Varicocele is a common disease among men, which is expressed in varicose veins around the spermatic cord, sometimes accompanied by nagging pain in the area of the left testicle and the formation of lumps on the scrotum. The most dangerous consequence of the disease is considered to be male infertility, which occurs in 70% of patients.
The only known treatment for varicocele is surgery. It consists of ligating and cutting off the veins in the area of the spermatic cord. This operation is most often used to treat varicocele, since it is considered quite easy and most often occurs without complications.
Four methods of surgical treatment of this disease are used:
- Ivanissevich method. It involves cutting off the vein through an incision in the groin area. Performed under local anesthesia. Disadvantages are a long postoperative period and a high probability of relapses, up to 9%.
- Laparoscopic intervention is performed through three punctures in the abdominal cavity. Advantages: low invasiveness, short recovery period.
- Microsurgical treatment using the Marmara method is performed through a small incision in the groin area under local anesthesia. It is highly accurate and the risk of damage to blood vessels is negligible.
- Sclerotherapy. Can be used in the initial stages of the disease.
Why surgery is the only way out
The causes and mechanisms of development of varicocele are purely mechanical in nature - the affected testicular (spermatic) vein is not able to ensure the outflow of venous blood from the testicle due to:
- damage to the valves located inside the lumen and responsible for ensuring that blood moves in only one direction - from the testicle up into larger veins;
- the presence of an obstruction or increased pressure (venous hypertension) in those large veins into which the spermatic veins flow, which impedes blood flow in them and causes venous stagnation;
- weakness and flabbiness of the walls of blood vessels.
All this leads to the fact that blood not only does not flow away from the testicle, but accumulates in its venous plexuses due to backflow (reflux) from large vascular trunks. In conditions of venous congestion, the sensitive tissue of the genital organs loses its normal structure and the ability to produce full-fledged seminal fluid and hormones.
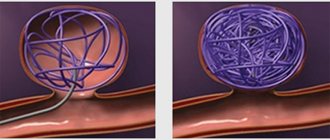
The mechanism of blood circulation in healthy and varicose veins. Click on photo to enlarge
Since testicular varicose veins become not vessels transporting blood, but pathological storage for it, the only solution to the problem is to interrupt the vicious connection between them, which will eliminate reflux and blood stagnation. This is the purpose of varicocele surgery. It involves isolating, ligating, crossing or completely removing the main stems of the spermatic veins above the level of their branching into small branches that form plexuses among themselves.
Thus, the pathological stagnation of blood in the vessels and testicular tissues will be eliminated without compromising blood circulation. Venous outflow from the scrotum will occur through a system of other vessels, since the spermatic vein is the main, but not the only route for blood flow. Moreover, in conditions of stagnation and increased pressure in the spermatic vein, additional outflow pathways are already well formed at the time of surgery and will continue to form in the postoperative period.
Surgical treatment in 80–85% is performed for left-sided varicocele. This is due to the fact that the left testicular vein flows into the renal vein, and the right one into the inferior vena cava. Due to the anatomical location, branching angle and other features of the left renal vessels, the pressure in them is increased. Therefore, the left-sided localization of varicocele prevails over the right-sided one.
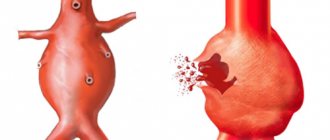
Comparative diagram of the structure of a healthy testicular vein and an affected varicocele
What is surgery for varicocele?
With varicocele, the coronary vessels that supply blood to the pelvis and male genitals are affected. Veins dilate and their elasticity decreases. Blood flow increases, the ovarian vein is deformed.
More than 15% of men suffer from the disease and some are not aware of the health problem they have. After all, the disease has no obvious symptoms. The only manifestation may be discomfort in the groin area, and after physical activity, nagging pain in the scrotum. The consequences of the disease for those who want to have children can be sad.
You should not self-medicate; you should definitely consult a doctor for help.
The disease is completely curable, but only if diagnosed in a timely manner and the necessary measures are taken. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention, you should undergo regular examinations, first with a pediatric surgeon, then with an andrologist or urologist.
In this case, before the operation, damaged veins must be identified and the nature of changes in the body determined. The disease has the following four degrees:
- the first is a slight enlargement of the veins, changes in which can only be seen on an ultrasound and therefore this degree is rarely taken into account;
- second - varicose veins can be felt by palpating the scrotum with the patient standing;
- third - here there is already an abnormal expansion of the veins, which can be felt in any position of the patient;
- in the fourth degree, varicose veins are determined visually when examining the genital organ.
The last two cases are mandatory indications for surgical intervention. Its purpose is to redirect the blood flow to another direction, blocking the veins of the spermatic cord.
Endoscopic (laparoscopic) procedure
The purpose of the operation is the same as according to the methods of Marmara, Ivanissevich and Palomo - ligation and intersection of the testicular vein. But the procedure is performed using endoscopic technology, which avoids blood loss, complications and reduces tissue trauma .
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. It is based on complete blockage of the testicular vein, after which blood flow through the vein is impossible.
To perform the operation, three punctures are made on the patient's abdomen . One of them is in the navel area, into which a miniature video camera is inserted, and into the other two - a miniature instrument - scissors and clamps.
First, an insufflator tube is inserted through one of the punctures to fill the retroperitoneal and preperitoneal area with gas.
The video camera transmits an enlarged image of the illuminated operating area to the monitor, which the surgeon can use to navigate, isolating the artery and veins of the testicle from under the peritoneum, after which he will apply titanium staples to the veins of the testicle or tie them with a surgical thread, and cut the vessels between the staples.
After the operation, the patient can leave the hospital on the third day .
The endoscopic procedure allows for immediate treatment of bilateral varicocele . All other operations are done separately for each party.
Quite effective and low-traumatic . It is performed under general anesthesia. Cases of relapse after surgery are very rare. It is done for severe pain in the scrotum or an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Recording manipulation process:
Testicular varicocele in men: what does the diagnosis mean?
If a man is diagnosed with varicocele, then initially one might think that the disease is somehow related to varicose veins, since both names have the same root. Indeed, the names are similar, as are the mechanisms of pathology development.
Testicular varicocele is a varicose vein in the spermatic cord. This disease is observed mainly in adolescents aged 14–15 years and in young men of reproductive age. Statistics show that in general the pathology occurs in 15% of men.
Varicocele disease in men belongs to the category of pathologies that occur without significant symptoms. Most often, originating during puberty of a young person, it quickly develops to some extent and then stops. There are also cases when the disease regresses on its own and then disappears altogether.
However, the following alarming signs of this disease may indicate a developing varicocele:
- Increase in size and descent of the left testicle (if the pathology is localized on the left).
- Mild “pulling” pain in the scrotum and groin. While walking or during heavy physical activity, these sensations may become more pronounced and cause discomfort.
- If the scrotum is severely drooping on one side, this may interfere with normal walking.
- Pain in the scrotum, bulging of its veins, shrinkage of the left testicle (with severe varicose veins of the testicle).
If signs of varicocele are detected, it is better to immediately go to a specialist rather than wait for the pathology to regress.
What types of varicocele removal operations are there?
Refers to the most common methods of surgical treatment. This method is considered traditional and involves tying the internal testicular vein to block back blood flow to the testicles. Why is it not always effective to operate using this technique? According to statistics, in 40% of cases the long-term consequence of the intervention is relapse. But varicocele can be treated in this way both in adult men and in boys after 13 years of age.
Today, there are different types of testicular surgery to remove varicocele. Among them are the most important:
- Marmara operation for varicocele;
- laparoscopic varicocelectomy;
- laser surgery;
- Ivanissevich operation.
The Marmara microsurgical operation is the best method for replacing a diseased testicular vein with a healthy vein. To do this, doctors provide themselves with mini-access to the required area of the body, without penetrating the abdominal cavity. The microsurgical technique is considered the least traumatic among all other techniques, since it almost never causes the appearance of cosmetic skin defects.
Also, microsurgery has the lowest risk of relapse and serious complications. Its advantages include a quick recovery period and low invasiveness.
We invite you to read: Ischemia on the ECG: changes, signs, explanation, what it looks like
Microsurgical manipulation does not require mandatory hospitalization of the patient in a hospital and can even be performed on an outpatient basis. The preparatory period is standard, as for all other surgical interventions.
Operation Marmara
The patient is given an anesthetic injection, which has an anesthetic effect. The anesthesiologist decides how much anesthetic to administer based on the patient’s total weight and age. Next, the surgeon makes a small incision in the groin area no more than 2-3 cm. After the swollen vein is found, it is bandaged, stitched and crossed. This helps normalize blood flow and relieve the negative symptoms of varicocele.
During Marmara microsurgery, in rare cases, accidental nerve damage in the groin or bleeding may occur. The recovery period is only 3 days, and the stitches are removed already 8-10 days after they are applied. The only disadvantages of this technique include the high cost, because special tools and expensive optics are used.
During the postoperative period, it is recommended to avoid severe physical activity and sudden movements. You cannot have sex for one month and you must protect the incision area from friction. Underwear should be natural and not tight.
After three months, you should take a spermogram in order to assess the ability of sperm to fertilize. Six months after treatment, you can return to your normal lifestyle.
Operation Ivanissevich
This type of treatment for testicular varicocele is considered cheaper. The essence of the method is to cut and ligate the left vein in the testicle. This helps eliminate the main negative factor that causes backflow of blood into the plexus of the testes.
During the Ivanissevich operation, complete closure of the lumen of a varicose vein is performed under local anesthesia for adults. For children, surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia. It takes about 30 minutes.
The postoperative period in this case is longer, and the risk of complications is quite high. During all manipulations, the femoral artery and other anatomical formations in the inguinal canal may be damaged. In addition, the disadvantages include complete dissection of the abdominal wall and penetration into the abdominal cavity.
Laparoscopic intervention
The most non-invasive operation is considered to be laparoscopic, which occurs with minimal trauma to the patient. In this regard, it carries a lower risk of complications than other types of surgical interventions, which often cause bleeding or the formation of infiltrates. After using the laparoscopic technique, the patient does not receive a cosmetic defect, since the seam remains almost invisible.
Endoscopic varicocelectomy is performed in cases where the patient has bilateral dilatation of the veins of the spermatic cord. Incisions are made in the navel, left and right iliac region. Their size very often does not exceed 1 cm. Endoscopic devices, instruments and an endoscopic television camera pass through them. Therefore, the doctor can monitor the progress of the operation and, if necessary, adjust his actions.
Disadvantages include the high cost of the operation and the need for general anesthesia. The postoperative period usually takes about 3 days, after which the patient is discharged. The doctor tells him when he needs to come to have the stitches removed, how many days it will take to fully recover after varicocele surgery, etc.
Laser surgery
Laser coagulation
Laser treatment of varicocele is one of the most modern methods of solving this problem. To do this, there is no need to make an incision in the groin area, and all manipulations are performed using an intravascular endoscope. Fiber optics helps to find the exact area of vessel dilation and coagulate it under the action of a laser beam. After this, it is switched off from the general bloodstream.
The advantages of this type of intervention include the absence of the need for anesthesia and a quick rehabilitation period. You can also highlight the minimal risk of complications or serious consequences. Surgeries for varicocele have significant differences from circumcision of the foreskin, surgery to remove a testicle in men, or amputation of the penis. Only a doctor can answer the question of how long the rehabilitation period will take and what the cost of surgery to restore the testicle will be.
It should be noted that during this type of operation the vessels are not removed from the body. They are either glued together by introducing special drugs, or bandaged.
For varicocele, several types of operations are performed
Based on technology, it is customary to distinguish three main types of surgical intervention for varicocele:
- Sclerotherapy. It does not require hospitalization of the patient. The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia in a medical office. The essence comes down to gluing varicose vessels with a special solution. The rehabilitation period is short and the patient can go home almost immediately after the operation. However, the effectiveness of this method is considered low.
- Laparoscopy. It is carried out using high-tech equipment - a laparoscope. This is a surgical tube with a built-in light and camera. The process is low-traumatic and has a low rate of subsequent relapses. During this procedure, the dilated veins are ligated. Postoperative hospitalization lasts 3–7 days, depending on the anesthesia chosen.
- Open surgery using the methods of Marmara, Ivanissevich, Palomo, the essence of which is the same as in the previous paragraph - ligation of a vein with varicose veins. Surgical intervention is performed through an incision (up to 10 cm) in the abdomen or groin area.
- Classical - through an incision (Ivanissevich operation).
- Minimally invasive - through punctures (endoscopic, microsurgical and endovascular).
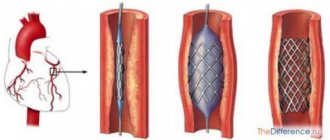
Ivanissevich's operation. Click on photo to enlarge
Endovascular surgery to remove varicocele. Click on photo to enlarge
The goal of all methods is the same - to eliminate the discharge along the testicular vein, blocking its lumen. The ways to achieve this goal vary.
| Operation characteristics | Classic intervention | Minimally invasive intervention |
| Incision | From 2–3 to 5–7 cm (depending on the patient’s physique) | Not needed, 2–3 skin punctures 1 cm |
| Operation time | From 10–15 to 30–40 minutes | About 15–20 minutes |
| Anesthesia | Intravenous or local | Deep with apparatus breathing |
| Extract | On days 3–5 | For 2–3 days |
| Pain after surgery | Moderate or severe, relieved with conventional painkillers | Light or absent |
| Indications | Varicocele grade 2–3 | Varicocele of any degree (1–2-3) |
| Possibility of relapse | From 10 to 20% | No more than 2–3% |
| Scar | Small, unnoticeable | Absent |
| Price (depending on the clinic) | From 250–300 to 650–700 USD. e. | From 450–500 to 10,000 USD. e. |
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- acute, infectious or purulent processes in the body;
- decompensation of the functions of internal organs (renal, cardiac, pulmonary, liver failure);
- decreased or increased blood clotting;
- severe anemia.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Cardiac glycosides include
Removal of testicular varicocele occurs through surgery. There are several types of surgeries that can help patients with varying degrees of disease. The methods of conducting them change over time, as outdated and dangerous ones fade into the background, while more modern and safe ones take their place.
Today, many types of varicocele operations are quite similar, with the exception of some nuances. After all, they are all aimed at the same goal. The severity of surgery depends on the stage of the disease. The main types of operations include:
- According to the Ivanissevich method. One of the classic varieties, which passes through a special incision in the iliac cavity. The incision must be made in the area of the inguinal canal. This helps provide easy access to the spermatic vein, located deeper inside. It is this that has to be bandaged during the operation in order to completely limit the blood flow in the problem area. This operation has been around for a relatively long time, so many consider it obsolete. The reason for this is the high traumatic nature of the entire procedure and possible complications for the patient. Also, multiple cuts will leave behind scars. The Ivanissevich operation requires a fairly long recovery period, the probability of complications is about 30% in severe stages of the disease.
- According to the Marmara method. This is a microsurgical operation. Here a slightly shorter incision is made in the groin area, up to 3 cm long. To ensure visual control over the procedure, the main stage of which is also ligation of the vein, a special magnifying device is used. Thanks to this, while the varicocele is being removed, other organs are practically not affected and the anatomical structures are not disturbed. This gives a low percentage of complications, due to which the Marmar operation is considered one of the most popular in modern practice. The level of danger here is comparable to the circumcision procedure.
- X-ray endovascular method. Here, a special probe is inserted into a vein on the thigh, the thickness of which is only 2 mm. The movement of the probe is monitored using an X-ray machine. The probe moves along the inferior vena cava and passes into the left renal vein. It then descends into the seminiferous, reaching the site of expansion. When the target is reached, the probe injects substances that cause thrombosis and local inflammation. The technique is not very painful and the sensations here are approximately the same as during a testicular biopsy. One of the advantages of this technique is that the patient can leave the medical facility within 3 hours after the operation. No scars remain on the skin, and complications practically do not appear.
- Laparoscopic method. The operation to remove varicocele in men using this method is performed using an endoscopic instrument. This special device is inserted into the punctures made, which are located in the abdominal wall. With its help, those veins that have undergone varicose veins are clamped using staples. After that they intersect. The operation is quite popular.
- Microsurgical bypass surgery. The operation to remove varicocele on the testicle in this way is associated with the movement of veins. This method is based on the fact that one of the main causes of the disease is a malfunction of the vein valves, which already give serious failure in aggravated circumstances, causing varicocele. Thanks to this, the spermatic vein is connected to others whose valves work normally. To carry out the procedure, it is necessary to make a special incision 5 cm long. Control optics are also needed here, but even with this in mind, the risk of vein thrombosis remains.
- Laser surgery. For varicocele, surgical treatment can also be performed using laser instruments. This is a modern technique in which there is no need to make an additional incision in the groin area, since all basic manipulations are carried out using an endoscope, which is placed inside the vessels. For this, a small puncture with a diameter of a few millimeters is enough. Thanks to the use of fiber optics, the accuracy of determining vessel dilatation is unmistakable. After this, it is coagulated under the influence of a laser beam, which excludes it from the general circulatory system. The operation is performed without anesthesia and has a short recovery period.
In addition, there are several more branches and nuances for each method, because in all cases there are their own individual manifestations that need to be addressed. These are the most accessible ways for people to get rid of varicocele once and for all.
Ivanissevich
This operation is performed at any stage of the disease and is performed under local anesthesia. It is considered one of the first operations for the treatment of varicocele; it is ineffective and traumatic .
It is based on open access to the lower abdominal cavity in order to identify and ligate the veins that are directed to the testicle at the level of the retroperitoneal region.
Before the operation, the patient's condition is examined. Blood and urine tests are taken and a cardiogram is done .
After the examination, local anesthesia is made and an incision is made in the abdominal wall in the left iliac region at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine parallel to the course of the inguinal canal. The incision is made no more than 5 cm .
In the abdominal space, the testicular vein is isolated, which is mobilized in a small area, ligated and crossed between two ligatures. The same must be done with all branches of the testicular vein.
It is precisely because not all affected branches are detected that varicocele relapses in approximately 40% of cases after surgery . This is due to the fact that the surgeon does not have the opportunity to examine the entire testicular vein in a small area.
The wound is sutured tightly and a sterile bandage is applied.
After the operation, pain is possible , for the relief of which painkillers are prescribed. To exclude the development of infectious diseases, antibiotics are prescribed.
For several days after manipulation on the scrotal area, it is necessary to wear a support bandage to reduce tension on the spermatic cord and discomfort.
After 8-9 days, the stitches are removed . In the first few days it is necessary to limit physical activity. In the next six months, no physical activity is allowed.
Complications such as dropsy and bleeding occur rarely.
Operation video:
Complications
Surgery for varicocele may be accompanied by the following complications:
- Neuralgic pain that occurs due to injury to nerve endings.
- Relapse (reoccurring disease).
- Hydrocele of the testicle as a result of injury to the lymphatic vessels.
- Deep vein thrombosis due to hematoma in the puncture area or contrast injection.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Lymphatic edema is another consequence of surgery due to injury to the lymphatic vessels.
- Reduction in testicular size. Caused by affecting the spermatic artery.
- Damage to the ureter or intestines due to the inexperience of the doctor.
After the operation, a complication arises; no one is immune from this. And although the risk is not that great, you need to know what you can expect after the intervention. The doctor will inform you about this, but the complications are:
- inflammatory process. It is characterized by a number of signs and is detected on a control ultrasound. Treated with medications;
- neuralgic pain. Occurs when nerve endings are damaged. Such pain is difficult to stop, but you can try. Physiotherapeutic procedures and acupuncture are prescribed;
- lymphatic edema. Observed if a lymphatic vessel is damaged as a result of surgery. Treatment may include wearing compression garments;
- hydrocele. Dropsy occurs in the testicle due to damage to the lymph nodes. Treatment – wearing a bandage;
- testicle reduction. This is a complication, the reason lies in damage to the spermatic artery, this situation is difficult to stop;
- recurrent varicocele. Treated surgically;
- damage to the urinary tract or intestines. This development of events occurs in inexperienced surgeons;
- blockage of deep veins. Thrombosis occurs due to a reaction to contrast or internal hemorrhage in the puncture area.
Varicocele can leave a serious mark on a man’s health and lead to complications.
To summarize the above, it should be noted that varicocele is a pathology that can lead to serious health problems. The main consequences of varicocele are impotence, infertility, and cancer.
You should not self-medicate, as this will worsen the course of the disease. As soon as the first signs of varicocele appear, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
- Hydrocele of the testicle is an increase in size due to swelling and accumulation of fluid in the scrotum.
- Bleeding, hematoma, suppuration of a postoperative wound.
- Testicular atrophy is a decrease in size and decreased function of the operated testicle.
- Pain syndrome in the area of the postoperative scar.
We suggest you read: Home remedies for hypertension
There is no need to be afraid of surgical intervention due to the possibility of complications, since they occur very rarely, in no more than 1–2% of those undergoing surgery.
Contraindications
Not all patients can undergo surgical treatment of the testicle, as there are certain contraindications. Laparoscopic surgery cannot be performed if the patient has already undergone such an intervention earlier or if he has a malignant tumor. Microsurgical operation is prohibited if the patient has diabetes mellitus or severe cardiovascular pathologies.
Before undergoing surgery to remove testicular varicocele, the patient must undergo a thorough examination so that the doctor can identify the exact cause of the disease. After this, it will be possible to select the optimal type of surgical intervention, taking into account the individual pathology, the patient’s age and his financial capabilities.
Indications for surgical treatment
Due to the expansion of the veins, the normal blood supply to the testicular tissues and the process of thermoregulation are disrupted. The number of sperm decreases and they become less mobile. In most cases, the left side is affected, although bilateral pathology sometimes occurs.
Varicocele can be congenital and usually begins very early, but does not manifest itself in childhood. The first clinical signs begin to appear as the child grows older (in adolescence).
Varicocele
The course of the disease in a teenager may be asymptomatic, so the indication for surgical removal of varicocele may be data obtained as a result of the Valsalva maneuver, ultrasound examination or palpation of the pampiniform plexus. The effectiveness of treatment depends entirely on the degree of the disease and the chosen technique. If necessary, the patient is prescribed a testicular biopsy.
Surgery to remove varicocele is needed if the following symptoms are present in a teenager or adult man:
- pain in the groin;
- feeling of discomfort;
- swelling;
- testicular swelling.
The technique of surgical manipulation depends on the size of the testicle and the age of the patient. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to prepare for testicular surgery for varicocele in order to avoid serious complications and consequences.
Non-drug treatment: Conservative treatment of varicocele is not effective.
Drug treatment: Drug treatment is prescribed only after surgery to stimulate spermatogenesis. Most often, a complex of vitamins and biologically active food supplements (containing selenium and zinc) are prescribed. Sometimes hormonal drugs are prescribed (androgens, human chorionic gonadotropin), they are used under strict laboratory control.
Preparation for surgical treatment: involves taking tests before surgery (to exclude decompensation of any organ or organ system). The following tests are required:
- General blood test (to determine the state of hematopoiesis)
- Blood type and Rh factor (for blood transfusion if necessary)
- Urinalysis (to check kidney function)
- Biochemical blood test (glucose, creatinine, urea)
- ECG (electrocardiogram) – to determine the work of the heart
- Chest X-ray (to exclude lung pathology)
Surgical treatment Currently, there are more than 120 types of surgical treatment for varicocele. All operations can be divided into two groups:
- Group I – operations in which the connection with the renal artery is preserved.
- Group II – operations in which the communication with the renal artery is interrupted
Currently, microsurgical techniques are successfully and widely used in the treatment of varicocele. This made it possible to reduce the number of relapses (repeats) of the disease, as well as significantly reduce the risk of complications after surgery.
Classical operations on varicocele One of the most common operations is according to Ivanissevich. It consists of ligation and further resection of the left testicular vein. This leads to the elimination of reflux from the renal vein into the pampiniform plexus. But with this operation there is a possible risk of developing renocaval anastomosis due to difficulty in the outflow of venous blood from the kidney.
| Indications for surgery according to Ivsanissevich | Contraindications to surgery according to Ivanissevich |
| Varicocele 3 degrees | The patient has diseases in the stage of decompensation (diabetes mellitus, hemophilia) |
| Acute diseases (peritonitis, appendicitis) |
Microsurgical methods for the treatment of varicoceleLaparoscopic clipping of the testicular veinLaparoscopic varicoetomy is an endoscopic and minimally invasive method for the treatment of varicocele.
| Indications for laparoscopic testicular vein clipping surgery | Advantages of the laparoscopic method over classical operations | Contraindications for laparoscopic testicular vein clipping |
| Varicocele 1, 2, 3 degrees | Possibility of vein clipping for bilateral lesions | Abdominal surgeries in the past. |
| Reno-testicular type of varicocele | Reduced risk of postoperative complications | |
| Ileo-testicular type of varicocele | The length of hospital stay is reduced to 2-3 days | |
| Mixed type varicocele | Almost complete absence of pain in the wound | |
| No pain when walking on the first day | ||
| Good cosmetic effect | ||
| Good sperm count after surgery | ||
The operation is performed under general anesthesia (the patient is put under anesthesia). A trocar is inserted near the navel and the abdominal cavity is examined. Then the veins of the testicle are found, and the artery and lymphatic vessels are carefully separated from the veins. Then the veins are clipped (applying special clips) and the operation is completed.
Endovascular phlebosclerosis The method consists of clogging the testicular vein with various substances or special devices.
| Indications for the use of endovascular phlebosclerosis | Advantages of endovascular phleboskerosis | Contraindications for endovascular phlebosclerosis | |
| Reno-testicular type varicocele | The operation is performed under local anesthesia (the patient is conscious) | Large reno-testicular collaterals, which can lead to drug entry into the systemic circulation | |
| No renal vein stenosis | Hospital stay is reduced to 2 days | Renal venous hypertension | |
| Absence of venous hypertension | Absence of surgical intervention as such (with this method there are no incisions) | Loose vein type | |
| This method allows you to avoid complications such as hydrocele. | |||
| Possibility of re-occlusion of the vein in case of relapse of the disease |
Endovascular obliteration (occlusion) of the testicular vein is performed in both adults and children. Various substances are used for occlusion:
- Spiral emboli
- Fabric glue
- Wire umbrella devices
- Various cylinders
- Drugs that cause vein sclerosis
Complications developing after classical operations.
Hydrocele (hydroxycele) is a complication in which fluid accumulates in the lining of the scrotum. In this case, hydrocele appears due to a violation of the outflow of lymphatic fluid. Disruption of lymph outflow occurs due to ligation of the lymphatic vessels along with the testicular vein during surgery.
This complication is treated, as a rule, either by puncture of the affected part with pumping out fluid or by surgery to restore lymph outflow.
Testicular atrophy. A very rare but serious complication is testicular atrophy. Testicular atrophy is characterized by a decrease in testicular size and a significant decrease in its function. According to statistics, this complication develops in 1:1000 patients operated on for varicocele.
Postoperative pain occurs due to blood overflow of the epididymis and, as a result, stretching of its capsule. But most often, after surgery, patients experience a decrease in pain sensitivity. Complications that develop after laparoscopic clipping of the testicular vein.
Complications develop extremely rarely. The most common complication is mild abdominal discomfort after surgery, which is due to pneumoperitoneum (abdominal cavity filling with air). Performed during endoscopic surgery for better visualization of organs. Over time, air is absorbed and the discomfort goes away. Complications that develop during embolization of the testicular vein:
- Allergic reactions to contrast agent. Can be avoided by administering desensitizing drugs before surgery
- Thrombophlebitis of the veins of the pampiniform plexus. Can be avoided by preventing thrombosis.
- Perforation of vessel walls.
Tags: varicocele, operation, occur
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Postoperative period
Usually the postoperative period is easy. If anesthesia has been administered, patients may experience dizziness and mild nausea. The first minutes are disorienting in space, but the negative consequences after the operation quickly pass.
The pain at the intervention site is insignificant, but if the pain threshold is high, you can ask the doctor for a painkiller. An adhesive plaster sticker remains at the incision site; the doctor will remove it after a few hours or the next day. The patient will receive instructions on how to care for the suture.