The most dangerous types of strokes
Depending on the underlying causes, there are several types of cerebrovascular accidents, which are accompanied by focal or general cerebral symptoms throughout the day.
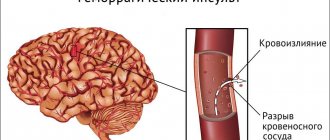
There are ischemic stroke, microstroke, hemorrhagic, spinal stroke, as well as subarachnoid hemorrhage. If the first and second types pose less of a threat, although they are more common, then the last three are accompanied by hemorrhage, serious consequences and a crisis course. Patients may be left disabled, fall into a coma, or experience cerebral edema. The symptoms in this case will be much more pronounced, and, as a result, a heart attack and problems with the spinal cord may begin.
Survival rates
It is impossible to give a definite answer to the question of how long people live after a stroke. This figure depends on a large number of factors that cannot be calculated. To characterize life expectancy, doctors use two indicators: survival and mortality. The first characterizes the percentage of people who live longer than a specific period (month, year, 5, 10 years), the second - the percentage of deaths for a specific period.
This figure is very variable. For example, Russian patients die 4 times more often than residents of the United States and developed European countries. Even within the territory of one country, the mortality rate can vary greatly from region to region.
The most critical period is considered the first month after a brain stroke. 15-25% of patients die from ischemic stroke in the first 30 days, and 40-60% from hemorrhagic stroke. With a long-term forecast, this difference smooths out a little.
Survival rates for various forms of apoplexy are shown in the table.
| Survival period | Ischemic stroke | Hemorrhagic stroke |
| 1 year | 60% | 38% |
| 5 years | 31% | 24% |
Signs of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke have different symptoms, since they are two different types of disease. The first includes symptoms such as:
- redness of the facial skin;
- interruption of breathing, pulse;
- partial paralysis of the limbs;
- sagging cheeks.
Repeated ischemic stroke has all the traditional symptoms. That is why it is the one that is most easily recognized, since its signs are known to everyone and are repeated in both women and men.
Causes of stroke
The prognosis of the first stroke and the risk that it will occur again is associated with the nature of a person’s life and compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician. The main reasons why pathology recurs are:
- vascular diseases;
- impaired blood supply to the brain;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertonic disease;
- prolonged or excessively exhausting physical activity;
- infectious processes;
- exposure to stressful situations;
- tendency to be overweight;
- increased level of weather sensitivity;
- bad habits.
Hemorrhagic stroke most often begins against the background of a hypertensive crisis, provoked by stress or emotional overstrain. The risk of developing pathology also increases with:
- non-compliance with the rules of rational nutrition (consuming excessive amounts of fatty, smoked foods and spices);
- drop in blood pressure;
- use of anticoagulants;
- non-compliance with the work and rest regime;
- low level of physical activity.
Observational data indicate that most often repeated stroke occurs when the doctor’s instructions are not followed. Patients who have suffered from the disease should be very attentive to their health and rhythm of life in the future.
It is almost impossible to avoid the development of a second attack, especially if we talk about pensioners, or about unfinished rehabilitation, when brain cells have not been completely restored, and foci of inflammation have not been eliminated. One factor is enough to cause an attack. This could be a traumatic brain injury, a surge in pressure, great physical or emotional stress, the presence of chronic diseases, lack of diet and exercise. Although often the problem lies in improper blood circulation or heart disease.
If, after recovery, a person returned to his previous life, could not give up smoking and alcohol, sits a lot at the computer, his physical activity is reduced, and his blood sugar and cholesterol are exceeded, then in a couple of years you should expect a second attack. It can even be triggered by an emotional shock or a slight surge in blood pressure.
Vascular tone
Vascular tone and poor functioning of the circulatory system can be a prerequisite for the development of a stroke a second time. We are talking about atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, diabetes, high cholesterol and other pathologies. In this case, the vessels lose their elasticity, thicken or become too thin, and a lot of toxins and fats settle on their walls, which leads to thrombosis and rupture. Often, a repeated attack due to problems with blood vessels ends in hemorrhage.
Increased pressure in the blood vessels causes not only a recurrent stroke, but also a myocardial infarction, as chaotic contraction of blood vessels, stagnation and unstable blood flow to some parts of the body are observed. All this leads to thrombosis and blockage, the formation of aneurysms or lacurnas. If this was preceded by a primary attack, then the second time may result in rupture of capillaries and hemorrhage in the brain.
Summer season
Prolonged exposure to the sun, increased exercise in the heat, and even walking in high summer temperatures can also cause a stroke. The fact is that the water balance drops significantly during this period, and almost no oxygen and glucose reach the cells. Patients suffer from dehydration and swelling may occur.
Heart problems
Heart problems such as arrhythmia, primary myocardial infarction, and atrial fibrillation should be treated immediately after the first stroke occurs. After all, they can be the cause of an attack a second time. This happens due to uneven blood pumping, irregular functioning of the atria, constant contraction and lack of relaxation during work. It is enough for the pressure to rise a little or a little stress to occur that a stroke develops.
This high prevalence of repeated strokes is explained by the fact that many risk factors (age, chronic diseases, heredity) and the main causes of pathology (high blood pressure, atherosclerosis) do not disappear.
Cerebral circulatory disorders are often accompanied by a number of consequences that lead to a shortened life after a stroke. The deadliest of these is cerebral edema, which is the cause of death in every second patient. To prevent it, diuretics are administered to patients during the acute period of the disease. Other dangerous complications:
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of a pulmonary vessel by a blood clot that has broken off from a vein of the limb. Often occurs in bedridden patients.
- Pneumonia. Develops when food fragments enter the lungs. This often happens if the swallowing process is disrupted due to paralysis of the muscles of the face and pharynx.
- Heart disorders. A common group of violations. Most of them are harmless if treated correctly. Severe pathologies include heart failure, heart attack, and atrial fibrillation.
There are a number of reasons why any type of stroke can develop, but the most common are:
- the presence of chronic heart disease and vascular pathologies
- diabetes
- obesity
- traumatic brain injury and inflammatory processes in the brain
- taking contraceptives or the moment of birth of a child
- great physical and emotional stress
- heredity and genetic factor
Even migraines, epilepsy and various mental disorders can lead to the development of a stroke in the future, so when the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Treatment
Relapse can only be localized in an inpatient setting. In this case, the therapy for the second stroke does not differ from the treatment used for the first stroke.
Medical therapeutic methods include a set of surgical and conservative measures based on a comprehensive diagnostic examination. The first of these include:
- normalization of blood pressure;
- reduction of cerebral swelling;
- use of hemostatic and vasodilator drugs;
- normalization of blood viscosity.
The patient is provided with bed rest and constant supervision by a doctor. A strict diet is mandatory. If there is such a need, urine is removed using a catheter. Prevention is carried out, bedsores are prevented, body temperature is monitored.
After a few weeks, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, using massage and physical therapy.
After discharge, any solution to issues related to the restoration of impaired functionality must be agreed upon with the attending medical specialist.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
Hypertension is one of the key risk factors for stroke.
- Floor. Life expectancy after a stroke is much higher in men than in women. For example, the 28-day survival rate for men is 22% and for women 28% (1). According to some data, young, middle-aged men live shorter lives: 5-year survival rates are 60%, 64.5%, respectively (2).
- Age. The younger the person is at the time the stroke develops, the better the prognosis. This is one of the reasons why men have better survival rates: they experience strokes at a younger age.
- Late medical care. From the moment the first symptoms appear until the start of hospital treatment, no more than 3-4.5 hours should pass.
- Complete loss of speech, pain sensitivity, eye reaction to external stimuli.
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Low hemoglobin level.
- The presence of unhealthy habits: overeating, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, tobacco, drug, and alcohol addiction.
- Relapse.
There are also specific unfavorable factors characteristic of certain forms of cerebrovascular accidents that worsen the prognosis.
| Ischemic stroke | Hemorrhagic stroke |
|
|
Stroke survivors at an average, young age have a much better chance of living a long life than older patients. How many years do people of working age live after a stroke? The survival rate for this category of patients is (2):
- 82% – 1 year;
- 75% – 3 years;
- 58% – 7 years.
The worst prognosis after suffering an acute cerebrovascular accident is for unemployed people, men, and patients with hemorrhagic stroke. Survival rates also decrease with increasing age.
The most important thing, if a stroke does occur, is to recognize its symptoms in time. The easiest way to do this is to remember the “IMPACT” rule:
- “U”, the smile is asymmetrical, one corner of the mouth is downturned;
- “D”, movement – inability to raise and hold both arms at the same time;
- “A”, articulation – speech is confused, slurred, tongue-tied;
- “R”, solution - if at least one of the signs is present, call an ambulance.
Later, you can increase your life expectancy by changing your lifestyle:
- reviewing nutrition. They try to completely exclude fried, pickled, smoked, canned, confectionery, and baked goods from the diet. Limit salt, sources of saturated fats (lard, butter, coconut, palm oil, red meat, cheese, cottage cheese);
- giving up cigarettes;
- by reducing or better eliminating the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- making your life more active.
Following the doctor’s recommendations, active rehabilitation exercises, and a positive attitude also help reduce the risk of complications and recurrence after a stroke.
First of all, it is necessary to focus on the fact that the risk group includes not only individuals who have suffered a stroke, but also those who experience short-term transient attacks. To prevent the formation of a recurrent stroke, you must contact a neurologist, follow all his recommendations and undergo periodic preventive examinations.
Diagnostics
To prescribe adequate therapy and its correction, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics, namely:
- Ultrasound of the carotid arteries and large vessels of the brain;
- echocardiograms;
- electrocardiograms;
- determination of blood lipid profile;
- coagulograms.
The listed examinations allow us to obtain a complete picture of the patient’s condition, determine further tactics of action and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen. The key to a successful fight against a second stroke is following all the doctor’s instructions.
Treatment
Treatment for stroke consists of:
- Diagnosis of the type of lesion and characterizing features of the disorders.
- Use of medications. Their choice will depend on the type of pathology; these may be antihypertensive, hemostatic, decongestants and anticoagulants.
- Carrying out resuscitation measures.
- Probing and catheterization (if necessary).
- Compliance with the rules of rational nutrition.
The average duration of treatment is a month. After this, the patient is given recommendations and sent home to undergo rehabilitation.
To avoid a recurrent stroke, it is recommended:
- for preventive purposes, take medications prescribed by a doctor;
- engage in physical therapy;
- follow dietary rules;
- monitor blood glucose and cholesterol levels;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- control weight;
- visit a physiotherapy office.
One of the first steps of preventive measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of stroke is a set of actions aimed at normalizing and controlling blood pressure levels. To stimulate brain function, drugs such as Cinnarizine and Cavinton can be used.
If 2 strokes of the hemorrhagic type are diagnosed, angioprotectors are prescribed, namely Troxevasin or Detralex. These medications have a strengthening effect on the vascular wall. You also need to be careful about the process of lowering blood pressure levels, because a sharp drop in blood pressure can provoke the development of the pathology again.
Particular attention must be paid to the diet; it should consist of the maximum amount of fruits and fresh vegetables, juices, fermented milk products, as well as those that help thin the blood and prevent blood clots. It is recommended to eat foods that help normalize cholesterol levels.
To summarize, we can confidently say that the formation of pathology again depends on the person himself, namely his lifestyle and diet. It is important to carefully follow all recommendations of your doctor.
Stroke is a disease that affects more often older people (the older a person is, the higher the risk of developing pathology). After diagnosing the first case of the disease, it is necessary to pay more attention to the state of your health, because a secondary stroke poses a danger not only to it, but also to a person’s life. The prognosis of the pathological condition is usually disappointing.
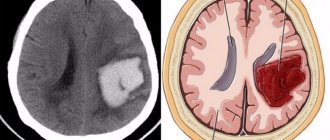
The consequences of a second cerebral stroke and the severity of their course depend on the location of the lesion and its size. It is necessary to emphasize that the neurological consequences after a secondary relapse are much more pronounced compared to the first case of the disease. With stroke, which is diagnosed for the second time, there is a significant impairment of motor functions (problems on the right and left sides) and the ability to think.
Many people are interested in the question of how long a person can live in this case and what is the prognosis for life in old age. So, according to observational data, life expectancy longer than 5 years after pathology is only 15%. In most cases, patients remain bedridden for the rest of their lives or are confined to a wheelchair. It is not possible to achieve complete recovery.
As a result, I would like to emphasize that a recurrent stroke is a rather dangerous and unpredictable condition, as it leads to the development of severe complications and can cause death. That is why people who have a history of similar problems need to take their health very seriously. It is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations and be under the supervision of a neurologist.
After a stroke, patients have to overcome many problems. One of the main ones is mobility impairment. Many people who have suffered a stroke have residual effects in the form of hemiparesis - loss of sensitivity and weakness of the muscles on one side of the body. The consequences after the second and third cerebral infarction are much more severe.
Depending on the location of the source of damage, paralysis develops. For example, problems with the left side of the body and limbs are associated with occlusion of the arteries of the right hemisphere of the brain. In addition, patients experience impairment of vision, hearing and touch.
Another consequence of a stroke is weakness of the facial muscles and difficulty swallowing. Almost all patients are depressed. Some are prone to fits of anger and mood swings.
In fact, previous family ties with family members have been broken. The patient withdraws into himself. If his relatives do not communicate with him, he falls into apathy and loses his appetite.
In severe cases, with extensive foci of damage, patients fall into a comatose state, spending a long time in the intensive care unit. Not all of them survive; 70% of patients die without regaining consciousness.
Even if the signs of a transient attack have regressed on their own, they signal that there is a bomb in the body in the form of a tendency to form blood clots. After all, the mechanism of a stroke is a blockage of cerebral vessels by a blood clot or a large atherosclerotic plaque.
A stroke can be triggered by a rise in blood pressure and vasospasm. A heart attack can recur due to nervous tension or at the table after overeating. Drinking alcohol and smoking are a direct road to destruction of the vascular wall from the inside and increased blood pressure.
At the same time, a stroke is possible after excessive physical exertion, which often happens during the summer season with older people. We must not forget that after the first ischemic stroke, the body's reserve capabilities are limited. You should work in moderation and rest profitably.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the carotid arteries and large vessels of the brain.
- Echocardiogram;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Blood lipid profile analysis.
- Coagulogram.
- Determination of the level of the amino acid homocysteine. When it increases, the risk of thrombosis and early vascular atherosclerosis increases. The risk of stroke increases by 6–8 times.
How can you increase your life expectancy?
Of course, a stroke cannot occur on its own. A negligent attitude towards lifestyle and health will make its own negative adjustments. It is for this reason that a person who has had a first or second attack should monitor his health and blood pressure for the rest of his life. How long do people live after a repeat incident?
In fact, this is all individual and depends on a person’s lifestyle, and a repeated stroke can not only be survived, but also returned to a normal lifestyle. It is important to adhere to a healthy diet, not to eat fatty, sweet, or smoked foods. If you don't follow these simple rules, another stroke could be your last. This is probably the most terrible consequence of any disease.
It is worth noting that experts have more than once observed a long life expectancy after a stroke (several decades). It has been established that if death occurs, it can occur within the first month or first year.
How long do patients live after a stroke? This question worries both the patient himself and his relatives. Life expectancy is determined by the following factors:
- quality of life after an attack;
- absence of stressful situations;
- age of the victim;
- general health and presence of other diseases;
- elimination of all causes that caused the stroke;
- compliance with all doctor's recommendations.
Every year, specialists diagnose about 5 million seizures worldwide. Of these, approximately 30% of males and 42% of females die. Agree, quite often you can see such a situation on the street when someone faints. How many times does this happen on the street and at home among family and friends.
How can you independently verify that a person has suffered from a stroke? The first thing you need to do is bring the victim back to consciousness (for example, pat him on the cheeks). When he comes to his senses, ask him to smile. If the fainting was due to a stroke, the smile will be skewed to one side. Next, you need to ask them to say a simple sentence.
The most important thing, if a stroke does occur, is to recognize its symptoms in time. The easiest way to do this is to remember the “IMPACT” rule:
- “U”, the smile is asymmetrical, one corner of the mouth is downturned;
- “D”, movement – inability to raise and hold both arms at the same time;
- “A”, articulation – speech is confused, slurred, tongue-tied;
- “R”, solution - if at least one of the signs is present, call an ambulance.
Later, you can increase your life expectancy by changing your lifestyle:
- reviewing nutrition. They try to completely exclude fried, pickled, smoked, canned, confectionery, and baked goods from the diet. Limit salt, sources of saturated fats (lard, butter, coconut, palm oil, red meat, cheese, cottage cheese);
- giving up cigarettes;
- by reducing or better eliminating the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- making your life more active.
Following the doctor’s recommendations, active rehabilitation exercises, and a positive attitude also help reduce the risk of complications and recurrence after a stroke.
What could be the consequences of a recurrent stroke?
Rehabilitation after Stroke
Brain damage can cause not only physical disability, but also perceptual difficulties and sensory discrimination disorders. The consequence of this is partial paralysis of the body (the patient may not feel the limbs or cannot name the position of his body). In addition, depending on the location of the injury, a person may experience difficulties with smell, vision, hearing, and touch.
There may also be psychological and emotional problems as a result of a stroke. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, and mood swings as part of the process of adapting to a new situation. Consequently, a prognosis such as a stroke can lead to significant changes in the relationship between the patient and his family members. In addition, the patient after a stroke is often isolated from relatives and friends.
Unfortunately, many cases of recurrent stroke are fatal. You should always remember that the consequences of a second or third stroke will be severe and a person may remain a “houseplant” for life. This means that he will be recumbent, and thinking, speech, and memory may be impaired.
- partial loss of the ability to speak and see
- numbness of hands and loss of sensation
- paralysis
- partial memory loss
- loss of coordination and problems with fine motor skills
- urological disorder
- mental health problems
The consequences can be mild or severe, when a person needs at least six months to recover, a special rehabilitation course and regular medical assistance.
The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are paralysis, loss of the ability to see and speak, motor impairment, problems with mental activity, the development of mental disorders, tissue necrosis, infarction and cerebral edema. Often, even after recovery, patients only partially regain their physical capabilities, and older people cannot survive the attack at all.
Most patients experience complete or partial paralysis, numbness, loss of vision and memory, speech and mental disorders, cerebral edema, coma, dementia, blood poisoning due to inflammatory processes, and loss of sensitivity. They can be restored only in 20% of cases and only partially.
Consequences and forecasts
Unfortunately, a secondary stroke leaves the patient with less chance of survival.
The second and third attacks are caused by:
- development of paralysis. The area of damage depends on which part of the brain has undergone pathological changes associated with circulatory disorders;
- impairments of hearing, vision and touch, as well as thinking abilities;
- inability to cope with natural needs independently;
- swallowing disorders;
- emotional instability;
- comatose state;
- lethal outcome.
As practice shows, 70% of patients who have suffered a second stroke and fall into a coma die without regaining consciousness.
About 80% of patients remain disabled, since as a result of relapse, irreversible changes occur in the cerebral cortex.
If the patient survives after a relapse, then the predicted life span is no more than 3 years.
The third stroke is the most difficult to tolerate and in almost all cases inevitably leads to death.
In the article “Gymnastics and exercises after a stroke,” you will learn about the benefits of therapeutic exercises after a stroke.
How long do they live?
Most patients are interested in the question, how long do they live after a stroke? Future life, its development and rhythm depend on this, because everyone will have to strictly follow certain rules of prevention, take medications and constantly undergo diagnostics.
Typically, life expectancy is not significantly reduced, although such patients live three to six years less than others, but only due to the development of a recurrent stroke in old age. The average life expectancy is about 65-70 years, provided that the doctor's recommendations are followed.
Statistics
No more than 25% of patients die from a stroke before the age of 45, but after 50 years this figure rises to 40%. Women suffer the most, although strokes often occur in men. As for restoration, 40% of patients require it, and half of them remain disabled for life. No more than 20% of patients can survive a stroke after 70 years of age, and there is no talk of their full recovery.
At-risk groups
And people who are considered at risk due to the presence of certain diseases or pathologies need to be especially careful. This is about:
- hypertension and atherosclerosis
- diabetes and obesity
- vascular pathologies
- excessive consumption of alcohol, cigarettes and coffee
- about heavy physical and emotional stress
- taking contraceptives
- pregnancy
- traumatic brain injuries
- mental disorders
- newborn children
- elderly people
People with such problems should be diagnosed more often than others, and at the first symptoms go to the hospital for treatment.
Risk factors
- stress,
- smoking,
- alcohol,
- infectious and traumatic lesions of the central nervous system.
However, not only people with bad habits can become patients of neurologists. A person who lives at the limit of his capabilities, constantly experiences stress and chronic fatigue, also risks ending up in a hospital bed.
To prevent a recurrent stroke, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations:
- measure pressure,
- do a cholesterol test.
If the patient is young, cholesterol will not play a key role in the risk of another stroke, but blood pressure may. Also, other risk factors for recurrent stroke are heredity and age. After 65 years, the chances for both sexes become equal. According to statistics, in old age the risk of an attack in men and women is practically no different.
For older people, the statistics are completely disappointing, however, in recent years, the increase in hypertensive patients has also occurred at the expense of young patients. According to statistics, a third of attacks occur in people of working age.
Left or right stroke: which is better?
The key point that determines the prognosis is the timeliness and completeness of medical care. Researchers have found that people who have had a stroke on the left side have a longer life expectancy on average.
The identified pattern is associated with a more difficult diagnosis of right-sided disorders of the blood supply to the brain, which is not accompanied by speech impairments - the main sign that others pay attention to. Also, most people are right-handed, so the loss of functionality of the “working” hand is more noticeable to strangers.
Prognosis after recurrent attack
According to doctors, repeated illness occupies a leading position among other factors causing death and disability. Having overcome a vascular accident for the first time and managed to restore the functionality of the body, many believe that the disease will not return.
However, according to statistics, people over 45 years of age after a stroke should be wary of the following consequences:
- a 15-fold increase in the risk of a second strike;
- death (in 65-70% of cases) after the second attack;
- a much longer and more complex recovery process (if you manage to survive).
There is little comfort in the prognosis of a recurrent stroke. However, the first bitter experience gained should motivate to prevent relapse.
As statistics show, the majority of people who managed to suffer a first stroke did not experience an attack a second time only due to compliance with the necessary preventive measures.
To avoid another stroke
To avoid a recurrent stroke, it is important to follow a few simple rules that can prolong the patient’s life for decades. If this is not done, the risk of a second attack doubles, and it is almost impossible to survive it, especially for older people. If this succeeds, the patient falls into a coma, cerebral edema begins, and death occurs a little later.
The main preventive measures are:
- diet
- outdoor walks, gymnastics, swimming in the pool
- taking medications, quarterly examination by a doctor
- quitting smoking and alcohol
- control of diabetes mellitus, blood pressure levels
- treatment of chronic diseases and pathologies
- reducing stress and physical activity
- visit a doctor in a timely manner when the first symptoms are detected
Even if the symptoms go away after a couple of hours, still go to the doctor, because the foci of the stroke have already formed in the brain, and the subsequent attack may be the last.
Prevention
How to avoid another stroke? Only with the help of prevention, which includes a review of lifestyle. It is worth considering your age and health status.
Prevention includes:
- Regular observation of a doctor after the first attack, taking the necessary medications.
- Regular examination in order to timely identify the risk of relapse.
- Compliance with a regimen that includes adequate sleep, feasible physical activity, and diet.
- Performing physical therapy exercises.
- Treatment of chronic diseases.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Avoiding stressful situations.