Characteristics of the disease
Stroke is a brain disease in which a sudden disruption of blood circulation in the brain occurs, caused by blockage of the vessels supplying it or rupture of the latter.
This can lead to:
- emboli,
- blood clots,
- atherosclerotic plaques,
- severe vasospasm,
- compression due to tumors.
Blockage of the vessel leads to the fact that the tissue area begins to lack oxygen, and if blood circulation is not restored within 7 minutes, the neurons will begin to die and irreversible changes will occur in the tissue.
Causes
Diseases that provoke stroke in men and women are:
- diabetes,
- atherosclerosis,
- arterial hypertension.
Risk factors include:
- old age,
- smoking and drinking alcohol,
- cervical osteochondrosis,
- lipid metabolism disorders,
- systemic vasculitis and connective tissue pathologies,
- deep vein thrombosis,
- inflammatory diseases of the heart and its defects,
- the presence of artificial valves or a pacemaker.
Reference! The brain, as we know, is divided into two hemispheres. Their functions are partially duplicated, which means that the degree of damage to different hemispheres varies.
Symptoms
A stroke on the left side is much more severe than on the right, and its consequences are more destructive.
In this case, the right half of the body is paralyzed, basic functions are lost - memory, logic, speech, thinking, information perception, writing and reading skills.
Reference! There are 3 groups of signs of left-sided stroke: general cerebral, autonomic and focal.
General cerebral symptoms are always present, regardless of which hemisphere is damaged: severe nausea and frequent vomiting, severe headache, loss of consciousness.
Focal ones allow you to determine which hemisphere of the brain is damaged:
- decreased vision and hearing on the left side;
- distortion of half the face;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin on the left side of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements, balance;
- memory lapses, distortion of long-known information.
How does the psyche change after a left-sided stroke?
The mental state after an attack also changes, and doctors distinguish two completely opposite states, which depend on the degree of brain damage and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Apathy
Apathy most often appears in severe post-stroke lesions, when most of the most important functions are impaired. A person becomes indifferent to everything, he loses interest in life and communication. Such people avoid the company of relatives and friends, they prefer to be alone with themselves, and are not interested in the events happening in the family. Untidyness appears; attempts by loved ones to tidy up the person can be perceived aggressively.
Asthenia as a consequence of stroke
Important! Against the background of apathy, depressive disorders often develop, and suicidal tendencies may appear. Under no circumstances should such people be left alone. It is important to provide them with a calm environment and constant supervision without signs of imposition.
Aggressive behavior
Uncontrolled aggression usually manifests itself in people who have partially retained their functions, but have lost their usual quality of life. For example, a person who has preserved the functions of the speech apparatus, but lacks control over the processes of emptying the bladder and intestines, experiences anger and irritation towards the people caring for him. It is very important for relatives to remain calm and self-controlled at such moments, since a response can aggravate the patient’s condition and reduce the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures and drug treatment.
Consequences of stroke in numbers
A person experiencing aggression after a stroke may throw objects that come to hand at others, break dishes, and bite. If the patient’s behavior becomes threatening to the normal living indoors of the rest of the family, it is necessary to consult a doctor about the advisability of isolation.
Video - Consequences of a stroke
Types of diseases of the left hemisphere of the brain
Ischemic
The second name is cerebral infarction.
It is characterized by poor circulation due to the formation of blockages in the vessels and their narrowing. Cells can be revived within the first 48 hours. High risk of death and disability.
Attention! It most often affects people over 50 years of age. Another risk group is people with excess weight, hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances, and hereditary predisposition.
What is an ischemic stroke is explained in the video:
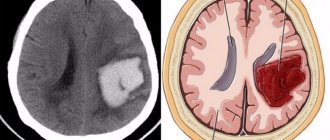
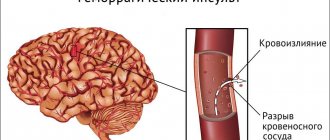
Hemorrhagic
This type is less common than ischemic and most often affects young people. Death occurs in 90 cases out of 100.
Hemorrhage is observed, and it can be either with a rupture of the walls (blood flows out under pressure and forms tumors and hematomas), or without violating the integrity of the vessels (the walls stretch without letting blood out).
Factors provoking a blow
Cholesterol contained in food is the main enemy of healthy blood vessels. Accumulating in their walls, it first forms deposits. They then form cholesterol plaques and prevent free blood circulation.
At the next stage, thrombosis occurs - a phenomenon in which blood clots form around cholesterol plaques. Thrombi are the main catalysts of the embolic process. An embolism is a blockage of blood vessels in the brain by blood clots, blood clots or tumors.
The picture is complicated by the fact that risk factors are interconnected, and some causes give rise to others. In addition, stroke occurs during pregnancy and after childbirth. In older people, an attack occurs as a result of the development of previous diseases. At a younger age, the cause is often an unhealthy lifestyle.
Treatment of the disease
Before the ambulance arrives, the person should be laid horizontally, raising his head above body level and turning it to the side (if vomiting occurs). Further assistance is provided only in a hospital.
Held:
- Ultrasound of the heart,
- ECG,
- EGG,
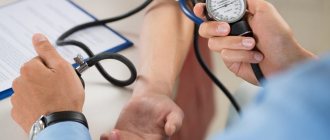
- blood pressure monitoring,
- urine and blood tests.
The patient is prescribed:
- antithrombolytics, which prevent the formation of blood clots and reduce blood clotting;
- means to improve fluidity indicators (Heparin, Warfarin);
- thrombolytic drugs (Actilyse);
- neuroprotectors (Semax, Ceraxon, Diakarb);
- antioxidants, vitamins, if necessary - antipyretics, sedatives, Glycine to reduce vasospasm.
- In some cases, microsurgical intervention is required to destroy the blood clot.
The rehabilitation period is the most important
The goal of the rehabilitation period is to prevent another stroke. Depending on whether there was a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, the doctor prescribes medications that must be taken for a long time.
The list of such drugs includes: drugs against the formation of blood clots, neuroprotectors, anticoagulants, vascular drugs and, if necessary, antidepressants.
If the patient’s condition allows, then spa treatment will be beneficial. With the home method of treatment, physical therapy and classes with a speech therapist should continue. Light sports are acceptable. It is necessary to radically change the previous way of life.
Consequences
Consequences after a stroke on the left side are always of interest to patients.
Several factors play an important role here: the severity of the disease; size of the affected area; patient's age.
Most often the patient experiences:
- partial paralysis of the body due to increased muscle tone (maybe both arms and legs together or separately, facial asymmetry);
- impaired sensitivity of the muscles and skin of the right side;
- problems with orientation in space or complete loss of it;
- motor and sensory disorders (inability to recognize objects and distance to them);
- speech problems;
- inability to perform mathematical calculations, read and write;
- violation of abstract thinking, inability to build a logical chain;
- mental disorders (sharp outbursts of aggression, angry attacks, depression).
Treating stroke at home with folk remedies
It is appropriate to talk about diet here. During this period of time it must be special. It is best to balance your diet with dairy products and plant foods. It is optimal to offer the patient berries, fruits, cottage cheese, kefir, and cereal porridge.
Meat and fish are excluded until the general condition improves. At this time, it is good to prevent vitamin deficiency. Decoctions of rose hips, hawthorn, and currant compote are perfect for this. Vitamin C can improve immunity, which will allow the body to recover faster.
A strict diet for people with paralysis is mandatory! Do not forget that there should be a positive atmosphere around the patient. He himself must be configured for rapid recovery. You should not cry near a paralyzed person and feel sorry for him; you should set the person up only for the best.
To restore muscles faster, you need to do restorative exercises daily. A suitable set of exercises must be selected by the attending physician. For three weeks after a stroke, it is necessary to rub the patient with burning ointments to restore blood flow.
Herbs will help speed up recovery. In folk medicine there are many ways to make recovery go much faster.
- Maryin root. The dried herb is poured with boiling water and left for 5 hours. To put your body in order, you need to drink 2 tablespoons a day.
- Mumiyo. Dilute the drug in water. You need to drink this drink once a day, 1 glass.
- Bay leaf. An infusion of bay leaves will quickly restore the body after a stroke. An infusion is made from ground laurel leaves and sunflower oil is added. This infusion should be lubricated on the affected areas of the body. Can be used as a massage oil. You need to infuse this remedy for a week.
- Lemon and garlic. Take 100 g of lemon and 100 g of garlic. Mix everything. Leave for about 7 days. This mixture should be given to the patient twice a day. It is better to take after meals.
All these remedies will help to cope perfectly with the patient’s difficult condition and will quickly put him on his feet.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is carried out several weeks after the complete restoration of normal blood supply to the brain and the threat to the patient’s life has been eliminated.
The acute phase requires mandatory medical supervision; in the future, the person can be transported home or to a special center.
Attention! Doctors are faced with two tasks: to restore motor function and stabilize a person’s psychological state.
Massage the affected part of the body. Can be targeted, manual or classic.
Physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, ultrasound, acupuncture, electrophoresis) and therapeutic baths that help restore the connection of neurons with each other and improve blood circulation.
Special gymnastics:
- To begin with, the patient needs to undergo a passive course, in which the patient is helped by his relatives or medical staff.
- Next, exercises appear to complicate motor skills - the patient is taught to handle a fork and spoon, walk, stand up, open doors, etc.
- Gradually, having strengthened the body, you can move on to independent work on exercise machines with increasing loads, collecting puzzles and mosaics, sorting through small objects, opening locks and zippers.
To restore speech, lessons with a speech therapist . Classes are conducted from the first stage of rehabilitation.
Gradually, when the patient can show more initiative, he will be allowed to study independently.
Important! The main thing is to have a positive attitude and focus on results.
A psychologist first talks with the patient (this is necessary to assess his mental state). If a person suffers from depression or mental disorders, the necessary treatment is prescribed. The complex necessarily includes breathing exercises.
Establishing diagnosis
In order to determine the affected areas of the brain, computer () and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are prescribed.
In addition, the condition of the heart is checked using ECG and ultrasound. A blood test is taken and an eye examination is performed. In particularly severe cases, a cerebrospinal fluid puncture may be prescribed.
A complete picture of the disease is compiled based on the following studies:
- X-ray of the skull;
- chest x-ray;
- electroencephalogram (EEG);
- endocrinological examination;
- echocardiography (Echo CG).
The most accurate data when identifying a left-sided stroke is provided by computed tomography, as it allows you to examine the brain from different angles, including its internal part.
On visual examination, a left-sided stroke is marked by paralysis of the right side of the body, including the facial muscles. The patient also has a pronounced impairment of mental, speech, and auditory activity. He has difficulty pronouncing words and can only produce parts or simple sounds. There is also difficulty in perceiving the words of others.
For prevention purposes
In order to prevent both left- and right-sided strokes, it is important to adhere to preventive measures. These measures are divided into three types:
- primary – prevention measures,
- secondary – complex procedures to prevent recurrent stroke,
- tertiary – restorative measures after an attack.
People suffering from diabetes, hypertension or atherosclerosis need to pay special attention to their health. If you are overweight, you should get your diet in order. It is necessary to eliminate bad habits. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of stroke by 50%.