Sinus bradycardia of the heart in a child: causes and indicators
Possible causes of childhood bradycardia:
- hereditary predisposition;
- presence of infectious diseases;
- rapid growth of the child;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
About childhood bradycardia in the video of the Russian Pediatricians Union:
In newborns
The normal heart rate for newborns is 120-140 beats. This value is variable and depends on whether the child was born in a timely manner.
The criterion for sinus bradycardia in an infant is a heart rate of less than 100 per minute for more than 10 seconds . The clearly pathological nature of bradycardia is considered when the heart rate is less than 90 in premature infants, and less than 80 in full-term infants.
From 1 year and older
Over time, the heart rate begins to decrease.
By the first year of life, 130-132 beats are considered the norm. By the age of two, the heart rate will drop to 124 beats. However, at this age, this indicator is influenced by the activity of children, physical activity and other factors; the heart rate can be from 95-155 beats. The normal heart rate for children aged 5-6 years is 105 beats.
A deviation from the norm and a sign of the disease is a decrease in heart rate to 80-90 beats per minute.
In school-age children
For schoolchildren, the normal heart rate ranges from 80-110 beats. The disease in school-age children manifests itself as a decrease in heart rate to 70 beats per minute.
It is more convenient for children to measure their heart rate with a pulsometer. They come in different types. For example, a finger device is very convenient during sports activities, wrist devices are compact and easy to use, and a chest device is a classic version of a portable heart rate monitor.
In teenagers
In children aged 13 to 15 years, the pulse is considered normal if it ranges from 65-95 beats. The heartbeat of a teenager over 15 years of age should normally be the same as that of an adult. With bradycardia in adolescents, heart rate decreases to 50-60 beats per minute.
Mechanism of development of bradycardia
Regular physical training leads to thickening of the muscle fibers of the heart, which requires a more intense supply of oxygen to them. In such a situation, the work of the heart is compensated by tachycardia. But with further thickening of the heart muscle, a compensatory branched vascular network develops in it, capable of supplying the heart with blood in full even under heavier loads.
With such a constructive modification, the increase in heart rate is irrational, and athletes develop sinus bradycardia - a noticeable decrease in the heart rate. The heart switches to an economical mode of operation: more rare, but more powerful contractions. With increasing physical activity, the heart rate increases from 2 to 5 times. After the load is reduced, it returns to its original state. A heart capable of working in this mode is called physiologically athletic.
It ensures normal blood supply to all organs and systems, normal functioning of the body as a whole.
If the heart grows too intensively, then a pathological athlete’s heart develops, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- low heart rate;
- weak muscle contractility of the heart;
- high hypertrophy of the heart muscle;
- changes in the conductivity and rhythm of the heart muscle;
- replacement of muscle fibers with connective tissue, which leads to cardiosclerosis and functional heart failure.
Types and differences
Depending on the causes, the disease is divided into three types: pathological bradycardia, drug-induced and physiological.
Physiological occurs quite often in absolutely healthy people . The reason is physical activity, for example, active training. If a child plays football, hockey or martial arts, it is likely that after training there may be a slow heartbeat due to fatigue.
Drug-induced bradycardia may manifest itself after the child undergoes a course of treatment with certain medications . Taking medications incorrectly can cause the disease. Such drugs include:
- cardiac glycosides - herbal products that are taken for acute or chronic forms of heart failure (Corglicon, Celanide, Digoxin);
- muscle relaxants - drugs that are used for anesthesia to relax skeletal muscles (Mivacron, Lystenon, Arduan);
- potassium preparations.
You should be wary when the disease develops against the background of other ailments, for example, with diseases of the heart (intracardial bradycardia) or other organs (extracardiac).
Symptoms
There are three degrees of the disease: moderate, severe and mild bradycardia. Each degree has its own heart rate and symptoms.
Light form
This degree is characterized by a decrease in heart rate to 60 beats per minute . A slow heart rate can occur in healthy people. The following factors may influence this:
- physical activity;
- hypothermia;
- dream.
Moderate degree
In this case, the child may not be bothered by anything. The baby's heart beats at a rate of about 50 beats per minute .
However, even with little physical activity, the child’s body will lack blood supply. The following symptoms may appear:
- fainting;
- dizziness when rising from a chair or bed;
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- sleep disturbance;
- pain in the chest area;
- loss of strength and inability to perform any physical activity.
No less attention should be paid to this disease in adults. In the materials on our website, we wrote about the symptoms and treatment of the disease, the causes of its occurrence, bradycardia in athletes, and how dangerous it is for the fetus or pregnant woman.
Severe bradycardia
With severe bradycardia, fainting and falling often occur. This condition is accompanied by a decrease in heart rate to 40 beats per minute.
Can there be one-time manifestations? Yes, and this happens quite often. For example, if the child was very scared.
Therapy of the disease
Treatment of bradycardia in children of different age groups is carried out only by a cardiologist, who, based on examination data, establishes the cause of the disease and eliminates it therapeutically, thereby normalizing the heart rhythm.
An individual course of taking medications and their dosage for each small patient are selected taking into account the type and degree of development of the disease. If a newborn experiences acute attacks of suffocation and fainting, after mandatory consultation and recommendations of a cardiac surgeon, electrical stimulation is prescribed.
Congenital bradycardia is corrected with drug therapy. Effective drugs are used with a high content that normalize oxygen and carbohydrate metabolism, eliminate oxygen starvation and regulate the electrolyte balance of substances.
Surgical intervention with the installation of a pacemaker is possible in case of advanced disease, when there is a threat to the life of a newborn child.
As a maintenance therapy, a diet with a high fiber content in foods is introduced, it is recommended to take vitamins and timely treatment of diseases (even a banal acute respiratory infection) in compliance with medical instructions about the timing and dosage of medications.
Such simple rules, as well as attentiveness to changes in the child’s body and timely seeking medical help will help maintain the health of the child’s heart.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of decreased heart rate in children is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Interviewing parents and compiling a list of complaints.
- Conducting an analysis of the history of all previous infectious diseases and operations.
- Mandatory examination by a pediatrician and cardiologist.
- Urine and blood analysis.
- Carrying out an electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Carrying out a heart rate deviation test.
- Determining the need for treatment.
Attention: the list is not complete, as some situations require additional laboratory tests or consultation with other specialists, for example, a neurologist.
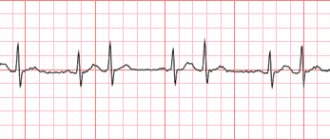
Signs on ECG
On the ECG, bradycardia manifests itself in the form of a decrease in heart rate (indicator below 60 beats), as well as in the presence of the P wave. Electrocardiography allows you to determine the severity of bradycardia, as well as establish the form of the disease (sinus bradycardia, blockades, etc.).
An ECG is often performed with various tests (physical activity, orthostatic test) . This research method allows you to determine the nature of bradycardia (relative or absolute), and also makes it possible to assess the increase in heart rate.
What is the diagnosis?
Infantile bradycardia is usually not particularly difficult to diagnose. To identify it, the following research methods are used:
- examination of the patient with mandatory assessment of the pulse, as well as auscultation (listening to the heart);
- various methods of recording an electrocardiogram (ECG) - from a standard ECG study to Holter ECG monitoring;
- stress tests, among which the most common is bicycle ergometry.
Treatment
In newborns and infants, if a heart defect or other serious diseases are detected, urgent hospitalization and surgery are required. During attacks, it is not recommended to put the baby to sleep , since at rest the heart rate will slow down even more. Sometimes a doctor prescribes:
- caffeine;
- theophylline;
- Eleutherococcus extract;
- ginseng root.
If the symptoms are pronounced, then hospitalization is required. To alleviate the patient's condition, it is necessary to control nutrition.
In children who have grown out of infancy, treatment of mild and moderate degrees of the disease is carried out by strengthening the body (for example, taking a vitamin complex and following a diet).
The diet includes walnuts, seafood and fiber-rich vegetables. The doctor may prescribe taking eleutherococcus.
In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization and always regular examinations by a cardiologist are sometimes required. Drug treatment is possible.
How to treat teenagers? The course of treatment often includes herbal adaptogens. These include:
- Schisandra, zamanika, aralia (potent drugs);
- Licorice root and strong tea (moderately stimulating);
- Nettle and kelp have a general tonic effect.
The most famous adaptogen of animal origin is an extract from deer horns (pantocrine).
Drug therapy is prescribed by a doctor , who may prescribe the following medications:
- nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Phenotropil, Biotredin);
- belladonna preparations (for severe bradycardia), for example, bellataminal;
- Gutron (for loss of consciousness);
- multivitamin complex enriched with minerals.
For secondary bradycardia, which occurs against the background of other diseases, their treatment is recommended. For bradycardia due to congenital AV block or sick sinus syndrome, a pacemaker is implanted.
How is pathology treated?
Bradycardia in newborns, as well as in older children, is an indication for observation by a cardiologist.
The basis of treatment in each specific case is the elimination of the factor that is causing the heart rhythm disturbance (disease or environmental factor).
If a child has a relative bradyarrhythmia, then, as a rule, to eliminate the rhythm disturbance it is enough to exclude the influence of the causative factor. There is no need to prescribe special therapy.
If a child has mild absolute bradyarrhythmia, then folk remedies (strongly brewed tea, infusion of pine branches, and others) can be used to correct this condition. But it should be remembered that even traditional methods of treatment can only be used with the permission of the attending physician.
You need to be sure that your child has this particular type of heart rhythm disorder. In addition, many traditional medicines are active allergens and often cause the development of an individual intolerance reaction.
If the child has a pronounced absolute bradyarrhythmia, then after a full comprehensive examination and identification of the causative factor, they resort to prescribing medication.
For the treatment of bradyarrhythmia in children, medications such as caffeine, isadrine, atropine and ephedrine are effectively used.
Patient Valeria, 10 years old. Over the past two months, the patient became lethargic, apathetic, and her school performance noticeably decreased. At home, the girl periodically complained of headaches, dizziness, and began to refuse meals. The patient’s mother contacted her family doctor, after which a comprehensive examination of the patient was carried out. The ECG revealed sinus bradycardia. In addition, the neurologist gave a conclusion about the presence of neurocirculatory dystonia and appropriate recommendations for drug correction of this pathology. During the follow-up examination a month later, the patient had no complaints; the ECG showed normal sinus rhythm.
So, bradycardia can serve as a signal that a pathological process is occurring in the body that affects the functioning of the heart. Or it could be a sign that there is an external irritant affecting the child’s heart. In any case, this condition requires a comprehensive examination of the patient, identification and elimination of the causative factor.
Author of the article:
Elena Demidova
about the author
Did you like the article?
Let us know about it -
rate
Lifestyle with arrhythmia
A child with bradycardia is recommended to engage in swimming, gymnastics and hardening . Physical activity is not prohibited, but you need to choose a calm sport. Weightlifting and exhausting workouts are contraindicated.
Adolescent children should be closely monitored to ensure they do not develop bad habits (smoking).
The patient's diet should include seafood, walnuts, strong tea, vegetables and fruits containing high levels of potassium and magnesium. Giving coffee to children is not recommended.
Which sport is suitable
Moderate physical activity is what has a beneficial effect on children diagnosed with bradycardia. They will benefit from long leisurely walks in the fresh air, morning exercises and water treatments. Sports should be low-energy and calm.
If your child wants to play big sports, encourage him to look at the following types:
- Swimming will strengthen the heart muscle and increase endurance. Due to the horizontal position of the swimmer, it will improve the pushing of blood through the arteries.
- Golf has a beneficial effect not only on the body, but also on the intellect. It does not require explosive, static or vigorous exercises. Competitions and training take place outdoors, and golfers travel a lot on foot. Almost ideal sport for bradycardia.
- Race walking. Like golf, most of your training takes place outdoors. At the same time, there is no heavy load on the heart as with fast running.
- Volleyball . It will not only strengthen the body, but also improve blood circulation.
- Rowing. During rowing, the concentration of oxygen in the blood increases. In addition, it has been noticed that the rowing technique is somewhat reminiscent of a pacemaker. Therefore, this sport has a beneficial effect on the heart.
- Classic cross-country skiing. The principle of aerobic exercise, which enriches the blood with oxygen, also applies here. Considering that training takes place in the fresh air. The efficiency of classic cross-country skiing increases significantly.
Thus, it is best for children with bradycardia to engage in sports that do not put too much strain on the heart, enrich the blood with oxygen, and take place in the fresh air.
Possible complications and consequences
The risk of complications will be minimal if parents and their child consult a doctor in a timely manner. If you do not pay attention to the disease, the following complications may occur in later life:
- ischemia;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- tachycardia;
- asystole;
- and other serious conditions.
Of the above diseases, myocardial infarction is one of the most dangerous consequences of bradycardia. This disrupts the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system. We invite you to find out more information about this terrible disease. Read these articles:
- Classification of myocardial infarction and differences between types, including atypical forms.
- Diagnosis of the disease.
- How does extensive myocardial infarction, as well as ischemia of the posterior wall of the left ventricle of the heart, manifest itself?
- Symptoms and first signs in different sex groups.
- What medications are usually prescribed and what is rehabilitation at home?
- Whether they give disability or not, quality of life and ability to work.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to apply preventive measures immediately after the baby is born:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- harden the child (water procedures, walks);
- monitor your diet;
- provide the child with timely and adequate treatment for any illness, while refraining from self-medication.
In children, a pathological decrease in heart rate is rare. Physiological does not pose any danger . If there are no serious cardiovascular diseases, no special treatment is required.