Heart rate norms
You can determine that a child has a rapid heartbeat depending on whether the number of heart beats per minute corresponds to the norm for his age.
In the first two days of the year, it should beat at a frequency of 122 to 158 beats per minute. In the future, the rules should be as follows:
- from three to six days from birth - 13 - 167 beats per minute;
- from one to three weeks - 106 - 180 beats per minute;
- from one to two months - 120 - 180 beats per minute;
- from three to five months - 105 - 185 beats per minute;
- from six to eleven months - 110 - 170 beats per minute;
- from one to two years - 90 - 150 beats per minute;
- from three to four years - 70 - 140 beats per minute;
- from five to seven years - 65 - 135 beats per minute;
- from 8 to 11 years - 60 - 130 beats per minute;
- from 12 to 15 years - 60 - 120 beats per minute.
| Age | Norm of blows per minute |
| In the first days of a baby's birth | 140—160 |
| Up to 6 months | 130—140 |
| 6-12 months | 120—130 |
| 1-2 years | 110—120 |
| 2—3 | 105—110 |
| 3—5 | 100—105 |
| 5—8 | 90—100 |
| 8—12 | 80—90 |
| From 12 years old | 60—80 |
In order for your child to feel normal, it is enough to follow the following preventive measures:
- ensure that the child has a normal weight (obesity of any degree is an additional burden on the heart);
- active sports for tachycardia are undesirable, but as a preventive measure for pathology, physical exercise will not be superfluous;
- eliminate or minimize the consumption of caffeine-containing products;
- take care of a healthy diet, limiting the consumption of fatty foods and dishes based on quickly digestible hydrocarbons;
- maintain a calm regime at home and in a preschool (school) educational institution;
- Make sure that your child does not abuse alcohol and smoking.
If these recommendations are followed, attacks of tachyarrhythmias in the child will be minimized.
All athletes, not just children, must monitor their health. The easiest way is to measure your heart rate before and after exercise. In this case, you need to especially pay attention to the frequency of the beats and their rhythm. It is obvious that there is a certain connection between sports activity and the number of heart beats per minute. The higher the load, the faster the heart beats. Calculation formula: (HRmax-NPP)* %HRmax NPP
- HRmax – maximum heart rate according to the Roberges-Landwehr formula. 205.8-(0.685*age).
- %HRmax is the percentage of the maximum heart rate. 50-60% is a warm-up. In untrained people, such a pulse may appear during normal walking. 60-70% is the fat burning zone. At this time, the overall endurance of the body is developed. It is recommended to stay in it most of the time during training.
- 70-80% – aerobic zone or cardio zone. At this time, the stroke volume of the heart increases.
- 80-90% is anaerobic zone. Speed, strength and muscles increase.
- 90-100% is the competition zone. This is the maximum load zone. You shouldn’t let it get to this point, it’s simply unhealthy.
- RPP – resting heart rate. Measured immediately after waking up in the morning. As described above, subject to change.
Tables can be found on the Internet. In athletic children, the pulse is restored 10 minutes after stopping the exercise.
But the most important advice for parents is that parents need to monitor the child’s health. If unusual abnormalities occur, contact your doctor immediately. The child’s body recovers from illness quite easily, so even in serious cases, therapy usually ends in the child’s recovery.
▼We RECOMMEND YOU TO STUDY▼
Reasons for formation
During this period, a person’s problem can be triggered by a stressful situation.
Tachycardia in a child 10 years of age or older most often manifests itself under the influence of stressful situations. Thus, the body tries to protect itself and adapt to unfavorable external stimuli. In children under one year of age, identifying the exact cause of the pathology is quite difficult, since there is a need to exclude many abnormalities in the functioning of the body. Some external factors can trigger the development of the condition. These include:
- physical exercise;
- improper water diet;
- abuse of caffeinated drinks;
- drinking alcohol;
- smoking;
- insect bites;
- therapy with certain medications.
Internal causes of tachycardia in children:
- decrease in hemoglobin concentration in the blood;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- endocarditis;
- circulatory disorders;
- psychosomatic disorders;
- infections;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
Tachycardia in a newborn baby can occur with the slightest actions towards the child, for example, during swaddling. As a rule, this condition goes away on its own and does not require any special measures.
First aid
If an acute attack of palpitations occurs, the child should be given calming heart drops or tablets, which have a quick relaxing effect. You also need to give him a drink of water, put him to bed and try to distract him from the pain, open the window to provide fresh air in the room, calm him down, and possibly call an ambulance. Even if there is one symptom of myocardial dysfunction or a one-time attack of tachycardia, you should consult a cardiologist, since interruptions in heart function in childhood are fraught with serious complications in the future.
Return to contents
Types of pathology
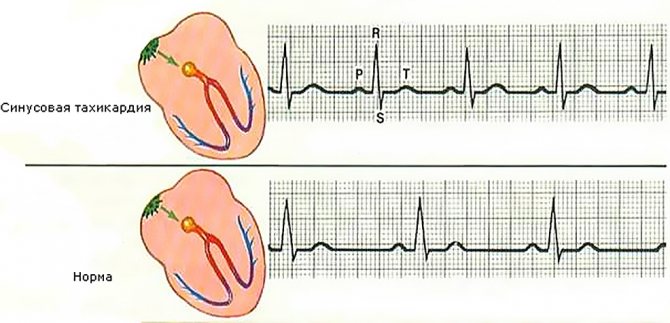
Rapid heartbeat in children is divided into the following types:
- Sinus. This condition occurs when the activity of the sinus node of the heart increases. Attacks of the pathology are short-lived, the heart rate increases from 10 to 60%, depending on the severity of the disease. Sinus tachycardia in a child under one year of age most often develops due to physiological characteristics, but sometimes it can also be a symptom of serious diseases.
- Paroxysmal. The condition occurs suddenly and is quite dangerous for newborns, as it can cause central organ failure. This type of tachycardia is characterized by the occurrence of an impulse that does not stimulate the sinus node. Pathology occurs against the background of myocardial damage or due to the influence of extracardiac abnormalities.
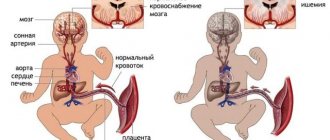
Baby's heart and blood vessels
In newborns, both the heart and blood vessels are different from the organs of adults. The shape of the baby's heart resembles a ball - the width is even slightly greater than the length. As you probably know, the heart consists of four sections - two ventricles and two atria. The right ventricle and left atrium close the pulmonary circulation, the left ventricle and right atrium close the systemic circle. Since it is much more difficult to “push” blood through a large circle, the left ventricle in adults is larger, and the walls are almost twice as large.
“Even the heart of children is located differently from that of adults! Due to the highly raised diaphragm (the baby eats a lot and often, the stomach requires a lot of space), the heart is located higher than that of mom and dad.
Well, the blood vessels of a newborn are also much more elastic than those of adults.
Symptoms of the disorder
Rapid heartbeat in a child has some features of manifestation depending on age. Signs of pathology are presented in the table:
| Age, years | Symptoms |
| From 0 to 12 months | Pale skin |
| Blue fingers and tip of nose | |
| Shortness of breath accompanied by retraction of the subclavian fossa | |
| Protrusion of lips when exhaling | |
| Profuse sweating | |
| Fast pulse | |
| 2-4 years | Lethargy, fatigue |
| Increased heart rate | |
| 6—10 | Gagging |
| Dizziness | |
| Fainting | |
| Bloated veins in the neck | |
| Feeling of fast heartbeat | |
| 10—14 | Aching pain in the heart area, which intensifies with physical activity |
| Low blood pressure | |
| Feeling of an accelerated heartbeat, and then a feeling of the organ freezing | |
| Constant weakness and apathy |
Paroxysmal tachycardia
Paroxysmal tachycardia is characterized by a sharp increase in heart rate. At the same time, the indicators increase quite significantly. The child may experience unpleasant pain in the chest or abdomen, signs of cyanosis, shortness of breath, dizziness, and weakness throughout the body. It is important that the attack passes as suddenly as it began.
Parents need to remember that sinus tachycardia in childhood is much more common than paroxysmal tachycardia.
Arrhythmia is a disease that can persist for many years. At the same time, attacks of tachycardia in chronic form are regularly accompanied by a feeling of suffocation, low blood pressure, nausea, increased sweating, convulsions, chest pain, fainting and dizziness.
A certain difficulty in diagnosis lies in the fact that children are often unable to clearly formulate what exactly is bothering them, describe their symptoms, or complain to their parents about the deterioration of their condition. In this case, it is necessary to suspect the presence of tachycardia or other similar pathologies. Parents can notice that something is wrong with the child by the baby’s loss of appetite, pronounced anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
In this case, you should carefully examine the child, measure his heart rate, and, if necessary, seek help from a doctor.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of “tachycardia” in a child 5 years old or any other age requires research that identifies the cause of the pathological condition. Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- ECG. It will help determine the severity of the disease and determine the presence of other abnormalities in the activity of the heart muscle.
- Echo-KG. Evaluates the functionality of the heart and great vessels, and will also show the congenital anatomical features of the organ.
- Electrophysiological study. Determines the electrophysiological properties of the conduction system of the myocardium, atrium and ventricles.
Sinus tachycardia in a child – what do you need to know?
Sinus tachycardia in a child occurs more often than other types of arrhythmias. It is a consequence of body growth, hormonal changes and immaturity of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
This form of arrhythmia is detected mainly after stress and overload. It is enough for parents to calm the baby down and give him a rest to improve his well-being.
Things are different if the failure manifests itself in a calm state, or is too intense. In such a situation, you will need the help of a specialist.
Features of sinus tachycardia
The coordinated work of the heart contributes to the saturation of all tissues of the body with useful substances. When sinus tachycardia occurs, minor disruptions in hemodynamics (blood flow) occur.
They are not particularly harmful, but over time they can cause various complications (atrial fibrillation, heart attack, cardiac hypertrophy). A similar form of arrhythmia manifests itself as a rapid heartbeat while maintaining the sequence of contractions.
The signal comes from the sinus node (natural pacemaker), which is influenced by external (stress, overwork) and internal (illness, endocrine disruptions) factors.
Classification
Sinus tachycardia in children is divided into certain types according to various criteria. According to the degree of increased heart rate, arrhythmia is classified as follows:
- A mild form of sinus tachycardia in a child is manifested by an increase in contraction frequency up to 20% of the permissible norm.
- Arrhythmias of moderate intensity are characterized by an increase in heart rate by 20-40%.
- A pronounced type of malfunction is manifested by a significant increase in heart rate up to 60% or higher of normal values.
The normal heart rate for each age is different; for example, in infants it is much higher than in adolescents. You can see the acceptable indicators below:
AgeNormal
| From birth to 6 months | 145-165 |
| From 6 to 12 months | 135-140 |
| 1-2 years | 110-125 |
| 2-3 years | 105-115 |
| 3-5 years | 100-110 |
| 5-8 years | 90-105 |
| 8-10 years | 80-95 |
| 10-12 years | 75-80 |
According to its course, sinus tachycardia is of the following types:
- An adequate form manifests itself as a result of exposure to various irritants (diseases, stress, physical activity). Attacks (paroxysms) last only for a certain time.
- An inadequate variety occurs even at rest. Irritating factors only worsen the child’s well-being. Paroxysm of tachycardia may be accompanied by a feeling of palpitations, increasing weakness and lack of air.
Arrhythmias arise due to the influence of various factors; accordingly, they are classified as manifestations of diseases, and not independent pathological processes.
Sinus tachycardia develops not only for harmless reasons, but also under the influence of heart diseases.
It actually does not cause dangerous complications, but due to the myocardium being under constant tension, its structure may begin to change over time, which will lead to various pathologies.
Causes
Sinus arrhythmia can be of physiological or pathological origin. Its second type is also divided into cardiac (heart) and extracardiac (pericardial) forms. In both cases, the heart begins to contract more intensely under the influence of various factors.
The physiological type of failure is a consequence of the following reasons:
- stressful situations;
- physical and psychological overload;
- exposure to elevated temperature;
- excessive consumption of food and water;
- staying in an insufficiently ventilated area;
- altitude sickness caused by decreased partial pressure.
After the influence of the mentioned factors ceases, the attack passes in about 5-10 minutes. The paroxysm occurs in a mild form.
The extracardiac type of heart rhythm disturbance occurs due to the influence of internal factors. Their list is as follows:
- high body temperature;
- decrease in blood sugar concentration;
- anemia (anemia);
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- increased production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland;
- adrenal tumor (pheochromocytoma);
- the effects of certain medications.
Extracardiac attacks are moderate. Rapid heartbeat begins to bother you with any physical and mental overload. This type of failure is typical mainly for girls 9-11 years old.
The cardiac type of failure is closely related to diseases of the cardiovascular system. You can see their list below:
- inflammatory processes (pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis);
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiosclerosis;
- dystrophic processes;
- ischemic disease;
- decreased or increased concentrations of potassium and magnesium.
The attack usually occurs in a pronounced form even without any special influence of external factors. The child must be shown to a doctor.
During school years, the causes of sinus arrhythmia are usually as follows:
- frequent experiences;
- psycho-emotional and physical overload;
- hormonal changes associated with puberty;
- anemia caused by a lack of iron.
In a newborn baby, tachycardia is often caused by the following factors:
- overheat;
- prolonged crying;
- swaddling process;
- heart defects.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
Mild paroxysms of sinus arrhythmia in children from 12 months to 4 years, passing after 5-10 minutes, are considered a completely natural phenomenon. The young body lacks oxygen, which leads to the launch of compensatory mechanisms.
If attacks occur quite often in a child over 10-12 years of age and last more than 10 minutes, then it is recommended to visit a cardiologist.
For their timely detection, it is necessary to study the characteristic symptoms of sinus tachycardia:
- loss of consciousness;
- pale skin;
- increased heart rate;
- dry cough;
- dizziness;
- shortness of breath after physical activity;
- pain in the heart area;
- general weakness;
- nausea.
The severity of the clinical picture depends on the causative factor and other pathologies. Increased frequency of attacks threatens the development of heart disease and aggravation of the child’s condition.
Diagnostics
If signs of sinus tachycardia are detected, it is advisable to show the child to a pediatrician or cardiologist. The doctor will examine and interview the patient (if possible) or one of his parents. To make a diagnosis and determine the cause, the following examinations may be prescribed:
- Donating blood for tests allows you to find out the concentration of hormones (thyroid, adrenal glands) and identify the presence of pathologies (leukemia, anemia).
- Electrocardiography (ECG) is needed to determine the frequency and rhythm of the heartbeat.
- Analysis of urine (urine) will help eliminate endocrine disruptions associated with an excess of adrenaline and other hormones.
- Holter electrocardiography is a round-the-clock monitoring of the work of the heart muscle. Due to the variable nature of arrhythmia, it is used extremely often, since various factors influence a person during the day. The data recorded on the device will allow you to identify or exclude the presence of arrhythmia.
- Bicycle ergometry is performed on an exercise bike to assess the work of the heart when the body receives physical activity.
- Electrophysiological research helps to detect failures in the conduction system.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart is used to identify disturbances in the functioning of the sinus node, as well as defects and dystrophic changes in the myocardium.
- The doctor will recommend electroencephalography of the brain if there is a suspicion of diseases of the central nervous system.
Treatment methods
Most attacks of sinus tachycardia occur unnoticed. Treatment is required if the child experiences obvious discomfort or the attack lasts more than 10 minutes. The doctor, based on the results of the diagnosis and examination, will be able to draw up a treatment plan. It usually looks like this:
- compliance with the rules of prevention;
- taking vitamin complexes, sedatives;
- use of vagal tests;
- surgical intervention.
Surgeon assistance may be required if thyrotoxicosis or pheochrocytoma is present. The essence of the operation is to remove the pathological area of the gland. Other types of intervention are also used, depending on the cause of the abnormal heart rhythm.
Medicines are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. Self-administration of medications can cause the development of side effects (bradycardia, hypotension, allergic reaction).
Drug treatment
Treatment of more advanced cases involves taking medications:
- Sedatives (Phenibut, Tenoten for Children, Phytosedan) are used to reduce excitability and normalize the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
- Preparations based on magnesium and potassium (Panagin, Asparkam) eliminate arrhythmia by improving impulse conduction, regulating pressure and maintaining optimal vascular tone.
- Iron-based products (“Aktiferrin”, “Totema”) help eliminate arrhythmia caused by anemia.
- Cardiac glycosides (Digoxin, Celanide) are used to improve heart function and stabilize blood pressure.
If the sinus form of tachycardia is a consequence of various diseases, then after their elimination the arrhythmia will go away. The basis of treatment is methods aimed at stopping the causative factor.
First aid measures
Parents should learn what to do during an attack to alleviate the child's condition. The list of effective methods for reducing heart rate is as follows:
- Remove clothing from the neck and chest area for better air intake.
- Place the child on a bed in a well-ventilated area or take him outside.
- Give sparkling water to drink.
- Apply vagal tests.
- Apply cold compresses to the head and neck. If the case concerns a child under 2 years old, then this method is contraindicated.
Vagal tests stimulate the vagus nerve through physical stimulation, thereby reducing the intensity of heart contractions. Not all of them are suitable for stopping an attack in children due to the characteristics of a young body. A list of the most effective and safest methods is given below:
- Take a deep breath and hold your abdominal muscles tense. After 10-15 seconds, exhale through pursed lips. Perform the test 7-8 times.
- Close your eyes and pull them slightly over your eyelids. After 10-15 seconds, reduce the strength. Repeat 5-6 times.
If the attack cannot be stopped, you will need to call an ambulance. The arriving doctors must be told about the actions taken.
Prevention
Regardless of the form of tachycardia, the child must be taught a healthy lifestyle. The following rules will help with this:
- play sports (without overload);
- maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- be examined annually;
- body weight control;
- staying in a calm environment at home and at school;
- follow the doctor's recommendations;
It is equally important to adjust your diet by removing fatty foods and reducing the amount of sweets consumed. It is better to diversify the daily menu with vegetables, fruits, and berries. It should be cooked by steaming or boiling. It is advisable to avoid fried and smoked foods.
Sinus tachycardia is considered one of the most common forms of arrhythmia in children. If it has a physiological nature, then there is nothing special to worry about. The situation with a pathological type of failure is completely different. The child will have to be examined to identify the causative factor and eliminate it. Medicines combined with compliance with the rules of prevention will help with this.
Source: https://MirKardio.ru/bolezni/uchashhenie/sinusovaya-tahikardiya-u-rebenka.html
Treatment of pathology
Emergency help
During an attack, you must follow these recommendations:
- let fresh air into the room;
- cover the child's forehead with a cold towel;
- contact a specialist.
If tachycardia is of the paroxysmal type, then first aid depends on the location of the origin of the abnormal impulse. For the supraventricular form, the following steps must be taken:
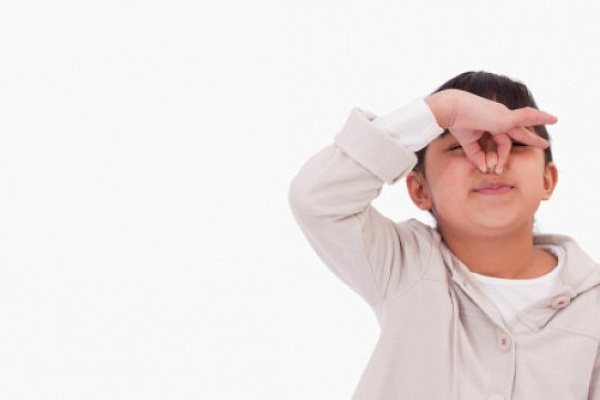

To alleviate his condition, the baby should push with his nose closed.
- Child 3-4 years old: close the baby’s nose and ask him to push;
- massage the carotid artery.
- press on the root of the tongue;
If an attack of the ventricular form occurs, then help is provided with drugs:
- Intravenous administration of "Lidocaine 1%" approximately 1-1.5 mg/kg.
- If the attack does not subside, then you need to administer a solution of Gilurythmal 2.5%, diluted with 10-20 ml of sodium chloride 0.9% in an amount of 1 mg/kg.
- If the attack continues, Amiodarone 5% diluted with glucose 5% is administered - 10 ml.
Medicines
Treatment of tachycardia in children with medication is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor, who can adjust the dosage and course of therapy depending on the patient’s condition. Frequently prescribed drugs are presented in the table:
| Group | Drugs |
| Sedatives | "Seduxen" |
| "Luminal" | |
| "Valerian" | |
| "Asparkam" | |
| Potassium-containing | |
| Cardiac glycosides | "Digoxin" |
| "Verapamil" | |
| Beta blockers | "Pindolol" |
Surgery
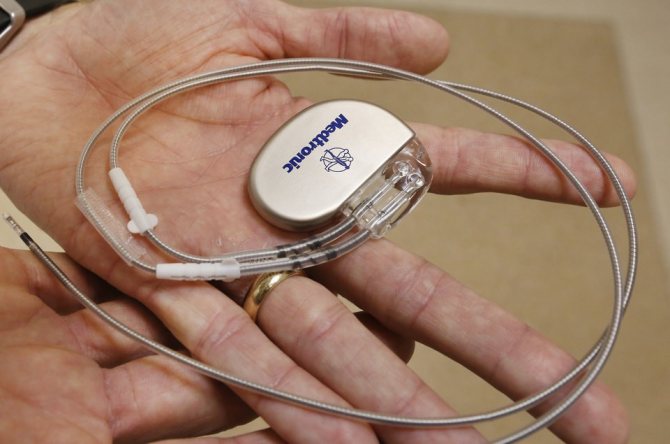
If other treatment options have not brought positive results, the attending physician may decide to perform surgery. Surgical procedures for tachycardia:
- Radiofrequency ablation. The method is based on the destruction of areas that supply the wrong impulse.
- Introduction of a pacemaker. An artificial pacemaker maintains the correct heart rate.
- Heart valve surgery. The operation is performed if there are certain congenital abnormalities.
Healers' recipes
Mild sinus tachycardia is treated with alternative medicine methods. Any influences can be carried out only after consultation with a specialist. Effective recipes:
- Motherwort infusion. One tbsp. l. dry herbs should be steamed with 1 cup of boiling water and left for 60 minutes. Strain the mixture, add 3 drops of peppermint oil, 1 tsp. honey The composition must be mixed and drunk. The course of therapy is 30 days.
- Valerian root decoction. Two tsp. The root is mixed with 1 teaspoon of dry dill, lemon balm, and hop cones. The mixture is poured with 350 ml of boiling water and left for half an hour. Drink 200 ml of the decoction before meals.
- Herbal collection. Mix 10 grams of horsetail, motherwort and hawthorn and add 0.5 liters of water. The mixture is heated in a water bath for 20 minutes and then cooled for 50 minutes. The strained tincture is taken 50 ml 4 times a day.
Diagnostics
In some cases, tachyarrhythmias in children are asymptomatic, and such conditions are detected during a clinical examination.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- An ECG provides the opportunity to obtain data on the rhythm of cardiac contractions even in newborns, therefore an electrocardiogram is considered the primary and most accessible research method;
- daily monitoring (Holter) is also suitable for use at any age, this method allows you to obtain more informative data on the work of the heart over 20 - 24 hours;
- Echo CG is a procedure that allows you to determine the presence of sinus tachycardia, a potentially dangerous cardiac pathology;
- electrophysiological study makes it possible to determine the mechanism of pathology;
- an electroencephalogram is performed if it is necessary to exclude diagnoses such as diseases of the central nervous system and hematopoietic pathologies.
Correct and timely diagnosis of the disease is the key to eliminating cardiovascular problems in the future.
Tachycardia is detected by interviewing parents and examining their child. The information obtained helps to establish the cause of this condition. If necessary, treatment is prescribed. The examination includes the following methods:
- ECG (Electrocardiography).
- Holter monitoring ECG.
- Electrophysiological study (EPS) - transesophageal or intracardiac.
- Load tests.
- MRI.

An ECG image for various forms of tachycardia provides data characteristic of a certain spectrum of diseases. Depending on the pathology and heart rate, therapy is prescribed. It is carried out under the supervision of examination and additional research methods.
In childhood, a sinus variant of tachycardia is most often detected on the cardiogram. It does not exceed 150 beats per minute. The rhythm remains within normal limits, and the P wave remains positive.
The supraventricular form differs from that described above. The contraction frequency can be 250 per minute. QRS remains normal. The P wave may have changes in the form of:
- negative option;
- deformed;
- two-phase.
The electrocardiogram with the ventricular form of tachycardia looks altered. The QRS complex is deformed, and the child’s heart rate remains within the range of 160-210 beats per minute. Dissociation may occur when the ventricles contract in their own rhythm, and the atria in their own.
If the child does not have the paroxysmal variant, then the above symptoms will persist. There are differences in the number of heart contractions. Children are characterized by moderate tachycardia in the range of 110-120 beats per minute.
In addition to the electrocardiographic method, Holter monitoring is used. All data is collected within 24 hours. For this reason, it is carried out only among older children. The results, which are obtained within 24 hours, are assessed by a doctor. Sometimes questions remain in clarifying the form of tachycardia or it is difficult to find its cause.
To resolve controversial issues or confirm the diagnosis, a transesophageal examination is performed. The method allows you to evaluate the lesions that provoked the increased rhythm and caused associated symptoms.
For ventricular and supraventricular forms of tachycardia, stress tests are indicated. A treadmill test or bicycle ergometry is used. They are given to older children.
It is important to consider all possible complications and contraindications. If a child has a ventricular variant, then caution is needed. This is associated with a high risk of developing an attack, which occurs during intense physical activity.
In unclear situations (or to obtain complete information about the condition of the heart), a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study is performed. A complete examination allows you to get a clear picture and assess the severity of the pathology.
To diagnose the patient’s condition, the doctor first of all conducts a survey of the minor and his parents in order to find out all the complaints that bother him. After this, an initial inspection is carried out.
Often, additional examinations must be performed to make an accurate diagnosis. This is a urine test, biochemical and general blood test, echocardiography, electrocardiogram.
How dangerous is the pathology?
If the baby's condition is not kept under control, the disease may be complicated by pulmonary edema.
Tachycardia in a one-year-old child or at a younger age requires constant monitoring. Especially advanced forms of the disease threaten cardiac arrest and death. Pathology without appropriate control can cause the following complications:
- development of arrhythmic shock;
- pulmonary edema;
- oxygen starvation;
- hypoxia;
- failure of the heart muscle.
Sinus tachycardia in a child: symptoms and treatment
Children's heart rate is significantly higher than that of an adult. This is due to the body’s high need for oxygen and rapid metabolism. In addition, babies are constantly on the move. But sometimes the heart rate begins to exceed normal. And after the examination, sinus tachycardia is diagnosed in the child. What kind of pathology is this and how to treat it?
Characteristics of the pathology
Let's look at what sinus tachycardia is in a child. As mentioned above, this is a disease associated with an increase in heart rate. The pulse can significantly exceed the age norm.
This rhythm is formed from the sinus node, which is a pulse generator that determines the frequency of contractions. A wave of excitement appears in him.
It extends to the entire heart muscle and promotes its synchronous functioning.
Sinus tachycardia in a child can be long-term or transient (situational).
An increase in heart rate is, as a rule, the body’s response to the influence of internal and external factors:
- mental stress;
- physical exercise;
- emotions;
- prolonged hypoxia;
- pathologies of the heart and lungs.
Causes
Initially, it should be said that sinus tachycardia in a child 6 years old and at a younger age is often considered normal. These children do not require any treatment. These violations are periodic. Over time they go away on their own.
An increase in heart rate to 100-160 beats per minute, resulting from stress, physical activity, hyperthermia, or prolonged exposure to a stuffy room, is not a sign of pathology. But if this condition is accompanied by additional symptoms (we’ll talk about them below), then the baby will need professional treatment.
And special attention should be paid to pathology if a disorder is found in a completely healthy baby who was in a calm state.
What can lead to the development of such a disorder? Doctors say that sinus tachycardia appears, as a rule, as a result of the following reasons:
- heart failure (congenital);
- myocarditis;
- anemia or hypoglycemia;
- damage to the central nervous system.
At older ages, the sources of the disease in children can be:
- unevenly developing organs, leading to malfunction;
- stressful situations;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems;
- too much physical activity;
- disruption of the thyroid gland.
Characteristic symptoms
To determine which pulse is considered a symptom of tachycardia, you should familiarize yourself with age standards. Doctors give the following indicators:
- infants up to 5 months – 140-160;
- children 6 months – 130-135;
- 1 year old babies – 120-125;
- children 2 years old – 110-115;
- children aged 3-4 years – 105-110;
- guys 5-7 years old – 100-105;
- schoolchildren 8-9 years old – 90-100;
- children 10-12 years old – 80-85;
- teenagers from 12 years old – 70-75.
Pathology is diagnosed if the pulse rate exceeds the specified age norms by 10-60%. Thus, sinus tachycardia is suspected in a 1-year-old child with readings above 140 beats.
However, the development of pathology is indicated not only by the number of heart contractions. Additional symptoms characterizing the disease are:
- pain in the heart area;
- sudden dizziness;
- shortness of breath for no reason;
- weakness;
- darkening of the eyes with sudden movements;
- fainting state.
This is how severe sinus tachycardia manifests itself in a child.
Stopping an attack
Parents should be prepared for the fact that at any time the child may suddenly develop negative symptoms. If an attack occurs, you must act as follows:
- Be sure to provide air access. Unfasten the collar, bring or bring the baby to the window.
- Place a cool towel on your forehead.
- Ask your child to take a deep breath and hold it for a few seconds. This simple procedure allows you to lower your heart rate.
If these actions were not enough, and the baby’s condition does not improve, then call the doctors immediately.
Prevention
When carrying a child, a woman should avoid stressful situations, reduce the consumption of caffeine-containing drinks and lead a healthy lifestyle. Compliance with such recommendations will significantly reduce the chance of developing tachycardia in a newborn. To prevent pathology in children, it is necessary to monitor the baby’s diet and avoid drinking drinks with a stimulating effect. It is also very important that the child maintains a correct daily routine, that is, that physical activity alternates with proper rest. If necessary, vitamin therapy can be carried out. This treatment is carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
Requirements and recommendations
In order for the child’s treatment to be as productive and effective as possible, adults must adhere to all medical recommendations received, as well as organize the correct diet and appropriate daily routine for the young patient.
Coffee, tea, spicy and salty foods, and products containing cocoa must be excluded from the patient’s diet. The diet should be rich in fiber, nutritious, and rich in light carbohydrates. Particular attention should be paid to protein foods - their quantity should be limited.
In some cases, parents can use traditional medicine to combat arrhythmia. Such methods should only be used if the disease does not have a functional origin. In addition, you should definitely consult your doctor.
How to act
There is no need to regularly check your child's pulse. Moreover, you should not use tonometers (pressure measuring devices) designed for adults with a large cuff for this purpose.
When registering tachycardia on an ECG, you must show this ECG to the doctor who referred you for the study (pediatrician or cardiologist). Since tachycardia is not a disease, its identification requires a medical examination, and, if necessary, additional research to identify the cause of the accelerated heartbeat.
When to see a doctor and how often to get checked
If the child is feeling well and is developing normally, periodic palpitations are not a cause for concern. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- high body temperature, headache;
- dry skin and retraction of the fontanel in infants;
- shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty breathing;
- interruptions in heart function, dizziness or fainting;
- weakness, deterioration in school performance, pale skin and mucous membranes, drowsiness, swelling of the face or legs.
The first way to detect tachycardia in a child is electrocardiography. With sinus tachycardia, the following ECG signs are noted:
- increase in heart rate per minute compared to the age norm;
- all teeth are present;
- the RR interval is shortened due to the shortening of the diastolic pause - the TP segment.
With supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardias, the P wave is negative or not detected at all on the ECG. Ventricular tachycardia is manifested by regular widened QRS complexes without connection with P waves. An experienced functional diagnostics doctor will easily make a differential diagnosis between these conditions.
ECG in children with normal health and absence of heart murmurs is recorded during medical examinations at the age of 1 year, 6 years, 15 and 17 years. The doctor will refer you for a cardiogram if you have complaints of pain in the chest, shortness of breath, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, exercise intolerance, or if a heart murmur is detected.
If tachycardia is registered, the child may be prescribed 24-hour ECG monitoring. This study will provide information on the average daily, average night and average daily heart rate, compliance with age standards, rhythm disturbances, duration of the QT interval and other indicators.
If persistent tachycardia occurs, echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is prescribed. It provides information about the structural condition of the heart, such as minor malformations (patent foramen ovale) or congenital defects.