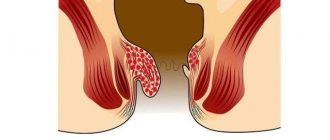
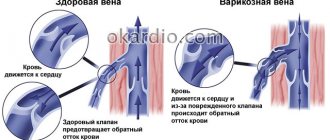
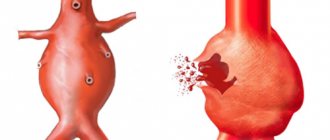
Hemorrhoids are the formation of a volumetric process (nodule) from the venous vessels of the rectum. Its development is long-term and chronic. Drug treatment in most cases does not lead to the reverse development (involution) of the hemorrhoid, so radical therapy for this pathology consists of removing the mass formation of the rectum.
Indications for surgery
The need for surgical removal of hemorrhoids as quickly as possible arises in the following cases:
- Lack of effect and result of conservative drug therapy for hemorrhoids with ongoing clinical symptoms of the pathology and growth of hemorrhoids (surgical treatment is usually prescribed if there is no effect within 3 months).
- A later (3-4) stage of the disease, in which prolapse of hemorrhoids from the rectum develops without their independent reduction.
- The development of complications of hemorrhoids at any stage of its development - profuse bleeding from hemorrhoids, the development of an abscess and fistula of the rectum are indications for immediate surgical intervention in a hospital setting.
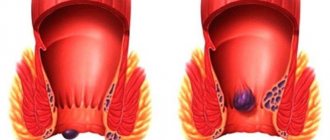
- Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is the formation of a blood clot that can separate from the hemorrhoid and begin to circulate with the blood flow in the arteries (thromboembolism). This condition is dangerous due to the development of necrosis (death) of individual sections of various organs, due to blockage of the artery feeding them by a detached blood clot.
- Combined development of hemorrhoids with other pathological space-occupying formations of the rectum - surgery is performed in the case of the parallel presence of polyps, anal canal fissures, chronic inflammatory processes in the pararectal tissue (connective tissue surrounding the rectum).
The method of choice for the treatment of hemorrhoids in older people is conservative therapy or minimally invasive methods of removing hemorrhoids. This is due to a decrease in tissue regeneration processes with age, which can worsen the postoperative period after surgery.
Do you know that…
- Hemorrhoids are one of the most common human diseases. More than half of the population has symptoms. They usually develop after age 30.
- Most often, a person who discovers symptoms does not seek specialized medical help for a long time and tries to treat himself.
- Pregnant women often experience symptoms of this disease, but they usually go away after pregnancy. However, in some women the disease can become chronic. In this case, they will need specialized medical care.
- For any bleeding from the anus, it is very important to consult a specialist, since it can be caused not only by hemorrhoids, but also by other serious diseases.
- About half of the patients who visit a specialized medical facility to treat hemorrhoids have other diseases of the anorectal area, such as anal fissure, anal fimbria, or irritation of the perianal skin.
- Outpatient treatments are usually relatively painless.
- Only a small number of patients require surgical treatment for hemorrhoids.
Types of surgical radical treatment of hemorrhoids
The main goal of surgical radical treatment of hemorrhoids is the removal of hemorrhoids with maximum preservation of healthy tissue of the rectum and anus. An operation to remove hemorrhoids is considered successful if there is no relapse (exacerbation, re-development) for a period of at least 10 years. For this purpose, modern proctology uses 2 main groups of methods for removing hemorrhoids - minimally invasive techniques and surgical intervention.
Minimally invasive techniques for removing hemorrhoids
Such radical treatment methods are also called non-surgical methods, which is not entirely correct, since a small degree of tissue damage is present. In minimally invasive techniques, instead of a scalpel, various physical and chemical factors are used to destroy the hemorrhoid and remove it, which have minimal damaging effects on surrounding tissue. Minimally invasive techniques for the radical treatment of hemorrhoids include:
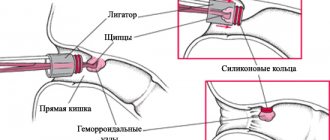
- ligation with latex rings - a special latex ring is placed on the stem of the hemorrhoid, which compresses it, compresses the feeding vessel and leads to the death of its tissue;
- infrared coagulation – destruction of the feeding vessel through local exposure to thermal radiation, which ultimately leads to the death of the hemorrhoid (necrosis) and its overgrowth with connective tissue (sclerosation);
- radical laser treatment - the hemorrhoid is exposed to a high-energy laser, which leads to its necrosis and sclerosis;
- cryodestruction – destruction of hemorrhoids by cold (local temperature down to -196º C);
- sclerotherapy is the introduction directly into the hemorrhoidal node of a special chemical compound, which causes its necrosis and subsequent sclerosis;
- Desarterization of a hemorrhoidal node is a minimally invasive operation in which a proctologist surgeon, using special micro-instruments, ligates the artery supplying the hemorrhoidal node, which causes its subsequent necrosis and sclerosis.
Most minimally invasive methods for radical removal of hemorrhoids are effective at earlier stages of hemorrhoid development (stage 1-2). Due to the low morbidity, after such procedures there is no need for hospital treatment and special recommendations regarding the rehabilitation period. They require special expensive equipment and highly qualified specialists. Therefore, not every medical clinic has the opportunity to use them.
Non-invasive technologies
Modern technologies make it possible to remove hemorrhoids without surgery, i.e. non-invasive methods. The following main methods for removing hemorrhoids can be distinguished:
- Sclerotherapy is successfully used at stages 1-3 of the disease. To remove hemorrhoids, a sclerosing agent is pumped into the node using a syringe, which glues the blood vessels together, leaving the hemorrhoidal tissue without blood supply, which leads to their sclerosis. The formation decreases in size and gradually dies. The venous wall itself sticks together at the base of the bulge, which ensures the normal functioning of the vein.
- Infrared coagulation (photocoagulation) is carried out using a special device - a photocoagulator. The device supplies a laser beam to the tip of the light guide, which is inserted into the base of the hemorrhoid. Under the influence of heat flow, the entrance to the formation closes and bleeding stops. Complete removal of hemorrhoids cannot be achieved in this way, but bleeding is blocked.
- Cryotherapy is based on the treatment of hemorrhoidal swelling with liquid nitrogen, which ensures its complete targeted freezing. This operation on hemorrhoids lasts only 3.5-5 minutes. After treatment, the node dies, which ensures the removal of hemorrhoids. Healing of wounds on the venous wall is carried out through the use of regenerating drugs. This is the easiest way to remove external swelling.
- Ligation with latex rings is ensured by placing a special elastic ring on the hemorrhoidal cone. To simplify the procedure, a vacuum ligator is used. Due to the blocking of the blood supply to the tissues, after 12-14 days the lump is rejected along with the ligature, which ensures the removal of hemorrhoids.
Operative surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
This type of treatment is radical and aimed at completely removing the hemorrhoid and treating its possible complications. This surgical intervention includes several main types of operations:
- hemorrhoidectomy;
- surgical intervention to remove hemorrhoids and other space-occupying formations of the rectum;
- radio wave removal of hemorrhoids.
The choice of surgical treatment method for hemorrhoids is carried out by a proctologist on an individual basis, depending on the type and stage of hemorrhoids, the presence of concomitant pathology of the rectum and complications, the age and gender of the patient.
Creams and suppositories for hemorrhoids
Creams, ointments and suppositories can be used to treat hemorrhoids at home, but only a doctor can prescribe them. These drugs are used to relieve symptoms, relieve inflammation and pain, normalize vascular tone and strengthen their walls. They have a softening and healing effect. Many hemorrhoid suppositories also make bowel movements easier.
The most famous are suppositories with propolis, with sea buckthorn oil, various homeopathic suppositories with extracts of medicinal plants, as well as suppositories with ichthyol, suppositories posterizan, olesthesin, etc. The doctor may also prescribe suppositories with papaverine, glycerin, etc.
The most common ointments and creams used to treat hemorrhoids are Levomekol, Fleming ointment, Bezornil, heparin ointment, etc. They have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing effects. These medications are prescribed by your doctor.
Hemorrhoidectomy
This technique is the surgical removal of hemorrhoids using various operating techniques and surgical techniques. In proctology, several technical modifications of this surgical intervention are used, which include:
- method according to Milligan-Morgan - the essence of the operation is to suturing the feeding artery with subsequent removal of the hemorrhoid. Then sutures are placed on the area of the postoperative wound, and the rectum is tightly tamponed with sterile napkins to prevent swelling of the mucous membrane and postoperative bleeding. This operation is used for stage 3-4 hemorrhoids with a significant increase in the volume of hemorrhoids.
Surgery using the Milligan-Morgan technique
- Longo's technique (transanal resection of the mucosa or hemorrhoidopexy) - partial removal of the mucous membrane is performed, without affecting the hemorrhoids. Due to deterioration of blood circulation in them after resection, they gradually decrease in size and disappear, and the mucosal defect is sutured with special titanium staples. The main advantage of this operation, developed by the Italian surgeon Long, is the maximum preservation of the anatomical structure and innervation of the rectum. This type of surgical intervention is relatively low-traumatic and is used for stage 2-4 hemorrhoids with internal localization of hemorrhoids.
A modification of hemorrhoidectomy, regardless of the surgical technique, is plastic surgery of the hemorrhoidal stump, with its suturing into the submucosal layer of the rectum. This modification significantly improves the subsequent prognosis of radical treatment with a minimum number of relapses of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoidectomy with parallel removal of other formations or treatment of complications
Such surgical treatment of complicated hemorrhoids or its course with concomitant pathology is more extensive and traumatic. The following operations are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids:
- hemorrhoidectomy with removal of polyps - usually excision of tissue in the area of the hemorrhoid and polyps is performed en bloc, followed by suturing and plastic surgery of the postoperative wound;
- removal of hemorrhoids with plastic surgery of a rectal fissure - resection of the mucous membrane in the area of the fissure is performed with suturing of the edges of the wound. The hemorrhoidal node is removed, with the stump sutured into the submucosal layer;
- plastic surgery of the fistula tract - depending on the size of the hole in the area of the complicated course of the hemorrhoidal node, partial removal of the entire wall of the rectum is performed, followed by its plastic surgery. This is a complex and traumatic operation that requires a subsequent long period of rehabilitation;
- opening of an abscess - a purulent cavity in the perirectal tissue, formed as a result of infection of the hemorrhoid, is dissected, a special tube (drainage) is inserted into it, through which the pus is released and antiseptic solutions are injected. Only after complete removal of pus and regeneration (healing) of the abscess area is the issue of hemorrhoidectomy decided.
Operations to treat hemorrhoids with concomitant pathology or complications are carried out only under general anesthesia (medicated sleep) and last at least an hour. After surgery, the patient should be under the supervision of medical workers in a hospital for some time (about a week) for the normal course of the early postoperative period and to prevent the development of complications.
Surgical treatment of pathology
In advanced stages of the disease, circumstances may arise that require urgent measures to be taken to remove hemorrhoids. Radical surgery on hemorrhoids should be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and eliminating dangerous consequences (Fig. 1). The successful outcome of surgery to remove hemorrhoids depends on how the patient is prepared and how the surgery itself is performed.
When is surgical treatment prescribed?
Surgery for hemorrhoids is prescribed for the following absolute indications for surgery:
- Prolapse with the inability to reduce the hemorrhoid by hand.
- Pinched swelling and thrombosis of the node.
- Excessive bleeding that cannot be controlled by therapeutic methods.
- Stage 3-4 pathology with frequent exacerbations, not amenable to conservative treatment.
The reason for surgery to remove hemorrhoids can be the frequent release of a significant amount of blood, which threatens the development of anemia and also creates a favorable environment for infection in the anal area. The patient may undergo surgical removal due to frequent pain, severe itching, and chronic swelling, which reduces the ability to work and causes psychological impact.
Preparation for surgical treatment
Preparation for surgery includes, first of all, reliable diagnosis. To do this, the necessary tests are carried out, the presence of background diseases is checked, possible contraindications and the risk of complications are determined. The condition of hemorrhoids is thoroughly studied - their size, location, presence of blood clots, etc.
A specific preparation condition is bowel cleansing. It is advisable to begin cleaning activities 2-3 weeks before surgery. To do this, you should optimize your diet in order to normalize the functioning of the digestive system. Immediately before the procedure, cleansing is done using laxatives or an enema. Before surgery, it is necessary to eliminate all inflammatory reactions in the anal area.
A cleansing enema is the introduction of 1.5 liters of liquid into the large intestine in order to remove feces and gases from the lower intestine in preparation for examination of the rectum before examination by a proctologist, before x-ray examination of the intestines, kidneys, before operations, childbirth, abortions, before administering medicinal enemas.
Types of surgical treatment
Surgery to remove hemorrhoids can be performed in several ways. In this case, the following main types of operations for hemorrhoids can be distinguished:
- Hemorrhoidectomy (Milligan-Morgan method) is the oldest, but still common surgical method. This operation for hemorrhoids proceeds as follows: the anus is widened; a section of perianal skin, anoderm and rectal mucosa is cut out; the node is ligated and excised. After manipulation, the intestinal lining is fixed to the underlying tissues. The method is considered quite traumatic, but in severe cases it is most effective. Main disadvantages: general anesthesia; significant blood loss. Possible consequences: long-term rehabilitation.
- The Parks method is a variation of the previous operation, but involves excision of only the hemorrhoid without damaging the mucous membrane. The operation is technically more complex, but less traumatic.
- Surgical treatment using the Longo method (desarterization) is a gentle method of surgical intervention. The surgical instrument is inserted into the rectum under ultrasound guidance, where the artery supplying the node is cut off and clamped. The duration of the operation is only 16-18 minutes. The main advantages of the method: the possibility of simultaneous treatment of several lesions; bloodlessness of the procedure; fast recovery; low risk of injury. However, this method is not applicable against external swelling.
- Transanal resection (according to the Longo method) is based on circular resection and suturing of the formation. Only a very small part of the mucosa located above the incision is removed. Hemorrhoids are not removed, but stretched out, decreasing in volume.
Radio wave removal of external hemorrhoids
A surgical technique in which, instead of a scalpel, a high-energy electromagnetic wave is used to remove the hemorrhoid, cutting through the tissue. This type of surgical treatment is used only to remove external or prolapsed hemorrhoids in stage 3-4 hemorrhoids. The operation is performed under general anesthesia or epidural conduction anesthesia (injection of an anesthetic into the lumbar spinal cord) and does not last long (up to half an hour).
Contraindications to surgery for the treatment of hemorrhoids
Surgery does not allow every person to cure hemorrhoids, because, like any procedure associated with violating the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, surgery to remove hemorrhoids has a number of contraindications:
- infectious diseases of any localization, accompanied by general intoxication and fever;
- chronic somatic pathology in the acute stage;
- cardiovascular diseases with the development of high blood pressure or heart failure;
- Crohn's disease - chronic granulomatous inflammation of the wall of the lower intestine;
- oncological process with the development of a malignant neoplasm with any localization in the body;
- pathology of the blood system, accompanied by a violation of its coagulation (high risk of developing surgical or postoperative bleeding);
- severe mental pathology with the development of productive psychosymptoms (delusions, hallucinations, motor or speech agitation);
- patient age over 70 years (relative contraindication).
Preparing for surgery
Surgery can cure hemorrhoids without complications if the preparatory period is properly organized. It includes an examination to identify possible contraindications to surgery:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- hemogram - study of indicators of the blood coagulation system;
- blood test for antibodies to HIV/AIDS, viral hepatitis and syphilis;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorographic examination of the chest organs;
- consultation with a family doctor or therapist who interprets the results of the study and makes a conclusion about the possibility of surgery.
In addition to the examination, during the preparatory period measures are necessarily taken to prepare the lower intestine for surgery:
- a diet excluding coarse plant fiber to prevent increased gas formation in the intestines;
- taking medicinal sorbents that bind and remove waste from the intestines;
- On the eve of the operation, laxatives are taken to cleanse the intestines.
The success of the operation and the prevention of complications depend on the correctness of the preparatory stage before the operation.
Important tips and rules for preparing for hemorrhoid removal
Before removing hemorrhoids, the patient must be examined. This is especially true for people who have chronic diseases. During the period of their exacerbation, no surgical interventions are performed. If any pathology is detected in the active phase, it is necessary to carry out a course of treatment so that the disease goes into stable remission.
It is important to exclude sluggish infectious processes and normalize cardiac and respiratory activity.
A week before surgery, bowel cleansing is required. For this purpose, a special diet, enemas, and laxatives are used. The doctor will tell you about this in detail at your appointment, and will also recommend the necessary medications for existing intestinal dysfunction.
7 days before surgery, you must begin to strictly adhere to your diet. On the eve of surgery it is recommended:
- last meal – 12 hours before surgery;
- before visiting the doctor, take a shower or bath, put on clean underwear;
- carry out cleansing enemas, following the recommendations, and, if necessary, take laxatives.
It is important to stop taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and NSAIDs a few days before surgery. For a positive psychological attitude, it is better not to read negative reviews from patients, but to trust the doctor.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period after surgery to remove hemorrhoids consists of an early postoperative period and late rehabilitation. The early postoperative period lasts after completion of the operation and until the sutures are removed and includes several activities:
- insertion of a sterile napkin into the rectum for its tamponade, prevention of swelling and bleeding in the first few days after surgery;
- insertion of a sterile gas tube;
- daily dressings using antiseptic solutions to prevent infection of the postoperative wound;
- pain control using painkillers on the first day after surgery;
- diet with the exclusion of solid foods.
Late rehabilitation lasts from the moment of removal of postoperative sutures (7-10 days after surgery) to several months. During this period, it is important to follow general and dietary recommendations for better tissue restoration and functional activity of the rectum:
- refusal of fried, fatty, spicy foods and spices;
- preference is given to plant foods with sufficient amounts of vitamins;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- limiting physical activity;
- sufficient 8-hour sleep, organization of work and rest schedule.
Provided that the operation is carried out correctly technically in accordance with the indications, all measures are taken during preparation for surgery and rehabilitation after it, surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is effective with a minimum number of complications and the development of subsequent relapse.
Do hemorrhoids lead to cancer?
No. There is no connection between the development of this disease and malignant tumors. However, some symptoms, especially bleeding, are also characteristic of colorectal cancer and other diseases of the digestive system. Therefore, it is very important to consult a coloproctologist if any symptoms of hemorrhoids appear. Today, there are a wide range of medications available in pharmacies that can reduce the symptoms of hemorrhoids, but you should not treat them yourself.
At an appointment with a coloproctologist surgeon, after a qualified examination and assessment of symptoms, you will be prescribed adequate treatment.